What is KBK and why is it used?
KBK (budget classification code) is a combination of numbers that indicates the purpose of the payment received by the Federal Tax Service.
Based on this number, funds contributed by an individual entrepreneur or legal entity are sent to the appropriate budget item.
Assigning the simplified tax system to KBK simplifies the control of receipts and planning of funds.
The code consists of 20 digits, which, in a group or individually, convey information about the purpose of the payment.
- The initial three digits represent the organ code.
- The next number indicates the transfer group - tax payment, free transfer and others.
- Then the third two digits indicate the tax code - on profit, on property and others.
- Based on the next five numbers, the article and subitem of the payment are determined.
- After that, two numbers indicate where the amount was paid - to the regional, federal budget or in favor of the Social Insurance Fund or Pension Fund.
- The next four digits indicate the purpose of the payment - tax contribution, payment of a fine or penalty.
- The final three numbers determine the type of transfer - tax, from property, etc.
These indicators are divided into 4 blocks:
- administrator block (code numbers 1-3);
- income block (numbers 4-13);
- program (numbers 14-17);
- classifying (numbers 18-20).
It is necessary to check the relevance of the codes annually, as they may change. Specifying an incorrect number will result in the tax received by the Federal Tax Service not being displayed.
This entails sanctions in the form of penalties and fines.
Important: if the simplified tax system was specified incorrectly when filling out the KBK documents, you will need to send a letter to the tax service with a request to transfer funds. If the amount has not been credited, the payment is repeated.
back to menu ↑
Where to find the required KBK
It is hardly possible to remember all the required budget classification codes.
To make it easier to fill out documents when making payments, special reference books are provided. The information in them is updated annually in accordance with legislative amendments.
Every accountant has such a KBK directory. Before filling out the forms, check the values indicated there for the “Income minus expenses” mode.
If you don’t have a reference book at hand, but have access to the Internet, you should go to the official website of the tax service www.nalog.ru. It displays complete and up-to-date information for 2017.
The KBK simplified tax system will need to be indicated on payment orders when transferring quarterly advance payments and transfers to the Pension Fund. In order for the amount paid to the Federal Tax Service to be received as intended, the code must be entered correctly.
back to menu ↑
What are the features of calculating and paying taxes according to the simplified tax system?
The rate under the “Income minus expenses” mode is 15%. In the regions, its size can fluctuate between 5-15%, which is associated with the use of differentiated tax rates.
To correctly determine the tax base and calculate the tax contribution, a ledger is kept to record incoming and outgoing transactions. It can be maintained manually or electronically.
The main difficulty for an accountant of an LLC or individual entrepreneur working under the “Income minus expenses” regime is recognizing the legitimacy of expenses.
This is necessary to correctly determine the tax base. If it is underestimated, an additional fee will be charged and fines will be imposed.
Important: if an enterprise suffers a loss based on the results of the previous tax quarter, the tax base in the current tax period can be reduced by the amount of this loss.
Cash receipts are calculated using the cash method: after funds are credited to the current account or to the cash desk of an LLC or individual entrepreneur, they can be indicated in the income item.
As for expenses, before making them, you need to prove their economic justification.
To classify the amount spent as an expense, two conditions must be met.
- Costs must be documented. The expense item includes amounts for concluded contracts and advance reports. The payment document is filled out in accordance with legal requirements and company rules.
- Only amounts paid for profit can be considered expenses. In addition, if the company has paid for the goods, its cost can be taken into account after it is delivered to the warehouse.
Important: funds spent on advertising are recognized as expenses only in an amount not exceeding 1% of the amount of cash receipts.
back to menu ↑
Kbk usn income minus expenses 2021
Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
» Article 346.16. Procedure for determining expenses
1. When determining the object of taxation, the taxpayer reduces the income received by the following expenses:
5) material costs;
2. The expenses specified in paragraph 1 of this article are accepted subject to their compliance with the criteria specified in paragraph 1 of Article 252 of this Code.
The expenses specified in subparagraphs 5, 6, 7, 9 - 21 of paragraph 1 of this article are accepted in relation to the procedure provided for calculating corporate income tax in articles 254, 255, 263, 264, 268 and 269 of this Code.
