USN 2021 in St. Petersburg: all information, the basic rate of 6% and “income minus expenses” of 7% each, latest changes, legislation, responsibility, reporting, and everything about this taxation scheme for individual entrepreneurs in St. Petersburg.
In St. Petersburg, you can do great business - the market is huge, the logistics are well-established, people have money, and most importantly, paying the state according to the “simplified” system from 2021, you can roll around like cheese in butter. The profitability limit has been increased, and from now on you can earn a little more than 1 million rubles per month while remaining on the simplified tax system.
Despite the fact that the “simplified” system has a number of shortcomings and bureaucratic delays, it is still a working scheme that makes entrepreneurship much more accessible than working according to the standard procedure. The calculation of the simplified tax system in 2021 is carried out according to the same two schemes - a percentage of the amount of income and a percentage of the difference between income and expenses.
This article is a complete educational program for those who are planning to open a business in St. Petersburg or the Leningrad region and want to understand the nuances of calculating bribes under the simplified taxation system.
Simplified “income minus expenses”: conditions for transition
In 2021, taxpayers will have the right to switch to the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” from next year (from 01/01/2020) subject to the following conditions:
- They do not engage in activities listed in paragraph 3 of Art. 346.12 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- The organization has no branches.
- The share of participation of other legal entities in the organization’s management company does not exceed 25%. There are some exceptions to this rule.
- The amount of income received by the taxpayer based on the results of 3 quarters of the current year did not exceed 112,500,000 rubles.
- The average number of employees a taxpayer has is no more than 100.
- The residual value of depreciable fixed assets (FPE) available as of October 1 of the current year does not exceed RUB 150,000,000.
In order to switch to the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”, you will need to submit a specially prepared application to the territorial Federal Tax Service by the end of the year. If a legal entity or individual entrepreneur has just registered, then such an application is submitted within 30 days from the date of registration (clause 3 of Article 346.13 of the Tax Code), otherwise the transition to the simplified tax system will be possible only from next year, provided that the application is submitted from October to December .
The notification form for the transition to the simplified tax system can be downloaded here.
Retention of the right to use the simplified tax system is conditioned by compliance with the above criteria and one more income limit - their maximum allowable amount for receipt per year of application of the simplified tax system (clause 4 of article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For 2021, this value is defined as 150,000,000 rubles.
To find out whether it is possible to have a separate division with simplified taxation, read the material “Opening a separate division under the simplified tax system .
Who pays?
First condition.
To switch to the simplified tax system in 2021, changes have appeared - it is necessary that income for 9 months should not exceed the level of 112,500,000 rubles. Previously, this figure was almost two times less. To remain on the “simplified” tax, annual income must be less than 150 million rubles (but not more than 200 million rubles according to the new limits for 2020).
Second condition.
The limit on fixed assets must be less than 150 million rubles. This figure has also increased with the latest changes. The total amount refers to the residual book value. Fixed assets are machines, equipment, computers, buildings, and all other property used in business activities.
Third condition.
The number of employees should be up to 100 people, and the share in the authorized capital (for LLCs) of other organizations should not be higher than 25%. For small businesses, all this, as a rule, is not particularly relevant.
Of course, for buildings and retail space the limit of 150 million in the conditions of St. Petersburg is meager, but any businessman can use rent.
As you can see, the conditions are very favorable. And if it were not for additional fees, inspections, bureaucracy inflated to incredible limits, talmuds of standards, GOSTs, as well as corruption, then the atmosphere for doing business in Russia could be called ideal.
Taxes under the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
Taxpayers using the simplified tax system are exempt from paying:
- property tax, except for real estate, the value of which is determined as cadastral (this, in particular, office, retail and service premises and buildings);
- VAT (with rare exceptions);
- income tax (for self-employed persons - personal income tax), except for income in the form of dividends and income taxed at special rates.
Other taxes, fees and contributions are paid on a general basis.
Read about what rules to follow when applying the simplified tax system in 2018-2019 in terms of insurance premiums.
If taxpayers have chosen a taxation system such as the simplified “income minus expenses” with a rate of 15%, then they must maintain KUDiR. You must have all documents confirming expenses and their payment. “Simplified” taxpayers are required to conduct cash transactions in accordance with the general procedure. And also submit tax and statistical reporting.
For information about the “simplified” option not to use online cash registers when providing services to the population (except for public catering services) until July 1, 2019, read the publication “A deferment for online cash registers has been introduced.”
