The image of the company depends on the size of the authorized capital, since it acts as a guarantor of its investment attractiveness. For this reason, founders may register an amount that does not correspond to their real capabilities. As a result, a debt arises, the repayment of which, as well as its reflection in the accounting accounts, has its own characteristics.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique. Write your question using the form (below), and our specialists will quickly prepare the best options for solving your problem and call you back on the day you submit your application. It's free!
How does arrears in contributions from the founders of an LLC arise and what are the consequences?
Within the time limits established by the constituent documents (but no later than 4 months after the registration of the company), all founders of the LLC are required to make their contribution to the authorized capital to the balance sheet of the company (Clause 1, Article 16 of the Law “On LLC” dated 02/08/1998 No. 14-FZ ).
Immediately upon completion of registration of the company with the Federal Tax Service, the debt of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital (AC) is recorded in the accounting registers. It exists until all founders make full contributions to the management company.
If any of the founders refuses to contribute their share to the authorized capital, then individual sanctions provided for in the constituent agreement may be applied to him. The release of the founder from the obligation to pay for such shares is, in principle, not allowed (Clause 2 of Article 90 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, such founders must, within the limits of unpaid shares in the management company, bear joint liability for the debts of the company (clause 1 of Article 87 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
All founders bear subsidiary liability for the company’s debts until the debt on the authorized capital is fully repaid (Clause 4, Article 66.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Until contributions to the management company are made in full, the founders do not have the right to distribute the company’s profits (Clause 1, Article 29 of Law No. 14-FZ).
But what should the partners of the founder do, who, for one reason or another and despite the sanctions, fundamentally refused to pay for the authorized capital - in whole or in part?
Accounting accounts 80 and 75
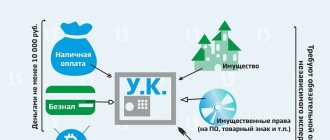
Once the amount of the authorized capital has been determined, it is necessary to reflect this amount in the accounting department of the new organization using the appropriate entries. Reflection of the authorized capital is the first business transaction with which the activities of any organization begin. For this purpose, there is a corresponding account in the Chart of Accounts.
First of all, with its help, start-up capital is formed for the subsequent commercial activities of the enterprise. It consists of contributions from the founders, which can be either in the form of tangible property or in cash. Each founder has his own certain share in the capital, depending on its size, he will subsequently receive the corresponding profit from the commercial activities of the enterprise (dividends). The company is responsible for its obligations within the framework of this capital, so for creditors this is a kind of guarantee of satisfaction of their interests.
The authorized capital has not been paid: what should the company do?
If payment for the share in the company’s management company is not made within the prescribed period, then this share becomes the property of the company (Clause 3, Article 16 of Law No. 14-FZ). After this, the founders of the company must:
1. Within a month, inform the Federal Tax Service by sending there Form R13014 about the transfer of the share to the LLC (clauses 2, 3, 6 of Article 24 of Law No. 14-FZ).
2. During the year, buy back and redistribute (or sell to third parties) this share. Within a month after the redistribution or sale of the share, also notify the Federal Tax Service about this.
If the founders do not do any of the above actions, then the authorized capital is subject to reduction by the amount of the share that has not been redeemed or redistributed or sold (clause 5 of Article 24 of Law No. 14-FZ). The Federal Tax Service must also be informed about the reduction in the capital within a month.
See also “Procedure for reducing the authorized capital of an LLC.”
If the final amount of the authorized capital is less than the minimum (for an LLC - 10,000 rubles), then the enterprise can be liquidated at the request of the Federal Tax Service as having failed to comply with the requirements of the law on registering a business company (subclause 1, clause 3, article 61 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Next, we will consider a situation where the founder nevertheless agreed to repay the existing debt on time.
Net assets
Net assets must not only be positive, but also exceed the authorized capital of the organization. This means that in the course of its activities, the organization not only did not waste the funds initially contributed by the owner, but also ensured their growth. Net assets less than the authorized capital are permissible only in the first year of operation of newly created enterprises. In subsequent years, if net assets become less than the authorized capital, the civil code and legislation on joint stock companies require that the authorized capital be reduced to the amount of net assets. If the organization's authorized capital is already at a minimum level, the question of its further existence is raised.
The liabilities accepted for calculation include all liabilities, except for deferred income.
.
But not all future income, but those recognized by the organization in connection with the receipt of government assistance, as well as in connection with the gratuitous receipt of property
. These incomes are actually the organization's own capital, therefore, for the purposes of calculating the value of net assets, they are excluded from the short-term liabilities section of the balance sheet (line 1530).
