All individual entrepreneurs are required to keep a Book of Income and Expenses, abbreviated as KUDiR, with a few exceptions. We will talk about the specifics of the document for different tax regimes in the article.
First, about the exception. The exception is for individual entrepreneurs who use UTII. They may not fill out the Book, provided that they work only for UTII. However, when combining UTII with other tax regimes, the individual entrepreneur is obliged to ensure separate accounting of property and transactions, that is, fill out the KUDiR for each tax regime.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation together with the tax service have developed 4 KUDiR forms:
- for individual entrepreneurs on OSNO;
- for individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system;
- for individual entrepreneurs on PSN;
- for individual entrepreneurs on the Unified Agricultural Tax.
The book of income and expenses for individual entrepreneurs is a tax register that forms the basis for calculating taxes in connection with the use of special regimes.
Rules for maintaining a ledger of income and expenses
Entries in the book are made only if there is appropriate supporting primary documentation. If there is no document, then information about the operation is not allowed to be entered into the book.
- The obligation of the individual entrepreneur is to provide reliable and complete information, to ensure the continuity of its reflection in a special book. The correct display of the necessary indicators during the period will allow the entrepreneur to correctly calculate the base and amount of the agricultural tax.
- Organizations working for the Unified Agricultural Tax are required to keep full accounting records using accounting registers, consistently reflecting each transaction performed using double entries. If, according to the necessary criteria, an LLC can be classified as a small enterprise, then this does not eliminate the need for accounting, but accounting activities can be carried out in a simplified form. Read also the article: → “What types of activities on UTII are suitable for an LLC?”
Results
Compliance with the rules for maintaining CDR under the Unified Agricultural Tax allows you to timely and fully reflect the income and expenses involved in the calculation of agricultural tax.
Particular attention must be paid to expenses - their documentary evidence, economic feasibility and compliance with the list of expenses allowed by the Tax Code. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Rules for filling out the accounting book for the Unified Agricultural Tax
The following requirements apply to registration of an account book:
- Filling out is carried out in Russian, information about documents in a foreign language must be translated into Russian;
- The chronological sequence, reliability, and continuity of records must be ensured;
- The registration of the book is carried out throughout the calendar year, at the end of which the accounts are entered into a new book;
- Entering information into the book is only possible if primary paper is available;
- Making corrections to the paper version of the accounting book is possible if each adjustment is certified by the signature and seal of the individual entrepreneur (if there is a seal), as well as by indicating the date of the changes. Moreover, corrections must be justified.
Features of the use of unified agricultural tax
Agricultural tax can only be used by farms for which the relevant activity is the main one. The share of income from the sale of agricultural products must be 70% or more.
Existing peasant farms, users of the simplified tax system or OSNO, can switch to the unified agricultural tax from the beginning of the new calendar year. New companies are advised to submit an application for a change in tax regime at the same time as their registration documents.
Unified agricultural tax users have to report to the tax authorities once a year – in March. Summary data is entered into the Unified Agricultural Tax declaration, according to the book of income and expenses. It is important to take into account the existence of restrictions on allowable costs.
The agricultural tax rate is 6%. It is paid in two stages: advance payment - until July 25 of the current year, actual - until April 1 of the year following the reporting one. In case of delay, the taxpayer is charged a penalty.
Penalties are also provided for failure to submit a declaration and non-payment of taxes. Forgot to submit a report and pay your budget? Be prepared to pay 20% of the assessed tax amount.
Method of maintaining an accounting book for individual entrepreneurs
Electronic and paper methods of maintaining an accounting journal are allowed; the decision on a convenient method of registration is made by the entrepreneur independently. Each method of maintaining a book has its own characteristics that must be taken into account when organizing accounting activities.
The paper format of the ledger must have sequential page numbering and all sheets bound together. On the last page the total number of sheets of the book is written, this entry is certified by the personal signature of the individual entrepreneur; if there is a seal, then it must be placed next to the signature.
Before you start maintaining a paper copy of the book, you must submit it to the tax office to receive a mark from a tax specialist and a stamp from the Federal Tax Service.
At the end of the tax period, an electronically prepared book is put out on paper; after printing, the number of pages of the book is written on the last sheet, this entry is certified by the signature of the individual entrepreneur.
