Who is obliged to attach explanations to the financial statements?
An explanatory note is required as part of the annual reporting of all organizations that maintain full accounting records.
An exception is organizations entitled to simplified accounting:
- small businesses;
- non-profit organizations;
- participants of the Skolkovo project.
Such entities have the right to report on a reduced set of accounting forms and are not required to provide explanations, or provide them only in relation to the most important information, without which it is impossible to assess the financial condition of the company.
Regulatory framework
Key aspects regarding the need for registration and correctness of explanatory notes are disclosed in the following documents:
- Article 14 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n;
- PBU 4/99, which regulates the financial statements of organizations.
What data is included in the notes to the financial statements in 2021
The explanatory note must reflect information about the accounting policies, because its provisions establish the accounting rules for the enterprise. Additional data not included in the main reports helps assess the financial condition of the entity and the reasons for the current situation as of a specific date.
PBU 4/99 determines the content of the notes to the balance sheet and financial statements:
- data at the beginning and end of the year, as well as the movement of intangible assets, fixed assets, accounts receivable and payable, financial investments and capital;
- composition of income and expenses;
- composition of reserves;
- extraordinary facts of economic life and their consequences;
- conditional facts of economic life, events after the reporting date, etc.
An example of writing a note on liabilities
- Section "Liabilities".
3.1. Line 1410 of the balance sheet reflects long-term (under agreements for a period of more than 12 months) debt on loans issued by JSC CB Gazstroykapitalinvest (amount - 300 thousand rubles, rate - 17% per annum, repayment period - 03/31/2022, agreement No. 1 dated 09/17/2019).
3.2. Line 1420 reflects deferred tax liabilities formed due to differences in accounting and tax accounting:
- depreciation of fixed assets (150 thousand rubles);
- the cost of software for which exclusive rights have not been acquired (50 thousand rubles).
3.3. Line 1520 reflects accounts payable:
- To counterparties:
- supplying raw materials and materials (700 thousand rubles);
- supplying fixed assets (200 thousand rubles);
- who provided work and services (300 thousand rubles).
There are no overdue debts included in accounts payable.
- Before the budget:
- for personal income tax (300 thousand rubles);
- for income tax (100 thousand rubles);
- for VAT (200 thousand rubles);
- for corporate property tax (400 thousand rubles);
- for insurance premiums (800 thousand rubles).
- In the form of advances received:
- from subsidiaries (100 thousand rubles);
- from Russian counterparties (300 thousand rubles);
- from counterparties from the EAEU countries (200 thousand rubles);
- from counterparties from countries outside the EAEU (RUB 70 thousand).
- To the employees of the company:
- at the main production (100 thousand rubles);
- in auxiliary production (30 thousand rubles);
- in service departments (40 thousand rubles).
This is what individual excerpts from the explanatory note to the balance sheet may look like in terms of significant reporting indicators.
Another component of an enterprise's reporting—the income statement—can also be supplemented with explanations. Let's consider what they can be.
Who is interested in explanations of financial statements?
Explanation of financial statement indicators is necessary for a fairly wide range of interested parties, including:
| Interested people | Cause |
| State control authorities (including the Federal Tax Service) | Explanation of the dynamics of indicators, transcript of articles |
| Owners | Explanation of financial result |
| Creditors | Assessing the readiness of the debtor organization to repay the debt |
| Investors | Assessing the stability of the organization and its investment attractiveness |
What form is used to prepare an explanatory note for 2019?
Clause 4 of Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 07/02/2010 provides for the provision of explanations in tabular or text form. These methods can be combined. The organization independently decides what data requires clarification, but must take into account the recommended forms from Appendix No. 3 to Order No. 66n.
The document is usually drawn up according to the following plan:
- Information about the organization: location; Kind of activity; information about managers, founders and affiliates, etc.
- Data on accounting policies: methods of evaluating products, inventories; methods of calculating depreciation, information about changes in accounting policies during the year, if any.
- Financial indicators for the reporting year: revenue and costs by type of activity; It is possible to decipher large income and expense transactions.
- Actually, explanations for individual balance sheet items.
The specifics of the company’s activities in each specific case determine which indicators should be excluded and which ones should be added.
Explanations when discrepancies with tax reporting are identified
Such reporting undergoes a desk audit along with the submitted declarations.
If contradictory data is identified, the declarant is given 5 working days to provide explanations. There are no fines or other penalties for failure to submit explanations, but it is in the interests of the company to send such a document. For example, if an error in an accounting report led to a reduction in the amount of tax, such an action may be regarded as tax evasion, with all the ensuing legal consequences. To correct the situation, it is necessary to submit an updated report or declaration to the Federal Tax Service.
