Contribution to the authorized capital upon income
The difference between the value of the property contributed to the authorized capital and the nominal value of the share in this capital does not affect the tax base.
“Thus, when making a contribution to the authorized capital, the excess of the estimated value of the contributed fixed asset over its residual value by the transferor is not taken into account for tax purposes” (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated December 17, 2021 No. 03-07-11/491). Clause 2 of Art.
34 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint-Stock Companies” provides for payment of shares in the management company with property. In this case, the organization’s charter may establish types of property that cannot be contributed to pay for shares in the authorized capital of the company.
Tax-free income under the simplified tax system
- Temporary disability benefits;
- Maternity benefits;
- One-time benefit for the birth of a child;
- A one-time benefit for women who registered in the early stages of pregnancy;
- Monthly allowance for child care up to 1.5 years old, etc.
We recommend reading: Example of a purchase and sale agreement for an apartment using maternity capital
An organization or individual entrepreneur can transfer its fixed assets as a contribution to the authorized capital of another organization, partnership, or cooperative. Such a transfer is an investment, not a sale of goods (clause 4, clause 3, article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and is classified as non-taxable income under the simplified tax system .
Is a contribution to the authorized capital in the event of an incorporation an income?
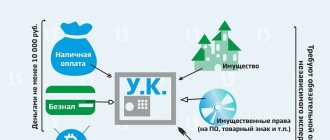
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 14 of Federal Law No. 14-FZ of 02/08/1998 “On Limited Liability Companies” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 14-FZ), the authorized capital of a limited liability company (hereinafter referred to as LLC) is made up of the nominal value of the shares of its participants. In this case, the size of the share of a company participant must correspond to the ratio of the nominal value of his share and the authorized capital of the company (clause 2 of Article 14 of Law No. 14-FZ). By virtue of clause 6 of Art. 66 Civil Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1, art. 15 of Law No. 14-FZ, contributions to the authorized capital of a company can be made in money, securities, other things or property rights or other rights that have a monetary value. That is, contributions to the authorized capital can be made by fixed assets, inventories (materials, raw materials, etc.), as well as goods. According to paragraph 2 of Art. 15 of Law N 14-FZ, the monetary value of property contributed to pay for shares in the authorized capital of an LLC is approved by a decision of the general meeting of company participants, adopted by all company participants unanimously, provided that the nominal value of such a share, paid in kind, is no more than twenty thousand rubles
Organizations using the simplified tax system, in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 4 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 N 129-FZ “On Accounting” keep records of fixed assets and intangible assets in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting. At the same time, no special features have been established for maintaining OS accounting for such organizations. Therefore, fixed assets accounting is carried out in accordance with PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”. In accounting, the value of property received as a contribution to the authorized capital is not taken into account as part of income (clause 2 of PBU 9/99 “Income of the organization”). In accordance with PBU 6/01, an asset is accepted into the OS if the conditions established by clause 4 of PBU 6/01 are simultaneously met, and also provided that the object has been brought to a state in which it is suitable for use in the organization’s activities. At the same time, assets in respect of which the conditions stipulated in clause 4 of PBU 6/01 are met, and with a value within the limit established in the accounting policy of the organization, but not more than 40,000 rubles per unit, may be reflected in accounting and financial statements in composition of inventories (clause 5 of PBU 6/01). In other words, property that meets all the established criteria for a fixed asset, with the exception of cost, can be reflected as part of inventories. However, the corresponding provision must be enshrined in the accounting policy of the organization for accounting purposes, namely, the accounting policy must approve: - limit on the cost of fixed assets; — the possibility of accounting for acquired (including those received in the form of a contribution to the authorized capital) property within this limit (but not more than 40,000 rubles) as part of inventories. If the organization’s accounting policy contains such provisions, then accounting for such “low-value” assets is carried out in accordance with PBU 5/01 “Accounting for inventories” (hereinafter referred to as PBU 5/01). If the provisions of the organization’s accounting policy do not provide for such accounting for “low-value” assets, then the organization must take them into account as part of fixed assets. Thus, the organization has the right to choose a method acceptable to it for reflecting such property (either as part of fixed assets or as part of inventory), reflecting the chosen method in its accounting policies. Please note that the initial cost of a laptop received as a contribution to the authorized capital, regardless of the method of its reflection for accounting purposes (as part of the operating system or as part of the inventory) approved by the accounting policy, will be its monetary value, agreed upon by the founders (participants ) organizations taking into account the requirements of the law (clause 9 of PBU 6/01, clause 8 of