Taxpayers who have chosen income-minus-expenses taxation are not exempt from performing the duties prescribed for tax agents. In addition, they must comply with all controlling person regulations if they hold relevant interests in controlled foreign companies.
How to close the year without errors to correctly fill out the simplified taxation system declaration?
There is nothing complicated about submitting the simplified tax system quarterly - determine the advance tax payment and pay it. However, I advise you to immediately deposit a larger amount - if the tax office withdraws part of the expenses, you will have a “reserve” that will save you from the accrual of penalties.
But you can’t do this with an annual declaration: at the end of the reporting period you need to pay the exact amount. It is calculated simply: advance payments for the previous 3 quarters are deducted from the accrued tax amount.
And here the preparatory stage is important, because the correct entry of documents into the program guarantees us the correct preparation of reports. What should be done?
· Preparatory stage
1. You need to remember what in tax accounting refers to expenses and what to income.
Income includes: income from the sale of goods and property rights, non-operating income and property. A complete list of income can be found in Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The organization's expenses must be justified and documented. These include costs for the acquisition and production of fixed assets, rental payments, material costs and more. A complete list of costs is described in section 346.16. Tax Code of the Russian Federation (applies only to the taxation object “Income minus expenses”). Knowing this list, in receipt documents, as well as in payment orders, you can indicate in the “NU Expenses” field whether these costs are accepted as expenses or not.
2. Be sure to check the balances in warehouses. This is easy to do: you need to create a balance sheet for the 10th account, but in the settings specify the display of the report by quantitative indicator (see Fig. 1). How to test yourself? Often, if a document is entered incorrectly into the program, the remainder of some items will show a “minus” sign (see Fig. 2). This way you can check both 10 and 41 accounts.
Rice. 1. Setting up the balance sheet for account 10
Rice. 2. Negative account balance 10
3. Don’t forget about purchasing fixed assets and calculating depreciation. Be sure to track whether the corresponding amounts are included in the balance sheet for accounts 01, 02 and 08 (see Fig. 3), and whether these cost items are included in expenses under the simplified tax system and in KUDiR.
Rice. 3. Postings upon receipt of fixed assets
4. Check all amounts for balances on accounts 50 and 51. Don’t forget to make entries for accruals, for example, of state duties, tax penalties, interest on a loan or loan.
5. Please note that if the year is closed correctly, you should not have balances on accounts 90, 91 and 99 (see Fig. 4). If there are balances on the accounts at the beginning or end of the year, then you need to look for which transactions or documents you made a mistake in.
Rice. 4. Balances on accounts 90, 91 and 99
· We fill out a declaration according to the simplified tax system in 1C
The declaration form itself consists of 4 sheets.
The first page is the title page. First of all, check that the organization details are correct. If you submit a declaration for the year, check the tax period (code) - it should be 34. Also check the OKVED code if it suddenly changed last year.
Section 1.2 indicates the amounts of the advance payment payable by the 25th day of the month following the previous quarter of the reporting year.
Section 2.2 of the declaration indicates income quarterly and for the entire year, as well as the amount of expenses quarterly and in total. The tax base from which the corresponding tax rate is taken is also calculated.
Section 3 indicates property, work, services within the framework of charitable activities, targeted income and targeted financing. If such funds were not received, this section is not completed.
What percentage is the tax on the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
The rate for the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” is set at 15% based on clause 2 of Art. 346.20 of the Internal Revenue Code. Subjects of the Russian Federation may set reduced tax rates - from 5 to 15%.
The establishment of the right to such a reduction is due to the provision of regions with the opportunity to stimulate the development of certain types of activities or an increase in the number of taxpayers of certain groups. Payers of the simplified tax system do not have the obligation to confirm their right to apply a preferential regional tax rate (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 21, 2013 No. 03-11-11/43791).
How to check your rate
If you decide to check the rate for last year, take a look at the 2020 table. The search that is called by the Ctrl+F keys will help you.