Explanatory note to financial statements - sample in 2020
Explanations for the balance sheet can be formatted as follows:
| Explanations to the accounting (financial) statements LLC "Bread Factory No. 3" for 2021 1. General information Limited Liability Company (LLC) "Bread Factory No. 3" was registered by the Federal Tax Service No. 18 for Moscow on September 02, 2012, OGRN 1117711111111, INN 7711123456, KPP 771101001; legal address: Moscow, st. Lenina, house 155. 1.1. Authorized capital: 1,800,000 (one million eight hundred thousand) rubles (fully paid). 1.2. Founders and affiliates of the organization:
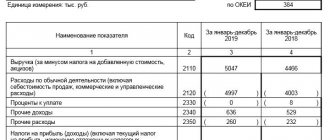
1.3. The main activity of the organization according to OKVED: 10.71.1 - Production of bread and non-durable bakery products. 1.4. The number of employees as of December 31, 2021 is 77 people. 1.5. There are no branches, representative offices or other separate divisions. 2. Basic accounting policies The accounting policy of LLC Bread Factory No. 3 was approved by order of the General Director O.N. Saushkin. dated December 28, 2018 No. 162. 2.1. A non-linear depreciation method is used. There is no revaluation of fixed assets. 2.2. The financial result from the sale of products and goods is determined by shipment. 2.3. Inventory and finished products are assessed at actual cost. 2.4. The write-off of inventories into production is carried out at an average cost. 3. Financial indicators The general meeting of founders on February 17, 2020 approved the financial statements for 2021. The accounting (financial) statements of Bread Factory No. 3 LLC for 2021 were generated based on the accounting and reporting rules in force in the Russian Federation. 3.1. Net profit at the end of 2021 amounted to RUB 5,841,600. Payment of dividends to the founders in accordance with their shares in the authorized capital was made on 02/20/2020. 3.2. Revenue for 2021, rubles:
3.3. Costs of production and sales of products in 2021, rubles:
4. Explanation of balance sheet items as of December 31, 2019 4.1. Fixed assets: Name | As of 12/31/2018 | Change | As of 12/31/2019 | ||||
| Initial cost | Depreciation | Received | Dropped out | Accrued depreciation | Initial cost | Depreciation | |
| Fixed assets of all, including: | 1 300 300 | 1 001100 | 2 192 100 | 45 200 | 341 100 | 3 447 200 | 1 342 200 |
| Building | 900 100 | 800 800 | 1 200 600 | — | 200 300 | 2 100 700 | 1 001 100 |
| Equipment | 400 200 | 200 300 | 90900 | 45 200 | 90700 | 445 900 | 291 000 |
| Vehicles | — | — | 900 600 | — | 50 100 | 900 600 | 50 100 |
4.2. MPZ
| Name | As of 12/31/2018 | Change | As of 12/31/2019 | |
| Cost price | Received | Dropped out | Cost price | |
| MPZ total, including: | 846200 | 79600 800 | 79 806 500 | 640500 |
| Raw materials | 820 400 | 36 500 100 | 36 680 000 | 640 500 |
| Finished products | 25 800 | 43 100 700 | 43 126 500 | — |
4.3. Accounts receivable
| View | As of 12/31/2018 | Change | As of 12/31/2019 | |||||
| Accounted for under the terms of the contract | Reserve | Admission | Disposal | Accounted for under the terms of the contract | Reserve | |||
| Redeemed | Written off | Reserve restored | ||||||
| Accounts receivable total, incl. | 18 100 500 | — | 76 701 700 | 68 601 100 | 27 700 | — | 26 173 400 | — |
| according to payments to suppliers | 2900 300 | — | 1 500 400 | 2 300 600 | 1 300 | — | 2 098 800 | — |
| according to settlements with buyers | 15200 200 | — | 75 201300 | 66 300 500 | 26 400 | — | 24 074 600 | — |
4.4. Accounts payable
| View | As of 12/31/2018 | Change | As of 12/31/2019 | |||||
| Accounted for under the terms of the contract | Reserve | Admission | Disposal | Accounted for under the terms of the contract | Reserve | |||
| Redeemed | Written off | Reserve restored | ||||||
| Accounts payable total, incl. | 33 547 400 | — | 47 900 300 | 49 800 600 | 45 900 | — | 31 601 200 | — |
| Short-term total, including: | 23 600 700 | — | 47 900 300 | 46 200 400 | — | — | 25 300 600 | — |
| according to payments to suppliers | 22 100 500 | — | 38 300 100 | 36 500 100 | — | — | 23 900 500 | — |
| according to budget calculations | 1 500 200 | — | 9 600 200 | 9 700 300 | — | — | 1 400 100 | — |
| Long-term total, including: | 9 946 700 | — | — | 3 600 200 | 45 900 | — | 6 300 600 | — |
| according to payments to suppliers | 45 900 | — | — | — | 45 900 | — | — | — |
| on credits, loans | 9 900 800 | — | — | 3 600 200 | — | — | 6 300 600 | — |
4.5. Salary
There are no payables and receivables for wages as of December 31, 2019.
The average number of employees as of December 31, 2019 is 77 people.
General Director of LLC "Bread Factory No. 3" Saushkin O.N. Saushkin
22.02.2020
An example of writing a note on current assets
- Section "Current assets".
2.1. The main category of reserves on the company's balance sheet is raw materials and materials.
As of the end of the reporting year, the book value was determined:
- unprocessed raw materials - 300 thousand rubles;
- materials transferred for processing - 700 thousand rubles;
- spare parts - 200 thousand rubles;
- fuel - 400 thousand rubles;
- containers - 10 thousand rubles.
2.2. The company's expenses for unfinished production are made:
- within the framework of the main production - in the amount of 2 million rubles;
- within the framework of auxiliary production - in the amount of 700 thousand rubles;
- within service departments - in the amount of 200 thousand rubles.
2.3. The goods on the balance sheet include:
- goods in warehouse worth 500 thousand rubles, incl.
- small household appliances – 300 thousand rubles;
- electronics – 150 thousand rubles;
- accessories for electronics – 50 thousand rubles.
A provision was accrued for the depreciation of finished goods in the amount of 20 thousand rubles.
2.4. The Company has taken into account VAT on acquired assets in the form of:
- fixed assets - in the amount of 70 thousand rubles;
- inventories - in the amount of 200 thousand rubles;
- works and services - in the amount of 300 thousand rubles.
In the reporting year, the company claimed the corresponding VAT for deduction because the necessary documents were not prepared.
2.5. The company has accounts receivable:
- buyers - in the amount of 2 million rubles;
- in the form of advances issued - in the amount of 500 thousand rubles;
- state bodies - in the amount of 1,500 thousand rubles.
At the end of the reporting year, a reserve for doubtful debts was accrued in the amount of 300 thousand rubles.