How can the founder's debt be repaid?
The debt of the founders on contributions to the authorized capital can be repaid:
- in cash;
- securities;
- property;
- rights of claim on receivables.
Find out in ConsultantPlus how to reflect the contribution of funds to the authorized capital in accounting and what are the nuances of tax accounting for the contribution of property as a contribution to the management company. Get free access to the K+ help system to find out all the details of this procedure.
In this case, the minimum amount of the authorized capital must be represented in cash. An assessment of the value of property that is planned to be added to the balance sheet as a management company is carried out by an independent appraiser (Clause 2 of Article 66.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Funds can be contributed to the authorized capital in cash or by transferring them to a current account. In the first case, a PKO is issued according to form No. KO-1.
The procedure for repaying debt under a capital company using the receivables of the company’s founder is also common. Let's study its features.
UTII
The object of UTII taxation is imputed income (clause 1 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, contributions made by the founders to the authorized capital do not affect the calculation of the tax base.
An example of how to take into account the value of property contributed by the founder to the authorized capital of the company. The organization pays UTII
LLC "Torgovaya" pays UTII.
In March, the founder of Hermes made a copying machine as a contribution to the authorized capital of the organization. The founder's share in the authorized capital is 20 percent or 160,000 rubles. The valuation of the copier, agreed upon by the participants and confirmed by an independent appraiser, amounted to 142,000 rubles.
That same month, the copier was handed over to the accounting department, where it began to be used. Hermes has set the useful life of the copier to 37 months.
The organization's accountant made the following entries in the accounting.
In March:
Debit 08 Credit 75-1 – 142,000 rubles. – the photocopier was received as a contribution to the authorized capital;
Debit 01 Credit 08 – 142,000 rub. – the copy machine was put into operation.
Monthly starting from April until the end of the useful life of the property (37 months):
Debit 26 Credit 02 – 3838 rub. (RUB 42,000: 37 months) – depreciation has been accrued on the copier for the current month.
Operations related to the receipt and operation of a copy machine do not affect the calculation of the single tax.
Formation of authorized capital at the expense of receivables: nuances
This legal relationship assumes that the founder, who has the right to claim on receivables, will pay off his own debt under the authorized capital by placing his receivables in the management company as an asset. To do this, he, together with other founders, needs to hold a meeting at which the value of such a contribution to the management company will be assessed. If the amount of the debt claim is above 20,000 rubles, then an independent appraiser will be required to evaluate the deposit (Clause 2, Article 15 of Law No. 14-FZ).
Supporting documents on the basis of which the receivable will be attributed to the authorized capital may be, in particular:
- agreement on the assignment of rights of claim (if it is required under the agreement between the founder and the debtor);
- loan agreement;
- receipt;
- writ of execution if the debt is already being collected.
A scenario is also possible in which the debt under the charter capital is partially repaid by the founder.
Accountant's Directory
It is worth noting that account 98.02 “Gratuitous receipts” is not used when receiving financial assistance in the form of cash, since it takes into account income from gratuitous receipts of non-monetary assets.
Error 404
Example 2. Contributions of the founders in money to cover damage For 2020, damage was calculated in the amount of 300,000 rubles. Its founders (3 people) decided to fill the gap with their own money. Free cash assistance on behalf of the founders was provided in the following proportions:
If the total amount of debt exceeds 20 thousand rubles, then by law it is necessary to attract a third-party, independent appraiser to calculate the value of the deposit. The basis for transferring the property rights to the management company may be:
The contribution to the authorized capital has been partially repaid: legal consequences
The founder who partially paid the debt on the authorized capital:
1. Will retain responsibilities:
- to pay the remaining share before the expiration of the established period for the formation of the management company;
- participation in further redistribution of the unpaid share;
- bearing joint and several liability for the debts of the company.
2. At the same time, he will receive the rights:
- for part of the profit after redistribution based on the unpaid share;
- sale of the paid part of the share (its receipt upon liquidation of the company);
- participation in the meeting of founders and decision-making on business issues.
But the founder will not be able to count on profit, since the company will not have the right to distribute it.
Let us now study what is the procedure for accounting for the debts of the founders for contributions to the authorized capital.
Terms and rules
All participants in a joint stock company must make payments on time. The chronological framework and order of investment are specified in the contract. If there is only one founder, then he personally determines the date and amount.
