Simplified income minus expenses and BCC
Using the simplified taxation system “income minus expenses” in his business activities, a businessman has a number of economic advantages. They are as follows:
- Minimum tax payments.
- The minimum amount of reporting documentation.
Using this mode, you can avoid paying taxes such as personal income tax, VAT, income tax, and property tax. No matter how tempting this tax regime may be, not all commercial organizations can use it.
There is a certain limit on employees, on enterprise profits, on fixed assets, exceeding which no longer allows the use of the Simplified Taxation System. As a rule, this mode is used in small and medium-sized businesses. Therefore, most often, simple businessmen who understand little about accounting reporting fill out the payment form and indicate the KBK according to the simplified tax system.
To simplify their task in searching for the current BCC, when paying tax, you can provide a table of codes in which a simplifier can select their current BCC:
| What payment is being paid? | —-STS (income reduced by expenses). | —-STS (income). |
| Mandatory tax. | — 18210501021011000110 | — 182 1 0500 110 |
| Penalties for mandatory tax. | — 18210501021012100110 | — 182 1 0500 110 |
| Fines. | — 18210501021013000 10 | — 182 1 0500 110 |
KBK penalties USN
The number of days of congestion was 4 days. Penalties are calculated as follows: 1/300*11%*4*15,200 = 22 rubles.
Where 11% is the refinancing rate of the Central Bank. Almost everyone has to calculate and pay penalties, and the faster the amount of the main tax and penalties on it are paid, the less the penalty itself will be. The calculation is carried out for each overdue day. Therefore, when calculating penalties, you should take into account the period when the delay occurred and enter into the payment document the current BCC in force at the time of the delay. What tax 2021 BCC 18210501011012100110 will commercial organizations have to pay? There is only one answer, these are penalties that were paid under this BCC in 2021 and earlier.
This code has not been changed for a long time, which allows simplifiers on “income” not to look for current codes in 2021. To more accurately understand a complex twenty-digit number, you can decipher the code, in 2021, KBK 18210501011012100110.
KBK for paying taxes according to the simplified tax system for individual entrepreneurs
| Decoding the code | Budget classification code |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501011011000110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as an object of taxation (penalties on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501011012100110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (interest on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501011012200110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as an object of taxation (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501011013000110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501012011000110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (penalties on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501012012100110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (for tax periods expiring before January 1, 2011) (interest on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501012012200110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as an object of taxation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501012013000110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (including the minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled payments) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501021011000110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (including the minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation) (penalties on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501021012100110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (including the minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation) (interest on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501021012200110 (short code) |
| A tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (including the minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation) (the amount of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501021013000110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501022011000110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (penalties on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501022012100110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (interest on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501022012200110 (short code) |
| Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501022013000110 (short code) |
| Minimum tax credited to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds (paid (collected) for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501030011000110 (short code) |
| Minimum tax credited to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds (paid (collected) for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (penalties on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501030012100110 (short code) |
| Minimum tax credited to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds (paid (collected) for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (interest on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501030012200110 (short code) |
| Minimum tax credited to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds (paid (collected) for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501030013000110 (short code) |
| Minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2021) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt) for the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501050011000110 (short code) |
| Minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2021) (penalties on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501050012100110 (short code) |
| Minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2021) (interest on the corresponding payment) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501050012200110 (short code) |
| Minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2021) (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 0500 110 (original code) 18210501050013000110 (short code) |
simplified tax system income minus expenses
When choosing the simplified taxation system for income minus expenses, a commercial structure has a number of advantages. This primarily affects the maintenance of documentation and the tax itself, which is reduced. The usual rate for this tax regime is 15%, but at the regional level it can be reduced to 5%.
Initially, when you get acquainted with this system, it may seem that there is no more comfortable system for paying taxes in Russia. However, the attractiveness of the system can be said after a certain period when the entrepreneur has worked in business.
You can consider in more detail how attractive the system will be for your specific case. To calculate what tax a businessman will have to pay under KBK 18210501021011000110, he will need to subtract the company's expenses from the profit.
Of course, there is a risk that tax authorities will not accept a specific expense declared in the declaration. And then a fine and penalties in the amount of 20% of the unpaid amount of the debt will be imposed.