PBU 5/01). When reflecting the operation of making a contribution to the authorized capital, the accounting entries will look as follows: Debit 75, subaccount “Settlements with founders” Credit 80 - 10,000 rubles. — the debt of the founders for the contribution to the management company with property is reflected (in the monetary value agreed upon by the founders). Further accounting entries depend on which property (fixed assets or inventories) the laptop will be included in. If a laptop is subject to accounting as part of fixed assets, its actual (initial) cost is subject to formation on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” in correspondence with the credit of account 75: Debit 08, subaccount “Purchase of fixed assets” Credit 75, subaccount “Settlements with founders” - 10,000 rubles. — a laptop was received as a contribution to the authorized capital (in monetary value agreed upon by the founders). The actual (initial) cost of an object formed on account 08 when accepting it for accounting as fixed assets (at the time of commissioning) is written off to the debit of account 01 “Fixed assets”: Debit 01 Credit 08, subaccount “Acquisition of fixed assets” - laptop accepted for accounting as a fixed asset. Please note that if a laptop is accepted for accounting as a fixed asset, the organization will have to charge depreciation for this object in the generally established manner during its useful life (clause 17 of PBU 6/01). Accounting for a laptop as part of the inventory is reflected in the following entries: Debit 10 Credit 75, subaccount “Settlements with founders” - 10,000 rubles. — a laptop was received as a contribution to the authorized capital (in monetary value agreed upon by the founders). Such assets must be included in the organization’s expenses (with their value reflected in the corresponding cost accounting accounts) upon commissioning (clause 93 of the Guidelines for accounting of inventories, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2021 N 119n): Debit 26 (20, 44) Credit 10 - 10,000 rub. — the laptop is written off as expenses at the time of commissioning. In order to ensure the safety of these objects during operation, the organization must organize proper control over their movement (paragraph 4 of clause 5 of PBU 6/01). For this purpose, it is necessary to ensure that it is assigned to financially responsible persons approved by the order of the organization.
Interesting read: What can you get a subsidy from the state for?
We form capital and evaluate the contribution
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 15 of the Federal Law of 02/08/98 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies” (hereinafter referred to as the LLC Law), as well as clause 1 of Art. 66.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the founder can pay for his share in the authorized capital of the organization in things. The constituent agreement or law may establish a ban on the inclusion of a certain type of property in the authorized capital of the company (Clause 2 of Article 66.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Let’s assume that when creating an organization, the founders decided to form the authorized capital from their property. How to evaluate the contributed property? After all, it is quite possible that the nominal value of the founder’s share is, for example, 50,000 rubles, and he contributes property worth 1 million rubles. Or vice versa, the share is determined to be 1 million rubles, and the founder transfers the object at a price of 50,000 rubles. What criteria should be used when assessing a non-monetary contribution?
Let us turn to the provisions of the LLC Law. As a general rule, the monetary valuation of property contributed to the authorized capital of an organization is approved by a decision of the general meeting of participants (clause 2 of Article 15 of the LLC Law), that is, based on this norm, the founders themselves must evaluate the non-monetary contribution. But it's not that simple.
There is an exception to this rule. If the nominal value of the share of the founder of the organization exceeds 20,000 rubles. and he contributes property towards this share; an independent appraiser is needed to evaluate it. In this case, the nominal value of the founder’s share, paid in kind, cannot exceed the amount of the valuation of the specified property, which was named by an independent appraiser.
In paragraph 2 of Art. 66.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation also states that the monetary valuation of the property contribution to the authorized capital of the company is carried out by an independent appraiser. Participants in a business company do not have the right to determine the monetary value of such a contribution in an amount exceeding the amount of the valuation determined by an independent appraiser. Therefore, an appraiser must be involved regardless of the size of the nominal value of the participant’s share. And the general meeting of participants cannot approve the value of property contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital in a greater amount than such property was valued by an independent appraiser.
Please note: in paragraph 1.4 of the Review of judicial practice on disputes involving registration authorities No. 4 (2016), brought to the attention of the tax authorities by letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 28, 2016 No. GD-4-14 / [email protected] , it is said that the provisions The LLC Law should be applied to the extent that does not contradict the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
General Audit Department on the issue of reflecting a decrease in the authorized capital (STS)
According to paragraphs. 17 clause 1 art. 251 of the Code, when determining the tax base for income tax, the taxpayer’s income in the form of amounts by which the authorized (share) capital of the organization was reduced in the reporting (tax) period in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation.
