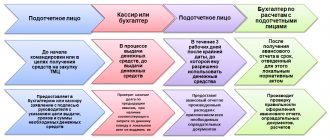
The concept of special tax regimes is spelled out in Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation. They provide for a special procedure for determining the elements of taxation, as well as exemption from the obligation to pay certain taxes and fees. Special tax regimes include:
- taxation system for agricultural producers (UST);
- simplified taxation system (STS);
- taxation system in the form of a single tax on imputed income for certain types of activities (UTII);
- patent tax system (PTS).
Concept and types of special tax regimes
A special tax regime (STR) is a type of taxation that has distinctive characteristics from those generally established in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, with the exception of section 8.1, which sets out the rules governing the STR.
Among the special tax regimes, five regimes are distinguished:
- USN . A simplified tax payment system or the so-called “simplified” system, which is usually used when doing business. It includes a large number of payments that are part of health and pension insurance. This system is not compulsory, and involves two forms introduced in 2014. According to the simplified tax system, tax rates on income are 6%. However, if this is income paid to the state and reduced by the amount of expenses, the rate is 15%.
- UTII . This type of tax regime is also called “imputation”. Unified taxes on imputed income have also become non-compulsory since 2021. Such a system is usually used in conjunction with the main taxation system. It is intended for special types of activities, including veterinary services, motor transport and real estate businesses, advertising, etc.
- Unified agricultural tax . A taxation system regulating agriculture, which helps in the work of agricultural producers. It is applied instead of income tax, property tax and VAT. From 2021, the rate has risen from 18% to 24%.
- PSN . This is a patent system introduced to regulate patent activity. It can be used only by those individual entrepreneurs who are engaged in special types of activities indicated on the websites of the tax services of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. This system replaces VAT, personal property tax, and personal income tax. The rate is 6%.
- PSA . This system is rarely used and is relevant only when paying taxes during the implementation of a goods division agreement. Such legal relations are possible when foreign and national enterprises are engaged in the extraction of mineral raw materials. The rate is calculated individually.
Which chapters of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regulate special tax regimes, by whom they can be applied and on what grounds, it is proposed to find out from the table that can be found.
Knowing about special tax regimes is mandatory not only for an economist or accountant, but also for a businessman, since this is important for competent management of his business and optimization of work with funds within the enterprise.
What does the simplified tax rate depend on?
Taxpayers using the simplified tax system have the right to independently choose the object of taxation and the rate:
- income at a rate of 6%;
- income reduced by expenses at a rate of 15%.
The first option is simpler to account for. The date of receipt of income is considered the day of receipt of funds into bank accounts and (or) to the cash desk, receipt of other property (work, services) and (or) property rights, as well as repayment of debt (payment) to the taxpayer in another way (cash method).
In the second option, income is also determined using the cash method. Expenses are recognized as expenses after they are actually paid. In this case, expenses must be documented and strictly comply with the closed list in accordance with Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When applying the simplified tax system of 15%, a minimum tax of 1% of the amount of income received is taken into account. It is paid in the case when the calculated amount of tax of 15% ends up being less than the amount of the calculated minimum tax of 1% of the amount of income.
Note to the accountant
A low turnover rate is beneficial for highly profitable activities. A rate of 15% on the difference between income and expenses is preferable for less profitable activities. The feasibility of using special regimes also depends on the number of hired employees and their wage fund. More details
General characteristics of SNR
Special tax regimes are a special set of rules established separately for certain social groups, types of activities, etc. Among the main characteristics of special tax regimes are the following:
- With the exception of the SPR, all types of special regimes can only be used by representatives of small businesses.
- ONS, UTII and Unified Agricultural Tax can be used by enterprises and individual entrepreneurs, and PSA - exclusively by enterprises, PSN - exclusively by individual entrepreneurs.
- All special regimes (except for the simplified tax system) can only be used for certain objects that are specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation or established by local authorities. The simplified tax system is used by large business representatives under the conditions prescribed in Chapter 26.2 of the Tax Code.
- In all systems (except PSA), a single special tax is paid instead of income tax, property tax and VAT. As for the PSA, in this case a certain preferential system and a special tax will apply.
The tax period is determined depending on the specific system. Thus, the declaration for taxes of the Unified Agricultural Tax and the National Tax Service is submitted once a year, for the UTII - per quarter, for the PSN - per year or during the validity of the payment, PSA - depending on the period of each tax. These and other characteristics can be found in the table by downloading here.
UTII: what is the chance of extending the special regime?
Experts give 99% out of 100 possible that this tax regime will be abolished from 2021. The Federal Tax Service actively informs taxpayers about the upcoming abolition of UTII through the media, information materials in the premises of tax inspectorates, messages through personal accounts, etc. In March 2021, in this regard, the tax service even issued a letter numbered AB-4-19 / [email protected] - about conducting an information campaign to switch to other taxation regimes in connection with the abolition of UTII from January 1, 2021.
However, as we know, there is always hope. The following reasons give hope for the extension of this tax regime: the validity of UTII has already been extended (the regime should have been abolished back in 2018, but it was extended until the end of 2021), the Republic of Crimea extended the validity of UTII until 2024, business associations and regional The authorities are petitioning for an extension of this tax regime, in particular, such an initiative was made by the deputies of the Legislative Assembly of the Jewish Autonomous Region. Previously, the Ministry of Finance had already rejected such initiatives, but the coronavirus economic “hole” of 2021 makes us not lose hope that this lenient tax regime will be extended.