For example, let’s look at how tax is calculated according to this taxation system. LLC "Vesna" on the simplified tax system (income minus expenses), in the declaration indicated a profit in the amount of 500,000 and expenses for the development of the enterprise amounted to 250,000. The total, according to the taxpayer, the tax was:
500,000-250,000*15% = 37,500. The following items were included in expenses:
- Office rent – 50,000;
- Warehouse rental – 100,000;
- Employee communications – 10,000;
- Purchase of materials for production – 90,000.
The taxman did not include employee communications as expenses, so the tax amount was 39,000 rubles. The arrears amounted to 300 rubles (1500*20%). Therefore, in addition to the amount of the basic tax, you will also need to pay the arrears.
Now the company will have to fill out a payment order for arrears and penalties. They have their own BCCs, which are indicated on the receipt.
If a commercial structure is interested in decoding in 2021, KBK 18210501021011000110, then you can look at the classification codes in the directory, and there you will see that this tax is paid by simplifiers who have chosen the income minus expenses system to calculate the tax.
Penalty simplified taxation system income minus expenses
Often in a businessman’s entrepreneurial activity, not everything goes smoothly and smoothly. Errors, punctures and various force majeure situations happen. But government agencies do not forgive carelessness and mistakes. If you receive a letter demanding to pay tax, and KBK 18210501021012100110 is indicated, then you have found a mistake in the company, and you need to urgently deal with it.
What to expect in 2021 simplified tax system
Every year we expect innovations, and this year was no exception. First of all, this will affect the income limit for the transition to a simplified system. Online cash registers will be introduced, new reporting forms will be added, and probably the biggest change will be the change of regulatory authorities.
Now the reporting of the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund will go to the tax authorities. This will naturally lead to a change in the BCC in the payment order. And mandatory insurance contributions that were paid to the pension fund and social security. fear (except for injuries) will need to be paid to the tax office.
Therefore, all commercial structures will need to be extremely careful when paying fees and taxes. Carefully check the BCC in the payment slip so that the transfers reach the regulatory authority without delays or delays. So that the company does not face additional sanctions and unnecessary financial expenses.
The relevance of classification codes can be checked in a special directory, which is published on the official website of the tax service. There you can learn about new changes in legislation.
Why are the BCCs different for the simplified tax system?
Each classification code is responsible for its structure, for a certain type of tax, for state. the authority where the money is sent, and for many things upon closer examination. Therefore, those who simplify the system (income minus expenses) can use the BCC given in the table.
Almost every year, legislators make various changes to laws. And changes that concern the classification codes themselves do not remain aside. They are the current account of each budget organization; with the help of this set of numbers, funds quickly reach the recipient.
When filling out the next payment document for payment of the main tax, a merchant can use either one or the second BCC, and this will be considered correct. There is no doubt that the money will arrive. But, if you don’t want to tempt fate, then it’s worth checking the relevance of the current BCC in a special directory of classification codes.
In addition, there is no need to confuse what is being paid at the moment, tax, fine or penalty. This is where an error may occur if you enter just one digit incorrectly. Then, on the basic tax, there may be a fine for late payment and penalties will be charged for each day of delay.
BCC on trade tax for legal entities
Correct indication of the 2021 BCC trade fee in the payment order (field 104) is highly desirable.
Let's explore why. Indicating an incorrect BCC will not lead to penalties against the payer of the vehicle (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 19, 2021 No. 03-02-07/1/2145). But if the wrong BCC is entered on the payment slip, the payment will be classified as unclear. The Federal Tax Service will ask the taxpayer for clarification on the code (Clause 7, Article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In turn, errors in the instructions are critical (sub.
4 p. 4 art. 45 Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Federal Treasury accounts;
- the name of the bank in which the Federal Tax Service account is opened.
If such errors are made, the vehicle is considered unpaid. If arrears arise, penalties and fines will be assessed (clause 2 of article 57, clause 1 of article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The amount paid to the budget with erroneous details will be returned by the Federal Treasury to the account of the sender of the payment (clause 17 of the Procedure for accounting by the Federal Treasury of receipts..., approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 18, 2013 No. 125n)
KBC in 2021-2022: table of insurance premiums
Our KBK table in 2021-2022 reflects information regarding insurance premium codes that are most in demand among payers.
