What to do if expenses exceed income under the simplified tax system?
Is personal income tax included in expenses when applying the simplified tax system (income minus expenses)?
First, let's determine what taxes a company pays when applying the simplified taxation system (STS)? When applying the simplified tax system in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an enterprise is exempt from paying taxes such as: profit tax, property tax, VAT (except for cases when importing goods).
Organizations applying a special regime pay insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance and make contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and the Medical Insurance Fund.
Taxpayers using the simplified taxation system with the object “Income minus expenses” reduce their income by the amount of expenses according to the list of paragraph 1 of Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This list is exhaustive.
According to paragraphs. 22 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the tax base is reduced by the amount of taxes and fees paid in accordance with the law.
Also, organizations with a tax system – “simplified” - according to clause 5 of Art. 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not exempt from the duties of a tax agent.
In accordance with Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the calculation and payment of personal income tax occurs in relation to all income of taxpayers (employees) received from a tax agent (enterprise, organization, individual entrepreneur). The duty of tax agents is to withhold the accrued amount of tax from the taxpayer’s income at the time of actual payment.
Withholding of personal income tax from an employee’s earnings by a tax agent can be made at the expense of any funds paid by the tax agent to the employee at the time of payment of funds. Payment of personal income tax at the expense of tax agents (enterprises, organizations, individual entrepreneurs) is not allowed.
Therefore, amounts of personal income tax withheld from the wages of employees by an organization or individual entrepreneur applying a simplified taxation system are not included in the expenses specified in paragraphs. 22 clause 1 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Moreover, in accordance with paragraphs. 6 clause 1 and clause 2 art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, simplified taxpayers can reduce their income by the amount of labor costs (Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which includes all accruals to employees determined in employment contracts or collective agreements.
The salary of an employee of the enterprise was 20,000 per month. Personal income tax (if there are no deductions) - 2600 rubles. (RUB 20,000 x 13%). The enterprise's expenses include the total amount of accrued earnings - 20,000 rubles. Then part of it in the form of personal income tax (2,600 rubles) is transferred to the tax office, and the remaining part, 17,400 rubles. (20,000 - 2600) is paid to the employee in person.
Let’s summarize the topic “Is personal income tax included in expenses when applying the simplified tax system (income minus expenses)?”
From the above it follows that for employers the amounts calculated, withheld and transferred to the personal income tax are an integral part of the employee’s accrued wages. Thus, personal income tax amounts are taken into account as part of labor costs. If you include them in expenses separately, it turns out that they will be taken into account there 2 times: as part of labor costs and separately, which is unacceptable by law.
Send by mail
Is the state duty included in the expenses under the simplified tax system, at what point and how is it reflected, and what to do with the state duty in case of refusal of the registration action? You will find answers to these questions in the article.
The list of costs taken into account when determining the single tax during simplification is indicated in Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to sub. 31 clause 1 of the above-mentioned article, the state duty under the simplified tax system, income minus expenses, reduces the tax base. But according to paragraph 2 of Art. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, costs must meet the requirements of paragraph 1 of Art. 252 of the Code.
First of all, this paragraph mentions the economic feasibility of expenses. This means that as a result of paying the state duty, some significant result must be obtained. Otherwise, the fee paid cannot be considered an expense.
This applies, for example, to situations where, when submitting an application to make changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, the registration action was refused due to an error made by an employee of the enterprise when filling out the form. In this situation, the paid state fee is not returned to the legal entity, but cannot be accepted as expenses.
IMPORTANT! In case of reimbursement of state duty to an enterprise by a court decision, the amount received must be included in income. Thus, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation interprets the norms of the code in letters dated 02/20/2012 No. 03-11-06/2/29, dated 05/17/2013 No. 03-11-06/2/17357.
Read about what expenses are accepted for accounting under the simplified tax system here.
How the state duty is accepted as an expense under the simplified tax system depends on the action for which the duty was paid. If the state fee is paid for filing a lawsuit, registering changes in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, issuing duplicate documents or other similar actions, then such a fee is included in the costs for determining the simplified tax according to the norms of subsection. 22 clause 1 art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Check out this publication for a list of tax deductible expenses.