The maximum period for transferring funds is limited to one year from the date of establishment of the company. Any contribution is a financial transaction, so accounting entries must be made for them. There is no way to get rid of the need to deposit funds. The only way to refuse this is to leave the founders.
On the day when the company begins to operate, the charter capital must contain at least half of the amount that is required. When money is converted into capital, the shareholder loses ownership of those funds or property.
But it gains a number of new features:
- Receiving income from the operation of the enterprise corresponding to its share of investments.
- When leaving the founders, the investor has the right to receive the full nominal value of his part.
- When closing a JSC, a shareholder can claim a material portion comparable to his investment.
- Participation and influence on the activities of the organization.
With any transfer of funds or property contribution to the management company, the debt of the founders to the company is reduced.
After contributions to the authorized capital, the person receives part of the income from the activities of the institution
Payment of debt on authorized capital: accounting
When maintaining accounting records for transactions related to the formation and repayment of debts of the founders on the authorized capital, the following entries are used:
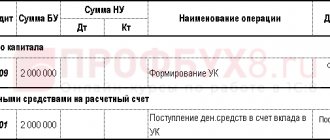
- Dt 75 Kt 80 - to reflect in accounting the fact of debt formation (when registering a company with the Federal Tax Service);
- Dt 50 (or 08, 10, 41, 51, 52 - depending on the method of payment of the authorized capital) Kt 75 - to reflect the fact of debt repayment (in whole or in part);
- Dt 80 Kt 75 - a reflection of the forced reduction of the capital when the debt is not repaid by the founder on time and is not subsequently redistributed.
If the authorized capital is formed at the expense of receivables, then the following sequence of transactions is applied:
- Dt 76 Kt 75 - the company has been transferred the right to claim the debt on account of the management company;
- Dt 51 Kt 76 - the debtor paid the company.
In the balance sheet, the authorized capital is classified as liabilities and is reflected in the amount determined by the constituent documents in line 1310 (even with partial payment). The current debt of the founders is, in turn, an asset, and it is reflected on the balance sheet in line 1230.
Read about the nuances of filling out the balance sheet in the article “Deciphering the lines of the balance sheet (1230, etc.).”
Accounting: non-cash deposits
Consider non-monetary contributions received from the founders depending on the type of property received:
- fixed assets;
- intangible assets;
- non-exclusive rights to use the results of intellectual activity;
- materials;
- goods.
Reflect non-cash contributions in the form of property using the following posting:
Debit 08 (10, 15,…) Credit 75-1
– fixed assets (materials, etc.) were contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital.
An example of how to reflect in accounting the non-monetary contribution of the founder to the authorized capital of the organization
In March, the founder of Alpha LLC A.V. Lvov contributed a Canon XL4 brand copier as a contribution to the authorized capital.
Lvov owns 20 percent of shares in the authorized capital of Alpha, which amounts to 160,000 rubles. The valuation of the copier, agreed upon by the participants and confirmed by an independent appraiser, amounted to 142,000 rubles. It is at this value that the property is reflected in accounting.
That same month, the copier was handed over to the accounting department, where it began to be used. Alpha set the useful life of the copier to 37 months.
The organization's accountant made the following entries in the accounting.
In March:
Debit 08 Credit 75-1 – 142,000 rubles. – the photocopier was received as a contribution to the authorized capital;
Debit 01 Credit 08 – 142,000 rub. – the copy machine was put into operation.
Monthly starting from April until the end of the useful life of the property (37 months):
Debit 26 Credit 02 – 3838 rub. (RUB 142,000: 37 months) – depreciation has been accrued on the copier for the current month.
The cost of non-exclusive rights to use the results of intellectual activity received as a contribution to the authorized capital should be reflected by posting:
Debit 97 Credit 75-1
– non-exclusive rights were introduced as a contribution to the authorized capital.
This procedure follows from paragraph 65 of the Accounting Regulations, paragraph 5 and paragraph 3 of paragraph 19 of PBU 10/99, paragraph 39 of PBU 14/2007, Instructions for the chart of accounts.
The chart of accounts does not provide for a separate account for accounting for intangible assets received for use. Therefore, the organization needs to independently open an off-balance sheet account and secure it in its accounting policies for accounting purposes. For example, this could be account 012 “Intangible assets received for use.”
An example of how to reflect in accounting the founder’s contribution to the authorized capital of the company in the form of non-exclusive rights to use the results of intellectual activity
In March, the founder of Torgovaya LLC A.V. Lvov made a non-exclusive right to use a computer program as a contribution to the authorized capital. The license agreement is valid for two years.
