The unified social tax is a tax that gives Russians the right to receive pensions and social security in old age, as well as medical care. It was introduced into use by citizens of the Russian Federation in 2001, but from January 1, 2010 this payment was canceled.
Instead, taxpayers pay special insurance premiums, although many, out of habit, consider the UST rates in 2020, the table of which divides the tax percentage into several funds of the Russian Federation.
UST in 2021: why is it needed?
The abbreviation UST stands for unified social tax. Before moving on to the issue of the size of the UST in 2021, let us briefly dwell on the nature of this tax, its objectives and objects of taxation.
To begin with, let us explain that legally this tax has not existed for several years; it was abolished 9 years ago. But out of habit, different contributions for this purpose are called a single social tax. In addition, there is a possibility that it will be returned.
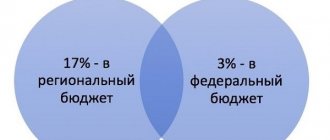
It is calculated using both budgetary and extra-budgetary sources of funds. The purpose of the UST is to provide employees with the opportunity to receive a state pension and a number of social benefits in the future. From the same source, the necessary amounts are allocated for free assistance in medical organizations, the list of which is determined by law.
simplified tax system
Merchants using the simplified tax system have the right to deduct the paid unified tax when calculating tax. On both simplified tax systems this happens in different ways:
- with the “income-expense” object, the amounts of the Unified Tax are included in expenses, thereby reducing the tax base;
- with the object “income”, the calculated tax itself is reduced, from the amount of which the paid contributions are deducted.
The presence of hired personnel also plays a role. If an entrepreneur works alone, he can deduct from the tax the entire amount of his contribution (Article 346.21 of the Tax Code). This means that you don’t have to pay tax at all if it is less than 36238 (if the businessman’s income does not exceed 300 thousand). When there are employees, the tax can only be reduced by half. Example: A businessman works alone. His annual income was 290 thousand rubles, which means that the amount of insurance premiums is 36,238 rubles payable. Let’s calculate the simplified tax system “income” 6%: 290,000x0.06=17,400 rubles. We reduce the tax by the amount of SV: 17400-36238=-18838 rubles - no need to pay tax. A businessman has 2 hired workers with a salary of 20 thousand per month. The annual amount of CB for them: (20000x0.2x12)x2=96000 rub. – the SV rate is taken to be 20%, since individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system are among the beneficiaries. Amount of SV (individual entrepreneurs + employees) = 96000 + 32385 = 224385 rub. We reduce the tax by the amount of SV: 17400-(50% tax) = 8700 rubles payable.
Who pays, what is the object of taxation
Everyone who officially works must pay this type of tax. These are two large groups of taxpayers.
1. Individual entrepreneurs engaged in private practice.
2. Individuals who do not belong to the category of individual entrepreneurs; Individual entrepreneurs, enterprises and organizations, specific people who make payments to individuals.
These groups have slightly different objects of taxation under the unified social tax. The first group must make deductions from all types of income remaining after taking into account the expenses specified by law. For those who fall into the second group, the entire volume of payments that were made to individuals under contracts of various types becomes objects of taxation: both labor and the entire range of civil law ones.
UTII
A businessman’s income on UTII is not real profit, but imputed income, depending on the established value of the basic profitability, coefficients and various physical indicators. The level of this income determines whether an individual entrepreneur needs to pay an additional 1% contribution if his annual earnings are more than 300 thousand rubles. As for reducing the amount of tax on SV, the system is similar to the simplified tax system:
- no workers, decreases without restrictions;
- there are workers, it decreases by a maximum of 2 times.
How is the UST rate calculated in 2021?
For the main group of taxpayers, UST rates in 2021 remained the same as before. What does it consist of? Of these three types of payments:
- contributions to compulsory pension insurance, the rate of which is 22%;
- contributions for compulsory health insurance, their amount is 5.1%;
- payments to the Insurance Fund amounting to 2.9%.
- payments for accident insurance, the rate depends on the risk group of business activity.
