The water tax is a relatively new fee, as it was introduced in 2005 to replace the then existing fee for the use of water bodies.
In its form, it is a direct federal tax and is levied on entities that, in their activities, use resources from the list established by law.
Such entities include:
- enterprises;
- individual entrepreneurs;
- individuals.
Who pays the water tax? Taxpayers of the water tax are recognized and those entities must use water bodies in a legally defined manner.
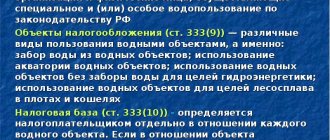
are recognized as objects of taxation for water tax :
- water intake;
- the use of certain objects (for example, rivers or seas) in order to ensure the functioning of a hydroelectric power station;
- taking water from water bodies;
- its use for timber rafting in purses and rafts.
In this case, the resources of seas, rivers, lakes, canals, swamps, underground springs and streams can be used. The activities of each of these entities must be carried out on the basis of a license or a special agreement.
Without these documents, the use of water bodies is considered illegal. Even after the expiration of the license or contract, the obligation to pay water tax is not removed if the entity continues to use water resources.
In all of the above cases, a water tax must be paid - the previously existing benefits have been canceled and uniform rules apply to all payers.
Since the water tax is federal or regional, the provision of benefits or changes in rates by regional authorities is not allowed.
However, this list has many exceptions. For example:
- intake of medicinal and thermal waters, as well as water to eliminate fires, natural disasters, accidents and to ensure the operation of technological equipment of sea vessels;
- use of water areas for landing and take-off of aircraft, for navigation on ships, as well as for hunting or fishing;
- placement in the water area of the facility of structures, installations, communications and buildings, the purpose of which is to ensure the protection of nature and environmental protection from the negative impact of hazardous factors;
- use of the facility for government needs (for example, to ensure the defense and security of the state);
- organization of water recreation for the disabled, children and veterans;
- a set of water for watering pastures, gardens, orchards and other land plots that are the property of citizens or agricultural associations.
All these situations are defined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as those that are not subject to water tax - in these cases, objects can be operated by citizens and other entities free of charge.
Water intake
If you use a water body to collect water, the tax base corresponds to the volume of water collected per quarter. Determine the volume based on the data from the measuring instruments. Record the same readings in the primary water use log. The form of the journal was approved by order of the Russian Ministry of Natural Resources dated July 8, 2009 No. 205.
But what if there are no water measuring instruments? Then determine the volume of water based on the actual operating time and productivity of the technical equipment. For example, when water is collected by a pump, the tax base depends on the pump’s performance (the volume of water taken per unit of time) and its operating time. Also take into account the height of the water rise (water column), its characteristics, which depend on time and depth, as well as the condition of the well.
If it is impossible to determine the volume using this method, use water consumption standards. The limit is specified in the license. It is established for each water body and purpose of use.
Such rules are contained in paragraph 2 of Article 333.10 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In what form and where to report?
KND form 1151072 has not been updated. The form of the declaration and the procedure for filling it out are set out in the order of the Federal Tax Service No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] dated 09.11.2015.
In Art. 333.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicates where to submit the water tax declaration: to the territorial tax office at the location of the water use facility. The largest taxpayers report to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration as the largest.
The delivery format is determined by the number of employees of the organization or individual entrepreneur. If, according to the tax report on the average headcount for the last year, the organization employs 100 people, submit the declaration electronically (clause 3 of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the institution employs less than 100 people, it is possible to choose the delivery method - on paper or electronically.
A step-by-step guide from ConsultantPlus experts will help you fill out the form correctly.