The assessment of the rights to use the computer program, agreed upon by the participants and confirmed by an independent appraiser, amounted to 60,000 rubles.
The same month the computer program was put into operation.
The organization's accountant made the following entries in the accounting.
In March:
Debit 012 “Intangible assets received for use” – 60,000 rubles. – the computer program is included in the balance sheet;
Debit 75-1 Credit 80 – 60,000 rub. – reflects the size of the participant’s share in the authorized capital of the company;
Debit 97 Credit 75-1 – 60,000 rub. – non-exclusive rights to use the computer program as a contribution to the authorized capital were obtained.
Monthly starting from April until the end of the license agreement (24 months):
Debit 26 Credit 97 – 2500 rub. (RUB 60,000: 24 months) – part of the cost of the non-exclusive right under the license agreement has been written off.
Upon expiration of the license agreement:
Loan 012 “Intangible assets received for use” – 60,000 rubles. – a computer program has been written off balance.
Tax accounting of debt on authorized capital: nuances
When maintaining tax accounting of deposits in the management company, you should keep in mind that:
1. Cash and property contributed to replenish the authorized capital by the founder-individual or legal entity:
- are not subject to VAT;
- do not form a tax base for personal income tax, income tax or the simplified tax system.
But if the founder-legal entity pays VAT, then if the tax is accepted for deduction (on property transferred to the authorized capital), the VAT must be restored (subclause 1, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the amount of recovered and paid VAT cannot be included in profit expenses. The organization for which the authorized capital is formed has the right, in turn, to receive a VAT deduction restored by the founder-legal entity (Clause 11 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When redistributing a share in a business in favor of a specific founder (or when increasing the nominal value of his share in the authorized capital), the founder does not have to calculate personal income tax. However, if the nominal price of the management company is reduced by decision of the founders (not for the purpose of fulfilling the requirements of the law), then the founders will have to pay personal income tax on the difference between the previous and new value of the shares (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 14, 2011 No. 03-04-06/3-88) .
Upon payment of contributions from all founders in full, the authorized capital may be increased:
- through additional contributions from the founders;
- as a backup option - by raising capital from third parties.
Let's consider the specifics of the main option for increasing the capital, when the owners of the company manage on their own.
Types of liability
The legislation provides for different options for the liability of the organizers of the enterprise:
- for the actions of the hired director;
- for your own actions.
Responsibility of a company director
In the first case, the management of the company is transferred to a third party, who provides management for a fee. It has certain legal and financial obligations to the owner of the company.
The hired director must monitor the state of current affairs, submit financial statements on time, and bear obligations before the law for his decisions. According to Art. 44 of Law N14-FZ , the director is liable to the owner for losses resulting from his erroneous actions or inaction.
The director will have to be responsible for:
- concluding obviously unprofitable transactions;
- concealing important commercial information from other founders;
- unjustified risks when concluding contracts and agreements;
- lack of due diligence checks on partners;
- deliberate destruction of financial and legal documents characterizing the company’s activities.
However, if the director proves that his actions were direct execution of the orders of the business organizers and they led to the liquidation and bankruptcy of the enterprise, then the financial burden will be borne by the founders.
1:07 – Fictitious bankruptcy and sanctions for it in the arbitration process? 3:12 – How can you remove assets from a company with debts? 7:04 – The founder denies that he knew about the conclusion of the agreement, what to do? 10:13 – The director’s actions led to the formation of debt, what should I do? 16:26 – Responsibility of the general director in an LLC? 16:49 – What does limited liability LLC mean? 17:21 – Can the founder of an LLC be fined for accounting errors? 18:05 – When agreeing with the organization’s debts, are the old founders responsible? 19:11 – How to hold the founder of an LLC jointly and severally liable? 20:20 – If the founder is a legal entity, why is the LLC at risk?
Responsibility of the founder and director in one person
If the founder himself acts as a manager, then it will not be possible to shift responsibility to an employee. If there are outstanding debts, he will have to take all possible measures to repay them. And if the company’s property is not enough, the founder will have to pay off debts from personal funds. The founder-manager is held accountable if he:
- exercised leadership incompetently;
- allowed an increase in debt on taxes and other areas of accounting reporting;
- used credit funds irrationally;
- chose unverified companies to work with.
Example from judicial practice:
The founder-director led a company that provided heat and water supply services. When holding a tender for servicing city property, he announced a new company with exactly the same name. The result of this action was that the former LLC lost the ability to provide services and was unable to repay the previously received loan.