KBK for insurance premiums for employees
| Payment type | KBK | ||
| Contributions accrued for periods before 2021, paid after 01/01/2017 | Contributions for 2017-2021 | ||
| Contributions to compulsory pension insurance | contributions | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 |
| penalties | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 | |
| fine | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 | |
| Contributions to compulsory social insurance | contributions | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 |
| penalties | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 | |
| fine | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 | |
| Contributions for compulsory health insurance | contributions | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0213 160 |
| penalties | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0213 160 | |
| fine | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0213 160 | |
| Contributions for injuries | contributions | 393 1 0200 160 | |
| penalties | 393 1 0200 160 | ||
| fine | 393 1 0200 160 | ||
KBK for insurance premiums of individual entrepreneurs
| Payment type | KBK | ||
| Contributions accrued for periods before 2021, paid after 01/01/2017 | Contributions for 2017-2021 | ||
| Fixed contributions to the Pension Fund, including contributions | contributions | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160* *Unified BCC for the fixed part and contributions from income over 300,000 rubles. valid from 04/23/2018 |
| Contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation 1% on income over 300,000 rubles. | contributions | 182 1 0200 160 | |
| penalties | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 | |
| fine | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0210 160 | |
| Contributions for compulsory health insurance | contributions | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0213 160 |
| penalties | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0213 160 | |
| fine | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0213 160 | |
Budget classification codes for taxes for 2021-2022
The BCCs for the taxes indicated in the tables below have not changed in recent years (the same for 2021 and 2021). So that you can easily and quickly find the CBC you need (among the most popular ones), we have divided them into groups:
KBK table for personal income tax for 2021-2022
| Personal income tax on employee income | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Penalties for personal income tax on employee income | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Personal income tax fine on employee income | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Personal income tax on individual entrepreneur income on OSNO | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Penalties for personal income tax on income of individual entrepreneurs on OSNO | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Personal income tax fine on income of individual entrepreneurs on OSNO | 182 1 0100 110 |
KBK income tax table
| Purpose of payment | Mandatory payment | Penalty | Fine |
| To the federal budget (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| To the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| To the federal budget (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| To the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 11 |
| When implementing production sharing agreements concluded before October 21, 2011 (before the law of December 30, 1995 No. 225-FZ came into force) | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| From the income of foreign organizations not related to activities in Russia through a permanent representative office | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| From the income of Russian organizations in the form of dividends from Russian organizations | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| From the income of foreign organizations in the form of dividends from Russian organizations | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| From dividends from foreign organizations | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| From interest on state and municipal securities | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 | 182 1 0100 110 |
| From the profits of controlled foreign companies | from the profits of controlled foreign companies | from the profits of controlled foreign companies | from the profits of controlled foreign companies |
KBK for VAT
| Payment type | Tax | Penalty | Fine |
| VAT on goods (work, services) sold in Russia | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| VAT on goods imported into Russia (from the Republics of Belarus and Kazakhstan) | 182 1 0400 110 | 182 1 0400 110 | 182 1 0400 110 |
| VAT on goods imported into Russia (payment administrator - Federal Customs Service of Russia) | 153 1 0400 110 | 153 1 0400 110 | 153 1 0400 110 |
What to do if KBK made a mistake when paying a tax or contribution? Find out the answer to this question in the Ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus by receiving free trial access to the system.
