The “Cash Flow Items” directory in 1C 8.3 is an additional analysis of accounts 50 and 51.
Let's consider several important points that must be taken into account when using DDS articles:
- Setting up the program.
- Features of the formation of the “Cash Flow Report”.
- Control over an enterprise's cash flows using DDS items.
For organizations that must submit Form No. 4 (“Cash Flow Statement”), filling out DDS items is mandatory. For organizations using the simplified tax system, accounting of funds by items may not be carried out.
In 1C programs, the corresponding setting is located on the “Accounting Parameters” tab - see Fig. 1
Fig.1
When filling out the directory of DS movement articles, it is important to choose the right type of movement. In 1C programs, types of movement are “hardwired” into the program and are not subject to adjustment; their list corresponds to the lines of the regulated report Form No. 4.
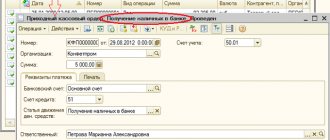
For example, cash receipts by type of movement “Receipt from the sale of products and goods, performance of work, provision of services” (Fig. 1) corresponds to line 4111 of the DS movement report (Fig. 2). In our example, this is the amount of 246 thousand rubles.
Fig.2
Setting up a chart of accounts
To work with the directory of articles, you must first complete the settings, which are located in the section “Administration/Accounting parameters/Setting up the chart of accounts/Accounting for DDS: By account and DDS items” or in the section “Main/Chart of accounts/Setting up the chart of accounts”.
Fig.1 Setting up DDS accounting by item
Setting up treasury in any 1C programs to suit your business processes
Using the DDS Articles Directory
When generating a DDS report in 1C 8.3, always check the amounts received with the balance sheet for accounts 50 and 51. If the amount in circulation is greater, it means that you did not enter the DDS article in some document. Otherwise, you could indicate a DDS article where this is not required.
Amounts from documents in which the item is not indicated will be displayed in the balance sheet with an empty grouping, so it is not difficult to find them.
If you group them in the DDS articles directory, then in reports you can get results for them by changing the grouping type of the article.
In some other 1C configurations, for example in ERP, DDS items are required for management accounting analytics.
For example, for a certain item, an expense limit is set for a specific month. Then an application is created to spend DS under this item. They are also used in the payment calendar.
Proper accounting for cash flow items not only allows you to submit financial statements on time and without errors, but also helps management analyze the activities of the enterprise in a more structured manner.
Form No. 4 “Cash Flow Statement”
Accounting statements for the year using the fourth form can be generated in the section “Manager/Monitor of taxes and reporting/Accounting statements”.
Fig.6 ODDS form
When creating a report form, the monetary amounts registered by item will be attributed to one or another type of movement of assets, depending on the items specified when posting the relevant documents.
Let's demonstrate the above with an example. Let’s assume that through “Receipts to account” under the movement item “Receipts from the sale of products and goods, performance of work, provision of services” a payment from the buyer was recorded in the amount of 102,135.00 rubles, including VAT of 15,579.92 rubles.
Fig.7 Details “DDS Article” of the document “Receipt on account”
In the setting of the article we are considering, the type of movement of the same name is indicated.
Fig.8 Setting up the item sales receipts
Thus, the registered payment from the buyer under the DDS article with the type of movement “Receipts from the sale of products and goods, performance of work, provision of services” on form No. 4 of the report will be included in the total amount on line 4111 “Receipts from the sale...”.
Fig.9 Payment from the buyer in ODDS
Decoding line 4111 allows you to see the components of the total amount for this line. In our example, the final amount of 87 thousand rubles was obtained as the difference between the amount of payment from the buyer of 102,135.00 rubles and VAT of 15,579.92 rubles (86,555.08 ~ 87 thousand rubles).
Fig. 10 Explanation for line 4111 “Proceeds from the sale...”
Input and example of filling out a list of DDS articles
The list of DDS articles itself is located in the “Directories” menu.
In the standard delivery of the 1C configuration in the reference book, for example, there is already a certain list of DDS articles. If it is necessary to add new articles, the most important thing is to correctly indicate the type of movement of the DS. The fact is that it directly affects the report on the movement of the DS.
The name can be specified arbitrarily. This directory also supports grouping of its elements. This is not necessary, but it is advisable for further ease of use. In addition, grouping cost items allows you to obtain results for different types of activities in the future.
If you need a specific item to be entered by default when creating any cash receipt or expenditure document, indicate the default operation in its card.
You cannot set multiple default cost items for the same operation. To avoid this, when selecting, those operations that already have a main item assigned will not be displayed.
In the list form, a list of cost items with types of operations is displayed when you click on the “Main Items” hyperlink.
Cash flow analysis report
This management analytics is available to “Manager/Cash”.