But if the state duty is paid to register a vehicle or register real estate, then such a fee will increase the amount of depreciable property and will reduce the tax base in accordance with the procedure described in paragraph 3 of Art. Code 346.16. But this applies only to those fees that were paid before the depreciable property was put into operation. If the fee is paid after, then the state duty is included in the expenses under the simplified tax system at a time in accordance with clause 2 of Art. 346.17 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
To reflect the operation of calculating state duty in accounting, it is necessary to remember that, according to Art. 333.40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in certain cases, the duty may be returned to the payer or, at his request, offset against other actions of government agencies. Therefore, until the expected legally significant action is completed (or a government agency refuses to perform it), the duty cannot be included as an expense either in accounting or tax accounting.
When using a simplified taxation system, a businessman may not pay some taxes. But transport tax is not included in this list. Therefore, the answer to the question of whether transport tax is paid under the simplified tax system will be unambiguous - taxpayers using this special regime pay it in the usual manner.
Simplified individual entrepreneurs pay tax only on the transport that is used in their business activities. But they do not submit a transport tax declaration to the Federal Tax Service - this obligation applies only to legal entities (Article 363.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT! Individual entrepreneurs make a payment to the budget on the basis of a notification issued by the tax authorities (clause 3 of Article 363 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the individual entrepreneur has not received it, he is obliged to initiate an appeal to the Federal Tax Service on his own and transfer to this department all the necessary information about his transport. Such an obligation was introduced in 2015 (clause 2.1 of Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation); previously it did not exist.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Return of over-transferred funds - postings
Let's consider how transport tax affects the taxable base under the simplified tax system. Transport tax is an expense for the taxpayer. Therefore, if he has chosen an object that involves accounting for expenses, then this obligatory payment reduces the taxable base.
IMPORTANT! Under the simplified tax system, expenses are taken into account on the basis of documents confirming actual payment (clause 1 of article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, the transport tax will be included in the expenses of those periods when it was transferred to the budget.
When using a taxation object that does not include accounting for expenses, there are a number of mandatory payments that reduce the final amount of tax payable. However, TN is not included in this list. Therefore, the transport tax under the simplified tax system on income does not have any impact on the tax base.
Taxpayers who have switched to the simplified tax system continue to pay part of their taxes on a general basis. This number also includes TN. Making this mandatory payment reduces the taxable base under the simplified tax system only when using an object that provides for accounting for expenses. If the object “income” is used, then the TN does not affect the amount of the tax payment under the simplified tax system.
Expenses under the simplified tax system - income minus expenses - are subject to the requirements set out in Chapter. 26.2 “STS”, a number of which refer to the provisions of Chapter. 25 “Profit Tax” of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Let's consider the list of expenses of the simplified tax system, as well as the features of their recognition.
For the first method, the issue of expenses for tax purposes does not matter, but for the second it plays a very important role.
- costs for the purchase, production and installation of fixed assets;
- costs of purchasing intangible assets;
- costs for the purchase of exclusive rights, know-how, intellectual property;
- costs incurred in obtaining patents;
- costs associated with R&D;
- costs of repairing and improving fixed assets - both own and leased;
- expenses incurred under lease agreements;
- material costs;
- labor costs;
- costs for all types of compulsory insurance (pension, social, medical, life insurance);
- expenses related to payment for services provided by credit institutions;
- costs in the form of input VAT amounts;
- costs aimed at paying customs duties;
- expenses associated with business trips (payment for travel to the place of performance of an official assignment and back, payment for accommodation, daily allowance);
- costs of accounting, auditing, legal and other similar services, including accounting services;
- costs of training and retraining of personnel;
For information on the procedure for writing off fixed assets for expenses under the simplified tax system, read the article “Accounting for fixed assets under the simplified tax system in 2017-2018.”
What services provided by credit institutions can be taken into account in expenses under the simplified tax system, read the article “Accounting (nuances)”.
Is it possible to take into account consulting costs under the simplified tax system, find out from the material “Consulting costs under the simplified tax system, income minus expenses”
Compensation paid to workers
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation stipulates the following types of compensation:
- In accordance with Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, there are additional payments to employees performing their work duties in special conditions, for example, in the regions of the Far North.
- In accordance with Art. 164 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, compensation is defined as the return to an employee of funds that he was forced to spend in the performance of his work duties, for example, for the use of personal transport on long trips.
The payments specified in the first paragraph can be attributed to expenses in order to reduce the tax base of the simplified tax system-15%, since this kind of additional payments are part of the salary.
But payments from the second paragraph do not apply to wages and are not included in the list of allowed expenses under the simplified tax system. It follows from this that it is impossible to reduce the tax base due to the costs incurred to pay compensation to employees. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation reported this in its letter dated March 21, 2019 No. 03-11-06/2/18724.