BCC 2021-2022 for special regimes (simplified taxation, imputation, patent, agricultural tax), trade tax and tax on gambling business will be as follows:
| Name KBK 2021-2022 | KBK for transferring tax or contribution | KBK for penalties | BCC for fine |
| Single tax under the simplified tax system “income” | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Single tax under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” (including minimum tax) | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 |
| UTII | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Unified agricultural tax | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Trade fee | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Patent (city district budget) | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Patent (municipal district budget) | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Patent (for residents of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol) | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Gambling tax | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
BCC for property taxes (transport, land, property tax)
| Name of KBK | KBK for transferring tax or contribution | KBK for penalties | BCC for fine |
| Transport tax for legal entities | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Transport tax for individuals | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Land tax for legal entities (for Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol) | 182 1 06 06 031 03 1000 110 | 182 1 06 06 031 03 2100 110 | 182 1 06 06 031 03 3000 110 |
| Land tax within the boundaries of urban districts for legal entities | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on land within the boundaries of inter-settlement territories for legal entities | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on land within the boundaries of rural settlements for legal entities | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on land within the boundaries of urban settlements for legal entities | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Land tax for plots within the boundaries of urban districts with intra-city division for legal entities | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Land tax for plots within the boundaries of intracity districts for legal entities | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Property tax for individuals (for Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol) | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property of individuals located within the boundaries of urban districts | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property of individuals located within the boundaries of inter-settlement territories | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property of individuals located within the boundaries of rural settlements | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property of individuals located within the boundaries of urban settlements | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property of organizations (not included in the unified gas supply system) | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property of organizations included in the unified gas supply system | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 | 182 1 0600 110 |
There are a number of changes in the BCC for excise duties, but the main codes remain the same:
| Name of KBK | KBK for transferring tax or contribution | KBK for penalties | BCC for fine |
| Excise taxes on ethyl alcohol produced in Russia from food raw materials (except for those listed in the following paragraphs) | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on ethyl alcohol produced in Russia from food raw materials (distillates of wine, grape, fruit, cognac, Calvados, whiskey) | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on ethyl alcohol produced in Russia from non-food raw materials | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on Russian-made alcohol-containing products | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on Russian beer | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on Russian alcoholic products with an ethyl alcohol content of more than 9% (except for beer and various wines) | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on Russian alcoholic products with a share of ethyl alcohol up to 9% (except for beer and various wines) | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on Russian wines | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on Russian motor gasoline | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Excise taxes on Russian diesel fuel | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 | 182 1 0300 110 |
Other sections of the KBK
- Pension contributions. Decoding codes for the budget classification of pension contributions for 2021.
- Contributions to compulsory social insurance. Decoding codes for the budget classification of contributions to compulsory social insurance for 2021.
- Contributions for compulsory health insurance. Decoding codes for the budget classification of contributions for compulsory health insurance for 2021.
- Personal income tax (NDFL). Deciphering the budget classification codes for personal income taxes (NDFL) 2021.
- Value added tax (VAT). Decoding the budget classification codes for value added tax (VAT) 2020.
- Income tax. Decoding the 2021 income tax budget classification codes.
- Excise taxes. Decoding the codes for the budget classification of excise taxes for 2020.
- Organizational property tax. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of property tax for organizations 2021.
- Land tax. Deciphering the codes for the budget classification of land tax for 2021.
- Transport tax. Deciphering the transport tax budget classification codes for 2021.
- Single tax with simplification. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of the single tax during simplification for 2021.
- Unified tax on imputed income (UTII). Decoding codes for the budget classification of the single tax on imputed income (UTII) 2020.
- Unified Agricultural Tax (USAT). Decoding the codes of the budget classification of the Unified Agricultural Tax (USAT) 2020.
- Mineral extraction tax (MET). Deciphering the budget classification codes for mineral extraction taxes (MET) 2021.
- Fee for the use of aquatic biological resources. Decoding the budget classification codes of the fee for the use of aquatic biological resources for 2021.
- Fee for the use of fauna objects. Deciphering the codes of the budget fee for the use of wildlife objects in 2020.
- Water tax. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of water tax for 2021.
- Payments for the use of subsoil. Decoding codes for the budget classification of payments for the use of subsoil for 2021.
- Payments for the use of natural resources. Decoding codes for the budget classification of payments for the use of natural resources for 2021.
- Gambling tax. Deciphering the budget classification codes for the gambling tax for 2021.
- Government duty. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of state duty for 2021.
- Income from the provision of paid services and compensation for state costs. Decoding codes for the budget classification of income from the provision of paid services and compensation for state expenses in 2020.
- Fines, sanctions, payments for damages. Decoding codes for the budget classification of fines, sanctions, payments for damages in 2021.
- Trade fee. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of trade tax for 2021.
- News. All news on changes in (KBK) budget classification codes for past and current years.
