The need to work part-time, while a woman continues to be on maternity leave for up to 3 years, may arise for her in connection with the desire to receive additional money and not lose her qualifications.
Sometimes the employer himself requires the employee to begin his duties, for example, due to a lack of specialists. This article will discuss how to competently formalize such labor relations between an employee and an employer and what needs to be taken into account.
Is it possible to work officially while on maternity leave?
We advocate exclusively for official employment and white wages.
It doesn't matter whether you're on maternity leave or not. Therefore, we will talk about how to do everything according to the law. By the way, there is no concept of “maternity leave” in the law. It is usually understood as the totality of:
- maternity leave;
- care leave following the birth of a child for up to 1.5 years;
- further leave until the child’s 3rd birthday.
And each of these stages has its own nuances and restrictions on work. Let's see which ones.
Feeding breaks at home
Article 258 of the Labor Code gives working mothers the right, if their children are less than one and a half years old, to take breaks for feeding - once every three hours and lasting at least half an hour (per child). If there is more than one child, feeding may take at least an hour. All such breaks are counted as working hours and are paid accordingly.
However, not all mothers work close to home, so leaving work for such breaks may not always be convenient. In this case, they can ask through an application to reschedule the breaks: for example, put them at the beginning of the work shift and simply come a little later, or, conversely, add them to the end of the work day, thus shortening their shift.
Some mothers prefer to postpone breaks until lunch (before or after), thus having time to go home to feed and have lunch themselves.
Is it possible to work while on maternity leave?
A woman receives maternity leave on the basis of sick leave. It is also the basis for paying her the appropriate allowance.
Sick leave is issued at 30 weeks for a singleton pregnancy and at 28 weeks for a multiple pregnancy.
For more details, see the article “When to give sick leave for pregnancy and childbirth” .
But the expectant mother is not obliged to leave work on the first day of leave under the BiR. She can continue to work as much as she sees fit. And he will receive a salary for it. But she is not entitled to maternity benefits during her work (see FSS information letter dated October 8, 2004 No. 02-10/11-6671).
See: “Procedure for payment of maternity benefits in 2021” .
As soon as maternity leave is issued, the employee must go on vacation. She will no longer be able to work until the end of this vacation, even on a part-time basis.
What to do if your boss refuses you?
While the employee goes on maternity leave, he retains his position, and at any time when the employee decides to return to his job ahead of time (by notifying the manager in advance), he has the right to do so. The employer is obliged to provide him with his previous place of work and has no right to refuse.
If a young mother nevertheless receives a refusal to her application, she has the right to ask to explain the refusal in writing or even write a complaint addressed to the head of the organization. If the case is not successful, you can complain higher - to the labor dispute commission, the prosecutor's office, or the court.
A manager who breaks the law may receive a warning or even a fine.
Is it possible to work on parental leave for up to 1.5 years?
The Labor Code states that while on maternity leave, you can work part-time, and you can also work remotely (see Part 2 of Article 93, Part 3 of Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the right to receive child benefits remains.
ATTENTION! We are talking about the baby’s mother, but father, grandmother, grandfather, and other relatives may be on vacation on the same basis.
See what documents are needed to apply for child benefits .
Is it possible to apply for maternity leave for another relative?
Today, not only the mother, but also the baby’s father and even close relatives, for example, grandparents, can go on maternity leave. This right is enshrined in Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
A guardian or relative can receive payments for the child until the child turns three years old. The amount of the benefit is calculated according to the same scheme as for mothers - it is forty percent of the average salary (however, the benefit cannot be less than the established minimum).
Arranging for such a vacation is quite simple.
The father or some other relative who will take on this function must write two applications at work: one for maternity leave, the second for payment of social benefits.- In addition, you should provide the child’s birth certificate and a certificate from the mother’s employer, which will indicate that she does not receive benefits. If the mother does not work, such a certificate is also issued by the social protection center.
IMPORTANT! If a relative does not work or is retired, he has the right to take care of the child with all payments only if the child’s parents cannot do this (for example, they died, are in prison, etc.).
How many hours can you work on maternity leave?
The work schedule during maternity leave is established by mutual agreement of the employee and the employer. For part-time, it can be a half-day or a half-week, or a combination of both. But if the working day is irregular - only a partial week with a full working day (Article 101 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). When working from home, the work schedule can be any, including reduced working hours.
Since a working mother will receive both a salary and a benefit, and the benefit is paid from the Social Insurance Fund, abuse must be avoided. Shortening the working day should objectively free up time for the baby. If it is 15–30 minutes a day or even an hour, social insurance will not reimburse the benefit.