Definition
What are taxes for entrepreneurs and organizations in Russia? To understand why taxation differs, it is necessary to first clarify in what cases taxes are generally paid in commercial activities. In principle, any organization pays at least some taxes, but the question is what exactly the conditional organization pays.
Let's look at the main taxes paid by individual entrepreneurs and LLCs. Among them there are several that can be installed in any field of activity. Since there are direct and indirect, we will analyze only the most remarkable from each category.
Personal income tax or income tax is the most common type of direct taxes. It is calculated as a percentage of the total income of an individual and deducting all confirmed expenses indicated in official documents and legalized in the Russian Federation.
The main taxpayers in this category are individual entrepreneurs and other individuals. They can either be actual tax residents of the Russian Federation - those who are on the territory of the Russian Federation for at least 183 days in one calendar year. Also, payers are considered persons who are not residents of the Russian Federation, but still receive income on its territory and according to its laws.
Value added tax is already the most common type of indirect taxes. This is a form of withdrawal of the value of goods, services and work, in which the money goes to the state budget. Withdrawal occurs at all production stages of the process of creating goods and services.
When applying value added tax, taxes are paid by consumers themselves when purchasing goods and services. The tax amount is included in the cost of the purchased good initially, but the amount reaches the state budget much earlier than the purchase. This is because the tax is paid by everyone who at least somehow participated in the production process of a product or service at any stage.
There are two tax rates for VAT in Russia: a rate of 18%, which applies to most products by default, but if some product is not included in this list, then it is taxed at a rate of 10%, or in extreme cases, a rate of 0%, under special conditions.
Minimum tax
Now let’s return to the object of our discussion - the minimum tax of the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”. This is a tax that is paid only under the given simplified tax system “15%”. It is paid only when this tax amount suddenly turns out to be greater than the total tax amount. The calculation occurs only based on the results of the reporting period, which is most often a year.
There are also cases when an unplanned transition to a general taxation system occurs; in such circumstances, the minimum tax under the simplified tax system is transferred to the budget upon request from the Tax Service. Thus, the Federal Tax Service equates the reporting year, which was the last for the organization, with the tax period. But such emergency situations occur extremely rarely, so the minimum tax here is very individual.
But, despite the differences, the minimum tax is paid in the same way as an ordinary tax, within the same terms and according to the same rules. In addition, to carry out the payment procedure, it is necessary in 2018 for each entrepreneur and company.
Main features
Many companies that have a relatively small profit and total number of employees prefer to work on a simplified taxation system, which significantly simplifies the procedure for calculating and paying taxes. This system allows you to eliminate a number of mandatory contributions to the budget, while the accountant’s responsibilities include filling out much less documentation, since reporting is much simpler.
Under the simplified system, the company is completely exempt from the need to remit income or property tax, and in a number of situations there is also no need to charge value added tax if the organization does not belong to the category of importers of commercial products.
It is worth noting that even in the case of using special regimes, both entrepreneurs and companies need to withhold and transfer insurance premiums in a timely manner.
If an organization that has decided to conduct its activities on a simplified system has itself chosen as an object of taxation profit reduced by expenses, this may allow it to significantly reduce the amount of the tax base, and for these purposes it is necessary to use the list prescribed in the Tax Code.
In accordance with the provisions of Article 346.14 of the Tax Code, an entrepreneur has the right to reduce the amount of the tax base by those amounts of fees or taxes that were previously transferred to the state budget. At the same time, the use of the simplified tax system does not provide organizations with the opportunity to free themselves from their duties as a tax agent in relation to their employees if they pay them salaries.
Thus, they must necessarily withhold the appropriate amount at the time of salary payment in order to deduct tax at the time of salary calculation, and the law does not provide for the possibility of paying it out of the company’s own money.
Tax offset
To determine who pays the minimum taxes, you must first understand who the taxpayers are in general.
So, annually, based on the results of the reporting period, all individual entrepreneurs and enterprises using the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” consider two tax bases:
After calculations, the tax that turns out to be higher must be paid to the Tax Office. It is important to highlight here that the final tax can never be less than the minimum, that is, 1% of all income received during the reporting period. It is also important that the result of the difference between regular taxes and the minimum that was paid can then be included in the expenses of subsequent years.
If you are still concerned about questions like “What tax should I pay?”, “Do I need to pay the minimum tax when receiving a loss?” and “What exactly to choose?”, then you should turn to a professional for help, for whom, by the way, you will also have to pay well, but it may be worth it, since he will help you avoid real problems.
