Who pays property tax
Russian organizations are required to pay tax if four conditions are simultaneously met:
- there is real estate on the balance sheet (including those transferred for temporary possession, use, disposal, trust management, contributed to joint activities, received under a concession agreement);
- this property is accounted for on the balance sheet as a fixed asset in accounts 01 “Fixed Assets” or 03 “Income Investments in Material Assets”;
- existing property is recognized as an object of taxation on the grounds specified in Art. 374 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- the tax base for such real estate is determined as the average annual value.
Also, property tax is paid on real estate located in the Russian Federation and, as a general rule, owned by an organization, obtained under a concession agreement, if the tax base for it is the cadastral value.
Please note that from 2021 the movable property tax has been abolished!
Enterprises will not have to pay tax on land plots, water and cultural objects, as well as on other types of property named in paragraph 4 of Art. 374 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A number of organizations, depending on the type of activity, are not charged tax (Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Fill out and send reports to the Federal Tax Service on time and without errors with Kontur.Extern. 3 months of service are free for you!
Try it
The tax base
Determine the basis for calculating property tax separately for the following property:
- located at the location of the head office of a Russian organization or permanent representative office of a foreign one;
- each separate division with a separate balance sheet;
- outside the location of the organization (separately for each facility);
- part of the Unified Gas Supply System;
- the tax on which is calculated based on the cadastral value;
- taxed at different tax rates;
- involved under a simple or investment partnership agreement;
- transferred into trust or acquired under such an agreement;
- when executing concession agreements.
This follows from the provisions of paragraph 1 of Article 376, Articles 377, 378, 378.1 and 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A special procedure for determining the tax base applies to real estate located on the territory of several constituent entities of the Russian Federation (pipelines, electrical networks, railways, etc.). In this case, determine the tax base separately. That is, the share of the tax base that relates to a particular region should be calculated in proportion to the part of the cost of the object located in the corresponding region. This is stated in paragraph 2 of Article 376 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The procedure for determining the tax base for organizations that have transport infrastructure facilities on their balance sheets has some specific features. They have the right to reduce the property tax base by the cost of completed capital investments in construction, modernization and reconstruction:
- navigable hydraulic structures located on the inland waterways of Russia. For example, locks, ship lifts;
- port hydraulic structures. For example, breakwaters, piers, berths, etc.;
- air transport infrastructure structures, with the exception of centralized aircraft refueling systems and the cosmodrome. For example, structures and equipment at airports.
When calculating property tax, the listed types of capital investments that are included in the book value of the named objects or taken into account as fixed assets starting from January 1, 2010 are not taken into account. In this case, the period of commissioning of the facility itself that has undergone reconstruction or modernization - before or after January 1, 2010, does not matter.
This follows from the provisions of paragraph 6 of Article 376 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 25, 2013 No. 03-05-05-01/23974 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 24, 2011 No. ZN-4-11/10123.
When determining the composition of transport infrastructure facilities, capital investments in which reduce the tax base, be guided by industry regulations. For example:
- in relation to air transport - the Air Code of the Russian Federation, Law of January 8, 1998 No. 10-FZ;
- in relation to hydraulic structures - by laws of July 21, 1997 No. 117-FZ and of November 8, 2007 No. 261-FZ.
Such clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 25, 2011 No. 03-05-04-01/37.
Tax calculation based on average annual cost
In turn, the average annual value = (total residual value of the property as of the 1st day of each month + residual value as of December 31) / 13.
Calculation example. Kompas LLC has been on the services market for 8 years. During this time, the Company purchased various fixed assets that help carry out its activities. Some of the property is still depreciated and considered taxable. In addition, the company purchased new equipment on July 4, 2020. The region applies a rate of 2.2%. The accountant, filling out the declaration for the past year, used the following data:
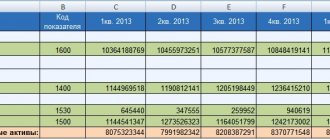
| As of: | Residual value, thousand rubles. |
| 01.01.19 | 100 |
| 01.02.19 | 95 |
| 01.03.19 | 90 |
| 01.04.19 | 85 |
| 01.05.19 | 80 |
| 01.06.19 | 75 |
| 01.07.19 | 70 |
| 01.08.19 | 234 |
| 01.09.19 | 207 |
| 01.10.19 | 191 |
| 01.11.19 | 174 |
| 01.12.19 | 146 |
| 31.12.19 | 118 |
Let's calculate the average annual cost: (100 + 95 + 90 + 85 + 80 + 75 +70 + 234 + 207 +191 + 174 + 146 + 118) / 13 x 1000 = 128,077 rubles.
Tax payable for the year = 128,077 x 2.2% = 2,818 rubles. (provided that the organization does not pay advances).
