Money is the most liquid part of operating assets and represents money on hand, as well as in settlement, current, currency, deposit and special accounts. The main source of data on their movements is Form No. 4 of the accounting report Cash Flow Report in 1C, which provides the ability to maintain analytical accounting in the context of DDS items. Cash flow items in 1C are additional analytics (sub-account) for some accounting accounts, for example, accounts 50/Cash and 51/Settlement accounts.
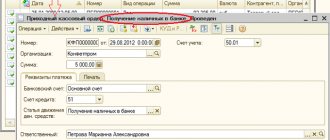
Another source of information about the movement of money is the management report “Cash Flow Analysis”. To generate a cash flow tax form or such a report, you need to set up cash flow items in 1C 8 (set up DDS items in the “DDS Items” directory). Its correct maintenance and timely completion of the required DDS items in the relevant documents of the “Bank and Cash Office” section is the key to the correctness of the report, which in turn will support the correctness of budgeting and treasury operations in 1C.
Free consultation with an expert on treasury automation based on 1C
So, let's look at the tools for maintaining accounting in the context of DDS in the 1C Enterprise Accounting 8.3 program.
General requirements
When filling out the report, distribute the cash flows among the three types of activities of the company:
- current;
- investment;
- financial.
Cash flows from current operations are associated with the normal operations of the firm.
These are, in particular:
- receipts from buyers for goods (work, services);
- rent, commissions;
- payments to suppliers for goods, materials (work, services);
- payments in favor of employees;
- payments of income tax from ordinary activities;
- payment of interest on debt obligations, except for interest included in the cost of investment assets;
- cash flows on short-term (no more than three months) financial investments purchased for resale.
Cash flows from investing activities are associated with the acquisition, creation or disposal of a firm's non-current assets. This is, for example:
- related payments to the firm's suppliers, contractors and employees, including R&D costs;
- interest included in the cost of investment assets;
- proceeds from the sale of non-current assets;
- proceeds from the sale of shares and interests in other organizations (except for short-term ones acquired for resale);
- provision of loans to other persons and their repayment;
- payments and receipts for settlements for debt securities;
- dividends from participation in other organizations, etc.
Cash flows in the form of receipts from buyers and customers, payments to suppliers and contractors should be shown in the report without indirect taxes (VAT and excise taxes). The cash flow related to each of these taxes is shown in collapsed form - the total amount for the year (paragraph “b”, paragraph 16 of PBU 23/2011). This rule has been in effect since 2011. VAT and excise taxes must be separated from cash equivalents received or used as a means of payment.
Important
The procedure for filling out a cash flow statement is discussed in detail in the book “Annual Report 2012″, edited by Vladimir Meshcheryakov.”
Along with the useful book, you will receive a free access code to the Internet portal in support of submitting the annual report www.buhgod.ru and will be able to use the book in electronic format.
Cash flows from financing activities are payments that result in changes in the size and structure of a firm's capital and leverage.
For example:
- cash contributions from owners (contributions to property), proceeds from the issue of shares, increases in shares;
- payments to owners for shares purchased from them or in connection with their withdrawal from the company;
- dividends to owners;
- receipts and payments from the issue of debt securities;
- loans and borrowings from other persons (receipt and repayment).
Fill out the header part of the report in the same way as the corresponding part of the balance sheet and other forms:
Methods for preparing a DDS report
There are two methods for compiling DDS: direct and indirect. In domestic practice, only the direct method is used. Indirect is more common abroad.
Direct method
When constructing a DDS report, the accountant uses all transactions corresponding to accounts 50-55. That is, it distributes all payments and receipts across the cash register and accounts by type of cash flow. This is the only method that is legally permitted in Russia.
The disadvantage of the direct method is that it does not correlate in any way with profit from the income statement.
Indirect method
Not used in Russia. In this way, the report is collected when applying IFRS. This method is closely related to the income statement and balance sheet. When compiling, the accountant uses the profit figure from the income statement and adjusts it for non-cash items, such as depreciation and exchange rate differences.