Use of water bodies for the purpose of rafting wood in rafts and purses
When using a water body for rafting wood in rafts and purses, calculate the tax base using the formula:
| The tax base | = | Volume of wood rafted in rafts and purses (thousand cubic meters) | × | Rafting distance (km) : 100 |
This procedure is contained in paragraph 5 of Article 333.10 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Responsibility for non-payment of tax and failure to submit a declaration
The absence of a declaration or failure to pay the tax amount to the budget is a violation of the law, for which certain liability is provided. The punishment for this type of violation is determined in the general manner, as for other similar offenses:
- In case of failure to submit a declaration, the payer will have to pay a fine - from 1000 rubles. up to 30% of the amount payable in accordance with this declaration (in general cases - 5% of this amount).
- For submitting a declaration in electronic form in violation of the established method for such document submission, a fine of 200 rubles is imposed.
- For tax, the amount of which was not paid partially or in full, a fine of up to 20% of this amount is imposed - if the actions were committed unintentionally, and up to 40% of the amount - in case of deliberate deception.
The characteristic of water tax is one of the types of payment for subsoil and the obligation to pay it applies to all entities that use water resources in the manner prescribed by law.
Regulation of the calculation and payment of this tax is carried out using two main documents - the Tax Code and the Military Code of the Russian Federation.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes an exhaustive list of situations in which water tax must be paid, and also specifies the procedure for determining the base and rate for its calculation.
However, the size of the rates may vary significantly depending on the specific body of water.
Tax rates
Water tax rates are listed in Article 333.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. They are different and depend on:
- from the object of taxation;
- from river basins, lakes, seas;
- from economic regions.
See the table for a list of all possible bets.
If different rates are established for one water body, determine the tax base separately for each rate. For example, if an organization collects water from the Volga River in the Northern and Northwestern economic regions, the tax base must be calculated separately. Despite the fact that there is only one water body - the Volga River, different water tax rates apply in these areas.
This is indicated in paragraph 1 of Article 333.10 and subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 333.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Please note that a coefficient is applied to water tax rates. Its size is set for each year. For example, in 2016, bets are applied with a coefficient of 1.32.
In addition, rates need to be increased additionally in two cases .
The first is when drawing water:
- by a factor of 1.1, if you do not have special instruments to measure the amount of water that is withdrawn from the water body;
- five times for an over-limit fence.
The second is for the extraction of groundwater for its processing, packaging and sale by a factor of 10. This case does not apply to the extraction of industrial, mineral and thermal waters.
Such rules are provided for in paragraphs 1.1, 2, 4 and 5 of Article 333.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When multiplying bets by odds, round them to the nearest ruble. This is stated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 22, 2015 No. GD-4-3/721.
Who reports and when?
Taxpayers are those who use surface and underground water bodies under a license (Chapter 25.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Federal Law No. 2395-1 of 02.21.1992 “On Subsoil”).
This is who submits the water tax declaration (Article 333.8 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) - commercial and non-profit organizations, individual entrepreneurs. IMPORTANT!
Individual entrepreneurs and enterprises that have entered into a water use agreement without obtaining a license do not pay tax and do not submit a report.
The reporting deadlines coincide with the deadlines for paying contributions to the budget. See the quarterly deadline for submitting the water tax return in the table:
| Quarter | Payment | Filing a declaration |
| 1 | 20.04 | 20.04 |
| 2 | 20.07 | 20.07 |
| 3 | 20.10 | 20.10 |
| 4 | 20.01 next year | 20.01 next year |
IMPORTANT!
For the 4th quarter of 2021, you must report and transfer funds by 01/20/2021. This is Wednesday, a weekday, there are no transfers.
Chapter 25.2. Water tax
Article 333.8. Taxpayers
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
1. Taxpayers of water tax (hereinafter referred to as taxpayers in this chapter) are organizations and individuals, including individual entrepreneurs, who use water bodies subject to licensing in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
2. Organizations and individuals who use water on the basis of water use agreements or decisions on the provision of water bodies for use, respectively concluded and adopted after the entry into force of the Water Code of the Russian Federation, are not recognized as taxpayers.