The Arbitration Court recognized that the insolvency of the LLC was caused by the unlawful actions of the director, and ordered him to pay damages. The amount of damage amounted to 4.5 million rubles, and the founding director had to pay off the debt using personal funds.
Increasing the authorized capital through additional contributions: nuances
The decision on additional investments in the authorized capital is made at a separate meeting of the founders. After its adoption, business owners must replenish the capital for the agreed amount within 2 months, unless they specify a different period (Clause 1, Article 19 of Law No. 14-FZ).
If the agreed amount could not be added to the authorized capital within the prescribed period, then all funds and property contributed by that time in order to increase the capital are returned to investors within a reasonable time. If it is missed, then the funds and property are returned with an additional payment, the amount of which is determined in accordance with Art. 395 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The legislation does not contain unambiguous criteria for determining a reasonable period. As a rule, it is established by the court. It is possible that the court will order additional payment under Art. 395 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation immediately after the expiration of the deadline for increasing the authorized capital by law (or in accordance with the decision of the founders).
No one has the right to oblige the founder to pay an additional contribution to the authorized capital (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 25, 2010 No. 446/10). Accordingly, even if it is known that it was not possible to increase the authorized capital due to the refusal of a particular founder to make an additional contribution, this founder will not be held liable for possible losses of the company.
Increase in capital due to various types of debt
According to current legislation, it is possible to increase the authorized capital using an assignment agreement (assignment of the right of claim). After its signing, the third party will be responsible not to the founder, but to the organization. It is mandatory to notify the debtor, but his permission is not required.
With the help of receivables and creditors you can increase the authorized capital
A receivable can be included in the Criminal Code only with the consent of the constituent meeting. Its participants evaluate the possibility of debt collection. When accounting, you must comply with certain requirements:
- The assignment must be accompanied by all necessary documents.
- In addition to the debt itself, the company acquires possible risks (inflation, bankruptcy of the borrower, etc.).
- It is assumed that this operation will bring a certain profit.
Funds received during such a transaction are included in operating income. If the debt is not paid, the company incurs unrealized expenses.
In addition to receivables, you can increase the capital account with the help of short supply. An enterprise can offer its lender to repay the loan by transferring a share in the company. Such debt restructuring is used quite often in large businesses.
Results
Within 4 months after registration of the LLC (or an earlier period determined by the constituent documents of the business company), the founders of the company must repay the debt on contributions to the authorized capital. This can be done at the expense of cash, property, securities, receivables. Until the debt is repaid, the founders have no right to distribute profits. If it is not repaid on time, then the authorized capital is reduced by the amount of the unpaid share (if it is not purchased by someone).
You can learn more about the features of forming the authorized capital of an enterprise from the articles:
- “Accounting entries for contributions to the authorized capital”;
- “Why is the authorized capital of an LLC needed and can it be spent?”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Formation of the management company
Even at the stage of creating an organization, its founders must determine the amount of capital. Its size reflects the entire property of the enterprise, its potential profitability, etc. Based on the current legislation, which determines the minimum volume of this indicator for various forms of business, the smallest figure should be equal to the number of shares purchased or the nominal price of the shares purchased.
When payments are made in the form of money, they must be reflected in the balance sheet. Replenishment of funds is an autonomous operation in relation to the owner of the enterprise, therefore financial assets form receivables in relation to the legal owners of the company. If one of the participants does not pay the appropriate amount on time, then a constituent meeting is convened to solve this problem.
Solutions may be as follows:
- Exclusion of the debtor from the list of founders.
- Reduction of the authorized capital to the amount of funds actually contributed.
- Liquidation of the enterprise. This is an extreme measure, so before this they try to find alternative ways out of a difficult situation.
If a decision is made to close the JSC, then the shares of the participants are returned. The shareholdings of co-owners who have not fulfilled their obligations are distributed to the others.