The maximum amount of contributions to pension insurance in 2019 was set at 234,832 rubles; in 2021, the maximum amount of pension contributions will increase to 259,584 rubles. The maximum amount of pension contributions is calculated based on eight times the size of the fixed contribution. Since the fixed contribution to pension contributions remained at the 2020 level, their maximum amount for 2021 was also retained - 259,584 rubles.
As for the interest rate, it varies somewhat depending on the amount of charges.
If the limit set for a given year is reached, it can be adjusted downwards. In 2021, the above-mentioned rate of 2.9% for the Social Insurance Fund applies to accruals for amounts less than 865,000 rubles. If the amounts are more than 865,000, then the rate on this fund will be zero. In 2020, contributions to the Social Insurance Fund are paid until the income reaches 912,000 rubles. For social insurance contributions in 2021, the income limit for calculating contributions is RUB 966,000. After one employee reaches such income, contributions to OSS are no longer accrued from his income in 2021, regardless of the number of places of work.
With regard to contributions to compulsory pension insurance, the rule is the same: if accruals are less than 1,150,000 rubles, then the unified social tax rate is set at 22%, and for payments for amounts over 1,150,000 rubles it is reduced to 10%. In 2021, with an income of 1,292,000, the rate is 22%, and above this amount the rate is reduced to 10%. In 2021, having reached the threshold of 1,465,000, the pension contribution rate is reduced from 22% to 10%.
In order to promptly begin to apply reduced rates, the amount of which depends on the employee’s income, when hiring a new employee, be sure to request a certificate of income received in the form of wages from the previous place of work.
There are no maximum restrictions for compulsory health insurance; in 2021, 5.1% is calculated from the entire amount of income.
Betting on VNim
When paying the unified social tax, we calculate contributions to the Pension Fund, Federal Migration Service, as well as maternity and temporary disability payments. However, there is another category of insurance premiums, the payment of which is still handled by the FSS. These are contributions for injuries and occupational diseases. You can calculate how much interest needs to be paid using the OKVED code or the occupational risk class that exists at the enterprise.
| Risk class | Bid | Risk class | Bid | Risk class | Bid |
| 1 | 0,2 | 12 | 1,3 | 23 | 3,7 |
| 2 | 0,3 | 13 | 1,4 | 24 | 4,1 |
| 3 | 0,4 | 14 | 1,5 | 25 | 4,5 |
| 4 | 0,5 | 15 | 1,7 | 26 | 5,0 |
| 5 | 0,6 | 16 | 1,9 | 27 | 5,5 |
| 6 | 0,7 | 17 | 2,1 | 28 | 6,1 |
| 7 | 0,8 | 18 | 2,3 | 29 | 6,7 |
| 8 | 0,9 | 19 | 2,5 | 30 | 7,4 |
| 9 | 1,0 | 20 | 2,8 | 31 | 8,1 |
| 10 | 1,1 | 21 | 3,1 | 32 | 8,5 |
| 11 | 1,2 | 22 | 3,4 |
There are state benefits when transferring contributions. If the company employs disabled people of 1-3 degrees, then insurance premiums for them should be calculated taking into account 60% of the original rate.
You can find out the OKVED code in the FSS. The type of activity is regularly determined when applying to the Social Insurance Fund. You must submit an application and attach a confirmation certificate to it.
Features of calculations for individual entrepreneurs
How much percent of the unified social tax will individual entrepreneurs have to pay in 2021? A slightly different payment system has been developed for individual entrepreneurs. Firstly, they are not obliged to pay into insurance funds; they can only do this on a voluntary basis. They retain mandatory contributions to two funds: Pension and Medical Insurance. In 2021, both were calculated in proportion to the minimum wage.
The formula was this. We calculate contributions to the health insurance fund based on the rate of 5.1% of the minimum wage for the year, that is, 12 * 5.1% * minimum wage. For the Pension Fund, the calculation is similar, but we apply a rate of 26%.