Next, the book must be taken to the Federal Tax Service office, where a tax specialist’s signature and tax stamp will be affixed. Certification by the Federal Tax Service must be completed within four months from the end of the tax period (until the end of March).
All of the above actions will allow you to avoid fraud, eliminate the deletion of sheets, their addition, and changes in the indicators used in the calculation procedure of the tax burden under the Unified Agricultural Tax. Read also the article: → “Conditions for applying the Unified Agricultural Tax + payers, calculation.”
| Contents: 1. Maintaining the accounting policy of the unified agricultural tax at the enterprise 2. Maintaining a book of income and expenses under the unified agricultural tax for individual entrepreneurs and organizations 3. Conditions for using the unified agricultural tax + infographics, calculation 4. Step-by-step instructions for registering private household plots 5. Taxation of peasant farms: comparison of the OSNO, simplified tax system, unified agricultural tax regimes 6. How to switch to the Unified Agricultural Tax from the general regime and the simplified tax system? Infographics 7. How to register a peasant farm: step-by-step instructions 8. Application of the Unified Agricultural Tax for peasant farms: infographics, calculation example, payment deadlines |
The procedure for filling out KUDiR for individual entrepreneurs in 2021
Filling out books of accounts is one of the key responsibilities of entrepreneurs. KUDiR forms have been developed for individual entrepreneurs and organizations that have switched to special tax regimes.
The documents contain data on all business transactions that affect the fiscal burden. The basic rules were developed by federal agencies a long time ago. However, business representatives regularly have to deal with changes.
In 2021, you need to work with an updated accounting book. Additional sections have appeared in the magazine.
The adjustments are aimed at improving accounting systems and adapting to the development of legal regulation.
Requirements for the presence of an accounting register are imposed on the simplified system and the unified agricultural tax. In addition, the income journal is maintained by patent holders. In each case, the order of entering data into the book will be special.
ModeRules for registration of KUDiRLegal basis of the simplified tax systemCompleting the main section of the book differs for different categories of “simplified”. It is necessary to reflect business expenses in column 5 when withholding tax on net profit.
For merchants using the simplified tax system with a calculation base in the form of gross income, the requirement is irrelevant.
You only need to enter information on the expenditure of budget subsidies and preferences in this line. In Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol, businessmen must document trade fees (section 5). The table of insurance premiums is filled out by all payers. Employers reflect amounts transferred for hired employees.
Businesses without staff indicate only fixed contributions.
The third section is filled out by entrepreneurs who received a negative result in the reporting year. There is no need to certify the book with the seal of the Federal Tax Service. The journal form has been approved. The obligation to maintain a ledger is established by the Unified Agriculture System. Every year, until March 31, agricultural producers present the logbook to the territorial tax office.
Certification is a prerequisite for validity ( and ).
On the title page
Filling out the title page for individual entrepreneurs under the Unified Agricultural Tax
On the title page of the accounting book the following is filled in:
- The year for which the data is entered;
- The date from which the bookkeeping began;
- OKUD form code;
- Individual entrepreneur details, including full name (without abbreviations, as in the passport), OKPO (from the notification of the state statistics body), TIN (assigned by the tax office upon registration);
- Unit of measurement - taken from OKEI, for rubles the code corresponds to 383;
- Elements of the address where the individual entrepreneur is registered - data is entered on the basis of confirmation paper;
- Details of accounts and banks where they are opened.
General accounting points
One way or another, farm accounting revolves around inventory. Specialists monitor data on receipt and use of materials. Particular attention is paid to the costs of receiving products and determining costs. The specific nature of the activities of peasant farms requires taking into account the natural loss of raw materials or agricultural products when reflecting accounting data.
Primary data, as a rule, is reflected in accounting in quantitative terms. Determining the cost of manufactured products has a number of features. In this case, crop production, livestock farming, and raw material processing have their own nuances.
