What tax agents should do
During the year, tax agents (organizations and individual entrepreneurs with employees) must calculate personal income tax, withhold and transfer it to the budget each time income is paid to an employee/other individual. For example, when transferring salaries, this is done monthly.
In addition, tax agents for personal income tax are required to report to the Federal Tax Service. In 2015 and earlier, they had to do this only at the end of the year, submitting Certificates 2-NDFL. But from 2021, in addition to the existing obligation to submit Certificates, the obligation to submit quarterly reports in Form 6-NDFL has been added.
Personal income tax is one of the most profitable contributions. The state charges 13% from every salary of any employee, thereby replenishing its budget by 30% annually. For example, according to economists’ calculations, the capital of the Moscow region consists of 43% personal income tax.
This type of tax is more federal, since it applies equally to all citizens throughout the country. The period for its deduction varies, depending on the time of creation of the enterprise (details are specified in Article 55 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is not necessary to make deductions every month or quarter; You can withdraw the accumulated amount once a year. Therefore, for the purity of the operation, it must be formed correctly. To do this, the employee needs to work for a year (most often this is the amount of time allotted) and deduct 13% of each salary every month. So, after 12 months there will be an amount that forms the payment base of an individual, which he will have to make annually. The time it took for this to happen is the personal income tax period.
Objects of personal income tax taxation
According to the Tax Code, the following types of income are subject to personal income tax taxation:
- remuneration for work;
- dividends on shares;
- income from the transfer of property for rent;
- income from the sale of property, sale of securities and other assets;
- insurance payments upon the occurrence of an insured event;
- income received from the use of copyright or related rights in the Russian Federation;
- pensions, benefits, scholarships and other similar payments;
- income received from the use of any vehicles, including sea, river, aircraft and automobile vehicles, in connection with transportation to the Russian Federation and (or) from the Russian Federation or within its borders;
- income received from the use of pipelines, power lines (power lines), fiber-optic and (or) wireless communication lines, and other means of communication, including computer networks, on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- payments to the legal successors of deceased insured persons in cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation on compulsory pension insurance.
Tax legislation establishes the types of income of citizens on which income tax is levied.
However, not all income is taxable.
This means, for example, the following:
- financial assistance that the organization pays to an employee after the birth of a child (its amount should not exceed 50 thousand rubles);
- maternity benefits for employees on maternity leave;
- compensation for damage caused to employee health;
- reimbursement of employee expenses for paying interest on loans and credits received for the purchase or construction of housing;
- gifts, the cost of which does not exceed 4 thousand rubles. per year received by individuals from organizations and individual entrepreneurs.
Full list in Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax system of the Russian Federation
Personal income tax is the main source of replenishment of the state treasury
The definition of “tax system” is understood as a set of fees, duties, penalties, and taxes levied on citizens for certain actions. They are spelled out in the Tax Code, which also specifies the principles, objectives, functions, forms of taxation and participants in the structure. All payments made are sent to budgets of different levels, which are divided depending on the type of collection.
- Federal - VAT, excise taxes, personal income tax, taxes on profits, on the extraction of minerals, on the use of water resources, wildlife, state duties for the work of authorized bodies.
- Regional - tax on transport, gambling, property of organizations.
- Local - fees for land and movable and immovable property.
According to this scheme, all payments are distributed among budgets and then used for the needs of the state. The federal budget allocates salaries to people with unproductive professions - the Ministry of Emergency Situations, firefighters, police, teachers and educators, various services, etc. In addition, part of the funds goes to support the armed forces, construction, restoration of infrastructure, as well as social benefits. The remaining two budgets deal with the improvement of only certain areas and regions.
Objectives of the tax system of the Russian Federation
The work of the tax office is based on a number of basic principles that allow it to be a transparent, clear and fair system. Thanks to them, it exists and functions in 2021, and also performs the most important task - redistributing state profits among all segments of the population. In addition, there is another purpose:
- A safety net in case of a decline in production - fees and duties are conditional profits that can be put to use. But there are situations when some enterprise of national importance suffers losses, for example, due to sanctions on the import of products into another country or simply poor sales and high production costs.
- Do not interfere with entrepreneurship - the tax applies to any income, including organizations with companies. As a rule, they always have a significant profit, therefore, they need to pay more. In order not to interfere with their activities, the state provides them with an expanded list of benefits.
- Implementation of social programs - all discounts and free services are paid for from one of the budgets. An excellent example would be veterans and military personnel who can take advantage of benefits.