The adjustment occurs as follows: non-monetary items with a “+” sign are subtracted from profit, and those with a “-” sign are added. For example, accounts receivable is a non-cash item with a “+” sign that is deducted from profit because it is money not received.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
Cash flows from current operations
The main source of income is money received from buyers and customers. Therefore, in line 4111 of the report, reflect the revenue received from the sale of products (goods, works, services) and the amount of advances from buyers minus indirect taxes - VAT and excise taxes. To fill it out, summarize the debit turnover of the cash and cash equivalents accounts (50, 51, 52, 55, 58) in correspondence with account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” or 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” (for a loan) . From these turnovers it is necessary to exclude the amounts of VAT and excise taxes received from buyers.
In line 4112, enter the amounts of royalties, rent, licenses, commissions and other similar payments excluding VAT.
Show other income on line 4113 “Other income”. It can be:
- amounts returned to the cash desk by accountable persons;
- amounts received in compensation for damage from the perpetrators or the insurer;
- received fines, penalties, penalties for violations of contract terms, etc. (minus received VAT).
Payments received from tenants for the use of your property can be reflected in the report in different ways. This depends on whether the rental of property is a normal activity of the company. If yes, then enter the rent received in the line “from the sale of products, goods, works and services.” If not, then include it in other income.
In lines 4121-4129 of the report, disclose the main areas of spending funds.
Please note: the expense of cash and cash equivalents is indicated in the report in parentheses. VAT and excise taxes paid to suppliers and contractors are not included in the cash flow.
On line 4121 “suppliers (contractors) for raw materials, materials, works, services” show the company’s paid expenses for current activities. Enter here the amounts of payments made to your suppliers (contractors). Take the necessary data from the credit turnover of cash accounting accounts (50, 51, 52) in correspondence with account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” or 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” (by debit). From them you need to subtract the VAT paid to contractors. But the transfer of cash equivalents to counterparties (their disposal) is reflected through subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses”. In addition, cash can be spent through accountable persons.
On line 4122 of the cash flow statement, include the amounts of wages paid to the company's employees. In this case, use the data on the debit of account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” in correspondence with the credit of account 50 (if salaries are issued from the cash register) or 51 (if salaries are transferred to employees’ plastic cards).
If in the reporting (last) year the company paid interest on debt obligations, then show their amount in line 4123 of the report.
Show the payment of income tax on line 4124. Show the payment of all other taxes, except indirect ones, as well as mandatory social insurance contributions on line 4129.
If the company received a refund of overpaid taxes from the budget, with the exception of VAT and excise taxes, or contributions from state extra-budgetary funds, then reflect these receipts on line 4119.
These amounts are identified in accounting through the correspondence of account 51 with accounts 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” and 69 “Calculations for compulsory social insurance”.
Show other paid expenses for current activities in the line “other payments”.
Summarize the total cash flow associated with current activities in line 4100 “Balance of cash flows from current operations.” Reflect in it the difference between the amounts of money received and spent and cash equivalents for the current activities of the company.
Show the amount of VAT, as well as excise taxes related to current activities, in a collapsed form.
An example explains how to do this. Example
In the reporting year, JSC Aktiv, while carrying out its current activities, received from buyers and customers VAT in the amount of 500,000 rubles as part of cash and cash equivalents, paid suppliers and contractors a total of VAT in the amount of 400,000 rubles, and transferred it to the budget 150,000 rubles, and received compensation in the amount of 350,000 rubles from the budget. The cash flow for VAT amounted to RUB 300,000. (500,000 - 400,000 - 150,000 + 350,000). The Aktiva accountant will show this amount (300 thousand rubles) on line 4119 of the profit and loss report for the reporting year.