We invite you to read: State duty for inheritance of land
In fact, calculating the minimum income is a piece of cake that can be done in a matter of minutes using the appropriate formula:
- Minimum tax = Tax base x 1%
The tax base here is cumulative, determined from the beginning to the end of the entire reporting period for which the tax must be paid. Specifically, for the minimum tax, this base is calculated in accordance with Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Sometimes it happens that some taxpayers want and combine the simplified taxation system “Income minus expenses” with the patent taxation system, for example. In such cases, where circumstances dictate complexity, the minimum tax will be based only on income that is earned under the simplified system and not on the patent. This is legalized by one of the letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 13, 2013 No. 03-11-09/3758.
Calculation example
Let’s look at the minimum tax using specific examples to make it easier to understand how everything is organized.
So, let’s take the limited liability organization “Sila”, which uses the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” in organizing its activities and calculate the tax.
- The results of her work over the past year amounted to an income of 250,000 rubles.
- It includes 30,000 rubles for the first quarter, 70,000 rubles for the second quarter, 80,000 rubles for the third quarter and again 70,000 rubles for the fourth quarter.
- Expenses amounted to 240,000 rubles, of which 32,000 rubles for the first quarter, 65,000 rubles for the second quarter, 72,000 rubles for the third quarter and 71,000 rubles for the last.
- We get the tax base, which is equal to 10,000 rubles, based on calculations.
- The rate applied in this case is 15%.
After this, Sila’s accountants need to make the following calculations:
- Calculate the tax amount from the tax base based on the tax rate established in this example: 10,000 rubles x 15% = 1,500 rubles.
- Calculate the amount of the minimum tax from the tax base, based on a one-percent tax rate, without deducting expenses: 250,000 rubles x 1% = 2,500 rubles.
- Carry out a comparative analysis of the final results: 1,500 < 2,500 rubles.
- It is quite clear that in this case the amount of the minimum tax is much more than the fifteen percent tax.
- The tax that is the least is paid, in this case it is the minimum.
Summing up the results of the year, Sila LLC pays exactly the minimum tax according to the simplified tax system, since its amount is greater than the tax, which is calculated at fifteen percent.
It is also important to note that in the case where advance payments were also accrued at the end of the reporting period, the minimum tax is paid with the deduction of all amounts of advance payments. Applying this to the above example, the amount of contributions for 9 months of the organization’s operation is equal to 1,650 rubles. This means that at the end of the year it is necessary to pay a much lower minimum tax - 850 rubles.
Another point to mention is the difference between taxes. The amount of the minimum tax and the tax, which is calculated in the usual manner, can be taken into account in the expense item for the period to calculate the tax using the simplified “Income minus expenses” for future tax periods in the declaration. Moreover, in the case when a loss is received, it is increased by the above difference and transferred to the same future periods.
In total, in this specific example, starting from 2021 as a tax period, the entire difference that can be included in expenses will be a maximum of only 1,000 rubles. This is 2,500 rubles from the minimum - 1,500 from the regular tax.
Although the unified tax regime is divided into simplified ones and so on, one should not confuse the regimes and the BCC for them. Since a simplified individual entrepreneur pays taxes under the simplified tax system in 2021 according to absolutely the same codes, which means offset is also possible. This is because the minimum tax is not any kind of extraneous, but only the same part of the simplification as advance payments and taxes.
This means that all contributions paid by organizations and payers (tax subjects) can be offset against the same minimum tax under Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. All this is provided for by law, as are tax returns.
To offset advance payments against tax paid to the tax office, you must submit a correct application for tax offset. Also attach to it all copies of documents that would confirm the fact of payment of contributions. In the event that the credit is still denied and the company has to pay the full tax, the advance payments will not be lost, but will be credited to future contributions.
Normative base
The legislative part of the question can also take a long time, but in order to understand how this system with a minimum tax functions, it is important to first familiarize yourself with the Tax Code, which is the most important thing.
And then, in order to specifically rely on the articles, it is worth reading everything about the minimum tax, and it is especially important to read such as:
- Article 346.19 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- clause 6 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- clause 7 art. 346.21 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Art. 78 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
By reading all this and applying it to any necessary situation, you can easily resolve even the most difficult dilemma. Therefore, the litigation of forming the minimum tax can be very easily eased, only by checking with the legislation.