2021 rates:
| Region | Region name | Law | Rate year | Income | Income minus expenses |
| 01 | Republic of Adygea (Adygea) | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 01 | Republic of Adygea (Adygea) | Law of the Republic of Adygea dated July 2, 2015 No. 426 | 2021 | 15 | |
| 02 | Republic of Bashkortostan | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 02 | Republic of Bashkortostan | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 03 | The Republic of Buryatia | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 03 | The Republic of Buryatia | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 04 | Altai Republic | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 04 | Altai Republic | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 05 | The Republic of Dagestan | Law of the Republic of Dagestan dated May 29, 2020 No. 27 | 2021 | 3 | |
| 05 | The Republic of Dagestan | Law of the Republic of Dagestan dated May 29, 2020 No. 27 | 2021 | 6 | |
| 06 | The Republic of Ingushetia | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 06 | The Republic of Ingushetia | Law of the Republic of Ingushetia dated December 29, 2018 No. 53-RZ | 2021 | 14,7 | |
| 07 | Kabardino-Balkarian Republic | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 07 | Kabardino-Balkarian Republic | Law of the CBD of May 18, 2009 No. 22-RZ | 2021 | 12 | |
| 08 | Republic of Kalmykia | Law of the Republic of Kalmykia dated November 30, 2009 No. 154-IV-Z | 2021 | 6 | |
| 08 | Republic of Kalmykia | Law of the Republic of Kalmykia dated November 30, 2009 No. 154-IV-Z | 2021 | 10 | |
| 09 | Karachay-Cherkess Republic | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 09 | Karachay-Cherkess Republic | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 10 | Republic of Karelia | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 10 | Republic of Karelia | Law of the Republic of Karelia dated December 30, 1999 No. 384-ZRK | 2021 | 12,5 | |
| 11 | Komi Republic | Law of the Komi Republic dated 05/08/2020 No. 12-RZ | 2021 | 3 | |
| 11 | Komi Republic | Law of the Komi Republic dated 05/08/2020 No. 12-RZ | 2021 | 7,5 | |
| 12 | Mari El Republic | Law of the Republic of Mari El dated October 27, 2011 No. 59-Z | 2021 | 6 | |
| 12 | Mari El Republic | Law of the Republic of Mari El dated October 27, 2011 No. 59-Z | 2021 | 15 | |
| 13 | The Republic of Mordovia | Law of the Republic of Mordovia dated 04.02.2009 No. 5-3 | 2021 | 6 | |
| 13 | The Republic of Mordovia | Law of the Republic of Mordovia dated 04.02.2009 No. 5-3 | 2021 | 15 | |
| 14 | The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | Law of the Republic of Sakha dated 07.11.2013 No. 1231 | 2021 | 6 | |
| 14 | The Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) | Law of the Republic of Sakha dated 07.11.2013 No. 1231 | 2021 | 10 | |
| 15 | Republic of North Ossetia-Alania | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 15 | Republic of North Ossetia-Alania | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 16 | Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan) | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 16 | Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan) | Law of the Republic of Tatarstan dated June 17, 2009 No. 19-ZRT | 2021 | 10 | |
| 17 | Tyva Republic | Law of the Republic of Tyva dated December 3, 2020 No. 658-ZRT | 2021 | 3 | |
| 17 | Tyva Republic | Law of the Republic of Tyva dated December 3, 2020 No. 658-ZRT | 2021 | 7 | |
| 18 | Udmurt republic | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 18 | Udmurt republic | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 19 | The Republic of Khakassia | Law of the Republic of Khakassia dated November 16, 2009 No. 123-ЗРХ | 2021 | 4 | |
| 19 | The Republic of Khakassia | Law of the Republic of Khakassia dated November 16, 2009 No. 123-ЗРХ | 2021 | 7,5 | |
| 20 | Chechen Republic | Law of the Chechen Republic of November 27, 2015 No. 49-RZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 20 | Chechen Republic | Law of the Chechen Republic of November 27, 2015 No. 49-RZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 21 | Chuvash Republic - Chuvashia | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 21 | Chuvash Republic - Chuvashia | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 22 | Altai region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 22 | Altai region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 23 | Krasnodar region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 23 | Krasnodar region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 24 | Krasnoyarsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 24 | Krasnoyarsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 25 | Primorsky Krai | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 25 | Primorsky Krai | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 26 | Stavropol region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 26 | Stavropol region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 27 | Khabarovsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 27 | Khabarovsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 28 | Amur region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 28 | Amur region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 29 | Arhangelsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 4 | |