Article 254. Material expenses
1. Material expenses, in particular, include the following expenses of the taxpayer:
1) for the acquisition of raw materials and (or) materials used in the production of goods (performance of work, provision of services) and (or) forming their basis or being a necessary component in the production of goods (performance of work, provision of services);
2) for the purchase of materials used:
for packaging and other preparation of manufactured and (or) sold goods (including pre-sale preparation);
for other production and economic needs (testing, control, maintenance, operation of fixed assets and other similar purposes);
3) for the purchase of tools, fixtures, inventory, devices, laboratory equipment, work clothes and other property that is not depreciable property. The cost of such property is included in material costs in full as it is put into operation;
4) for the purchase of components undergoing installation and (or) semi-finished products undergoing additional processing from the taxpayer;
5) for the purchase of fuel, water and energy of all types, spent on technological purposes, production (including by the taxpayer himself for production needs) of all types of energy, heating of buildings, as well as costs for transformation and transmission of energy;
6) for the acquisition of works and services of a production nature, performed by third-party organizations or individual entrepreneurs, as well as for the performance of these works (provision of services) by structural divisions of the taxpayer.
Works (services) of a production nature include the performance of individual operations for the production (manufacturing) of products, performance of work, provision of services, processing of raw materials (materials), monitoring compliance with established technological processes, maintenance of fixed assets and other similar work.
Works (services) of a production nature also include transport services of third-party organizations (including individual entrepreneurs) and (or) structural divisions of the taxpayer itself for the transportation of goods within the organization, in particular the movement of raw materials, tools, parts, workpieces, and other types of goods with base (central) warehouse to workshops (departments) and delivery of finished products in accordance with the terms of agreements (contracts);
7) related to the maintenance and operation of fixed assets and other property for environmental purposes (including costs associated with the maintenance and operation of treatment facilities, ash collectors, filters and other environmental facilities, costs for the disposal of environmentally hazardous waste, costs for the purchase of services from third-party organizations reception, storage and destruction of environmentally hazardous waste, wastewater treatment, payments for maximum permissible emissions (discharges) of pollutants into the natural environment and other similar expenses).
When are payments made?
Based on Articles 346.19 and 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, advance payments under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” are transferred until the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter. As for the payment of the single tax according to the data for the past year, the deadlines differ:
- for individual entrepreneurs - until April 30 of the year following the reporting year;
- for LLC – until March 31.
When an enterprise stops operating under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” before the end of the calendar year (currently 2017), the tax contribution is transferred within the time limits specified for the incomplete period.
When the payment date falls on a non-working day, the amount is paid on the business day closest to that date. This procedure is determined by paragraph 7 of Article 6.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
back to menu ↑
KBC when paying fines and penalties
Separate codes have been established for the payment of penalties and fines.
Penalties are charged for each day of late payment. When transferring penalties to the budget, you must indicate
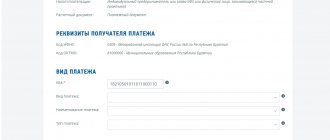
KBK - 182 1 0500 110.
A fine differs from penalties in that it is a fixed amount (for example, 1000 rubles or 10% of income) and is paid once, and not for each day of delay.
KBK when paying fines - 182 1 0500 110
KBK table for simplified tax system income minus expenses 2016
| Purpose of the code | KBK number |
| transfer of single tax - “income minus expenses” scheme | 182 1 0500 110 |
| transfer of penalties for a single tax - the “income minus expenses” scheme | 182 1 0500 110 |
| transfer of fines for a single tax - the “income minus expenses” scheme | 182 1 0500 110 |
| transfer of the minimum tax (1%) - any simplified tax system | 182 1 0500 110 |
| transfer of penalties for the minimum tax | 182 1 0500 110 |
| transfer of minimum tax penalties | 182 1 0500 110 |
What is the difference in payments according to the simplified tax system?