Expenses during business trips
Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that travel expenses can reduce the size of the tax base under a simplified taxation system. However, if the individual entrepreneur himself was on a business trip, then the provisions of the article cannot be applied to such expenses.
When traveling on a business trip, according to Art. 166 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the organization, represented by the manager, must send an employee to perform an official task outside the place of permanent work, and in the case of an individual entrepreneur, no one can send him on a trip. This opinion is reflected in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 16, 2021 No. 03-11-11/62269.
Payment
To understand more specifically who, what, where, why and how pays, you need to understand the instructions for paying the simplified tax system:
- Throughout the year, it is impossible to say for sure whether you need to pay or not pay the minimum tax, because it is calculated only at the end of the year. This means that every reporting quarter or period it will be necessary to pay all advance payments as usual. This is income minus expenses multiplied by 15 percent.
- At the end of the year, individual entrepreneurs and enterprises determine what tax they need to pay. Usually all the deadlines are the same, regardless of what tax will be paid - these are the reporting deadlines. For individual entrepreneurs this is until April 30, and for enterprises this is until March 31.
- If it turns out that there is a need to pay the minimum amount of tax, then this entire amount can be reduced by all contributions paid; insurance payments are made according to the plan. And also, when the amount of taxes is greater than the minimum tax, then there is no need to pay it. And the rest of the advance payments can be taken into account when paying the next debts, in a year, or simply returned as profit, using an application to the tax office.
- It is also important to remember that starting from 2021, the entire minimum tax must be paid according to another BCC, according to the one established for the single tax of the simplified tax system. This KBK is 182 1 05 01021 01 1000 110.
We invite you to read: Changing a judge in civil proceedings
Standard data
In order to understand how to correctly calculate expenses under a simplified system, you need to take into account the basic rules for calculating each individual amount provided for by current legislation.
Is income included?
In connection with the above rules, the amount of employee income tax that is withheld from their wages by a company or private entrepreneurs operating on a simplified system cannot be included in those expenses that are noted in subparagraph 22 of paragraph 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code.
Do not forget that entrepreneurs are given the opportunity to reduce the amount of the tax base by the full amount of accrued wages, which also initially includes personal income tax.
Taking this into account, we can say that employers in any case must indicate the amount of personal income tax in the process of calculating costs when paying tax, but if they are included separately, then in this case they will be taken into account twice, which is not provided for by current legislation.
Accounting details
Personal income tax must always be withheld when a company pays any amounts to individuals, and in particular, this applies to the following situations:
- the company pays dividends to its founders, and personal income tax must be paid on these amounts;
- the company receives a certain interest-bearing loan from an individual, after which it returns the specified amount;
- the company draws up a civil agreement stipulating the need to accrue the appropriate payment amount to individuals.
Paragraph 40 of Article 217 of the Tax Code states that reimbursement of expenses that were allocated to pay interest on loans received for the purpose of acquiring or constructing residential real estate cannot be subject to personal income tax, but these payments are not taxed only if they were originally accounting will be carried out as part of the company’s expenses when calculating income tax.
Article 217. Income not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation)
Thus, this rule does not apply to those companies that operate on a simplified system, but at the same time use only the profit received as an object of taxation.
On January 1, 2021, new reduced rates for the simplified tax system came into force. The minimum tax of the simplified tax system for 2021 is indicated at the link.
Recognition of material expenses under the simplified tax system, as well as other types of expenses
2. Expenses incurred in connection with calculations for wages under the simplified tax system are recognized in the same manner as material expenses.
Regarding the list of simplified taxation system expenses related to payment for work activities, you should also be guided by the provisions of Chapter. 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These costs include:
- payment of wages to employees;
- bonuses and other incentive payments;
- the cost of utilities, food and products provided to employees free of charge;
- expenses for the purchase and production of uniforms for employees, which are given to them free of charge or sold to them at a reduced price.
- tax expenses are written off based on the date of actual payment of taxes;
- expenses for fixed assets and intangible assets are recognized at the end of the tax period in the amount of amounts paid;
- when paying by bill of exchange, expenses are taken into account on the date of payment of the bill of exchange, however, if the bill of exchange is transferred in favor of third parties, then the date of recognition of the expense corresponds to the moment of its transfer.
A complete list of labor costs is contained in Art. 255 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
3. Expenses for payment of the cost of goods that were purchased for the purpose of further sale are accepted as they are sold.
Read more about accounting for the write-off of goods when applying the simplified tax system here.