| 29 | Arhangelsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 30 | Astrakhan region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 30 | Astrakhan region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 31 | Belgorod region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 31 | Belgorod region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 32 | Bryansk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 32 | Bryansk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 33 | Vladimir region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 33 | Vladimir region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 34 | Volgograd region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 34 | Volgograd region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 35 | Vologda Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 35 | Vologda Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 36 | Voronezh region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 36 | Voronezh region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 37 | Ivanovo region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 37 | Ivanovo region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 38 | Irkutsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 38 | Irkutsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 39 | Kaliningrad region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 39 | Kaliningrad region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 40 | Kaluga region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 40 | Kaluga region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 41 | Kamchatka Krai | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 41 | Kamchatka Krai | Law of the Kamchatka Territory of March 19, 2009 No. 245 | 2021 | 10 | |
| 42 | Kemerovo region | Law of the Kemerovo region dated November 26, 2008 No. 99-OZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 42 | Kemerovo region | Law of the Kemerovo region dated November 26, 2008 No. 99-OZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 43 | Kirov region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 43 | Kirov region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 44 | Kostroma region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 44 | Kostroma region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 45 | Kurgan region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 45 | Kurgan region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 46 | Kursk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 46 | Kursk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 47 | Leningrad region | Law of the Leningrad Region dated October 12, 2009 No. 78-oz | 2021 | 6 | |
| 47 | Leningrad region | Law of the Leningrad Region dated October 12, 2009 No. 78-oz | 2021 | 5 | |
| 48 | Lipetsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 48 | Lipetsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 49 | Magadan Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 49 | Magadan Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 50 | Moscow region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 50 | Moscow region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 51 | Murmansk region | Law of the Murmansk region dated April 17, 2020 No. 2478-01-ZMO | 2021 | 1 | |
| 51 | Murmansk region | Law of the Murmansk region dated April 17, 2020 No. 2478-01-ZMO | 2021 | 5 | |
| 52 | Nizhny Novgorod Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 52 | Nizhny Novgorod Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 53 | Novgorod region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 53 | Novgorod region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 54 | Novosibirsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 54 | Novosibirsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 55 | Omsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 55 | Omsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 56 | Orenburg region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 56 | Orenburg region | Law of the Orenburg region dated September 29, 2009 No. 3104/688-IV-OZ | 2021 | 10 | |
| 57 | Oryol Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 57 | Oryol Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 58 | Penza region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 58 | Penza region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 59 | Perm region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 59 | Perm region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 60 | Pskov region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 60 | Pskov region | Law of the Pskov region dated November 29, 2010 No. 1022-oz | 2021 | 15 | |
| 61 | Rostov region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 61 | Rostov region | Law of the Rostov region dated May 10, 2012 No. 843-ZS | 2021 | 10 | |
| 62 | Ryazan Oblast | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 62 | Ryazan Oblast | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 63 | Samara Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 63 | Samara Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 64 | Saratov region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 64 | Saratov region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 65 | Sakhalin region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 65 | Sakhalin region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 66 | Sverdlovsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 66 | Sverdlovsk region | Law of the Sverdlovsk region dated June 15, 2009 No. 31-OZ | 2021 | 7 | |
| 67 | Smolensk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 67 | Smolensk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 68 | Tambov Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 68 | Tambov Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 69 | Tver region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 69 | Tver region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 70 | Tomsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 70 | Tomsk region | Law of the Tomsk region dated 04/07/2009 No. 51-OZ | 2021 | 10 | |
| 71 | Tula region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 71 | Tula region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 72 | Tyumen region | Law of the Tyumen region dated November 30, 2020 No. 87 | 2021 | 3 | |
| 72 | Tyumen region | Law of the Tyumen region dated March 31, 2015 No. 21 | 2021 | 5 | |
| 73 | Ulyanovsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 73 | Ulyanovsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 74 | Chelyabinsk region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 74 | Chelyabinsk region | Law of the Chelbinsk region of November 28, 2021 N 43-ZO | 2021 | 10 | |