Article 333.9. Objects of taxation
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
1. The objects of taxation by water tax (hereinafter in this chapter - tax), unless otherwise provided by paragraph 2 of this article, are the following types of use of water bodies (hereinafter in this chapter - types of water use):
1) water intake from water bodies;
2) use of the water area of water bodies, with the exception of timber rafting in rafts and bags;
3) use of water bodies without water intake for hydropower purposes;
4) use of water bodies for the purpose of rafting wood in rafts and purses.
2. The following are not recognized as objects of taxation:
1) withdrawal from underground water bodies of water containing minerals and (or) natural medicinal resources, as well as thermal waters;
2) abstraction of water from water bodies to ensure fire safety, as well as to eliminate natural disasters and the consequences of accidents;
3) water intake from water bodies for sanitary, environmental and shipping releases;
4) intake of water from water bodies by sea vessels, inland and mixed (river-sea) vessels to ensure the operation of technological equipment;
5) abstraction of water from water bodies and use of the water area of water bodies for fish farming and reproduction of aquatic biological resources;
6) use of the water area of water bodies for navigation on ships, including small boats, as well as for one-time landings (take-offs) of aircraft;
7) use of the water area of water bodies for the placement and parking of swimming facilities, placement of communications, buildings, structures, installations and equipment for carrying out activities related to the protection of waters and aquatic biological resources, protection of the environment from the harmful effects of water, as well as the implementation of such activities on water bodies;
 use of the water area of water bodies for state monitoring of water bodies and other natural resources, as well as geodetic, topographical, hydrographic and survey work;
use of the water area of water bodies for state monitoring of water bodies and other natural resources, as well as geodetic, topographical, hydrographic and survey work;
9) use of the water area of water bodies for the placement and construction of hydraulic structures for hydropower, reclamation, fishery, water transport, water supply purposes and for drainage purposes;
10) use of water areas for organized recreation by organizations intended exclusively for the maintenance and service of disabled people, veterans and children;
11) use of water bodies for dredging and other work related to the operation of navigable waterways and hydraulic structures;
12) use of water bodies to meet the needs of national defense and state security;
13) abstraction of water from water bodies for irrigation of agricultural land (including meadows and pastures), watering gardens, vegetable plots and land plots for personal farming, for watering and servicing livestock and poultry, which are owned by agricultural organizations and citizens ;
14) withdrawal of mine and collector-drainage waters from underground water bodies;
15) use of water areas for fishing and hunting.
Article 333.10. The tax base
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
1. For each type of water use recognized as an object of taxation in accordance with Article 333.9 of this Code, the tax base is determined by the taxpayer separately in relation to each water body.
If different tax rates are established for a water body, the tax base is determined by the taxpayer in relation to each tax rate.
2. When water is withdrawn, the tax base is determined as the volume of water taken from the water body during the tax period.
The volume of water taken from a water body is determined based on the readings of water measuring instruments reflected in the primary water use register.
In the absence of water measuring instruments, the volume of water taken is determined based on the operating time and productivity of the technical equipment. If it is impossible to determine the volume of water taken based on the operating time and productivity of technical equipment, the volume of water taken is determined based on water consumption standards.
3. When using the water area of water bodies, with the exception of timber rafting in rafts and purses, the tax base is determined as the area of the provided water space.
The area of the provided water space is determined according to the water use license (water use agreement), and in the absence of such data in the license (agreement), based on the materials of the relevant technical and design documentation.
4. When using water bodies without water intake for hydropower purposes, the tax base is determined as the amount of electricity produced during the tax period.
5. When using water bodies for the purpose of rafting wood in rafts and purses, the tax base is determined as the product of the volume of wood rafted in rafts and purses during the tax period, expressed in thousands of cubic meters, and the rafting distance, expressed in kilometers, divided by 100.
Article 333.11. Taxable period
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
The tax period is a quarter.