How to hire a young mother and not get into trouble?
If a woman leaves maternity leave early, an employer may face claims from government services. To avoid this, you need to remember these important stages of registration for a young mother:
- Notification of the Social Insurance Fund about a woman’s early return to work.
- Obtaining the written consent of the young mother for the offset between wages and benefits.
- Deduction of benefits paid in excess of the established norm from the employee’s salary.
IMPORTANT! The Letter from Rostrud stipulates that the employer is not obliged to hire a young mother. He has the right to refuse her if there are grounds for it.
The nuances of working on parental leave for children under 3 years old
In general, the rules for working on parental leave for a child up to 3 years, including documentation, coincide with the above rules for leave up to 1.5 years. The key difference is that when the child reaches the age of 1.5 years, the mother’s right to receive child benefits ceases. This means that the employer and employee no longer face accusations of insufficient (formal) reduction of working hours and there is no risk of refusal to pay social insurance benefits.
Instead of benefits, the mother who went back to work needs to be paid compensation. Its size is 50 rubles. per month, but some parents are now entitled to a larger amount.
For more details, see: “Benefits for children under 3 years of age have been increased .
Working conditions
As noted above, the employee can choose for herself how much her working day will be reduced. If desired, it can be set up for either a part-time or a part-time work week. It is also possible to work part-time with part-time work, i.e. not 5 days a week for 8 hours a day, but, for example, only 4 days for 7 hours a day.
Often both the employee and the employer himself have a question: what should be understood by part-time work? Based on the explanations of Rostrud on this issue (letter of Rostrud dated 06/08/2007 No. 1619-6), part-time working time should be considered that time, the duration of which is less than the normal working time.
Normal working hours, according to Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is 40 hours per week and should not exceed the established norm. Consequently, if you reduce the standard working time for an employee even by 1 hour per week, then such work will already be considered part-time. However, this right cannot be abused.
The legislation of the Russian Federation does not establish clear limits for the amount of time by which the working day can be reduced in order to consider it not full. That is, it can be reduced by an arbitrary number of hours.
Therefore, some employers allow themselves the practice of reducing the working hours of an employee on maternity leave by just a few minutes a day. Such actions are not approved by the Social Insurance Fund, and in the event of litigation, the court, as a rule, sides with the Social Insurance Fund.
We advise the employer to adhere to the rules established by the Social Insurance Fund (letter of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia No. 02-03-13/08-2498) and agree with the employee to reduce the length of her working day by at least 1 hour. Otherwise, the Social Insurance Fund may stop paying child care benefits or reimbursing them to the employer.
In order not to attract the attention of the FSS and to avoid possible proceedings in court, it is undesirable for the employer to reduce the working day by less than 1 hour, and the working week by less than 1 day (letter of the FSS of Russia No. 02-03-13/08-2498).
Salary rate
There is no such concept as a rate in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In the staffing table there is the term “staffing unit”. In this case, it is meant that the employee will work part-time and his payment will be in direct proportion to the time he worked.
An employee can work at a fraction of the full rate (0.75; 0.5; 0.25, etc.) depending on the number of working hours established for him, and this reduction will mean the establishment of part-time work for him. The salary will decrease according to the reduction in working hours. That is, at a rate of 0.5, the employee’s earnings will be 50% of his standard earnings.
To introduce these rules, you need to sign an additional agreement with the employee, stipulating part-time work (indicate the specific agreed mode) and including in the agreement the wording “Wages are calculated in proportion to the time worked.”
Benefit payment
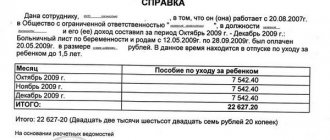
While working on maternity leave, in the event of a reduction in working hours, a woman continues to receive a monthly care allowance for up to 1.5 years. The benefit is paid at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund. The payment amount is 40% of the average monthly earnings for the 2 years preceding the birth of the child, and should not be lower than the minimum established by law.
The procedure for paying benefits when going on a shortened day will not change, but the Social Insurance Fund will need to submit a copy of the woman’s application and the order to transfer to part-time work during parental leave.
In addition, a working mother has the right to a tax deduction for each of her children until they reach 18 years of age. To provide a deduction, you need to take an application from the woman. This deduction is taken into account immediately when calculating personal income tax.