The authorized capital is formed on the basis of various contributions and the appearance of arrears in contributions has a negative impact on the enterprise
Line 1230 of the balance sheet, what it includes
- Balance on the debit side of the account. 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”, takes into account the debt on products, goods, work, services sold to the buyer;
- Account debit balance 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees,” speaks of the debt of budgetary authorities to the organization. Accounts receivable on this account may arise due to amounts transferred during the year, advance payments for taxes from budget funds. The amount of transferred advance payments exceeds the amount of calculated tax for a certain period of time;
- Debit balance by account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” tells us about the debt of the social insurance authorities to your company. It may arise, for example, due to the amount of excess expenses calculated by the organization on certificates of incapacity for work before accrued insurance premiums;
- Balance on the debit side of the account. 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”. A debit balance is very rare. It may arise, for example, due to transfers of amounts to an employee (employee) for accrued leave (labour or pre- and post-natal leave). This happens when, at the beginning of the month, the organization’s employees are paid arrears of wages accrued on the last day of the month, and payment is also made for accrued maternity and postpartum leave. The accrual amount will be reflected in the accounting accounts only on the last day of the month, and payment will be made on the current date;
- Debit balance of the account. 71 “Settlements with accountable persons.” Payments to persons to account for funds, non-cash and cash are accounted for on the debit side of the account. 71. After payment, submits a report on expenses incurred to the company’s accounting department. This may include payment for business expenses, payment for purchased materials, expenses for staying in a hotel during a business trip, expenses for moving to and from the place of business trip, and others;
- Debit balance of the account. 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations.” All relationships between employees of the organization are reflected in this active-passive account, except for payroll calculations and payments of funds to the account. The debit of the account reflects the employee's debt to the organization. An employee may be provided with borrowed funds for construction, rent, and other business needs. Also, the employee may have a relationship to compensate for material damage to the company. These are the situations that are reflected in the score 73;
- Balance on the debit side of the account. 75 “Settlements with founders.” The formation of the authorized capital is taken into account according to the D account. 75 and K-tu account. 80 “Authorized capital”. Until the founder deposits personal funds in the amount of the authorized capital, the debit balance will remain on account 75;
- Debit balance of the account. 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors.” Account 76 is active - passive, it reflects debts not reflected in account 60, 62 and other accounts. The account may reflect arrears of payment to the insurance company; claims settlements; withholding funds from employee salaries for third-party companies and persons under executive documents (acts).
We recommend reading: State program to support mortgage borrowers
Settlements with founders
Accounts payable". In particular, this article may reflect the organization’s debt on payments for compulsory and voluntary insurance of property and employees of the organization and other types of insurance, debt on contributions to extra-budgetary and other special funds (except for funds, debt on contributions to which is reflected under the article “Debt”) to state extra-budgetary funds"), the amount of rental obligations of the rental organization for fixed assets transferred to it on a long-term lease, etc. The amount on line 625 can be made up of the balance on accounts 62 (advances received), 76 (except for amounts reflected in other lines of the balance sheet), 71, 73. According to the general rules for preparing financial statements, significant indicators must be disclosed separately, i.e. either highlighted as a separate line or reflected in the notes to the balance sheet.
Income and expenses are brought into the balance sheet. A balance sheet is a way of grouping the assets and liabilities of an organization in monetary terms, designed to characterize its financial position as of a certain date, an element of financial reporting. It has the form of a two-sided table: one side is assets, that is, claims and investments, the second is liabilities, that is, liabilities and capital. The main property of the report is that total assets are always equal to total liabilities. This is due to the fact that when reflecting transactions on accounts in the balance sheet, the principle of double entry is observed. [edit] Classification of assets and liabilities Assets and liabilities are usually divided into current and long-term. In international practice, assets on the balance sheet are listed in order of their liquidity. Claims are listed in the order in which they must be paid. Requirements for liabilities are divided into two types: Liabilities - those funds owed by the company for which the balance sheet is prepared Shareholders' equity In accordance with RAS, assets are divided into: Non-current Intangible assets Fixed assets Construction in progress Income investments in tangible assets Long-term financial investments Deferred tax assets Other non-current assets Current Inventories Value added tax on acquired assets Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected more than 12 months after the reporting date) Accounts receivable (payments for which are expected within 12 months after the reporting date) Short-term financial investments Cash Other current assets In accordance with RAS, liabilities are divided into: Capital and reserves Authorized capital Own shares purchased from shareholders Additional capital Reserve capital Retained earnings (uncovered loss) Long-term liabilities Loans and credits Deferred tax liabilities Other long-term liabilities Current liabilities Loans and credits Accounts payable Debt to the participants (founders) for the payment of income Deferred income Reserves for future expenses Other short-term liabilities
This is interesting: If you paid the state fee for your license but can’t come to the exam
Postings for accrual and payment of dividends
Doing business involves making a profit. One of the areas for spending retained earnings is the payment of dividends to the founders of joint stock companies and other companies. How to reflect the accrual and payment of dividends in accounting, and what transactions are generated in this case, we will consider further.
Dividends: the procedure for their payment and features of their taxation
Dividends are part of the profit of an enterprise distributed among its founders. The size of dividends depends on the share participation of each of the founders - this can be a percentage in the authorized capital or the presence of a certain block of shares.