It must be borne in mind: if the income of an individual entrepreneur per year turns out to be above three hundred thousand rubles, then one percent of the amount by which this limit is exceeded is added to all the deductions listed above.
Rates with increased payouts
If contributions for an individual employee reach a certain limit, the insurance rate changes. This innovation has been in effect since 2018 and concerns contributions to pension insurance funds and contributions for temporary disability and maternity.
| Pension Fund | VNiM | ||
| Payments up to 1.021 million | Over 1.021 million | Up to 815 thousand | Over 815 thousand |
| 22% | 10% | 2,9% | Not paid |
Payments in the table are indicated for one employee.
Main changes to the unified social tax
Speaking about the table of UST rates in 2021, we must also remember about a number of amendments related to the payment of UST, which were introduced this year in connection with changes affecting the Tax Code of Russia.
1. Now it is impossible to round off amounts (in any direction) when making deductions of contributions under the Unified Social Tax.
2. The concept of a maximum indicator for accrual of payments for pension insurance has appeared. It is fixed by law, and corresponding changes have been made to local regulations relating to taxation. But such restrictions have not yet been provided for compulsory medical insurance.
3. Insurance premiums will not be collected from the amount of compensation payments that is less than three average monthly earnings if the employee resigns. This innovation also concerns the payment of travel expenses. And insurance interest will not be charged on them, but only if these expenses are documented.
4. From now on, employers will also be required to contribute the necessary amounts for the purposes of pension insurance for foreign citizens hired. Exceptions are provided only for high-class foreign specialists.
5. The number of enterprises granted the right to electronic reporting has increased.
6. Fixed contributions of individual entrepreneurs will not be calculated based on the minimum wage.
Tax calculator
To quickly calculate the required amount of deductions (including contributions for injuries), it is recommended to use fast and convenient online calculators.
The calculator allows you to calculate payments to the pension fund, FFOMS, and mandatory social insurance contributions. By default, the rate columns contain the percentages set by the state for standard taxpayers. If an organization or individual entrepreneur belongs to preferential categories, it is necessary to change the input data.
If the taxpayer transfers deductions at standard rates, it is enough to indicate the amount of wages to get the final results. They are displayed in the form of a table in which deductions for each type of contribution are indicated separately.
The user can change the template: for an organization, for an individual entrepreneur with employees or without employees.
Changes related to postponements and audits
Supervisory enterprises can now, if there are serious reasons, increase the duration of inspections from the previous four months to six. Such grounds are:
- serious violations that require urgent investigation and immediate action; they must be recorded and documented;
- violations in branches located in different constituent entities of the Russian Federation that require verification;
- inaccuracy in documents or lack of requested data;
- failure to timely make insurance payments, including due to force majeure.
The employer (IP) has the right and even must, in the event of such emergency circumstances, ask for a deferment or installment plan for payments for the unified social tax. These may be reasons such as an unreasonable delay in financing, and for enterprises conducting seasonal work, also force majeure: man-made and natural disasters, military operations, etc.
The subject of taxation will need to submit an application in the established form to the relevant organization. Based on it, a certain decision will be made.
Features of reporting
Calculations for these contributions must be regularly submitted to government agencies. Calculations for contributions controlled by the Federal Tax Service must be made and displayed on paper before the 30th day of the month following the reporting month. By the deadline for submitting reports, the calculation should already be in the local branch of the Federal Tax Service (at the place of registration of the branch).
The calculation of contributions to the Social Insurance Fund contains only calculations regarding contributions for injuries and occupational diseases and is called 4-FSS. The document is submitted either electronically or in writing. The delivery format depends on the number of employees in the organization. Paper documents are accepted until the 20th of the next month, and electronic payments are due until the 25th.
The documentation is prepared by the director or authorized representative.