Decoding of KBK 18210501012010000110 in 2021 and 2021
In the article we will look at KBK 18210501012010000110: what tax entrepreneurs will be able to transfer under it, what codes to indicate when paying fines and penalties
The code represents information responsible for the reason for transferring the payment: main, penalty or fine. The decoding of KBK 18210501012010000110, presented in the table, will help determine what tax a businessman can transfer to the budget
| Digit p/p | What is encoded | Decoding |
| 1–3 | payment receiver | 182 - Federal Tax Service |
| 4 | cash receipt group | 1 - income |
| 5–6 | tax code | 05 - tax on total income |
| 7–11 | state budget item code | 01012 - taxes according to the simplified tax system “income” until 2011. |
| 12–13 | budget ownership | 01 — Federal budget |
| 14–17 | reason for payment | 0000 - combined form to clarify the reason for the transfer:
|
| 18–20 | state budget income category | 110 - tax |
It follows from the table that the BCC is used to transfer tax under the simplified tax system “income”.
KBK 18210501012010000110 was canceled in 2011 for application for subsequent periods; what code is now in effect for transferring tax, fines and penalties, see the table:
| Year | Tax | Penalty | Fine |
| 2018 | 18210501011011000110 | 18210501011012100110 | 18210501011013000110 |
| 2019 | 18210501011011000110 | 18210501011012100110 | 18210501011013000110 |
Other KBK from this category:
| 18210501011011000110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) |
| 18210501011012100110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as an object of taxation (penalties on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501011012200110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (interest on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501011013000110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as an object of taxation (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) |
| 18210501012011000110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) |
| 18210501012012100110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (penalties on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501012012200110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as the object of taxation (for tax periods expiring before January 1, 2011) (interest on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501012013000110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen income as an object of taxation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) |
| 18210501021012100110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (including the minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation) (penalties on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501021012200110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (including the minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation) (interest on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501021013000110 | A tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (including the minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation) (the amount of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) |
| 18210501022011000110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) |
| 18210501022012100110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (penalties on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501022012200110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (interest on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501022013000110 | Tax levied on taxpayers who have chosen as an object of taxation income reduced by the amount of expenses (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) |
| 18210501030011000110 | Minimum tax credited to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds (paid (collected) for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt on the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) |
| 18210501030012100110 | Minimum tax credited to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds (paid (collected) for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (penalties on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501030012200110 | Minimum tax credited to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds (paid (collected) for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (interest on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501030013000110 | Minimum tax credited to the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds (paid (collected) for tax periods expired before January 1, 2011) (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) |
| 18210501050011000110 | Minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2021) (payment amount (recalculations, arrears and debt) for the corresponding payment, including canceled ones) |
| 18210501050012100110 | Minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2021) (penalties on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501050012200110 | Minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2021) (interest on the corresponding payment) |
| 18210501050013000110 | Minimum tax credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for tax periods expired before January 1, 2021) (amounts of monetary penalties (fines) for the corresponding payment in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) |
Detailed transcript of KBK 18210102010011000110 in 2021
d. What should companies do if they mistakenly indicated the wrong BCC in their income tax payment?
The answer to this question was given by the Ministry of Finance. As the editors found out, an overpayment of personal income tax can be offset against upcoming payments for this tax only if we are talking about amounts that the organization unnecessarily withheld from employees and transferred to the budget (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated January 22, 2021 No. 03-02-07/1/ 3224). If the tax was overpaid due to an error in the payment slip,...
But there is one caveat - the code is not suitable for all incomes. The table shows which payments the application of the KBK does not apply to.
And experts will tell you about the rules for filling out payment orders.
Read more in the program "".
If personal income tax is transferred by a tax agent, the payment order must include KBK 18210102010011000110. Use this code, including if you pay tax on dividends and material benefits.
Why do tax authorities impose fines?
Any simplified documentary reporting has a certain deadline for delivery. There are also deadlines for paying taxes and insurance premiums. And the first thing tax inspectors can fine you for is if the tax has not been paid or the declaration has not been submitted.
Every quarter, simplified taxpayers pay another tax; it is transferred every reporting quarter until the 25th. Before the 20th, a tax return is submitted, where the tax that must be paid is calculated. If you miss the deadlines, then you need to be prepared to accrue fines and penalties.
The penalty is charged immediately on the first day of delay. For example, if you need to pay a tax on the 25th of the reporting quarter, and its payment is made on another day, then starting from the 26th a penalty is accrued, and it accrues every day until the principal debt is repaid.