| 75 | Transbaikal region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 75 | Transbaikal region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 76 | Yaroslavl region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 76 | Yaroslavl region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 77 | Moscow | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 77 | Moscow | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
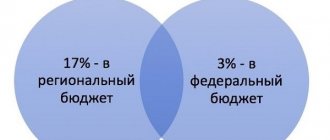
| 78 | Saint Petersburg | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 78 | Saint Petersburg | Law of St. Petersburg dated 05.05.2009 No. 185-36 | 2021 | 7 | |
| 79 | Jewish Autonomous Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 79 | Jewish Autonomous Region | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 15 | |
| 83 | Nenets Autonomous Okrug | Law of the Nenets Autonomous Okrug of June 11, 2021 No. 87-OZ | 2021 | 1 | |
| 83 | Nenets Autonomous Okrug | Law of the Nenets Autonomous Okrug of June 11, 2021 No. 87-OZ | 2021 | 5 | |
| 86 | Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 86 | Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug | Law of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug dated December 30, 2008 No. 166-OZ | 2021 | 5 | |
| 87 | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | Law of the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug dated December 22, 2020 No. 78-OZ | 2021 | 1 | |
| 87 | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug | Law of the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug dated December 22, 2020 No. 78-OZ | 2021 | 5 | |
| 89 | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | Tax Code of the Russian Federation (part two) dated 05.08.2000 No. 117-FZ | 2021 | 6 | |
| 89 | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug | Law of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug dated December 18, 2008 No. 112-ZAO | 2021 | 5 | |
| 91 | Republic of Crimea | Law of the Republic of Crimea dated December 29, 2014 No. 59-ZRK/2014 | 2021 | 4 | |
| 91 | Republic of Crimea | Law of the Republic of Crimea dated December 29, 2014 No. 59-ZRK/2014 | 2021 | 10 | |
| 92 | Sevastopol | Law of the city of Sevastopol dated 02/03/2015 No. 110-ЗС | 2021 | 4 | |
| 92 | Sevastopol | Law of the city of Sevastopol dated 02/03/2015 No. 110-ЗС | 2021 | 10 |
How we compiled the table
It is impossible to view the rates of all regions in one place: tax and legal reference services do not maintain such a directory. The tax office posts regional laws on rates on the website, but they are not always up to date. Therefore, we read the legislation of each region and double-checked it in several services. Now we will do this at the end of each year to find out the rates for the next one.
STS “income minus expenses” 15%: minimum tax
For simplifiers who have chosen “income minus expenses” as the object of taxation under the simplified tax system (rate 15%), a special tax is established in the amount of 1% of the total amount of income received during the year. A single tax in the established minimum amount is paid if the calculated tax amount (tax rate multiplied by the difference between income and expenses) for the year is less than the minimum.
The minimum tax is paid at the end of the year when submitting a tax return. In this case, taxpayers make advance payments on the basis of calculations made in the generally established manner.
For information on calculating the minimum tax, read the article “How to calculate the minimum tax under the simplified tax system in 2018-2019?”
Laws, forms, documents
Below are excerpts from legislation, forms and reports on payment of the simplified tax system in St. Petersburg, as well as other useful files. They can be viewed in doc format. or Excel.
Basic Law of St. Petersburg on establishing the tax rate under the simplified tax system at 7% “Income-expenses”:
Download file: osnovnoy-zakon-.zip [8.68 Kb] (downloads: 292)
“On amendments to the establishment of the tax rate for organizations and individual entrepreneurs in St. Petersburg” - a law for those who fall under preferential taxation of 0%:
Download file: o-vnesenii-izmeneniy.zip [8.08 Kb] (downloads: 132)
Excerpts from the Tax Code about simplified taxation system:
Download file: vyderzhki-iz-nk.zip [30.01 Kb] (downloads: 60)
Tax return form for individual entrepreneurs, new form:
Download file: blank-deklaraciya-usn.zip [45.38 Kb] (downloads: 146)
Additions and amendments will be corrected as the latest news arrives in St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region.
Last changes
Among the latest changes in the simplified tax system for the year, the following can be noted:
- Fixed contributions for individual entrepreneurs have increased: for medical insurance - 8,426 rubles, for pension - 32,448 rubles (from 6,884 and 27,354, respectively).
- From July 1, 2021, all entrepreneurs are required to switch to online ticket offices, except for ticket sellers and several other categories;
- Declarations for the simplified tax system with online cash registers are submitted for the last time in March-April. From July 1, the online simplified taxation system applies to such entrepreneurs. There is no need to submit a declaration; the system will calculate the tax itself and display it in your personal account.
An increase in rates in St. Petersburg and the Leningrad region, as well as changes in the terms of tax collection, are not yet expected.
Tags: taxes
Simplified “income minus expenses”: does the rate change?
For taxpayers using the simplified tax system “income minus expenses,” the tax rate (regional differentiated) can be revised annually. All changes are made through the adoption of relevant laws by the constituent entities of the Federation. The law establishing a new differentiated rate is adopted before the end of the year with the goal that a different tax rate will be in effect in the new tax period.