A woman working part-time who is on maternity leave for a child under 3 years old is entitled to a standard tax deduction in the amount of 1,400 rubles. for the first child and 3,000 rubles. for each next one. It is by this amount that her monthly income will be reduced to deduct tax at a rate of 13%.
Now, in many regions of the Russian Federation, a pilot FSS project called “Direct Payments” has begun to operate. This means that all the benefits listed above will be paid not by the employer himself, who may delay payments due to lack of funds at the enterprise, but directly by the Social Insurance Fund to the bank account of the young mother.
If a woman goes to work part-time, the Social Insurance Fund will continue to pay benefits. The employer must submit documents confirming the woman’s right to maintain payments, in the form of a copy of the application and order, to the Social Insurance Fund.
Feeding breaks
If a mother who is breastfeeding a child goes to work, she is given breaks to feed the child. They must be paid, last at least 30 minutes each and be provided at least every 3 hours (Article 258 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If a woman has more than one child under the age of 1.5 years, then the duration of each of these breaks increases and is at least 1 hour.
Since this right is directly provided for by the Labor Code, a woman cannot be denied such breaks. A woman can add them to the lunch break and move them to the beginning or end of the working day, reducing it. To do this, she needs to write a corresponding statement.
After this, you need to conclude an additional agreement with her and issue an order to provide such breaks (Part 2 of Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Annual holiday
A young mother cannot go on annual paid leave if at the same time she works and is on maternity leave, since she simultaneously receives child care benefits - clause 20 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated January 28, 2014 No. 1 ( read more about whether and when you can take annual leave after maternity leave).
To use it, the employee must interrupt maternity leave (read about how to draw up and submit an application to interrupt maternity leave for a child under 3 years old, and from this article you will learn how to apply for early leave from maternity leave). She will have to do the same if she decides to exercise her right to study leave.
Sick leave
If a maternity leaver falls ill while working part-time, she will be paid sick leave. The law provided for the possibility of simultaneously receiving two benefits for a woman working part-time and on maternity leave: a child care benefit and a temporary disability benefit. Sickness benefits compensate for lost earnings. Since it exists, the benefit must be paid.
It is interesting that in the event of a child’s illness, the employee must be issued a certificate of temporary disability to care for a sick family member, despite the fact that she already receives benefits for caring for the same child.
How much do they pay when working on maternity leave?
It all depends on the employee’s remuneration system. If it is time-based, payment should be proportional to the time worked. Piece workers are paid for the volume completed (Part 3 of Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Work at home is paid as usual if it is full time. If incomplete, only for the time worked.
Find out what payments for children are provided by the state from the materials in the special section of our website.
Can a woman return to service after maternity leave before 3 years?
If for some reason a young mother needs to start working, she can do this and at the same time retain the benefits paid to her by the state. The most important condition in such a situation is to choose the right working mode. Such work must be done part-time if the woman wants to maintain benefits.
Both the head of the enterprise himself, if he has an urgent need for personnel (Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), and his employee, taking into account his capabilities and desires (Article 93 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), can choose such a regime for his worker. In any case, the desire and consent of the employee herself to work with a shortened working day or a shortened working week is required.
The employer must not forget that he has no right to refuse a woman who wants to work a reduced number of hours and who also has a child under 3 years old (Article 256 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- firstly, he is obliged, at her request, to provide her with work;
- secondly, on the basis of an application and within the framework of the organization’s operating hours, establish part-time working hours.
Even when another employee was hired to replace the maternity leave under a fixed-term employment contract, all relations with him must be terminated immediately after the departure of the main employee (Part 3 of Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Otherwise, the main employee, i.e. a young mother, can file a complaint with the labor inspectorate: the employer will be obliged to hire her and may issue a fine.
In order not to lose benefits, a young mother should go to work part-time. If normal working hours are established for her, benefit payments will stop.
Is it possible to work part-time while on maternity leave or under a GPC contract?
It is possible to work part-time while on maternity leave. The same procedure applies here as at the main place, and the same restriction: you cannot work while on maternity leave, and after it ends - completely.
As for work under the GPC agreement, there are no obstacles at all. The conclusion of such contracts (contracts, provision of services) is regulated not by the Labor Code, but by the Civil Code. And it consolidates the free expression of the parties. In addition, the GPA does not give the employee any rights in terms of benefits and social guarantees related to children. This means that the employer will not have any trouble with regulatory authorities.
conclusions
The law allows women on maternity leave to work with a child on maternity leave, but to do this, they need to get the employer to establish a partial schedule. It may involve working a shorter week or shorter working day.