What tax 2021 KBK 18210501021012100110 should a taxpayer pay? The full decoding sounds like this - a tax levied on a simplified taxpayer who has chosen income to reduce expenses (tax penalties). So, now we know that under this BCC the organization needs to pay a penalty. How to calculate penalties correctly?
Correctness of penalty calculation
To correctly calculate penalties, you need to rely on the Central Bank refinancing rate.
This must be paid on the day when the next payment is planned to be made, so that penalties are not charged again. The calculation is taken inclusive of the day on which the principal debt is paid.
For example, you are 4 days late in payment. It was necessary to pay on the 25th, but the payment is made on the 29th, which means you also need to count the 29th.
But in addition to penalties, you will need to pay both a fine and basic tax. That is, you will have to fill out three payment orders, and there should be different BCCs everywhere. This must always be remembered.
KBK penalties
Explanation 2021 KBK 18210501021012100110 - what tax does it imply? This is a penalty for taxpayers who have failed. In field “104” (filled in on the payment slip) you will need to indicate this particular BCC. To fill out payment orders for simplifiers (income minus expenses) for taxes and fines, the following classification codes should be used:
- Code 18210501021011000110 – for payment of the basic tax for simplified people.
- Code 18210501021013000110 – transfer of sanctions in the form of a fine for late payment of tax.
Therefore, the taxpayer needs to be extremely careful when filling out payment documents. After all, any mistake in the KBK will already cause additional sanctions for the company. And it is advisable to comply with all the deadlines prescribed in the Tax Code, so as not to give rise to additional fines being applied to you.
Where are penalties and fines paid? After filling out the payment document, you can go to the bank, where the operator will accept your payment, or you can use the Client Bank, if it is connected to your organization. Through the client bank, payment documents and the amounts themselves are written off instantly. The program is configured so that it automatically checks all payment details without making errors.
In this case, you can be sure that even if you made a mistake, the program will report it and offer to correct it.
How to calculate penalties according to the simplified tax system
The penalty is the amount payable for late payment of tax or incomplete payment. Penalties are calculated from the day following the day set as the deadline for paying the tax, up to and including the day of payment of the arrears. In this case, the amount of penalties accrued on the arrears cannot exceed the amount of this arrears. This procedure applies when calculating penalties for arrears incurred after November 27, 2018.
Read more here.
With regard to penalties for older arrears, there are two positions on the question of the day from which the calculation of penalties stops. According to one of them, the penalty is calculated including the day of payment of the arrears. This position is given in paragraph 61 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 No. 57, clarifications of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2009. The second point of the position is that the accrual of penalties stops from the day the arrears are paid. This point of view is given in letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 5, 2016 No. 03-02-07/2/39318, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 6, 2017 No. ZN-3-22/ [email protected]
You will find other important nuances of calculating penalties in this article.
Example
The LLC paid tax for the year 20XX on 04/04/2020 in the amount of 1,100,000 rubles using the simplified tax system. At the same time, the deadline for paying the simplified tax for legal entities (in accordance with Article 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) is March 31. Starting from April 1, the LLC incurred tax arrears, which were repaid on April 4. The number of days of delay is 4 days. The refinancing rate is 7.75%.
Penalties = 1/300 × 7.75% × 4 × 1,100,000 = 1,136.66 rubles.
ATTENTION! If the delay is more than 30 calendar days, then from the 31st day, organizations calculate penalties as 1/150 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
You can calculate penalties according to the simplified tax system using our auxiliary service “Fine Calculator”.
You can see current information on the size of the refinancing rate for different periods of time in the ConsultantPlus system. Get a free trial of K+.