Article 333.12. Tax rates
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
1. Tax rates are established for river basins, lakes, seas and economic regions in the following amounts:
1) when taking water from:
— surface water bodies within the established quarterly (annual) limits of water use and underground water bodies within the limits of the permitted (maximum permissible) water withdrawal per day (year) established in the license for the use of subsoil for the extraction of groundwater:
| Economic region | River basin, lake | Tax rate in rubles per 1 thousand cubic meters. m of water withdrawn | |
| from surface water bodies | from underground water bodies | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Northern | Volga | 300 | 384 |
| Neva | 264 | 348 | |
| Pechora | 246 | 300 | |
| Northern Dvina | 258 | 312 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 306 | 378 | |
| Northwestern | Volga | 294 | 390 |
| Western Dvina | 288 | 366 | |
| Neva | 258 | 342 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 282 | 372 | |
| Central | Volga | 288 | 360 |
| Dnieper | 276 | 342 | |
| Don | 294 | 384 | |
| Western Dvina | 306 | 354 | |
| Neva | 252 | 306 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 264 | 336 | |
| Volgo-Vyatsky | Volga | 282 | 336 |
| Northern Dvina | 252 | 312 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 270 | 330 | |
| Central Black Earth | Dnieper | 258 | 318 |
| Don | 336 | 402 | |
| Volga | 282 | 354 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 258 | 318 | |
| Povolzhsky | Volga | 294 | 348 |
| Don | 360 | 420 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 264 | 342 | |
| North Caucasian | Don | 390 | 486 |
| Kuban | 480 | 570 | |
| Samur | 480 | 576 | |
| Sulak | 456 | 540 | |
| Terek | 468 | 558 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 540 | 654 | |
| Ural | Volga | 294 | 444 |
| Ob | 282 | 456 | |
| Ural | 354 | 534 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 306 | 390 | |
| West Siberian | Ob | 270 | 330 |
| Other rivers and lakes | 276 | 342 | |
| East Siberian | Amur | 276 | 330 |
| Yenisei | 246 | 306 | |
| Lena | 252 | 306 | |
| Ob | 264 | 348 | |
| Lake Baikal and its basin | 576 | 678 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 282 | 342 | |
| Far Eastern | Amur | 264 | 336 |
| Lena | 288 | 342 | |
| Other rivers and lakes | 252 | 306 | |
| Kaliningrad region | Neman | 276 | 324 |
| Other rivers and lakes | 288 | 336 | |
— the territorial sea of the Russian Federation and internal sea waters within the established quarterly (annual) water use limits:
| Sea | Tax rate in rubles per 1 thousand cubic meters. m of sea water |
| Baltic | 8,28 |
| White | 8,40 |
| Barentsevo | 6,36 |
| Azovskoe | 14,88 |
| Black | 14,88 |
| Caspian | 11,52 |
| Karskoye | 4,80 |
| Laptev | 4,68 |
| East Siberian | 4,44 |
| Chukotka | 4,32 |
| Beringovo | 5,28 |
| Pacific Ocean (within the territorial sea of the Russian Federation) | 5,64 |
| Okhotsk | 7,68 |
| Japanese | 8,04 |
2) when using the water area:
- surface water bodies, with the exception of wood alloy in rafts and bags:
| Economic region | Tax rate (thousand rubles per year) per 1 sq. km of water area used |
| Northern | 32,16 |
| Northwestern | 33,96 |
| Central | 30,84 |
| Volgo-Vyatsky | 29,04 |
| Central Black Earth | 30,12 |
| Povolzhsky | 30,48 |
| North Caucasian | 34,44 |
| Ural | 32,04 |
| West Siberian | 30,24 |
| East Siberian | 28,20 |
| Far Eastern | 31,32 |
| Kaliningrad region | 30,84; |