In the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated 04/03/12 in case No. A65-12721/2021, the court indicated that the decision to reduce the authorized capital was made in accordance with the requirements of Article 35 of Law No. 208-FZ[3]. Consequently, the decision of the tax authority to include in income the difference between the amount of net assets and the amount of authorized capital is unlawful.
Founders' contributions: lawyer's answers to clients' questions
Clients often ask how founders can best transfer funds to the accounts of their organizations. Specialists from Legal LLC have prepared useful legal information on the most pressing issues related to founders’ contributions.
2. Free assistance. This is a transfer of money to an organization’s account as financial assistance without the recipient’s obligation to return the money or provide other property, perform work or provide services. The procedure is regulated by the provisions of Art. 248, 250 and 251 of the Tax Code. It should be remembered that if the founder’s share in the authorized capital of the organization is 50% or less, the gratuitous contribution transferred by him will be recognized as non-operating income. This must be taken into account when paying taxes. The date of receipt of income will be the day the funds are received in the account or cash register of the recipient of the contribution. If the founder’s share is more than 50%, then in accordance with the provisions of Art. 251 of the Tax Code, non-operating income is not taken into account.
Tax on the authorized capital of LLC
3. Instead of the aforementioned tax deduction, the founder alienating the share can reduce the taxable income received by the amount of expenses that are associated with the acquisition of a share in the authorized capital (money contributed to the charter capital, expenses for its increase or acquisition of the share). An important rule: expenses must be supported by documents. Otherwise, the founder is given a tax deduction in the amount of no more than 250 thousand rubles for income from leaving the LLC (clause 2, clause 2, article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
1. If the share belonged to the owner - an individual until the moment of alienation for more than 5 years, personal income tax is not paid at all (clause 17.2 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, there is a significant note - the zero rate applies only to those shares that became the property of the founder after January 1, 2021, in accordance with clause 7 of Art. 5 Federal Law No. 395-FZ.
Selection
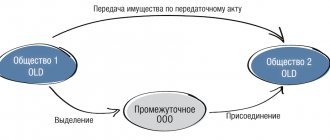
If a new project is launched, a separate legal entity is often created within the holding. It can not only be opened from scratch, but also separated from an existing company by transferring the necessary assets.
From a tax point of view, this is a very profitable option. The transfer of property during reorganization is not subject to either income tax or VAT. The transferring company also does not have to recover VAT. Naturally, the receiving party cannot deduct VAT.
Risks here arise only if the original company uses OSNO, and the receiving company will work on the simplified tax system. It turns out that an organization purchased an object on OSNO, received a VAT deduction, and then transferred it to a dedicated one. Those. in the future, this fixed asset will be used in activities not subject to VAT.
Although according to the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is not necessary to restore VAT during reorganization in any case (clause 8 of Article 162.1 and subclause 2 of clause 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), inspectors may accuse a businessman of receiving an unjustified tax benefit.
To reduce risk, it is better not to carry out reorganization immediately after purchasing those objects that are planned to be transferred.
Contributions to the authorized capital of small organizations on the simplified tax system
In order to carry out state registration of a new company, it is necessary that at least 50 percent of the authorized capital be paid up. The remaining unpaid portion of the Criminal Code must be paid within one year from the date of state registration.
Property received as a contribution to the authorized capital of an organization is accepted for profit tax purposes at the cost (residual value) of the property received. The cost (residual value) is determined according to the tax accounting data of the transferring party on the date of transfer of ownership of the specified property (property rights), taking into account additional expenses that, upon such payment, are made by the transferring party, provided that these expenses are defined as a contribution to the charter capital.
What income is recognized (taken into account) under the simplified tax system?
- from leasing property;
- from the transfer of intellectual property rights for use;
- in the form of interest on loan agreements or bank deposits;
- when receiving property free of charge;
- in the form of fines from counterparties for violation of the terms of the contract, including received compensation for legal expenses ;
- as income from previous years;
- in the form of surpluses identified during inventory ( how to take them into account, see more here );
- when writing off accounts payable;
- from participation in other organizations;
- like exchange rate differences;
- as compensation for self-demolition of unauthorized buildings, etc.