4. Other features of recognizing expenses are as follows:
Read about what changes related to the application of the simplified tax system came into force in 2017-2018. “STS “income minus expenses” in 2017-2018.”
Simplified people keep records of income and expenses in KUDIR. We described in this article how to fill out a book using the new form.
An example when personal income tax is not included in expenses
M.V.
Proshkin works at Zvezda LLC. The organization applies a simplified system with the object of taxation being income minus expenses. The employer pays the employee monthly compensation for renting an apartment in the amount of 25,000 rubles. So, on July 27, 2015, the organization transferred 21,750 rubles to his account, and personal income tax withheld from income in the amount of 3,250 rubles. - to the budget. Payment of compensation for rental housing is not provided for by either the labor or collective agreement. Does Zvezda LLC have the right to reflect these expenses in the tax base? No. As part of labor costs, you can take into account payments provided for by law or labor (collective) agreement (clause 2 of article 346.16 and article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Since compensation for rental housing is not specified in the employment or collective agreement and is not provided for by law, then 21,750 rubles paid to M.V. Proshkin, and 3250 rubles. Personal income taxes transferred to the budget will not affect the tax base of the organization.
“Simplified” must keep separate records of accrued and paid personal income tax amounts. This approach will allow you to avoid writing off unnecessary expenses. After all, employees are often paid income that is subject to personal income tax, but is not taken into account in expenses for the single tax. And since personal income tax is often paid by general payment, you need to track which personal income tax is due on payments included in expenses and which is not.
What to do if expenses exceed income under the simplified tax system?
When calculating and paying tax, you should pay attention to the fact that Art. 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the payment of a minimum amount of tax, defined as the product of 1% and the amount of income received.
Payment of the minimum tax is carried out in the following cases:
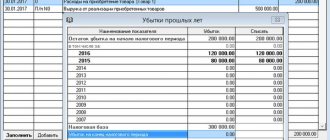
A loss should be considered the amount of excess of expenses over the amount of income received for the tax period.
With regard to the loss, the following possibilities and conditions for its write-off must be taken into account for the purposes of Chapter. 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
Procedure
Companies need to transfer the tax amount itself and all kinds of advance payments at the place of their registration, while private entrepreneurs make payments at their place of residence.
First of all, advance payments are transferred, and this must be done no more than 25 days from the end of the reporting period. In the future, advance payments made will be taken into account in the process of determining the amount of tax at the end of the calendar year.
After this, a declaration is filled out, after which it is sent to the Tax Service office. Legal entities must submit a declaration by March 31 of the year following the expired tax period, while private entrepreneurs are given the opportunity to send documentation by April 30 of the year following the last tax period.
Ultimately, the tax calculated based on the results of the full year is paid. It is worth noting the fact that the tax payment deadlines are exactly the same as those established for filing the relevant reports, and if the last day of the tax payment deadline falls on a non-working day or weekend, then in this case the payer will need to pay taxes on the next working day after him.
Filling out a declaration under the simplified tax system
In accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the declaration is submitted once a year after its end no later than:
The form and procedure for filling out a declaration under the simplified tax system for the report for 2017 are established by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 26, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/
When filling out a declaration form under the simplified tax system with the object of taxation “income minus expenses”, you need to pay attention to section 2.2, which contains information about the income received and the taxpayer’s expenses.
For information on where to find information about control ratios for checking a declaration, read the material “The Federal Tax Service has released control ratios for the declaration under the simplified tax system.”
Tax payment is made in advance payments based on the results of each reporting period (quarter) no later than the 25th day of the month following the end of the reporting quarter. In this case, the payment deadline for the 4th quarter corresponds to the reporting deadline for the specified period.
For more information about the deadlines for filing reports and paying taxes, read the article “What are the deadlines for submitting a declaration under the simplified tax system?”
Costs incurred under the simplified tax system need to be determined only if the tax object “income minus expenses” is used to calculate the tax. At the same time, Ch. 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the concept of a minimum tax that should be paid when expenses exceed the taxpayer’s income and a loss is incurred.
Be the first to know about important tax changes
Arrears on personal income tax
In accordance with Federal Law No. 325-FZ of September 29, 2021, an amendment was made to Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Since January of this year, an organization acting as a tax agent has the right to pay off income tax arrears from its own funds . However, there is no need to withhold this amount from the employee’s salary.
However, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, in its letter dated January 29, 2021 No. 03-11-09/5344, reports that the organization does not have the right to include personal income tax transferred at the expense of the employer as expenses. Since these costs are not justified from a financial point of view.