This is why the tax system exists. In one case, it acts as the main source of income for the state, in another - as assistance to the economy, entrepreneurship and vulnerable segments of the population.
The essence of the personal income tax tax period
The tax period for personal income tax in Russian legislation is established as a period of time after which the amount required to pay the fee is finally determined. Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1, art. 55: “...the period after which the tax base and the amount of tax are determined...”.
Determination of the tax and reporting period
If we talk about personal income tax, then for it this period is one calendar year, that is, 12 months of work for which a salary is paid.
Note! When officially employed at a registered enterprise, the employer independently calculates the amount of all contributions and gives the employee only a net salary. But there are situations when the employer deducts only personal income tax, and the employee has to pay other taxes (health insurance, unemployment, etc.) on his own. Then he will have to go to the tax office and take a declaration, which will then be handed over to the authorities to record his earnings and benefits with discounts from him.
In total, there are several tax rates in the Russian Federation - 9, 13, 15, 30, 35 percent. For example, a 9% contribution must be paid from company dividends. A share of 13% is personal income tax, and 15% is income from organizations to persons who are not foreign citizens. For them, the period for determining the base may vary slightly (all the nuances are specified in the Tax Code).
Basic tax rates
After repayment of the fee, the reporting period for personal income tax begins. This is done to save time for inspection workers, and also legitimizes all payments and deductions to the budget. An organization or individual entrepreneur is obliged to first formulate salaries for employees, then deduct all types of taxes from them, and give only a net paycheck in hand and at the same time certify everything in writing. The tax period for which the base is formed is one year. At the end, along with payment, a reporting period begins, the duration of which varies for different entities:
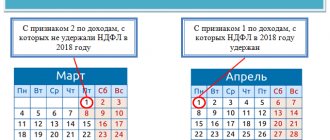
- employers - until April 1 in the next half of the tax period;
- individual entrepreneurs - until April 30 under the same circumstances;
- other persons - until April 30.
During this time, the inspection must be provided with a document - a report. It is an ordinary declaration in which all income and current tax benefits must be recorded. If this is not done, the employer will be fined 200 rubles for one 2-NDFL certificate. There should be as many of them as there are registered employees at the enterprise.
If we talk about individual entrepreneurs, then they need to provide a 3-NDFL declaration.
Important! Payment of the final tax is not made immediately, but at certain intervals throughout the subsequent tax period. First, you need to repay half for the period from January to June, then a quarter - from July to September, the last 25% - for October. If you ignore the obligation to provide a report, the violator will receive a fine of 1000 rubles.
The tax period is considered to be 12 months, but this is not always the case. Very often, enterprises or organizations are registered in the inspection register for different months, which is why this period is shortened. In this case, all issues with the tax authorities must be resolved before the end of the current year. If the individual entrepreneur was registered in December, then the time is extended for another month. Such taxpayers need to provide a 4-NDFL certificate immediately after the first month of profit so that agents can deduct possible advance payments. This document is also necessary if the profit amount changes by more than 50%: if the entrepreneur’s profit changes by half, then he is obliged to fill out a declaration and submit it to the inspectorate. Otherwise, a fine of 200 rubles per sheet will be imposed.
Declaration to be completed after the tax period
It is also worth mentioning about foreign citizens, since recently it has become important to open a business in a country other than your own. For them, everything is thought out in the same way - 1 calendar year of the tax period. However, there is no need to fill out and submit a declaration to the Federal Tax Service, since these persons are freed from the hassle of a payment report. Residents have more favorable conditions than entrepreneurs of the Russian Federation.
There is nothing difficult in the concept of a tax period - this is the time (for personal income tax - a year) for which the final amount of a particular tax is formed. As a rule, it is paid not every month, but after a year at once for all wages issued. And at the moment when the period established by law expires, the reporting period begins. It is also designed for a certain period of time and is needed to ensure that entrepreneurs not only pay all taxes for their employees, but also to provide written documentation. Usually, time is allotted for this until the end of April of the next year, during which it is necessary to provide declarations for all employees in order to avoid paying a late fee.
DATE OF PIT WITHHOLDING.
In accordance with paragraph 4 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax agents are required to withhold the accrued amount of personal income tax directly from the taxpayer’s income upon their actual payment, taking into account the nuances established by this paragraph. (Features of tax withholding are determined in relation to income in kind and income in the form of material benefits.)