To express your desire to work during maternity leave, you should write an application and submit it to your place of work. Next, you need to agree on working conditions and schedule with management. If the employer refuses, you need to make sure it is justified.
Perhaps the company really does not have the ability to provide the employee with work on a part-time basis or from home.
Establishment rules
Labor legislation provides for three options for reducing the work schedule:
- The duration of the shift is reduced, but the week remains full;
- the week is reduced, but the duration of the shift remains the same;
- The length of the week and shift are reduced at the same time.
But at the legislative level it is not established how many hours or days the reduction should be made. In each individual case, an individual approach is applied - the employer coordinates this issue with the employee. In practice, the day or shift is often shortened by one to two hours. Or an additional day off is provided each week.
With additional factors, reductions can be made to a greater extent, but this is not due to pregnancy, but to the special condition of the employee:
- if there is a disability group (first or second), working hours per week are reduced to at least 35 hours;
- the same rule applies to pregnant workers who have not yet reached the age of eighteen.
Women applying for a reduction in the number of working hours or days should take into account that:
- Along with the reduction in hours allocated for work, they will lose some part of their wages (income will decrease).
- When applying for maternity leave, the presence of a shortened work schedule will not affect the amount of maternity funds accrued. The calculation takes into account the last two years of employment.
- The reduction cannot affect the duration of annual leave or maternity leave.
- Reducing the number of working hours also does not affect the amount of accrued vacation payments.
Compensation for work in hazardous working conditions is mandatory! Are you interested in the taxation of bonuses? All the latest information is in our article. Does an employer have the right to fire a pensioner? Find out about this in our material.
If You Work Part Time How Maternity Pay
If an employee permanently resides in another state, but is in temporary work in the Russian Federation, he will not be able to qualify for benefits.
As a rule, all calculations are carried out in the accounting department. In this case, initial information about the presence of a certain length of service and days worked is provided by a human resources specialist in accordance with the working time sheet, as well as other internal documents of the company.
Business and labor allowance for women working part-time (read more...)
How to register an exit?
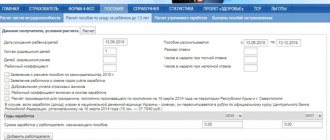
To return to work early while on leave granted for a child, you must write an application addressed to the director of the labor organization. It must indicate under what conditions the young mother wants to work (with a shortened working day, part-time week or remotely at home). It is also important to indicate exactly what days or hours the woman wants to work.
After submitting the application, an agreement is concluded between the employee and her manager, which further stipulates the conditions for the performance of her work. This is the period of her temporary employment, working hours and responsibilities, as well as payroll.
Based on an application accompanied by a formalized agreement, the manager must issue an order for the woman to go to work during her maternity leave.
What documents are needed?
The first thing to write to register for going back to work during the vacation period is an application. It is compiled in any form.
The application must indicate:
- Position and full name of the manager;
- Position and full name of the employee;
- Information about the order for leave to care for the baby;
- Working conditions (part-time, week, work from home);
- Hours and days of work;
- Date and signature of the employee.
Important! The Labor Code does not stipulate that an application must be submitted in advance. Therefore, submitting an application is free .
applications for part-time work - word:
an agreement is concluded between him and the young mother . This document can also be drawn up in any written form. It is written to agree on the terms of a part-time employee's work, as well as her working hours, days, wages and working conditions.
The agreement must indicate:
- Number of the additional agreement to the employment contract (date and number of the contract);
- Working days and weekends;
- Opening hours;
- Rest breaks and lunch;
- Feeding time for the baby (if he is not yet 1.5 years old);
- Changes in job responsibilities, if any;
- Date of entry to work and end date of the temporary employment contract;
- Information about the organization (its full name and address);
- Full name of the head;
- Full name and passport details of the woman on vacation;
- Date and signatures of both parties.
The last document is an order to enter service on a part-time basis with the condition of maintaining payment of benefits for up to 1.5 years. It is also compiled in free form in accordance with the regulatory documents of the organization.
In the order, in addition to the basic information and purpose of the document, you must accurately indicate the employee’s working hours by hours and days, the calculation of wages according to them and the effective date of the working period during the vacation. The order at the end is signed by everyone indicated in the document and certified with a seal.
order to establish part-time work for an employee and maintain benefits for up to 1.5 years - word:
Based on the order, the corresponding designations are placed on the working time sheet - how to indicate maternity leave and part-time work.
Who will not receive financial assistance?