Dividends are paid in accordance with the approved procedure, which is determined at the meeting of shareholders (the corresponding act is drawn up). They can be paid at the end of the year, semi-annually or quarterly.
The form of dividend payment can also be different, as shown in the figure below:
At the legislative level, it is prohibited to pay dividends in the following cases:
- There is a threat of bankruptcy;
- Their payment leads to a decrease in the authorized capital;
- Not fully formed authorized capital.
Since dividends are income that an individual receives, it automatically becomes subject to taxation. The personal income tax rate for resident shareholders is 13%, for non-residents – 15%. Tax withholding occurs on the day of dividend payment.
Reflection of dividend payments in accounting
Part of the profit received, which is accounted for in account 84, is distributed among its founders. In accounting, this operation can be displayed in two accounts:
- 75-2 – these founders are not full-time employees;
- 70 – these founders are full-time employees of the enterprise.
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
Accrual and payment of dividends in accounting entries
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| Payment of dividends in cash transactions | ||||
| 84 | 70 (75-2) | 175 000 | Accrual of dividends to a resident shareholder in proportion to the equity participation of each founder (RUB 500,000 / 200 shares x 70 shares) | Act of the shareholders' meeting |
| 84 | 70 (75-2) | 325 000 | Accrual of dividends (postings) to a resident shareholder in proportion to the equity participation of each founder (RUB 500,000 / 200 shares x 130 shares) | Act of the shareholders' meeting |
| 70 (75-2) | 68/NDFL | 22 750 | Income tax (NDFL) was withheld from dividends of a resident individual (RUB 175,000 x 13%) | Buh. calculation |
| 70 (75-2) | 68/NDFL | 48 750 | Income tax (NDFL) was withheld from dividends of a non-resident individual (RUB 325,000 x 15%) | Buh. calculation |
| 70 (75-2) | 68/Profit | 22 750 | Profit tax withheld from income of domestic organizations (RUB 175,000 x 13%) | Buh. calculation |
| 70 (75-2) | 68/Profit | 48 750 | Profit tax withheld from income of foreign enterprises (RUB 325,000 x 15%) | Buh. calculation |
| 70 (75-2) | 50 (51) | 152 250 | Dividends were paid in cash by cash (non-cash) payment to a resident individual (RUB 175,000 – RUB 22,750) | RKO, payment order |
| 70 (75-2) | 50 (51) | 276 250 | Dividends were paid to a resident individual in cash by cash (non-cash) payment (RUB 325,000 – RUB 48,750) | RKO, payment order |
| Issuance of dividends in commodity values | ||||
| 70 (75-2) | 90-1 | 275 000 | Proceeds from the sale of goods (finished products) are accrued towards the payment of dividends. | Act of the shareholders' meeting |
| 90-2 | 43 (41) | 150 000 | The cost of this product has been written off | Sales Invoice |
| 90-3 | 68/VAT | 49 500 | VAT charged (RUB 275,000 * 18%) | |
| Issuance of dividends by fixed assets | ||||
| 70 (75-2) | 91-1 | 100 000 | Fixed assets were transferred to pay dividends | Act of the shareholder meeting, act of acceptance/transfer of fixed assets |
| 91-2 | 10 | 75 000 | Materials that were transferred as dividend payments were written off | Write-off act |
| 01-B | 01 | 120 000 | The initial cost of the transferred OS has been written off | |
| 02 | 01-B | 20 000 | Write-off of depreciation for this object for the entire period of its operation | |
| 91-2 | 01-B | 100 000 | The residual value of the transferred object was written off (RUB 12,000 – RUB 20,000) | |
| 91-2 | 68/VAT | 18 000 | VAT charged (RUB 100,000 * 18%) | |
| Calculation of dividends in the event of a loss transaction | ||||
| 84 | 70 (75-2) | 180 000 | Dividends accrued to a resident of the Russian Federation | Act of the shareholders' meeting |
| 70 (75-2) | 68/NDFL | 23 400 | Personal income tax is withheld from this income (RUB 180,000 x 13%) | Buh. calculation |
| 70 (75-2) | 50 (51) | 156 600 | Payment of accrued dividends (RUB 18,000 – RUB 23,400) | RKO, payment order |
| 70 (75-2) | 84 | 180 000 | Reversal of accrued dividends | Fin. results |
| 91-2 | 73 | 180 000 | Other payments accrued to residents of the Russian Federation | Fin. results |
| 68/ personal income tax | 70 (75-2) | 23 400 | Reversal of withheld personal income tax from dividends | Fin. results |
| 73 | 68/NDFL | 23 400 | Personal income tax withheld from other payments made by a resident of the Russian Federation | Fin. results |
| 50 (51) | 70 (75-2) | 156 600 | Reversal of paid dividends | Fin. results |
| 73 | 50 (51) | 156 600 | Other payments to residents of the Russian Federation are listed | RKO, payment order |
| 99 | 68/Profit | 36 000 | A permanent tax liability has been accrued | Declaration |
Source: https://BuhSpraa46.ru/buhgalterskie-provodki/provodki-po-nachisleniyu-i-vyiplate-dividendov.html
Prosecution procedure
The founder's responsibility for the activities of the director appears in the bankruptcy process. If the LLC simply ceases to exist, having honestly paid all its debts, then no claims will arise either against the management or the organizers.