In order for the information in the report to be grouped by DDS items, you should select the “Cash flow item” checkbox in the report settings on the “Grouping” tab. The report settings are hidden under the “Show settings” function button.
Fig. 11 Report “Analysis of cash flows”
Fig.12 Report settings
Cash flow accounting programs - minimizing the occurrence of cash gaps and ensuring the effective use of cash flows
Settings
In order to configure the use of cash flow items in 1C 8.3, go to the “Administration” menu and select “Accounting Settings”.
In the form that opens, click on the “Set up chart of accounts” link. Next, select “By current accounts.” In this example, the item is called “By current accounts and cash flow items” due to the fact that all settings were previously set by default.
Our team provides consulting, configuration and implementation services for 1C. You can contact us by phone +7 499 350 29 00 . Services and prices can be seen at the link. We will be happy to help you!
A 1C setup form for DSS accounting will open in front of you. If the “By cash flow items” flag is not selected by default, select it. Depending on the settings, this flag may be set by default and changing this add-on will not be available.
Click on the “Record and close” button and you can proceed to setting up the DDS articles themselves.
Indirect method of compiling ODDS
The essence of the indirect method of forming ODDS is to establish the difference between net profit (or losses) for a specified reporting period in relation to the indicators of net amounts received from the main (current) activity.
It is calculated using the cash method, based on the data from the company’s balance sheets.
The indirect method is suitable for those companies and enterprises that keep records in accordance with IFRS, transforming data without the possibility of automating this process.
The data is generated on the basis of profit and loss statements and balance sheets from the beginning and end of the reporting periods. Also, additional data on flows used in the transformation of reporting may be involved in the formation of ODDS by an indirect method.
Accounting data on the actual movement of flows will not be required, and you can also do without automation. Using the indirect method of creating ODDS, you can understand the amounts of each line of the profit and loss statement.
When calculating a company's net profit, the report allows you to take into account "non-financial components", for example, if there are depreciation or other changes in the company's assets and liabilities. This will allow you to see accurate data on the amounts of net cash flows from core activities. There are two types of adjustments:
Adjustment related to income statement line item
In this case, the adjustment is used to eliminate so-called “non-cash” items that do not relate to cash flow. At the same time, they have an impact on net profit.
The adjustment also excludes items related to investing and financing activities.
This adjustment allows you to obtain interim results for operating profit before changes in working capital are introduced. This information will be useful for conducting financial analysis. Thanks to this, the owner or manager will be able to assess the real financial situation of the company before accruing various expenses.
Adjustment of changes in working capital
This type of adjustment makes it possible to have information on changes in balance sheet items.
For example, if receivables are paid in cash and they have increased towards the end of the period, then the operating profit before changes in working capital will need to be adjusted downwards. It should be reduced exactly by the amount of the change so that real cash flows are not less than revenue.
Investment operations
| Article title | Type of movement |
| Providing loans | Acquisition of debt securities, provision of loans to other persons |
| Proceeds from the sale of non-current assets | Proceeds from the sale of non-current assets (except financial investments) |
| Dividends from participation in organizations | Income from dividends, interest on debt financial investments |
| Receiving interest on deposits | Income from dividends, interest on debt financial investments |
| Receiving interest on loans issued | Income from dividends, interest on debt financial investments |
| Proceeds from loan repayments | Proceeds from repayment of loans, from the sale of debt securities |
| Acquisition, creation, modernization and reconstruction of non-current assets | Acquisition, creation, modernization and reconstruction of non-current assets |
Procedure for compiling BDDS
BDDS answers the question about changes in the financial position of the organization, presenting the said change in the context of current, investment and financial activities.
As you know, ODDS can be compiled by direct or indirect method. At the same time, the direct method is most suitable for planning problems, the indirect method - for analysis problems. This is why the BDDS is usually compiled using the direct method.
The technology for forming BDDS is quite simple. First, the data of the income and payment plan for current activities is filled in (at large planning intervals it is close to the income and expenditure plan of the BDS), then the investment budget is added, and based on the resulting excess or deficit of money, finally, the financial section of the BDS is compiled. The financial section must ensure a minimum balance of money (balance) throughout the entire planning period, for which the BDDS is divided into smaller time intervals.
Financial operations
| Article title | Type of movement |
| Dividend payment | Payment of dividends and other payments in favor of owners |
| Repayment of loans and borrowings | Repayment (redemption) of bills and other debt securities, repayment of loans and borrowings |
| Obtaining credits and loans | Obtaining credits and loans |
| Other contributions of founders to equity capital | Receipts of cash deposits from owners (participants) |
| Payments to owners in connection with the repurchase of shares (shares) from them | Payments to owners in connection with the repurchase of shares (shares) from them or their withdrawal from the membership of participants |