In the vast majority of cases, working women receive maternity payments without problems. Let's consider the nuances:
- A citizen of another state working under a fixed-term contract providing consulting services is not entitled to maternity benefits.
- An employee performing work under a civil law contract (CLA) is deprived of the right to maternity benefits.
- A woman working under a fixed-term contract, while pregnant, loses maternity leave if the contract expires if the pregnancy is less than 2 weeks. If a medical certificate confirms a period of more than 2 weeks, the place is retained until the end of the B&R leave, with the provision of appropriate payments.
Attention! If, within the framework of a civil contract, actual labor relations took place, according to Art. 11, art. 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer can recognize them as such voluntarily, or as part of a court decision, and pay the benefits required by law to the woman working for him
.
The legislative framework
Russian legislation contains a number of norms confirming the right of officially employed women and members of their families to receive maternity benefits.
Thus, labor and labor leave is prescribed in labor legislation, in particular in Art. 255 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 257 in relation to adoptive parents)
The nuances and features of calculating certain types of maternity benefits are considered by Federal Laws , in particular Federal Law-81 dated May 19, 1995, which deals with state benefits for persons with children, Federal Law-255 dated December 29, 2006 ., considering issues of social insurance payments, including those related to maternity.
A package of legislative initiatives, in particular, new benefits for the first, 2nd (subsequent) child, applied already this year, are considered in the new law FZ-418 dated 12/28/17.
Employer's refusal to shorten the working day by a few minutes
If an employee insists on shortening her working day by just a few minutes, then the employer has no right to refuse her. It is important to maintain the payment of benefits, otherwise the State Tax Inspectorate may be fined for violation. Fear of disputes with the Social Insurance Fund is not a reason for refusing to shorten an employee’s working day by a few minutes. However, in our opinion, the employer and employee in this case must find a compromise so that there are no claims from social insurance or the labor inspectorate, and it is convenient for the young mother to carry out her work duties (
Common mistakes
An application for maternity leave is not considered a mandatory document. Despite this, many employers require it from their employees. This is done to avoid claims in the event of controversial situations.
In this case, the document should not be submitted without a sick leave certificate. The basis for filing an application must be a sheet confirming incapacity for work or a certificate of adoption. Without these documents, rest days are not provided and compensation will not be paid. The application is also usually necessary to indicate the details and desired methods of receiving benefits.
Another common mistake is calculating the vacation period yourself. This is a gross violation of legal norms, since the terms and periods of leave correspond to the data from the sick leave.
In case of multiple pregnancy, the standard statement is not valid. Employees are often unaware of their right to multiple pregnancies, and employers withhold this information. In this case, it is important to pay attention to the sick leave data, which will indicate an extended period of 194 days.
Maternity leave
Earning money during maternity leave has already become a widespread phenomenon in our country.
As you know, every employee who becomes pregnant has the right to at least one hundred and forty calendar days to safely carry and give birth to a child. And after this, additional time is also given - from one and a half to three years - to accustom the child to relative independence, transfer him to a preschool institution and go to work. This entire long period is called maternity leave. And, of course, work during maternity leave is not provided - the employee comes to the enterprise only to hand over documents, receive benefits, perhaps in case of some urgent production need, but the employer has no right to demand this.
What does the law say?
According to Article 254 of the Labor Code, a shortened day can be established for medical reasons (and the request of the employee).
Employers are also obliged to reduce production standards or transfer the woman to a workplace with conditions more favorable to her health.
It is necessary to exclude all harmful or dangerous factors that may threaten
child's life and mother's health. In this case, the salary at the previous workplace is retained by the employee in full.
Also, the workplace and wages are retained for the entire period of examination or treatment in the hospital, if such was assigned to the pregnant employee. And during the period of searching for a suitable vacancy, a woman is relieved of her main job functions with mandatory retention of her salary.
Article 93 of the Labor Code shows the procedure for granting a shortened working day. Depending on the employee’s request reflected in the application, the employer sets the abbreviated form:
- shift;
- week;
- day.
At the same time, adoptive parents or persons guarding children under the age of fourteen can count on the same benefit. And if we are talking about raising a disabled person, benefits are provided until he turns eighteen years old. In addition, persons caring for sick relatives who have an appropriate medical certificate can reduce their work time.
Part-time work does not entail any restrictions in the accrual of vacation funds or the calculation of insurance (working) experience. Remuneration is carried out according to a proportional system - that is, depending on the hours worked or the volume of work performed.