Recently, many subjects of the Federation have begun to use differentiated rates, which are 2-3 times lower than the maximum. This suggests that regional governments are interested in creating acceptable conditions for the development of small businesses.
Extension of tax holidays on the simplified tax system
For five years - from 2015 to 2021 - a tax holiday program for individual entrepreneurs was in effect in Russia. This means that individual entrepreneurs’ income for certain types of activities was taxed at a zero rate for two tax periods. Moreover, it was necessary to declare the transition to the simplified tax system immediately after state registration.
Law No. 266-FZ dated July 31, 2020 extended the federal tax holiday program until 2024. However, in order for an individual entrepreneur to be able to work within the framework of the simplified tax system at a zero rate, it is necessary to adopt new regional laws.
Simplified tax system “income minus expenses”: changes in 2018-2019
There have been few changes relating only to the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” since 2017: the BCC for paying the minimum tax has become the same as for the regular tax paid under the simplified tax system. But there are changes common to the special regime, and they are quite significant:
- The benefit on insurance premiums has been canceled for some simplifiers named in Art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- the moratorium on routine inspections of small businesses was extended until 2022;
- the application of the deflator coefficient to the value of income limits has been suspended for several years (from 2021 to 2021).
For more information about the deflator coefficient in 2017-2020, read the material “New income limits under the simplified tax system will not change until 2021” .
How to pay tax on a simplified system
Personal income tax and income tax are not paid under the simplified tax system. VAT, in addition to that which is paid when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation, is also not charged. The basic tax is calculated based on the results of the calendar year and entrepreneurs must pay it no later than April 30 of the following year. For example, the simplified tax system tax for 2021 must be paid no later than 04/30/2022.
However, during the year there are reporting periods, at the end of which part of the tax must be paid in advance, i.e. in advance. These payments are called advance payments. Deadlines for their payment:
- for the first quarter – April 25;
- for the half-year – July 25;
- for nine months - October 25.
This is the official name of the reporting periods, associated with the calculation methodology, but in practice it is easier to assume that advance payments are made for each quarter. Moreover, they must be entered only if the entrepreneur received income in the reporting quarter. If there was no income, then you don’t need to pay anything.
Simplified tax system calculator
All advance payments that were paid during the year are taken into account when calculating tax for the year. In addition, every entrepreneur, regardless of the chosen tax regime, is required to pay insurance premiums for himself. These payments also reduce the tax amount.
For the convenience of paying taxes and insurance premiums, we recommend opening a current account. Moreover, now many banks offer favorable conditions for opening and maintaining a current account.
Individual entrepreneur on the simplified tax system “income minus expenses”
The simplified tax system “income minus expenses” is applied to individual entrepreneurs under the same conditions that apply to legal entities (Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- They carry out activities not prohibited by clause 3 of Art. 346.12 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- The established annual income limit is observed. At the same time, to begin applying the regime, the 9-month IP limit may not be observed (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 1, 2013 No. 03-11-09/6114).
- The average number of employees does not exceed 100.
- The residual value of depreciable fixed assets is less than RUB 150,000,000.
Newly registered individual entrepreneurs whose activities are related to production, provision of social services or scientific activities have the right to apply a preferential tax rate of 0% during the first 2 years of operation.
Read more about preferential simplified taxation rates in this article.
Which taxation system is better: “income minus expenses” or “income”?
Those who are looking for an answer to the question of which is more profitable: the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” or the simplified tax system “income”, you need to analyze your planned activities. Thus, a large share of documented and economically justified costs makes the choice of the “income minus expenses” object justified, and their absence - the “income” object.
The current regional legislation also plays an important role in this choice, because constituent entities of the Russian Federation can set their own differentiated tax rates both for individual groups of taxpayers and for specific types of activities.
Results
If a decision is made to apply the simplified tax system “income minus expenses” and all the conditions for switching to this regime are met, then a notification must be submitted to the tax authority. The deadline for submitting the notification and the moment from which it will be possible to begin to apply the simplified tax system of 15% differ for existing and newly registered taxpayers. The general tax rate for the “income minus expenses” object is set at 15%, but can be reduced by decision of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. A special feature of the application of the simplified tax system of 15% is the payer’s obligation to pay the minimum tax if the calculated tax is less than 1% of the amount of income received.