Unified Social Tax rate tables in 2021
Insurance premium rates in 2021
| To the Pension Fund for compulsory pension insurance | In the Social Insurance Fund for insurance in case of temporary disability and maternity (VNiM) | In FFOMS for compulsory medical insurance | ||
| From the amount of payments within the established limit of the base | From the amount exceeding the established limit value of the base | From the amount of payments within the established limit of the base | From the amount exceeding the established limit value of the base | 5,1% |
| 22% | 10% | 2,9% | Not credited | |
Reduced insurance premium rates in 2021
| Insured category | OKVED codes for types of activities* | Tariff for calculating contributions | ||
| to the Pension Fund of Russia | in FSS on VNiM | in FFOMS | ||
| Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system, conducting a preferential type of activity, the income from which is at least 70% of the total income of the simplified tax system. At the same time, the annual income of a simplifier should not exceed 79 million rubles. If this limit is exceeded, the payer of contributions loses the right to reduced tariffs from the beginning of the billing period (clause 5, clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, clause 6 of Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | 13, 14, 15, 16, etc. | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Pharmacy organizations, as well as individual entrepreneurs with a license to conduct pharmaceutical activities, on UTII. Reduced contribution rates apply only to employees engaged in pharmaceutical activities (clause 6, clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | 46.18.1, 46.46.1, 47.73 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Individual entrepreneurs applying the patent taxation system - in relation to payments and remuneration of employees who are engaged in a patent type of activity. For some types of activities, this “benefit” does not apply (clause 9, clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | 31.0, 74.20, 75.0, 96.01, 96.02, etc. | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Non-profit organizations on the simplified tax system, except for state and municipal institutions, operating in the field of social services for citizens, scientific research and development, education, healthcare, culture, art and mass sports (clause 7, clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, clause 7 Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | 37, 86, 87, 88, 93, etc. | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Charitable organizations on the simplified tax system (clause 8, clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, clause 8, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | 64.9, 88.10 | 20 | 0 | 0 |
| Organizations operating in the field of information technology (clause 3, clause 1, clause 1, clause 2, clause 5, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017). | 62, 63 | 8 | 2 | 4 |
| Business entities and partnerships on the simplified tax system that are engaged in the implementation of the results of intellectual activity (inventions, utility models, etc.), the rights to which belong to budgetary and autonomous (including scientific) institutions (clause 1, clause 1, clause 1 Clause 2, Clause 4 of Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation as amended, valid from 01/01/2017). | 72 | 8 | 2 | 4 |
| Organizations and individual entrepreneurs that have entered into agreements with the management bodies of special economic zones on the implementation of technological innovation activities, as well as tourist and recreational activities (clause 2, clause 1, clause 1, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid. from 01/01/2017). | 65.20, 79.1, 94.99, 62.0, 63.1, 63.11.1, etc. | 8 | 2 | 4 |
| Payers of contributions making payments and rewards to crew members of ships registered in the Russian International Register of Ships (with some exceptions) in relation to these payments (clause 4, clause 1, clause 2, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Organizations that have received the status of a participant in the project for the implementation of research, development and commercialization of their results “Skolkovo” (clause 10, clause 1, clause 4, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | 72.1 (Part 8 of Article 10 of the Law of September 28, 2010 No. 244-FZ) | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| Payers of contributions who have received the status of a participant in a free economic zone on the territory of the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol (clause 11, clause 1, clause 5, clause 2, clause 10, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01.01. 2017) | Any OKVED codes, except 05, 06, 07, 08, 09.1, 71.12.3 (Part 2 of Article 12 of the Law of November 29, 2014 No. 377-FZ) | 6 | 1,5 | 0,1 |
| Contribution payers who have received the status of resident of the territory of rapid socio-economic development (clause 12, clause 1, clause 5, clause 2, clause 10, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | Types of activities are established separately for each territory (clause 1, part 2, article 3 of Law No. 473-FZ dated December 29, 2014). | 6 | 1,5 | 0,1 |
| Payers of contributions who have received the status of resident of the free port of Vladivostok (clause 13, clause 1, clause 5, clause 2, clause 10, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | Any types of activities, except those prohibited by the decision of the Supervisory Board of the Free Port of Vladivostok (Part 1.2 of Article 6 of the Law of July 13, 2015 No. 212-FZ). For example, oil and natural gas production activities are prohibited, OKVED code 06.1 | 6 | 1,5 | 0,1 |
Tax benefits
There will be no special tax breaks in 2020, because the transitional grace period for insurance premiums under federal law is ending, so the majority of those people who were on the simplified tax system will pay 30 percent contributions.