Thus, if wages are paid not on the last day of the month for which they are accrued, but later, the date of actual receipt of income and the date of withholding personal income tax fall on different days and, quite possibly, different reporting periods. When paying for vacation, a similar situation does not arise, since the date of actual receipt of income and the date of withholding personal income tax coincide.
Duration of the tax period for income tax
Based on Art. 216 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the duration of the tax period is defined as a calendar year. After this period, it is necessary to make full payments and report to the state. The calendar year may not always be complete. Some features of the tax period are established by Art. 55 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, a newly registered organization is required to report from the beginning of its activities to December 31. When registering an employer in December, the tax period for personal income tax becomes the period of time from the beginning of the creation of the organization until the end of the next year, etc.
Individual entrepreneurs, whose responsibilities include paying personal income tax, also take the calendar year as a basis.
Reporting on accrued personal income tax by other persons
Other individuals who received income determined by clause 1 of Art. 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are required to report after the end of the personal income tax tax period, which is considered to be the previous calendar year. They also provide the 3-NDFL declaration until April 30. Tax obligations must be paid no later than July 15.
For the tax period for income tax for foreign citizens carrying out activities listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 227.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the calendar year is accepted. These groups of persons do not submit declarations at the end of the reporting period, except for the cases listed in paragraph 8 of Art. 227.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Look for materials that can help in drawing up a declaration.
How to maintain and submit reports to other individuals
Some types of income are not directly related to the employer or business activities. For example, this is the receipt of large gifts, the sale of property, winnings in lotteries and gambling, “author’s” heirs and assigns, etc. All of them are listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 228 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Based on the results of the tax period, which is also a calendar year, an individual is required to independently report on them.
Also, before April 30 of the next year, you must send a declaration to the inspectorate in form 3-NDFL. And no later than July 15 - pay off all tax circumstances for the tax to the treasury.
In paragraph 1 of Art. 227.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation lists the activities of foreign citizens that can generate income. The tax period for personal income tax for them is also a calendar year. However, they do not need to submit a declaration after the end of the reporting period. Exceptions are listed in paragraph 8 of the same article.
Thus, the tax period for personal income tax in all cases coincides with the calendar year. Accordingly, the entire 2021 is a tax period for personal income tax. And for individual entrepreneurs there is a mechanism for advance payments for this entire period and until July 15 of the next year.
Read also
27.07.2016
General income tax cycle
There is Art. 216 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which the duration of the tax period is determined by the calendar year. After it ends, it is necessary to pay the tax in full, as well as submit reports to the state.
It is noteworthy that a calendar year does not always mean a whole year of 365 or 366 days. So, if an organization or individual entrepreneur was registered during this period, they must submit personal income tax reports for the period until December 31. That is, the period of time that passes from the beginning of its activities to the end of the current year is considered.
When calculating the personal income tax budget, businessmen also base their calculations on the calendar year.
Where will the new personal income tax be paid and for what purposes will it be used?
For the transfer of ordinary personal income tax of 13%, the KBK is established - 18210102010010000110; for the excess tax amount at a rate of 15% - KBK 18210102080010000110.
Attention! Don't forget that in 2021 you will need to fill out payment orders in a new way.
Tax payments are not targeted; they are distributed for various purposes of spending budget funds. But an exception has been made for personal income tax of 15%: this is a targeted tax. The money received by the state will be used to treat children with rare and dangerous diseases.
According to forecasts, the amount of tax that will be collected during 2021 will be about 65 billion rubles. Medicines, treatment, and hospital stays for seriously ill children are very expensive, and these funds are intended for a truly good cause. We can only hope that they will go as intended, and the state will provide the opportunity to transparently and clearly track the movements of these targeted revenues.
Submission of reports by employers
Reporting to the tax authority must be submitted after the tax period for an individual entrepreneur or company is over. At the same time, these tax agents must reflect the income of their employees. Until recently, only the 2-NDFL certificate served for these purposes. It indicates the income tax withheld and transferred to the budget.
If we consider an individual entrepreneur in this context, then if he works under the general regime, he must make advance payments to the budget for personal income tax. And for those individual entrepreneurs who pay income to individuals or use the labor of hired workers, it is mandatory to perform the functions of a tax agent during the personal income tax tax period.
The duties of tax agents imply that when paying income to an employee or other individual during the year, they calculate personal income tax and withhold it. After which it is transferred to the budget. If we are talking about wages, then deductions must go every month - on the next days after the actual receipt of money, receipt on the bank card.