- returned deposit;
- money received from the supplier for defective goods returned to him;
- money returned due to incorrectly specified details;
- return of erroneously transferred amounts;
- funds from the Social Insurance Fund to reimburse expenses for disability and maternity benefits;
- refund of overpaid taxes and contributions;
- returned advance.
Sale of a share in the authorized capital
CJSC Gamma, which applies the simplified tax system, sold a share in the authorized capital of a limited liability company, previously acquired by this organization from the previous owner. In what order should Gamma CJSC take this income into account when calculating the tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system?
Taxpayers applying the simplified tax system, when determining the object of taxation, take into account income from sales and non-operating income determined in accordance with Articles 249 and 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and do not take into account the income specified in Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is stated in Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that income from sales includes proceeds from the sale of goods (works, services) both of one’s own production and those previously acquired and proceeds from the sale of property rights.
Income under a simplified taxation system
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxpayers applying the simplified taxation system, when determining the object of taxation, take into account income from sales determined in accordance with Art. 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and non-operating income determined in accordance with Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In paragraph 4 of Art. 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that income received in kind is taken into account at market prices, determined taking into account the provisions of Art. 40 of the Tax Code, but not lower than the residual value - for depreciable property and production (purchase) costs - for goods (work, services). Information on prices must be confirmed by the taxpayer - the recipient of the property (work, services) documented or through an independent assessment.
Postings 75 of the account for contributions to the authorized capital: to the current account, in the form of fixed assets and intangible assets
In order for an organization to be registered, it is necessary to contribute at least 50% of the authorized capital. But it should be noted that the legislation provides an exception for such an organizational and legal form as a joint-stock company. A joint stock company can obtain state registration without contributing authorized capital. But at the same time, half or more of the amount of the authorized capital must be paid for a period of no more than 3 months after state registration, the rest - no later than a year.
Let’s say Meduza LLC and the individual Slavkin P.V. are the founders of Megapolis LLC with an authorized capital of 755,000 rubles. The shares of the founders are distributed as follows: Meduza LLC - 75%, Slavkin P.V. — 25%. Payment of the authorized capital was carried out in 2 stages: 50% was paid before registration, 50% after.
In what cases may it be necessary?
A private entrepreneur will need a charter only in one case - if he decides to change the organizational and legal form of his organization. This need, in turn, may be due to several important business factors:
- An entrepreneur wants to operate in an area that is inaccessible to individual entrepreneurs. For example, one that requires a license.
- A businessman wants to expand his business. To do this, he needs to attract investment. In this case, investors become full partners of the entrepreneur.
- The market is changing, and financial risks are increasing as a result. The businessman fears the closure of the business and the loss of personal property, so he decides to change the legal form.
These factors can apply to any area of business and overlap with each other. Thus, business expansion often involves starting activities in a new area that was previously inaccessible to a private entrepreneur. An unfavorable market situation can prompt several individual entrepreneurs to combine their efforts and assets. Relatively little competition in the areas subject to licensing provides incentives to expand and operate in these areas.
In case of a change in the form of ownership, the procedure for declaring the authorized capital will be the same as in the case of legal entities. The founders also set the percentage of shares in the business themselves.
In connection with the possible transition from an individual entrepreneur to an LLC, it is better for private owners to decide in advance how much material resources they are willing to invest in the future organization, and save it in case of force majeure circumstances in the business.
Note! A change in the form of ownership is fully equated by law to the establishment of a new organization.
Individual entrepreneurs and LLCs are fundamentally different classes of business. Differences begin already in the constituent documents and predetermine the features of further activities. Businessmen prefer an easier path to their business. Convenient accounting, preferential taxation, favorable mortgage conditions - this is just a short list of the positive features of doing business as an individual entrepreneur. What makes it special is the lack of authorized capital: you can open your own enterprise with minimal costs and not declare the amount of your starting capital anywhere. This fact makes individual entrepreneurs a very attractive form of ownership for beginning entrepreneurs.
Free contribution from the founder taxation in case of registration
Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, there is no need to reflect the amounts received in the Income and Expense Book. There will also be no expenses when repaying the debt, since there is no such type of expense in the closed list of expenses taken into account under the simplified tax system (clause 1 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Note: When the loan is repaid, the founder does not receive income. When the loan is returned to the founder, he does not receive any economic benefit.