Filling out the 1st section of the accounting book
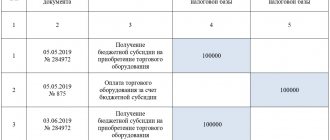
The first section directly provides information on income and expenditure indicators; externally, the section is presented in a tabular section. Filling out the table by column is discussed in the table.
| Column number | Information to be filled in |
| 1 | Consecutive numbering of records, starting with “1” and further in order |
| 2 | Details of the primary paper that served as the basis for recording the transaction during which the individual entrepreneur received income or expense taken into account in the taxable base under the Unified Agricultural Tax (date and number indicated on the document) |
| 3 | Brief explanation of the operation |
| 4 | The amount of income received as a result of the specified operation. Only those expenses are shown that are included in the base for calculating the tax burden under the Unified Agricultural Tax, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
Not taken into account:
|
| 5 | The amount of the expense indicator that arose when performing the reflected transaction. Also, only those expenses of individual entrepreneurs are shown that are taken into account for taxation; their list is given in clause 2 of Art. 346.5. |
The results are summed up based on the results of the first and second half of the calendar year, then the results for the half-year are summed up, the result is entered in the final bottom line of the table - “total for the year.” Indicators of generalizing lines are used when determining the base and calculating the unified agricultural tax.
Inventory on farms
Keeping records on farms is difficult due to the constant movement of assets, changes in value, and natural loss. To obtain reliable data on the condition of property and current assets, peasant farms regularly conduct inventories. The frequency and list of inspected objects and assets is determined by the peasant farm depending on the individual characteristics of the business.
Peasant farms monitor the status of:
- Property included in fixed or current assets.
- Composition, number of livestock taken into account in the main herd and young animals.
- Materials intended for sowing and ongoing use.
- Settlements with external counterparties.
- Other farm assets.
The inventory procedure is carried out by a commission approved by the head of the farm. The data identified during the event is recorded in the inventory list.
Filling out the 2nd section of the accounting book
In this section you need to show the following consumable information:
- Funds spent on fixed assets (their construction, creation, purchase, production), investments in their modernization. Only data on fixed assets involved in business activities is shown;
- Funds spent on intangible assets (creation, purchase) used in the activities of the individual entrepreneur.
Information is provided as of the last day of the period recognized as reporting and tax, for each object separately. Information for filling out the tabular part of the second section is taken from the technical passports of non-current assets. Filling out the table columns:
| Column number | Information to be filled in |
| 1 | Record number |
| 2 | Object name |
| 3 | The date of full payment for the object is indicated on the basis of the payment paper (order, receipt for the PKO) |
| 4 | The date of transfer of papers to the government agency for the registration procedure is filled out only in relation to those assets for which there is a need to register property rights in the state order |
| 5 | Date when the asset is capitalized - accepted for accounting or put into operation |
| 6 | The cost includes all expenses for an incoming asset purchased or created during work at the Unified Agricultural Tax. The entry is made in the period in which one of the following events occurred last:
If data on reconstruction or modernization of an existing asset is shown, then the same procedure should be followed in determining the date for reflecting cost data. |
| 7 | The number of years that the asset will be used for its intended purpose. The column is filled in only for those assets that were registered before work at the Unified Agricultural Tax. |
| 8 | The residual value of assets received before the unified agricultural tax is determined according to the rules provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depending on which regime the individual entrepreneur switched to the unified agricultural tax, the corresponding article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is applied:
The date of recording the value must fall in the period in which one of the following events last occurred:
|
| 9 | The number of six months during which the capitalized and paid asset was used. |
| 10 | The share of cost that is included in expenses for the tax period. To determine this value, the rules provided for in paragraphs are taken. 2 clause 4 art. 346.5. |
| 11 | The share of the cost of intangible assets or fixed assets that is included in expenses in half a year is determined by dividing the share of cost included in expenses for the year by the number of half-years specified in column 9. |
| 12 | Share of expenses included in the base for each half-year: Indicator gr. 6 or 8 * indicator gr. 11 / 100 |
| 13 | Share of expenses included in the base for the year: Indicator gr.6 or 7 * indicator gr.9 * indicator gr.11 / 100 |
| 14 | The amount of expenses included in the database for past years (taken from column 13 of the book for past years). The column is not filled in if the asset was received during the period of work at the Unified Agricultural Tax. |
| 15 | The balance of expenses that will be written off in future periods (column 8 – column 13 – column 14). The column is not filled in if the asset was received during the period of work at the Unified Agricultural Tax. |
| 16 | The date on which the asset was deregistered due to write-off or disposal. |
The table results are shown for each half-year and year in columns 6, 8, 12-15.