However, a reduced rate of 20% will apply to non-profit and charitable organizations that use the simplified tax system. The benefit is provided until 2024.
Previously, bills were discussed that provide for a planned increase in contributions for the simplified tax system. However, the authorities decided that such events were not planned. Today, the tax code has a single tariff of 30%. Accordingly, the single social contribution for entrepreneurs on a single tax and for those simplified, with a few exceptions, will remain the same.
The following companies can count on benefits under Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Organizations engaged in the IT field;
- Airlines; charitable foundations that use the simplified tax system;
- Residents of the seaport of Vladivostok;
- Companies that operate in the territory of the free economic zone of Crimea, as well as Sevastopol.
Categories of individual entrepreneurs for which the preferential tariff was canceled in 2021
| Organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system, conducting a preferential type of activity, the income from which was at least 70% of the total income of the simplified tax system. At the same time, the annual income of the simplifier did not exceed 79 million rubles. | 13, 14, 15, 16, etc. | 22 | 5,1 | 2,9 |
| Pharmacy organizations, as well as individual entrepreneurs with a license to conduct pharmaceutical activities, on UTII. | 46.18.1, 46.46.1, 47.73 | 22 | 5,1 | 2,9 |
| Individual entrepreneurs applying the patent taxation system - in relation to payments and remuneration of employees who are engaged in a patent type of activity. For some types of activities, this “benefit” was not applied (clause 9, clause 1, clause 3, clause 2, article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as amended, valid from 01/01/2017) | 31.0, 74.20, 75.0, 96.01, 96.02, etc. | 22 | 5,1 | 2,9 |
What you need to know about personal income tax
Since 2021, there have been some changes in the payment of personal income tax. And they will affect those companies that employ employees with high salaries.
Previously, personal income tax was calculated based on the actual income of employees for the month; a flat rate of 13% for residents of the Russian Federation “worked.” From January 1, 2021, the PFDL rate was introduced and became progressive. This means that the amount withheld will depend on the amount of income (Federal Law No. 372-FZ dated November 23, 2020).
If the annual salary exceeds 5 million rubles, then it is subject to personal income tax of 15%. At the same time, the increased rate does not apply to all income, but only to the part that goes beyond 5 million rubles.
For non-residents of the Russian Federation, personal income tax continues to apply in the amount of 30%.
Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs “for themselves” in 2021
| Fixed payment for compulsory health insurance | 6884 rubles |
| A fixed payment for compulsory pension insurance, if the amount of the individual entrepreneur’s annual income does not exceed 300,000 rubles. | 29,354 rubles |
| Additional payment to the Pension Fund if the annual income of an individual entrepreneur exceeds 300,000 rubles. | 1% of the amount of the annual income of an individual entrepreneur, reduced by 300,000 rubles, but not more than 234,832 rubles. The maximum amount of contributions paid by individual entrepreneurs to the Pension Fund in 2021 is RUB 234,832. (RUR 29,354 x 8). Minus the fixed payment for compulsory pension insurance, the result is 205,478 rubles. (234,832 – 29,354.) |
Dangerous Economy
Many entrepreneurs are looking for various opportunities to minimize employee costs. And salaries in envelopes are being replaced by new options for reducing the amount of payments from the payroll. But each of them carries certain risks.
Conclusion of GPC agreements
This option for minimizing costs is interesting to the employer because there is no need to provide the employee with guarantees and compensation provided for by the Labor Code. The employer is not obliged to pay benefits; it is not spent on creating working conditions. The only thing he needs from an employee is the result of his work.
However, in most cases, payments under GPC agreements are still subject to insurance premiums. In this case, personal income tax is paid in any case, since the company acts as a tax agent when paying income to individuals.