— territorial sea of the Russian Federation and internal sea waters:
| Sea | Tax rate (thousand rubles per year) per 1 sq. km of water area used |
| Baltic | 33,84 |
| White | 27,72 |
| Barentsevo | 30,72 |
| Azovskoe | 44,88 |
| Black | 49,80 |
| Caspian | 42,24 |
| Karskoye | 15,72 |
| Laptev | 15,12 |
| East Siberian | 15,00 |
| Chukotka | 14,04 |
| Beringovo | 26,16 |
| Pacific Ocean (within the territorial sea of the Russian Federation) | 29,28 |
| Okhotsk | 35,28 |
| Japanese | 38,52 |
3) when using water bodies without water intake for hydropower purposes:
| River, lake, sea basin | Tax rate in rubles per 1 thousand kWh of electricity |
| Neva | 8,76 |
| Neman | 8,76 |
| Rivers of the basins of Lakes Ladoga and Onega and Lake Ilmen | 9,00 |
| Other rivers of the Baltic Sea basin | 8,88 |
| Northern Dvina | 8,76 |
| Other rivers of the White Sea basin | 9,00 |
| Rivers of the Barents Sea basin | 8,76 |
| Amur | 9,24 |
| Volga | 9,84 |
| Don | 9,72 |
| Yenisei | 13,70 |
| Kuban | 8,88 |
| Lena | 13,50 |
| Ob | 12,30 |
| Sulak | 7,20 |
| Terek | 8,40 |
| Ural | 8,52 |
| Basin of Lake Baikal and the Angara River | 13,20 |
| Rivers of the East Siberian Sea basin | 8,52 |
| Rivers of the Chukchi and Bering Sea basins | 10,44 |
| Other rivers and lakes | 4,80 |
4) when using water bodies for the purpose of rafting wood in rafts and purses:
| River, lake, sea basin | Tax rate in rubles per 1 thousand cubic meters. m of wood rafted in rafts and bags for every 100 km of rafting |
| Neva | 1 656,0 |
| Rivers of the basins of Lakes Ladoga and Onega and Lake Ilmen | 1 705,2 |
| Other rivers of the Baltic Sea basin | 1 522,8 |
| Northern Dvina | 1 650,0 |
| Other rivers of the White Sea basin | 1 454,4 |
| Pechora | 1 554,0 |
| Amur | 1 476,0 |
| Volga | 1 636,8 |
| Yenisei | 1 585,2 |
| Lena | 1 646,4 |
| Ob | 1 576,8 |
| Other rivers and lakes along which timber is floated in rafts and bags | 1 183,2 |
1.1. Tax rates established in paragraph 1 of this article, taking into account the provisions of paragraphs 2, 4 and 5 of this article, are applied in accordance with the table:
| Year | Coefficient | Year | Coefficient |
| 2015 | 1,15 | 2021 | 2,66 |
| 2016 | 1,32 | 2022 | 3,06 |
| 2017 | 1,52 | 2023 | 3,52 |
| 2018 | 1,75 | 2024 | 4,05 |
| 2019 | 2,01 | 2025 | 4,65 |
| 2020 | 2,31 | 2026 | * |
* Starting from 2026, the tax rates specified in paragraph 1 of this article are applied with coefficients determined in accordance with this paragraph for the year preceding the year of the tax period, multiplied by a coefficient taking into account the actual change (on average per year) in consumer prices for goods (works, services) in the Russian Federation, determined by the federal executive body exercising regulatory functions in the field of analysis and forecasting of socio-economic development, in accordance with state statistical reporting data for the second year preceding the year of the tax period.
The tax rate, taking into account the specified coefficients, is rounded to the nearest ruble in accordance with the current rounding procedure.
2. When water is withdrawn in excess of the established quarterly (annual) water use limits, tax rates in relation to such excess are established at five times the tax rates established by paragraph 1 of this article, taking into account the coefficients established by paragraph 1.1 of this article. If the taxpayer does not have approved quarterly limits, quarterly limits are calculated as one-fourth of the approved annual limit.