KBK: insurance premiums 2018
Insurance premiums for compulsory health insurance in a fixed amount, incl. 1% contributions*
*Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 02/28/2018 No. 35n abolished the separate BCC for payment of 1% contributions, previously introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 12/27/2017 N 255n. Those who have already transferred 1% to a separate KBK will most likely have to clarify the payment
| Type of insurance premium | KBK |
| Insurance premiums for OPS | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Insurance premiums for VNiM | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Insurance premiums for compulsory medical insurance | 182 1 0213 160 |
| 182 1 0210 160 | |
| Insurance premiums for compulsory medical insurance in a fixed amount | 182 1 0213 160 |
| Additional insurance contributions to compulsory pension insurance for employees who work in conditions that give the right to early retirement, including: | |
| – for those employed in work with hazardous working conditions (clause 1, part 1, article 30 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ) (the additional tariff does not depend on the results of the special assessment) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| – for those employed in work with hazardous working conditions (clause 1, part 1, article 30 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ) (additional tariff depends on the results of the special assessment) | 182 1 0220 160 |
| – for those employed in jobs with difficult working conditions (clauses 2-18, part 1, article 30 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ) (the additional tariff does not depend on the results of the special assessment) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| – for those employed in jobs with difficult working conditions (clauses 2-18, part 1, article 30 of the Federal Law of December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ) (additional tariff depends on the results of the special assessment) | 182 1 0220 160 |
| Insurance premiums for injuries | 393 1 0200 160 |
KBK 18210501011011000110: what is the name of payment when paying tax in 2021
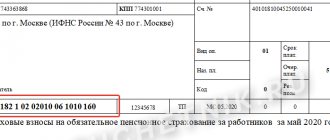
In field 104 of the payment order according to the simplified tax system (“Recipient”), you must put the budget classification code, which consists of 20 characters. In field 24, indicate the name of the payment, for example, “tax under the simplified taxation system with the object “income” for 2021, amount 10,000 rubles, excluding VAT.” See a sample payment form below.
If you indicate an incorrect BCC, then the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not prohibit clarification of the erroneous BCC. However, it can be clarified within the limits of one tax, for example, if instead of a new code the company has installed an old one. But this will have to be proven in court (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District dated January 31, 2013 No. A64-5684/2012).
In order not to argue with the inspectorate, it is easier to pay the tax again to the correct BCC. And ask for an erroneous payment to be offset against future payments.
Watch the video about KBK 18210501011011000110. Tatyana Novikova, Ph.D. in Economics, auditor, tax consultant, associate professor at Moscow State University of Management, Moscow Government, talks about the codes.
All existing organizations and individual entrepreneurs pay taxes to the Federal Tax Service. The tax office uses budget classification codes to determine the type of income of a company from which the amount was transferred to the state budget.
If you make a mistake with the name of the code in the payment document, the treasury may not be replenished in a timely manner. The money will be listed as unknown, and only the Federal Treasury will be able to know about its existence, because the amount will be in its accounts.
If the overlay is not quickly eliminated, the organization or individual entrepreneur may receive penalties and interest due to failure to comply with the tax deadlines established by law.
One of the well-known codes used in many companies with a simplified taxation system (STS) is 18210501011011000110 - KBK, the decoding of which you need to know in 2019, as well as what tax is implied in this case.
What to expect in 2021 simplified tax system
Every year we expect innovations, and this year was no exception. First of all, this will affect the income limit for the transition to a simplified system. Online cash registers will be introduced, new reporting forms will be added, and probably the biggest change will be the change of regulatory authorities.
Now the reporting of the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund will go to the tax authorities. This will naturally lead to a change in the BCC in the payment order. And mandatory insurance contributions that were paid to the pension fund and social security. fear (except for injuries) will need to be paid to the tax office.
Therefore, all commercial structures will need to be extremely careful when paying fees and taxes. Carefully check the BCC in the payment slip so that the transfers reach the regulatory authority without delays or delays. So that the company does not face additional sanctions and unnecessary financial expenses.
The relevance of classification codes can be checked in a special directory, which is published on the official website of the tax service. There you can learn about new changes in legislation.
How did the BCC change in 2020-2021 and were there any changes to the BCC for taxes?
If you want to send a letter to someone by Russian Post, you must indicate the address of the destination and recipient.
The budget classification code plays the role of the address for payment to the budget or declaration. The payer indicates the BCC in 2020-2021 in the payment order, and the treasury sends the money to the budget of the appropriate level for a specific item and sub-item of income. The same is with reporting: the KBK 2020-2021 contains information both about the tax itself and about the taxpayer. IMPORTANT! In 2020-2021, KBC is used not only by legal entities and businessmen. Ordinary citizens also use them, paying, for example, property taxes based on notifications received from the tax office.