In paragraph 4 of Art. 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation specifies cases when payments under GPC agreements are not subject to contributions. We are talking about situations where the subject of contracts is the transfer of ownership or other proprietary rights to property (property rights). This also includes agreements related to the transfer of property (property rights) for use, with the exception of copyright contracts, agreements on the alienation of the exclusive right to the results of intellectual activity specified in paragraphs. 1-12 p. 1 tbsp. 1225 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, publishing license agreements, license agreements on granting the right to use the results of intellectual activity specified in paragraphs. 1-12 p. 1 tbsp. 1225 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The essence of the risk is that GPC agreements, which actually regulate labor relations, can be reclassified as labor ones (Article 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). There are a number of signs that courts pay attention to when recognizing a relationship as an employment relationship.
The consequence of recharacterization of the contract is the accrual of arrears, fines, penalties, liability for violation of labor protection legislation, etc.
Registration of employees as individual entrepreneurs
This is another option to minimize employee costs. For example, if you take an individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system “income”, then the amount of payment of the actual salary will be 6%, you also need to take into account contributions to compulsory pension insurance - 32,448 rubles. and contributions for compulsory medical insurance - 8,426 rubles. If the income of an individual entrepreneur exceeds 300,000 rubles. per year, then plus 1% of the excess amount is paid.
In order to save money, employers even compensate the necessary amounts within 6%, which is also beneficial for individual entrepreneurs - in fact, the entrepreneur receives the full amount. In this case, the individual entrepreneur is deprived of all guarantees provided for by the Labor Code.
An agreement with an individual entrepreneur, as in the previous case, can be recognized as an employment contract if it contains signs that the individual entrepreneur is in fact involved in the production process, performs the same duties every day along with full-time employees, has a workplace in the company’s office and uses its equipment. The tax office takes into account the totality of signs and testimony of witnesses. If it turns out that the company really “hid” the employment relationship in contracts with individual entrepreneurs, then additional taxes will follow.
“Transfer” of employees to self-employed
This scheme became known as soon as the professional income tax came into force, which allowed people who work for themselves to become officially self-employed.
From January 1, 2021, all regions, without exception, joined the experiment with a tax on professional income. Those who have registered as self-employed pay a tax of 4% on income from transactions with individuals and 6% on income from transactions with individual entrepreneurs and legal entities. Some employers have decided to transfer some of their employees to professional income tax payers, that is, to fire them and re-register relations with them using GPC agreements.
Employers have realized that the benefit from this is quite large: they cease to be tax agents for personal income tax in relation to an employee who has become self-employed, and get rid of the obligation to pay insurance premiums. Accordingly, they are also not required to comply with any guarantees under the Labor Code. Self-employed employees remain without severance pay, paid leave and benefits in case of temporary disability.
However, it is worth considering that in addition to obvious signs that may indicate the real status of a “self-employed” (for example, the daily presence of a former employee in the office and his use of a specific workplace), there are also provisions of the law itself on the self-employed. They indicate that an employer can, within the framework of a GPC agreement, cooperate with a former employee who has become self-employed only under one condition - if at least two years have passed since the dismissal of this employee from the company.
Insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs “for themselves” in 2021
| Fixed payment for compulsory health insurance | 8,426 rubles |
| A fixed payment for compulsory pension insurance, if the amount of the individual entrepreneur’s annual income does not exceed 300,000 rubles. | 32,448 rubles |
| Additional payment to the Pension Fund if the annual income of an individual entrepreneur exceeds 300,000 rubles. | 1% of the amount of the individual entrepreneur’s annual income, reduced by 300,000 rubles, but not more than 259,584 rubles. The maximum amount of contributions paid by individual entrepreneurs to the Pension Fund in 2021 is RUB 259,584. (RUR 32,448 x 8). Minus the fixed payment for compulsory pension insurance, the result is 227,136 rubles. (259,584 – 32,448.) |
How much should you pay per employee per month?
Having studied all the taxes, let's calculate how much you need to pay per employee per month.