Meanwhile, separate accounting of VAT cash flows for current, investment and financial activities is usually not carried out (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 27, 2012 No. 07-02-18/01). With a collapsed VAT reflection, the total total of tax receipts and payments is displayed, including all receipts from buyers and customers, all payments to suppliers and contractors, as well as payments to the budget and refunds from it. The total amount is reflected as part of cash flows from current operations - on the line “Other payments” (code 4119) or “Other receipts” (code 4129). The same applies to excise taxes.
The difference between receipts and payments in the DDS report and income and expenses
There are many differences, so receipts and incomes should not be confused. Firstly, these two concepts are most often separated in time, for example, due to a deferred payment. Secondly, not every receipt is income, and not every payment is an expense.
Example . My Defense LLC sells tea. In June, the company sold tea for 300 thousand rubles. But in fact I received the money only in August. To produce this tea, 100 thousand rubles were spent on craft bags. But the director agreed with the package manufacturer on a deferment and will pay only in July. In addition, the company took out a loan of 50 thousand rubles in July. In the table we have broken down income, expenses, receipts and payments by month.
June, rub. July, rub. August, rub. Income 300 000 Consumption 100 000 Receipt/influx 50 000 300 000 Payment/outflow 100 000
As you can see, income in the example was recognized before the money actually arrived. The same goes for expenses. But a loan is not income at all, since the money must be returned. But the loan receipt appears in the DDS report. If My Defense LLC issued a loan to someone, we would count the amount as an outflow, but not as an expense.
With barter, there will be no cash flows in principle, since money does not move. But there will be income and expenses. Income is the value of the property received, expense is the value of the property transferred.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
Cash flows from investment operations
First, analyze your receipts.
On line 4211 “from the sale of non-current assets” of the report, indicate the amounts that the company received from the sale of fixed assets, intangible assets, capital construction in progress and equipment for installation (excluding VAT).
This data is taken from debit turnover on accounts 50, 51, 52, 58, subaccount “Cash equivalents” (minus received VAT), in correspondence with account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” or 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” .
In line 4212 of the report, indicate the company’s income from the sale of shares (participatory interests) in other organizations, and on line 4214 - income in the form of dividends and interest on debt financial investments. Take data on dividends from debit turnover on accounts 50, 51, 52, 58, sub-account “Cash equivalents”, in correspondence with account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, sub-account “Settlements for dividends”.
To identify the amount of interest that your company actually received in the reporting year from financial investments (for example, bonds, bills, loans issued, etc.), you need to take the debit turnover on accounts 50, 51, 52 in correspondence with account 76 “Calculations with different debtors and creditors”, subaccounts “Interest on bills”, “Interest on bonds”, etc.
Show repayment of interest-bearing loans issued in line 4213.
Let us remind you that in accounting these transactions are reflected in the debit of account 50 or 51 in correspondence with account 58 “Financial investments”.
Receipts from investment activities not listed in lines 4211-4214 of the report are reflected in line 4219 “other receipts”.
Next, reveal your payment structure.
In line 4221 “in connection with the acquisition, creation, modernization, reconstruction and preparation for use of non-current assets” of the report, reflect the payment in the reporting year of fixed assets (real estate, production equipment, etc.), intangible assets (rights to patents, inventions and etc.), exploration assets (in connection with the development of natural resources), as well as objects of unfinished capital investments - excluding VAT. Take the data for this line from credit turnover on accounts 50, 51, 52, 55, 58, sub-account “Cash equivalents” (minus VAT), in correspondence with accounts 60 and 76 regarding purchases of fixed assets, intangible assets, etc. In addition, cash for these purposes can be spent through accountable persons.
Record the amount of funds allocated for long-term financial investments in lines 4222 “in connection with the acquisition of shares (participation interests) in other organizations” and 4223 “in connection with the acquisition of debt securities (rights to claim funds against other persons), provision of loans to other persons." To fill out these lines, take the necessary data from the turnover in the debit of account 58. Although cash equivalents are reflected in account 58, they are not long-term assets.