The KBK simplified tax system is different for a single contribution under the “Income minus expenses” regime and when paying the minimum tax. The latter is charged in the following two cases:
- the tax on the difference between income and expenses turned out to be less than the minimum payment;
- According to the results of the year, the enterprise's expenses exceeded its income.
The deadlines within which the minimum tax must be paid without the accrual of penalties do not differ from the deadlines for paying the single tax. The tax period is also a calendar year, currently 2016.
If the enterprise is liquidated or no longer applies the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, this period is counted from the beginning of the year until the date of liquidation or until the day the preferential regime is applied.
If an organization has switched to another tax scheme, the minimum tax will be calculated based on the results of the previous reporting period.
Important: the minimum tax is 1% of cash receipts.
back to menu ↑
How are penalties calculated according to the simplified tax system?
The obligation to pay advances and taxes is considered fulfilled at the moment of presentation of the payment order for their transfer to the bank, if there is a sufficient amount of money in the payer’s account (clause 1, clause 3, article 45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Delay in the transfer of tax payments occurs the next day after the date established for their payment, and it is accrued for each calendar day before the day on which the debt is repaid (clause 3 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example
The advance payment for the simplified tax system for the 1st quarter of 2021 was paid on April 30. In this case, penalties will be accrued within 4 days (from April 26 to April 29). And if the advance payment had been delayed by only 1 day, having paid it on April 26, no penalties would have been accrued at all, since the day of payment of the debt is not included in the period for accruing penalties.
Please note that from October 1, 2017, a new procedure for calculating penalties is applied (clause 4 of article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- For individual entrepreneurs and individuals, penalties, as before, are calculated from 1/300 of the refinancing rate in force during the period of delay.
- For legal entities, 1/300 of the ref rate is applied only if there is a delay of up to 30 calendar days, and starting from the 31st day, penalties are calculated from 1/150 of the current ref rate for each overdue day.
Example
The deadline for paying the “simplified” tax for 2021 is 04/02/2018. The organization paid it only on 05/07/2018, the payment amount is 25,000 rubles. The period of delay is 34 calendar days (from April 3 to May 6). The refinancing rate from March 26, 2018 is 7.25% (let’s assume that it will remain at this level until May 7, 2018).
Let's calculate penalties for the first 30 days:
25,000 rub. x (7.25% x (1/300)) x 30 days. = 181.25 rub.
Starting from 31 days, penalties will be:
25,000 rub. x(7.25% x (1/150) x 4 days = 48.33 rub.
For the entire period, penalties of 229.58 rubles were accrued. (181.25 + 48.33).
Which KBK simplified tax system to indicate when filling out documentation in 2017
In the process of processing payment orders, the KBK simplified tax system is entered on the basis of the data presented in the order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 1, 2013 No. 65n (as amended on December 25, 2015 No. 215n).
For the single tax under the “Income minus expenses” regime and for the minimum tax, different codes are entered. Some BCCs of the simplified tax system have penalties and fines.
Important: advance payments are made according to the “Income minus expenses” mode. However, if at the end of 2021 the level of income falls under the minimum tax, it must be paid, but advance payments made are deducted from the amount.
It is important to correctly enter the KBK of the simplified tax system when preparing documentation for the Federal Tax Service. Then the deposited amount will go to its destination.
Accurate information on codes for 2021 can be obtained from regulatory documents or on the tax service website.
back to menu ↑
KBK 2015 NEW codes for classification of budget revenues of the Russian Federation
Calculation of penalties according to the simplified tax system: postings
“Simplified” accounting managers must carry out operations to accrue penalties and additional tax charges. The calculation of penalties is given in the accounting certificate, and for the amount of penalties according to the simplified tax system, entries are made in accounting as follows:
- Dt 99 “Penies” Kt 68 “STS” - the amount of penalties accrued for arrears on the “simplified” tax/advance payment; the posting date will be the date of the Federal Tax Service's request for payment, or the date indicated in the accounting certificate;
- Dt 68 “USN” Kt 51 – penalties are transferred to the budget.
In tax accounting, penalties and fines under the simplified tax system, as well as for other taxes, are not taken into account and the base for the “simplified” tax is not reduced (clause 1 of article 346.16; clause 2 of article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).