When extracting groundwater in excess of the permitted (maximum permissible) water withdrawal per day (year) established in the license for the use of subsoil for the extraction of groundwater, calculated for the tax period, tax rates in relation to such excess are established at five times the tax rates established by paragraph 1 of this article c. taking into account the coefficients established by paragraph 1.1 of this article. If the taxpayer does not have the permitted (maximum permissible) water withdrawal per day (year) established in the license for the use of subsoil for the extraction of groundwater, calculated by quarter, the quarterly values are calculated as one-fourth of the approved annual volume.
3. The water tax rate for the withdrawal (withdrawal) of water resources from water bodies for water supply to the population is established for one thousand cubic meters of water resources taken (withdrawn) from the water body; in accordance with the table:
| Period | Tax rate per 1000 cubic meters. | Period | Tax rate per 1000 cubic meters. |
| 01.01.2015 — 31.12.2015 | 81 | 01.01.2021 — 31.12.2021 | 186 |
| 01.01.2016 — 31.12.2016 | 93 | 01.01.2022 — 31.12.2022 | 214 |
| 01.01.2017 — 31.12.2017 | 107 | 01.01.2023 — 31.12.2023 | 246 |
| 01.01.2018 — 31.12.2018 | 122 | 01.01.2024 — 31.12.2024 | 283 |
| 01.01.2019 — 31.12.2019 | 141 | 01.01.2025 — 31.12.2025 | 326 |
| 01.01.2020 — 31.12.2020 | 162 | 01.01.2026 — 31.12.2026 | ** |
** Starting from 2026, the water tax rate for the withdrawal (withdrawal) of water resources from water bodies for water supply to the population is determined annually by multiplying the water tax rate for this type of water use, which was in force in the previous year, by a coefficient taking into account the actual change (on average for the year ) consumer prices for goods (works, services) in the Russian Federation, determined by the federal executive body exercising regulatory functions in the field of analysis and forecasting of socio-economic development, in accordance with state statistical reporting data for the second year, the previous year of the tax period.
4. Taxpayers who do not have measuring instruments (technical systems and devices with measuring functions) to measure the amount of water resources taken (withdrawn) from a water body apply the water tax rate determined taking into account the provisions of paragraph 1.1 of this article, with an additional coefficient of 1, 1.
5. The water tax rate for the extraction of groundwater (with the exception of industrial, mineral, and thermal waters) for the purpose of their sale after processing, preparation, processing and (or) packaging, determined taking into account the provisions of paragraph 1.1 of this article, is applied with by an additional factor of 10.
Article 333.13. Tax calculation procedure
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
1. The taxpayer calculates the amount of tax independently.
2. The amount of tax is calculated as the product of the tax base and the corresponding tax rate, multiplied by the coefficient (coefficients) established by Article 333.12 of this Code.
3. The total tax amount is the amount obtained by adding up the tax amounts calculated in accordance with paragraph 2 of this article in relation to all types of water use.
Article 333.14. Procedure and deadlines for tax payment
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
1. The total amount of tax calculated in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 333.13 of this Code is paid at the location of the object of taxation.
2. The tax must be paid no later than the 20th day of the month following the expired tax period.
Article 333.15. Tax return
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
1. The tax return is submitted by the taxpayer to the tax authority at the location of the object of taxation within the period established for payment of the tax.
In this case, taxpayers, in accordance with Article 83 of this Code, classified as the largest taxpayers, submit tax returns (calculations) to the tax authority at the place of registration as the largest taxpayers.
2. Taxpayers - foreign persons also submit a copy of the tax return to the tax authority at the location of the body that issued the water use license within the period established for paying the tax.
Contents of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Part I Part II
Taxation of transport
Ship owners are interested in calculating the water transport tax in 2021 using a calculator. It is regulated by Ch. 28 of the Tax Code. In fact, it has nothing to do with water intake, but is also calculated virtually.
You can calculate the water transport tax on the Pravio website. Here you will also find instructions on exactly how to do this, and what indicators need to be entered to get a reliable result. If the accrual of penalties has already begun, using the resource in question it is possible to find out its exact size.