DT 08, CT 83 (Founder's contribution to add net assets) - acceptance of fixed assets Contribution of fixed assets by the founder to add net assets DT 75 (Founder's money to cover damage), CT 84 - the decision to cover damage is fixed; DT 51, CT 75 (Founder's money to cover damage) - crediting monetary assistance (contribution) Contribution to cover damage DT 50 (51), CT 91-1 - contribution of money by the founder; DT 91-1, CT 99 - annual income; DT 99, CT 84 - net annual income; DT 84, CT 82 - contribution to add to the reserve fund in accordance with the norms of the organization’s Charter Contribution to add to the reserve fund Registration of gratuitous assistance of the founder: methods and related documents The process of registration of gratuitous assistance of the founder begins with a general meeting of participants, where the issue of its provision is initially raised and agreed upon .
Interesting read: How Land Tax is Calculated for Individuals
Contribution to the authorized capital upon income
When keeping records of fixed assets and intangible assets, you must be guided by PBU 6/01 “Accounting for Fixed Assets” and PBU 14/2021 “Accounting for Intangible Assets”. These documents provide for various methods for calculating depreciation of property, various rules for determining the useful life of property, etc.
Each founder of the company must pay in full his share in the authorized capital of the company within the period determined by the agreement on the establishment of the company or, in the case of the establishment of the company by one person, by the decision on the establishment of the company and cannot exceed one year from the date of state registration of the company. In this case, the share of each founder of the company can be paid at a price not lower than its nominal value. It is not permitted to release the founder of a company from the obligation to pay for a share in the authorized capital of the company.
What methods of transferring property are best used in different situations?
We will show in the table possible options for transferring property, depending on the relationship between the parties to the transaction.
| Transfer options/parties to the transaction | Sale | Contribution to the management company | Contribution to property | Free transfer | Selection |
| From founder to subsidiary | + — | + + | + — | + — | + + |
| From subsidiary to founder | + — | — — | — — | + — | — — |
| Between companies with a common owner | + + | — — | — — | — — | — — |
«+ +» - acceptable from a legal point of view and beneficial in terms of taxes
«+ —"- acceptable from a legal point of view, but unfavorable from a tax point of view
«— —» – unacceptable from a legal point of view
A businessman will have the most options if he transfers property from the founder to a subsidiary company. In this situation, the most profitable would be a contribution to the authorized capital or allocation.
If the object is transferred in the opposite direction - from the subsidiary to the parent company, then the only choice left is between sale and gratuitous transfer. The advantages of one method or another will depend on tax regimes and the ability to justify a low price.
In the case when both companies work for OSNO and the property is sold at its residual value, there will be no need to pay income tax and VAT for the group as a whole. Then buying and selling property will be more profitable.
And if the market price of a fixed asset significantly exceeds the residual value, or the receiving company operates on a special regime and cannot refund VAT, then it is better to use a gratuitous transfer.
If you need to transfer property between two companies that are connected only by a common owner, then there is only one option left - a standard purchase and sale agreement.
Non-monetary contribution to the authorized capital: tax consequences
In addition to the document on the value of the property, according to the transferring party, the recipient company must have a report from an independent appraiser on the market value of this property. It is necessary to compare the documented value of property according to a foreign organization with its market value. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the recipient cannot take into account property contributed by a foreign organization at a price higher than that determined by an independent appraiser. The appraiser must carry out the assessment in accordance with the legislation of the state of which the participant is a resident.
If the company received a fixed asset from a participant, it has the right to depreciate it. In paragraph 7 of Art. 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that the depreciation rate for this property can be determined taking into account the useful life reduced by the number of years (months) of operation of this property by the previous owners. From the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2021 No. 03-03-06/1/826 it follows that the depreciation rate for intangible assets received as a contribution to the authorized capital can be determined in a similar manner.
Income not taken into account under the simplified tax system
Let us recall that an organization can sell the receivables of its buyer to another company, that is, assign the right to claim this debt. Such a concession is formalized by an assignment agreement (Article 382 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The original creditor who assigns the right to claim the debt to another company is called the assignor. And the company that buys the right of claim is the assignee.