Peasant farm insurance premiums and reporting frequency
Amounts of accrued wages to farm personnel are subject to insurance contributions transferred to the funds. The rate of each type of contribution is determined depending on the chosen taxation system. Contributions and reporting on them came under the administration of the Federal Tax Service. In the Social Insurance Fund, control is carried out only on deductions for injuries and occupational diseases, for which an abbreviated report must be submitted.
| Reporting | Where to introduce yourself |
| Final calculation in the Social Insurance Fund for 2021 | FSS |
| Calculation in the Social Insurance Fund from 2021 | Social Insurance Fund regarding contributions for injuries |
| Final calculation of RSV-1 for 2021 | Pension Fund |
| Form SZV-M starting in 2017 | Pension Fund monthly |
Starting from 2021, reporting on contributions to the funds will be submitted to the Federal Tax Service. The reporting form will be submitted quarterly and will combine data on contributions to all funds.
books KUDiR
- A sample of the KUDiR of the simplified tax system for LLCs and (individual entrepreneurs), as well as instructions for filling out the KUDiR of the simplified tax system;
- Sample KUDiR for OSNO (IP), as well as instructions for filling out KUDiR OSNO;
- Sample KUDiR for Unified Agricultural Tax (IP), as well as instructions for filling out KUDiR Unified Agricultural Tax;
- Sample KUDiR for PSN (IP), as well as instructions for filling out KUDiR PSN.
I post all the current KUDiR samples and instructions on how to fill them out correctly on my Yandex Disk and you can download them from there at any time.
How to switch to a single agricultural tax
Registration of a company (individual entrepreneur, peasant enterprise or LLC) under the Unified Agricultural Tax system is of a notification nature. It is enough to indicate this type of taxation when registering with the territorial tax authority and confirm the validity of its application in the registration documents (memorandum of association or charter of the business entity). You may need a document confirming the possibility of using the unified agricultural tax (a long-term land lease agreement or a similar document).
If during registration you did not indicate the Unified Agricultural Tax as a type of taxation, then you are given 30 days to correct it . After this, the basic form (OSN) will be applied to the company. After this, the transition to the Unified Agricultural Tax will be possible only from the new calendar year. To do this, an application will need to be submitted to the tax authority before December 15 (taking into account the time required to process the transfer application).
It is possible to switch to a new taxation system by reorganizing the enterprise or liquidating the old one and organizing the company on a different form of ownership. This path is more difficult.
The main requirement for the use of Unified Agricultural Tax is that the company or peasant farm (peasant farm) receives more than 70% of its income from its core activities. The second condition is to limit the number of hired workers. No more than 300 people per year.
But this figure is acceptable for individual entrepreneurs, but for LLCs and private enterprises such a number of employees is an unrealistic condition. Unified agricultural tax is prohibited for state-owned enterprises.
Video: what conditions must be met to switch to Unified Agricultural Tax
Conditions under which the Unified Agricultural Tax system can be applied
To have the right to switch to taxation under the system in question, you can organize a full cycle of agricultural production - from cultivation to sale:
- production of agricultural products;
- primary processing;
- deep processing;
- sale of finished products.
It is permissible to exclude any link from the cycle. But the key point is agricultural production. goods. While applying the Unified Agricultural Tax, the company should not engage in excisable goods or gambling. Only under this condition is it possible to apply a single agricultural tax.
To apply the unified agricultural tax, it is necessary not only to independently process agricultural products, but also to produce them
Obtaining OKVED documents for LLCs and individual entrepreneurs
When selecting OKVED codes, you must indicate all the necessary codes on the appropriate sheet of the application for registration of a legal entity. But the main one should be a code containing the first two digits 01–03 (crop farming, livestock farming, forestry, fish farming and related industries). If the company does not have the necessary OKVEDs, their list should be clarified or supplemented.
The level of detail can be up to seven digits, but to confirm the agricultural focus of the business, four digits are enough. This meets the requirements for filling out the OKVED form. The same information must be submitted to the statistical authorities at the place of registration.
The legislative framework for the application of the Unified Agricultural Tax is fully regulated by the relevant articles of the Tax Code and amendments to it in accordance with Federal Law-84 of 04/06/2015.