Cancellation of transport tax
A few years ago, talk began about abolishing the transport tax in Russia as such and including it in the cost of fuel. At the moment, no decisions have been made in this regard.
Choose region
- 1. Republic of Adygea
- 2. Republic of Bashkortostan
- 3. Republic of Buryatia
- 4. Altai Republic
- 5. Republic of Dagestan
- 6. Republic of Ingushetia
- 7. Kabardino-Balkarian Republic
- 8. Republic of Kalmykia
- 9. Karachay-Cherkess Republic
- 10. Republic of Karelia
- 11. Komi Republic
- 12. Republic of Mari El
- 13. Republic of Mordovia
- 14. Republic of Sakha (Yakutia)
- 15. Republic of North Ossetia-Alania
- 16. Republic of Tatarstan
- 17. Republic of Tyva
- 18. Udmurt Republic
- 19. Republic of Khakassia
- 20. Chechen Republic
- 21. Chuvash Republic
- 22. Altai region
- 23. Krasnodar region
- 24. Krasnoyarsk region
- 25. Primorsky Krai
- 26. Stavropol region
- 27. Khabarovsk region
- 28. Amur region
- 29. Arkhangelsk region
- 30. Astrakhan region
- 31. Belgorod region
- 32. Bryansk region
- 33. Vladimir region
- 34. Volgograd region
- 35. Vologda region
- 36. Voronezh region
- 37. Ivanovo region
- 38. Irkutsk region
- 39. Kaliningrad region
- 40. Kaluga region
- 41. Kamchatka region
- 42. Kemerovo region
- 43. Kirov region
- 44. Kostroma region
- 45. Kurgan region
- 46. Kursk region
- 47. Leningrad region
- 48. Lipetsk region
- 49. Magadan region
- 50. Moscow region
- 51. Murmansk region
- 52. Nizhny Novgorod region
- 53. Novgorod region
- 54. Novosibirsk region
- 55. Omsk region
- 56. Orenburg region
- 57. Oryol region
- 58. Penza region
- 59. Perm region
- 60. Pskov region
- 61. Rostov region
- 62. Ryazan region
- 63. Samara region
- 64. Saratov region
- 65. Sakhalin region
- 66. Sverdlovsk region
- 67. Smolensk region
- 68. Tambov region
- 69. Tver region
- 70. Tomsk region
- 71. Tula region
- 72. Tyumen region
- 73. Ulyanovsk region
- 74. Chelyabinsk region
- 75. Transbaikal region
- 76. Yaroslavl region
- 77. Moscow
- 78. St. Petersburg
- 79. Jewish Autonomous Region
- 83. Nenets Autonomous Okrug
- 86. Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra
- 87. Chukotka Autonomous Okrug
- 89. Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug
- 91. Republic of Crimea
- 92. Sevastopol
What objects are not subject to taxation?
Clause 2 art. 333.9 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation contains a list of 15 items containing types of activities not subject to water tax. These include:
- irrigation of farmland, fields and pastures;
- fighting fires and other natural disasters where the use of water is justified;
- creation of summer camps and sanatoriums for children, disabled people and veterans on the territory adjacent to the water body;
- use of nearby territories as hunting and fishing grounds;
- other types of activities related to the interests of the state.
Calculation of transport tax
The amount of transport tax includes the following factors:
- Vehicle registration region.
- Vehicle ownership period (if it is necessary to calculate tax for an incomplete year).
- Type of vehicle.
- Vehicle engine power.
Additionally, for cars whose price is above 3,000,000 rubles, a special coefficient is applied.
Formula for calculating transport tax:
Tax = R × P × m
12
× Kpov
R
- tax rate,
P
- vehicle power in horsepower
m
- number of months of ownership per year
Kpov
- increasing coefficient.
The rate is determined by the vehicle type, capacity and region of registration. Rates are set by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and in different regions they can differ significantly.