A similar approach is applied when an individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system sells his share in the authorized capital of a company that he acquired without being registered as an individual entrepreneur. Indeed, according to the rules of paragraph 1 of Article 210 of the Tax Code, when determining the tax base for personal income tax, all income of an individual received by him both in cash and in kind, or the right to dispose of which he has acquired, is taken into account. According to the rules of another norm, income from the sale of a share in the authorized capital of an organization is subject to personal income tax at the generally established rate of 13% (clause 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, a citizen who received income from the sale of a share in the authorized capital of an organization pays personal income tax and reflects it in the declaration in form 3-NDFL. Moreover, regardless of the fact that at the time of the sale of the share the citizen was registered as an individual entrepreneur applying the simplified tax system (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 9, 2021 No. 03-04-05/46598).
Chapter 6
Try to answer a few questions right away, without looking at the Tax Code: 1. Is the LLC’s income the founder’s contribution to the authorized capital? 2. Is it necessary to impose a single tax on the simplified tax system on the amount of a loan received from a bank? 3. An enterprise issued a cash loan to its employee. The employee repaid the loan with interest. What amount is subject to single tax in this case? 4. The company is engaged in commission trading - takes goods “for sale”, sells them, pays the received amount to the principals minus the commission? What is the tax base in this case? 5. A similar situation, but the company does not take goods “for sale”, but buys them from suppliers for ownership under a purchase and sale agreement, and then resells them. How much is taxable? 6. The buyer has paid an advance payment (prepayment) for the goods, the goods themselves have not yet been transferred to the buyer. Do I need to pay tax on the advance amount received? 7. Almost the same situation, but the buyer paid not an advance, but a deposit. Is it necessary to pay tax on the amount received from the buyer in this case?
According to Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when applying the simplified tax system for the purposes of calculating the single tax, the same income is taken into account as when calculating the corporate income tax, which includes the types of income listed in paragraphs 1 and 2 of Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, the following income is not taken into account as part of taxable income: - income specified in Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; — income of an organization subject to corporate income tax at the tax rates provided for in paragraphs 1.6, 3 and 4 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in the manner established by Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; 3) income of an individual entrepreneur, subject to personal income tax at the tax rates provided for in paragraphs 2, 4 and 5 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in the manner established by Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; 4) income received by homeowners’ associations, real estate owner’s associations, management organizations, horticultural, gardening or dacha non-profit partnerships (non-profit partnerships), housing, horticultural, gardening, dacha or other specialized consumer cooperatives from the owners (users) of real estate in payment for utilities provided by third parties.
Revenue under the simplified tax system for 2020–2021
One of the main requirements regarding the possibility of using the simplified tax system by a company or individual entrepreneur is the established limit on the level of annual income, which should not exceed 150 million rubles.
(clause 4 of article 346.13 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). From 2021, income limits are increasing. Find out how the limits will change from 2021 by studying the explanations of ConsultantPlus experts. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
The procedure for accounting for income under the simplified tax system is determined by Art. 346.15, 346.17 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Regarding their composition, paragraph 1 of Art. 346.15 refers to sec. 1 and 2 tbsp. 248 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to the text of these paragraphs, the amount of income under the simplified tax system is formed by the sum of income:
- from implementation;
- non-operating;
- from gratuitously received property or rights to it.
Income does not include receipts listed in Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Revenue consists of sales (subclause 1, clause 1, article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- manufactured products;
- work or services performed;
- previously purchased goods;
- property rights.
In the case of intermediary activities, income will be a commission or other remuneration (see, for example, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 18, 2018 No. 03-11-11/25816).
For the simplified tax system, income is recorded using the cash method (Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which presupposes the actual receipt of money to the current account/cash, as well as the receipt of other property (work, services) and (or) property rights, repayment of debt (payment) in a different way.
For more information about the conditions that allow you to apply the simplified tax system, read the article “Procedure for applying the simplified taxation system” .
Formation of authorized capital in 1C 8
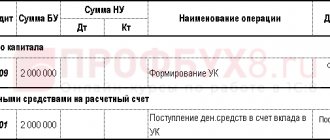
- Contribution of fixed assets. For example, the founder decided to repay the debt on the authorized capital in the form of equipment that can be immediately put into operation. In this case, two entries will be generated: Dt 08 – Kt 75.01 (repayment of debt on the authorized capital);
- Dt 01 – Kt 08 (commissioning of equipment).
Please note that if the debt on the authorized capital is repaid not in money, an assessment of this property must be carried out. The founders have the right to produce it themselves if the cost does not exceed 20,000 rubles. Otherwise, an external appraiser must be involved.