The tax period for personal income tax involves submitting reports to the employee income inspectorate by April 1 of the next year. If the certificates are submitted untimely, then for each unit of document that is overdue, a fine of 200 rubles will be imposed. It is noteworthy that you have the right to choose: submit certificates in paper form or using electronic reporting. The law allows for the first option for small companies if they employ less than 25 people.
Vacation pay
Vacation pay is subject to personal income tax at standard rates - 13% and 30% (for non-residents).
It happens that an employee quits before he has time to go on vacation. In this case, he is paid compensation for unused vacation days. This compensation is also subject to personal income tax.
The deadline for paying personal income tax on vacation pay or compensation is set differently than for wages. The tax amount must be transferred to the budget in the month in which the payment was made. The deadline is the last day of this month.
For example, an employee goes on vacation on July 1 . According to current legislation, vacation pay must be paid no later than 3 days before the vacation. Accordingly, payment will be made in June. This means that personal income tax must be transferred to the budget no later than June 30.
Let's look at the calculation of personal income tax on vacation pay using an example, the data for which is given in the following table.
Table. Data for calculating vacation pay and personal income tax
| Index | Meaning |
| Vacation day | July 1 |
| Employee salary amount | 50,000 rubles |
| Billing period | July 2021 - June 2021 (12 months) |
| Amount of payments for the billing period | 50,000 * 12 = 600,000 rubles |
| Number of vacation days | 28 |
| Personal income tax rate | 13% |
Vacation pay is calculated based on average daily earnings and the number of vacation days. Average earnings for calculating vacation pay are calculated using the formula: From the amount of payments for the billing period / 12 months / 29.3 (average number of days in a month). In our example, the average daily earnings will be: 600,000 / 12 / 29.3 = 1,706.48 rubles.
Let's calculate vacation pay: 1,706.48 * 28 = 47,781.44 rubles.
Let's calculate the amount of personal income tax on vacation pay: 47,781.44 / 100 * 13 = 6,211.59 rubles.
Before the vacation, the employee will receive: 47,781.44 - 6,211.59 = 41,569.85 rubles.
New reporting
Each of the tax agents for personal income tax maintains a report to their Federal Tax Service. Until 2015 inclusive and earlier, this had to be done only at the end of the year by submitting 2-NDFL certificates. Changes have arrived in 2021. From now on, it is necessary to submit not only the specified certificates, but also a new reporting form - 6-NDFL - on a quarterly basis. This report must also be submitted in 2021. Moreover, in 2021 a new form of calculation, 6-NDFL, was introduced.
Moreover, the penalty for late filing of this calculation is five times greater than for 2-personal income tax. And even to the point of freezing the bank account.
6-NDFL not submitted or submitted with delay
The fine for a tax agent in 2021 is 1,000 rubles. for each full or partial month from the day for submitting the calculation (clause 1.2 of Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The period of delinquency will be calculated from this day until the date on which you submitted the estimate (in person, through a representative, by mail or online).
If you do not submit the payment within 10 days from the due date, the tax inspectorate also has the right to block the bank account of the tax agent (clause 3.2 of Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In 6-NDFL there is inaccurate data
The fine for each payment with false information is 500 rubles. But if you discovered an error and submitted an updated calculation before the tax inspectors noticed it, there will be no sanctions (Article 126.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Inspectors may impose a fine due to any error in the calculation in Form 6-NDFL. Inaccuracy in income and deduction codes, total indicators. But in some cases, inspectors reduce the fine, citing mitigating circumstances (clause 1 of Article 112 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). These are cases where the tax agent, due to an error:
- did not underestimate the tax;
- did not create adverse budgetary consequences;
- did not violate the rights of individuals.
Not only the organization, but also responsible employees (for example, a manager) can be held accountable. The official faces an administrative fine of 300 to 500 rubles. (Article 15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). Individual entrepreneurs, lawyers, and notaries are not held administratively liable (Article 15.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Submission of reports by merchants
As was said, the tax period for personal income tax for individual entrepreneurs is also a calendar year. The income report must be submitted by April 30 of the next year by filing a 3-NDFL declaration.
The rules for paying income tax (clause 9 of Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) provide for several periods for entrepreneurs:
- until July 15 – 50% of annual advance payments for January-June;
- until October 15 – 25% for July-September;
- until January 15 – 25% for October-December.
If the 3-NDFL declaration is not submitted on time, a fine of no less than 1000 rubles will be imposed in accordance with Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.