If advance payments are established in the region, organizations need to pay them three times a year, and then reduce the tax payable for the year by their amounts.
Let us assume that in the proposed example, in addition to tax, it is required to calculate the amount of the advance for all reporting periods.
Average cost of taxable objects for the first quarter = (100 + 95 + 90 + 85) / 4 x 1000 = 92,500 rubles.
According to Art. 382 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the advance payment is equal to ¼ of the average cost for the reporting period, multiplied by the rate.
Advance payment for the first quarter = 92,500 x ¼ x 2.2% = 509 rubles.
The half-year payment is calculated in the same way.
Average cost for half a year = (100 + 95 + 90 + 85 + 80 + 75 + 70) / 7 x 1,000 = 85,000 rubles.
Advance for half a year = 85,000 x ¼ x 2.2% = 468 rubles.
Average cost for 9 months = (100 + 95 + 90 + 85 + 80 + 75 + 70 + 234 + 207 +191) / 10 x 1,000 = 122,700 rubles.
Advance for 9 months = 122,700 x ¼ x 2.2% = 675 rubles.
The annual tax is paid minus any advance payments.
Tax for 2021 payable to the budget = 2,818 – (509 + 468 + 675) = 1,166 rubles.
Title page
On the title page of the tax calculation, the organization must fill out all the necessary details, except for the section “To be filled out by a tax authority employee .
When filling out the “Adjustment number” in the initial calculation for the tax period, “0” is automatically entered; in the updated calculation for the corresponding reporting period, you must indicate the adjustment number (for example, “1”, “2”, etc.).
“Tax period” field is filled in in accordance with the codes given in the directory. If the calculation is submitted for the 1st quarter, then the code “21” is indicated, if for half a year or for the 2nd quarter (for payers calculating the tax based on the cadastral value), then - “17”, if the calculation is submitted for 9 months or for the 3rd quarter, then the code “18” is entered in the specified field.
When filling out the “Submitted to the tax authority (code)” , the code of the tax authority to which the calculation is submitted is reflected. It is selected from the directory. By default, the field is automatically filled with the code that was specified when the client registered in the system.
In the “By location (accounting)” , select a code, the list of which is given in the drop-down list. Organizations classified as the largest taxpayers choose code “213”. If the calculation is submitted by Russian organizations that are not the largest taxpayers, then they indicate the code “214”, etc.
When filling out the “Taxpayer” , the name of the organization is reflected, corresponding to the one indicated in the constituent documents.
Attention! The fields “Reorganization form (code)” and “TIN/KPP of the reorganized organization” are filled in only by those organizations that are reorganized in the reporting period.
In the “Reorganization form (code)” , the reorganization code is indicated in accordance with the directory.
Next, indicate the details “TIN/KPP of the reorganized organization” .
When filling out the “Contact phone number” , the organization’s phone number specified during registration is automatically reflected.
When filling out the field “On ____ pages”, indicate the number of pages on which the calculation was made. The field value is filled in automatically and recalculated when the composition of the tax calculation changes (adding/deleting sections).
When filling out the field “with supporting documents or their copies on ___ sheets”, the number of sheets of supporting documents and (or) their copies (if any) is reflected. Such documents may be: the original (or a certified copy) of a power of attorney confirming the authority of the taxpayer’s representative (if the tax calculation is submitted by the taxpayer’s representative), etc.
In the section of the title page “I confirm the accuracy and completeness of the information:” the following is indicated:
- Manager - if the document is submitted by the taxpayer,
- Authorized representative - if the document is presented by a legal or authorized representative of the taxpayer.
In this case, the full name of the head of the organization or an authorized representative is indicated, as well as the name and details of the document confirming his authority.
The date is also automatically indicated on the title page.
Tax calculation based on cadastral value
The tax base for a certain part of real estate corresponds to the cadastral value indicated in the Unified State Register as of January 1 (Article 375 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This includes real estate from clause 1 of Art. 378.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If a company pays tax based on cadastral value, then you must first find it out in the regional office of Rosreestr or in an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate. You can also view the cost online on the Rosreestr website or in the regulatory act of your region, which approved the results of determining the cadastral value. If your property is included in the regional list, but the cadastral value for it has not been established, you do not need to pay tax. However, residential premises, garages, unfinished construction and other objects from paragraphs. 4 paragraphs 1 art. 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is not indicated in regional lists. The tax on them is paid on the basis of regional law, which should provide for cadastral taxation of these objects. If the cadastral value for them has not been determined, calculate the tax at the average annual value.
Formula for calculating tax based on cadastral value:
Tax amount for the year = Cadastral value × 2.2% - advance payments.
Advance payment = Cadastral value of the property as of January 1 × 2.2% × ¼.
Calculation example . PlusMinus LLC owns an office in the business center. The cadastral value of the premises has not been determined, but it is known that it occupies 1/16 of the building’s area. According to Rosreestr, the cadastral value of the business center is 184 million rubles.