Conditions for applying special tax regimes
What conditions exist and apply today for the most popular special tax regimes, we will consider below:
Unified agricultural tax
This is a single tax on agriculture. Here are special requirements for the income of the enterprise:
- The share of income from the sale of agricultural products should be no less than 70% of total revenue. At the same time, there are no limits in terms of revenue - they can be absolutely anything.
- If the company is engaged in fishing and production of fish, then the number of employees should be no more than 300 people.
simplified tax system
“Simplified” can be used subject to the following conditions:
- The company should not be a state-owned or budgetary institution, nor an insurer, pawnshop or investment fund.
- The authorized capital may contain no more than 25% participation of third-party organizations or enterprises.
- The company cannot engage in gambling or mining.
- The annual number of employees cannot exceed 100 people.
- For 9 months of the year preceding the year the simplified tax system was established, the enterprise’s income was not higher than 45 million. This figure is calculated taking into account VAT and inflation.
UTII
It can be used as an independent tax regime, or as an additional one, for example, in combination with the simplified tax system. To switch to UTII, a company does not need to limit itself in any way in terms of revenue, but it is worth adopting the following rules:
- If a company is engaged in sales in an area specially available for this purpose, then this area should not exceed 150 square meters.
- The number of employees of the enterprise for the current and last year cannot be more than 100 people.
- The types of activities for which UTII is applicable are clearly reflected in paragraph 2 of Article 346.26 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When switching to a certain tax regime, it is necessary to take into account both federal and regional features of the transition. To clarify these features, you will need to contact your local Tax Service.
What criteria should an entrepreneur rely on?
- Tax optimization – it is important for you to reduce the amount of taxes you need to pay;
- Cost optimization – it is important for you to reduce the costs of accounting and tax accounting, filling out declarations;
- Compliance with the law - it is important for you to conduct your activities without breaking the law, so as not to be brought to administrative or criminal liability.
Let's consider each of the modes, giving them an assessment according to these criteria.
SNR among small businesses
The Tax Code provides special opportunities for small businesses. In this case, one important tax regime is noted - a simplified taxation system or “simplified”. It can be used by both organizations and individual enterprises. The advantages of such a system are as follows:
- For organizations . Taxation on the profit of an organization becomes unified and is no longer calculated in accordance with Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In the case of VAT, the tax will not be calculated according to Chapter 30 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These taxes are replaced by a single one, that is, the accountant will have to make calculations only for a single tax regulated by the “simplified tax”.
- For individual entrepreneurs . In this case, the income tax of an individual will not be calculated in accordance with Chapter 23 of the Tax Code, and the property tax will not be calculated either. Both of them are replaced by a single tax levy introduced by simplified taxation.
Note that the single tax introduced by the simplified system is not all the fees that will need to be paid in favor of the state. You will also need to pay insurance premiums to the Pension Fund; water taxes; government fees; taxes on personal income; transport and land taxes; mineral taxes.
Please note that not all enterprises and individual entrepreneurs can take advantage of the simplified tax regime - for this you must meet certain criteria. These criteria are enshrined in Chapter 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Allocation of VAT amounts in payment documents
In conclusion, I would like to dwell on one more problem. Often, accountants of organizations using the simplified tax system are faced with a situation where the sale of goods (work, services) is carried out without VAT, and funds are received with allocated VAT amounts in payment documents. In this case, the organization’s accountant, in order to justify the fact of non-payment of VAT received on the current account, can be advised to send a letter to the buyer about the unlawful allocation of VAT, enclosing copies of the settlement and shipping documents issued by the seller. The most favorable situation will be those organizations that receive a response from their customers confirming the fact of unlawful allocation of VAT.
Video: SNR for small tax entities
In the general study of taxes and taxation, careful attention is paid to special tax regimes. Detailed information about them with vivid examples is in the following video:
A person can choose any special tax regime completely independently. Of course, it is important to pay attention to which types of tax regimes are right for you, that is, which types you qualify for and which ones you do not. Either way, this is a great opportunity to avoid paying all or some federal taxes.
Self-employment
Self-employed are individuals who provide services personally, without hiring employees. The main condition is to work independently or, to put it simply, with your own hands: construction, repairs, driving a car, photography, performing arts, consulting, animal walking, renting out housing, private teaching, tutoring services, copywriting and so on.
The term “self-employed” is not entirely accurate and is still slightly blurred, since the law refers to the unemployed, lawyers, notaries, and even the notorious individual entrepreneurs as self-employed. When it comes to the new tax regime, which individuals have the right to apply starting from 2021, the correct wording is “professional income tax” or NIP. It is the payers of this tax who are most often considered “self-employed”.
In order to register as self-employed, just download the “My Tax” application and enter all the necessary data. After this, you can begin your entrepreneurial activity.
Unified agricultural tax
This tax system is even more specific, and is used quite rarely!
Unified agricultural tax can be applied by those individual entrepreneurs that meet the definition of agricultural producers given in paragraph 2 of Art. 346.2 NK. The share of expenses for agricultural activities is also important: they should occupy at least 70% of total expenses.
The Unified Agricultural Tax allows you to reduce the tax burden on individual entrepreneurs, the rate is 6%, and also significantly facilitates accounting and reporting.
Bottom line: the possibility of using the Unified Agricultural Tax should be considered by individual entrepreneurs who are classified as agricultural producers.