If the salary under the employment contract is 20,000 rubles. per month (before taxes), then for the year it will be 240,000 rubles.
Let's calculate personal income tax: 20,000 x 13% = 2,600 rubles.
The employee receives 17,400 rubles. (20,000 - 2,600).
Every month, under the same conditions, you will need to pay fees:
- for compulsory medical insurance: 20,000 x 5.1% = 1,020 rubles.
- for OPS: 20,000 x 22% = 4,400 rubles.
- on OSS: 20,000 x 2.9% = 580 rubles.
- “for injuries”: 20,000 x 0.2% = 40 rubles.
The total amount is 6,040 rubles. per month and 72,480 rubles. in year.
Total: costs per employee will be 26,040 rubles. per month or 312,480 rubles. in year.
In addition to wages, it is also necessary to take into account the employer’s costs for equipping each employee’s workplace. Until recently, it was believed that those who transfer employees to remote work save significantly. However, Federal Law No. 407-FZ dated December 8, 2020 amended the Labor Code and it became clear that remote work imposes separate obligations on employers.
In particular, the employer, at his own expense, is obliged to provide the employee performing his work functions from home with the equipment he needs for full-time work, software and hardware, and information security tools. Options are possible when an employee uses his own technology, equipment and programs, but then the employer must compensate him for the costs.
Read the article: Eight changes in working with employees in 2021
This might also be useful:
- How to make a Z-report at the cash register?
- How to reduce the simplified tax system for insurance premiums?
- Examples of calculating UTII in 2021
- Payment of 1% on income over 300,000 rubles
- Transport tax under the simplified tax system and OSNO in 2021
- Property tax for organizations and individuals
Is the information useful? Tell your friends and colleagues
Dear readers! The materials on the TBis.ru website are devoted to typical ways to resolve tax and legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific issue, please contact the online consultant form. It's fast and free!
Results
The UST was abolished in 2010 as a tax that did not solve the problems for which it was introduced. With the transition to the payment of insurance premiums, all parameters determining the amount of payments to the funds were significantly increased: the tax base, rates, and the range of payers. Since 2021, insurance premiums have been transferred under the control of the tax authorities.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Liability for non-payment
Payers of insurance premiums, in addition to paying them, have obligations to submit reports (only with employees) and maintain personalized records. Violators face various penalties:
- minimum 1 thousand rubles for missing the deadline for submitting a calculation, maximum 30% of the total amount of the calculated UST;
- for missing the deadline for submitting personalized accounting information to the Pension Fund, for errors in information - 500 rubles for each person;
- reduction in the calculation base for social tax, incomplete payment of insurance premiums: fines from 20 to 40% of the calculated amount;
- Gross violations in calculations, deliberate concealment of income and real payments to employees will lead to an additional recovery of at least 40 thousand rubles or 20% of the unified social tax amount.
Sanctions are quite strict when it comes to social payments to citizens of the country. Therefore, the administration of insurance premiums again passed to the Federal Tax Service, which shows good results in terms of collection of taxes, fees and contributions. Small business representatives can only pay them on time to avoid unnecessary hassle in the future.
Patent
Income for businessmen on a patent, as well as on UTII, is determined by average indicators. The cost of a patent per year depends on the potential annual income, which also depends on the number of employees. However, this regime does not imply a reduction in the value of the patent due to contributions paid for oneself or for workers. Individual entrepreneurs on PSN pay only a preferential 20% on compensatory pension for their employees.
Payment deadlines
Payment of social tax occurs according to different deadlines that must be observed. For example:
- the fixed amount of 36,238 rubles is paid for this year until its end;
- additional contributions of 1% for excess income must be repaid in the first six months of 2021;
- contributions for workers are made monthly until the middle of the next month (15th).
An individual entrepreneur can pay a fixed amount for himself either at one time or in parts. You can make advance payments every quarter, then you can take these amounts into account when calculating your tax (convenient for quarterly UTII). Additional contributions can also be paid ahead of schedule, when it becomes clear that the income limit of 300 thousand rubles has been reached.