Show the result of cash flows from investment activities in line 4200 “Balance of cash flows from investment operations.” That is, enter here the difference between the amounts of money and cash equivalents received and spent as part of investment activities.
Interest payments are shown as part of current transactions (line 4123), unless you include them in the cost of investment assets. In the latter case, show interest as part of investment transactions (line 4224).
It is difficult to overestimate the importance, and therefore the accuracy, of drawing up a cash flow statement. We present to your attention an excerpt from the book “Annual Report 2012, edited by Vladimir Meshcheryakov,” which describes in some detail the process of compiling this part of the final documents. You can view and purchase the book here
How to Use a Cash Flow Statement
To answer this question, you need to understand who is using the report. And there are two user groups.
External users are the Federal Tax Service. It is not for nothing that the DDS report is included in the group of financial statements. However, not everyone submits the DDS: small businesses are exempt from submitting it if they believe that it does not contain important information. Such a report is made once a year along with the balance sheet.
Internal users are top managers and owners of the company who want to understand the state of the main asset - money. For them, the DDS report is often even more interesting than the financial results report. The reason is that the DDS is based on actual data, that is, it allows you to really judge how much money came and went from the company.
But the financial results report is based on accounting data, which largely depends on the accounting methods.
Example . The head of My Defense LLC makes a decision to open a new business line. In the financial result report, he sees a profit of 300 million rubles. The number is not small. But then he looks at the DDS report and sees that the balance of money is three times less - 100 million rubles. The reasons are different, for example, the remaining 200 million rubles are receivables that are unknown when they will return. Since the business actually only has 100 million, the manager is holding back the opening of a new direction.
For internal use, the report is prepared at different intervals. Some once a month, some once a quarter.
Cash flows from financial transactions
Here, disclose information about money received and spent within the financial activities of the company.
Indicate the amounts received by the company in debt in the line “receipt of loans and borrowings.” To fill out this line, use the credit turnover of accounts 66 “Calculations for short-term loans and borrowings” and 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings” in correspondence with the cash accounts (50, 51, 52, 55) and cash equivalents (58) .
Let us remind you that sometimes loans are formalized not by an agreement, but by issuing your own bill. A bill of exchange loan, just like regular loans, is reflected in account 66 or 67, depending on the repayment period. However, to reflect such borrowings, the report provides a separate line - 4314 “from the issue of bonds, bills and other debt securities, etc.”
In lines 4312 and 4313, reflect the contributions of the company's owners made in the reporting year. For example, if participants made contributions to property in accordance with Article 27 of Law No. 14-FZ of February 8, 1996, show their amounts on line 4312. Other income should be indicated on line 4314. In particular, this includes state assistance (PBU 13/2000 ).
In the line “in connection with the repayment (redemption) of bills and other debt securities, repayment of loans and borrowings,” write down the amounts of loans and borrowings you repaid. Use the data on the debit of accounts 66 “Calculations for short-term loans and borrowings” and 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings” in correspondence with accounts for accounting for cash and cash equivalents.
If your company paid dividends, you need to fill out the line “for the payment of dividends and other payments for the distribution of profits in favor of the owners (participants).” Here indicate the amounts of all dividends paid in the reporting year.
In the line “Balance of cash flows from financial transactions,” reflect the difference between money received and spent and cash equivalents from the company’s financial operations.
Setting up a chart of accounts
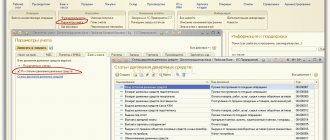
To work with the directory of articles, you must first complete the settings, which are located in the section “Administration/Accounting parameters/Setting up the chart of accounts/Accounting for DDS: By account and DDS items” or in the section “Main/Chart of accounts/Setting up the chart of accounts”.
Fig.1 Setting up DDS accounting by item
Setting up treasury in any 1C programs to suit your business processes