Cadastral value of the office = 184 million rubles / 16 = 11.5 million rubles.
Tax amount for the year = 11.5 million rubles × 2.2% = 253,000 rubles.
Advance payments will be = 253,000 / 4 = 63,250 rubles per quarter.
What taxes do you have to calculate in Russia?
In any country there are many types of tax deductions. The Tax Code of Russia (TC RF) identifies the following categories of taxes:
- VAT (on value added);
- excise taxes;
- Personal income tax (on the income of individuals);
- on the profit of legal entities;
- for mining;
- water tax;
- fees for the use of biological resources;
- government fees;
- for additional income from hydrocarbon production;
- on the property of legal entities;
- to engage in gambling business;
- for transport;
- to the ground;
- for personal property persons;
- trade fee.
The first nine of them are federal, the next three are regional, and the last three are local. This means that the amount of tax payable will depend on the decision made at the appropriate level, and the funds will go to the appropriate budget.
At the same time, at each level, benefits are adopted for different categories of citizens. Therefore, before calculating the amount of tax, you need to find out whether you have to pay it.
Procedure and deadlines for tax payment
The tax period is a calendar year (Article 379 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The reporting period is 1 year. Previously, advance payments had to be submitted every quarter. Now they have been included in the declaration, so there is no need to report separately. The last report on advances was submitted for 9 months of 2021.
At the end of the year, property taxes are paid, and at the end of quarters, advance payments are paid. Regional authorities may decide not to establish advance payments, in which case the tax will only have to be paid once a year.
The deadlines for payment are also set by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (Article 383 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Results
The need to accrue advances on property tax is established by the legislation of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation in which the object of taxation is located.
If advances are provided in the region, then the payment for them must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service within the same period for the entire territory of the Russian Federation (no later than the 30th day after the end of the next quarter). The formula by which the amount of the advance is calculated does not depend on the type of tax base, but is used with the features established for application in relation to objects assessed at cadastral value. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Property tax declaration
Please note that by Order of the Federal Tax Service dated August 14, 2019 No. SA-7-21/ [email protected] as amended on July 28, 2020, a new form of property tax declaration for 2021 was approved. The order comes into force on November 3, 2020. Based on the results of 2021 (before April 1, 2021), you already need to report using the new form.
Rules for filling out a declaration with line-by-line comments from the appendix to the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 14, 2019 No. SA-7-21/ [email protected]
In the first section, line 005 “Taxpayer Attribute” was added, which is related to coronavirus benefits, and line 007 “SZPK Attribute” for organizations that have entered into an agreement on the protection and promotion of capital investments. For section two, new codes for coronavirus federal and regional benefits were approved, as well as a special code for the property of FEZ participants.
The most important innovation is the appearance of the fourth section, in which organizations will again have to reflect information on the average annual value of movable property recorded on the balance sheet as fixed assets (it is still not subject to tax). The amendments are being made to assess the value of movable property, which is currently exempt from tax. It is planned that taxation of movable property will return in the near future, but tax rates will be reduced.
Tax on deposits opened before 2021
Even if the deposit was opened long before the law on the new tax came into force (January 1, 2021), then you will also have to pay tax on it if the interest paid on it in 2021 exceeds 42.5 thousand rubles. The Ministry of Finance is discussing tax exemption for interest income accrued before January 1, 2021 and paid after this date, but no final decision has been made, the ministry told RG.
42.5 thousand rubles is non-taxable interest income on deposits in 2021
In the case of deposits with interest capitalization, income accrued before 2021 will not be taken into account when calculating tax. According to the explanations of the Ministry of Finance, if interest is credited to replenish the deposit, then income in the form of such interest is taken into account when assessing personal income tax in the tax period in which this interest was credited.
Taxpayers - who are they?
According to the law, contributions to the country's treasury are required to be paid by citizens of Russia, which are both individuals, individuals, and companies owning real estate and other property that is subject to taxation. Companies are divided into:
- local;
- foreign.
It does not matter whether a foreign company has a representative office in Russia; the mere fact that it owns property located on the territory of our country is sufficient.
Those wishing to find out details regarding property tax payers should read Article No. 401 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 401. Object of taxation
Social deductions
The state allows the following social expenses of citizens not to be taxed:
- education (own and/or children);
- medical services (including the purchase of medicines);
- charity;
- insurance (medical and pension);
- funded part of the pension.
These benefits are not deducted when calculating personal income tax when paying wages. There is a procedure for refunding part of the tax paid. To do this, you need to submit a tax return, attaching copies of the relevant documentary evidence. The deadline for filing a claim for the return of part of the personal income tax on social benefits is 3 years from the date of the expenditure (Clause 7 of Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).