If the debts cannot be repaid, the law of October 26, 2002 No. 127-FZ “On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)” comes into force. This law describes in detail the procedure and outlines the conditions for holding accountable all involved persons - managers, owners and executive directors.
If the company's management does not timely file an application to declare the LLC bankrupt, the tax authorities will do it for them.
When considering a case of financial insolvency of a company, the director of the enterprise, founders, as well as persons recognized as beneficiaries are involved in the judicial process.
If the court recognizes the connection between the action (or inaction) of these persons and the inability of the enterprise to pay its debts, then penalties in the amount of creditors' claims will be imposed on both the company's property and the personal property of the persons involved.
How can self-bankruptcy affect you?
A business owner may fall under subsidiary liability for the activities of the director or his own mistakes, even if he begins bankruptcy proceedings on his own. Especially if deadlines were missed.
If debts cannot be repaid, then it is better to start the procedure for declaring bankruptcy yourself, without waiting for the tax authorities to do so. Advantages of self-bankruptcy:
- independent submission of documents without seizure;
- appointment of an arbitration manager of his choice;
- the ability to legally block creditors' claims.
However, even self-bankruptcy declared in a timely manner does not guarantee that you will not have to answer for debts with personal property. If the company's assets are insufficient, bringing the director and owners of the company to subsidiary liability is almost inevitable.
But it will be much worse if the bankruptcy procedure is initiated by the Tax Committee. Tax officials use every opportunity to raise funds to pay off debt, including seizing personal property and personal accounts.
Circumstances in which the owner’s guilt is recognized by default
The law provides for circumstances in the event of which responsibility for the activities of the director is assigned by default to the owner of the business. These are the following events:
- concluding a transaction by direct order or with the approval or insistence of the owner, provided that this transaction resulted in losses and led to bankruptcy;
- damage, loss or damage to accounting documentation for which the owner of the enterprise was responsible;
- actions that may be regarded as deliberate bankruptcy.
Additionally, the reason may be an unreasonable credit policy pursued by the owner and other errors leading to a violation of the property rights of creditors.
Options for protecting persons controlling the debtor
The adopted amendments treat CDLs quite harshly, denying them the presumption of innocence. However, there are situations in which the CDL has the opportunity to minimize the size of its financial obligations on the enterprise’s debts or avoid it altogether. To do this it is necessary to prove that:
- the person recognized as the controller of the debtor was not actually the controller, but the court must be provided with information about the real beneficiary;
- KDL acted as reasonably and conscientiously as possible, its actions were aimed at avoiding even greater losses;
- the amount of damage caused by the CDL is significantly lower than the financial obligations imposed on it.
These opportunities for CDL are recorded in Article 61.11 of Law No. 127-FZ in paragraphs 9, 10 and 11.
Accounts payable on balance sheet
- sch. 60 “Settlements with suppliers/contractors” for amounts for goods and materials/services purchased but not yet paid for by the company;
- sch. 62 “Settlements with buyers/customers” for received advance payments against agreed future deliveries;
- sch. 68 “Calculations for taxes/fees” for taxes intended for payment to the budget;
- sch. 69 “Calculations for social insurance and social security” for accrued contributions for payment to the funds;
- sch. 70 “Calculations for wages” based on the amounts of salaries of company employees calculated for payment;
- sch. 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” for amounts paid by financially responsible persons for the MC purchased by them as part of the overexpenditure of the advance advance issued;
- sch. 75 “Settlements with founders” for calculated but not yet issued dividends;
- sch. 76 “Settlements with other debtors/creditors” for other debts. For example, it may include the amount of penalties imposed for violation of the terms of agreements.