The list of KBK changes regularly. It is approved by the Russian Ministry of Finance. Thus, in 2021, the procedure for generating codes, their structure and principles of assignment, approved by departmental order No. 99n dated 06/08/2020, is applied. The list of BCCs for 2021 is determined by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 29, 2019 No. 207n (initially, Order No. 86n dated June 6, 2019 was adopted for this purpose, but Order 207n replaced it). In 2019, the procedure and list from the Order of the Ministry of Finance dated June 8, 2018 No. 132n were in effect.
Despite the replacement of regulatory legal acts, the BCC for 2021 for taxes and contributions has not changed compared to 2021. But their list was expanded - new BCCs were introduced for fines under the first part of the Tax Code. In addition, the CBC for administrative fines imposed in accordance with Chapter 15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation has been updated.
The previous (significant) change to the BCC occurred in 2021 and was associated with the transfer of insurance premiums (except for injuries) under the control of the tax service. That is, the recipient of these funds was the budget, and not an extra-budgetary fund. Accordingly, changes were required in the main BCCs for such payments. Subsequently, the Ministry of Finance adjusted the BCC several times for contributions to compulsory pension insurance accrued at additional tariffs.
Since 2021, the BCC has been introduced for the NAP of self-employed citizens - 182 1 0500 110.
There were no other significant changes that would be significant in 2020-2021 in the BCC list.
You can find out more about decoding the KBK in the material “Deciphering the KBK in 2021 - 2021 - 18210102010011000110, etc.”
Decoding KBK 18210501011011000110
What tax to pay when conducting a particular activity is of interest to many heads of organizations and individual entrepreneurs. When choosing the simplified tax system, employers are faced with the need to apply 18210501011011000110. This is one of the KBK, the interpretation of which in 2019, as before, is a tax on a simplified taxation system, required for deductions by organizations and individual entrepreneurs whose object of taxation is income.
Type of settlement document
When organizations pay taxes, penalties and fines, in the payment receipt in column number 104 they need to enter a special code - KBK. It contains information about the payment made:
- appointment;
- to whom it is addressed;
- type of payment;
- recipient fund, etc.
This budget classification code is noted both when preparing advance payments and in annual reporting. Both Russian companies and foreign ones that receive income through a representative office in Russia are required to fill out payment documents.
Both legal entities and individuals constantly work with budget classification codes and enter them into payment documents that reflect taxes, duties, contributions, penalties, penalties and other payments.
KBK
It is worth noting that KBK 18210501011011000110, which implies a payment made in 2021, is used to pay taxes and penalties from a certain category of companies, LLCs, JSCs operating under a simplified system. If the tax is calculated in a different order, the code will be different.
If you have difficulty finding the required code when filling out a payment order, you can call or send an electronic request to the state treasury or visit it in person. Also, detailed information is contained in the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. ММВ-7-1 / [email protected] , and many services provide for automatic completion of codes in the document.
Didn't find the answer to your question?
Find out how to solve your specific problem
Write your question to the Lawyer below:
KBK-insurance premiums (old periods)
If you need to transfer to the INFS contributions to compulsory medical insurance, compulsory medical insurance or VNIM for periods that expired before 01/01/2017, then they are transferred to the KBK, different from the “fresh” KBK:
| Type of insurance premium | KBK (for contribution) | KBK (for penalties) | KBK (for a fine |
| Insurance premiums for OPS | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Insurance premiums for VNiM | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Insurance premiums for compulsory medical insurance | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0211 160 |
| Insurance premiums for compulsory health insurance in a fixed amount | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Insurance premiums for compulsory health insurance in a fixed amount (1% contributions) | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0200 160 | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Insurance premiums for compulsory medical insurance in a fixed amount | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0211 160 | 182 1 0211 160 |
True, the BCC for additional contributions to compulsory pension insurance for periods expired before 01/01/2017 is the same as for periods starting from 01/01/2017.
When paying tax according to the simplified tax system (income minus expenses), each commercial organization indicates the corresponding BCC with completed payment documents. For example, a merchant using the simplified tax system, and who has chosen the income minus expenses system, must indicate KBK 18210501021011000110 in the payment. This will mean that the main tax is transferred to the simplified tax system.