Responsibility of the parties
After an employment contract has been concluded between an organization and a citizen, the parties must take into account the rights and obligations of each other. If facts of violation of rights or improper performance of duties are revealed, both the employee and the employer may be held liable for violating the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Responsibility for this type of violation is provided for both disciplinary (for an employee) and administrative and criminal (for a legal entity).
Responsibilities and basic rights of an employee
Based on the provisions set out in Art. 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee has the right to count on:
Articles on the topic (click to view)
- What to do if the employer does not give the employment contract
- What is the difference between a collective agreement and an employment contract?
- Apprenticeship contract with an enterprise employee: sample 2021
- Terms of remuneration in an employment contract: sample 2021
- Go on maternity leave from the labor exchange
- Notice of extension of a fixed-term employment contract: sample 2021
- Notice of termination of a fixed-term employment contract: sample 2021
- Conclude, terminate and amend an employment agreement in accordance with the laws of the country.
- Get the job described in the employment contract.
- To obtain a workplace that meets labor safety and health standards.
- To receive remuneration in a timely manner and in the amount specified in the agreement.
- To provide rest paid by the employer, including vacations, weekends and holidays.
- To receive complete and truthful information about working conditions.
- An employee can join , unite and create trade unions to effectively protect their rights, freedoms and interests.
- Manage the company within the framework specified by the collective agreement.
- Protect your rights by all available means provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
- Receive compensation for moral and physical harm caused in the process of performing direct labor functions.
- If the Federal Law provides for compulsory insurance , you can obtain it.
- A company employee is obliged to conscientiously and fully perform his functions prescribed in the concluded employment contract.
- Fully comply with the routine and discipline at the enterprise.
- Ensure the safety of the employer's property.
- Immediately notify the employer of dangerous situations that pose a threat to the life and health of the company’s employees and the safety of the employer’s property.
Responsibilities and basic rights of the employer
The employer has the right:
- Conclude, amend and terminate employment contracts.
- The employer can participate in collective bargaining , conduct them and conclude collective agreements.
- Take measures to encourage conscientious and efficient employees.
- Require the safety of the enterprise’s property and apply sanctions in case of non-compliance with this right.
- Require employees to follow the internal rules of the organization.
- Creating and joining communities in order to protect their legal rights.
Responsibilities of the employer:
- Ensure compliance with the standards established in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other legislative acts.
- Provide the work described in the employment agreement.
- It is prohibited to require employees to perform work that is not included in the contract.
- The employer must provide the employee with safety and working conditions that meet the standards.
- Fully provide employees with materials , equipment and tools necessary to perform their job duties.
- Comply with the principle of equal pay for work of equal value.
- Pay contractual remuneration to employees.
- Provide employees with complete and reliable information regarding their job responsibilities.
- Timely inform employees of changes in regulations that directly affect their work.
- Provide employees with household needs that arise during the performance of job duties.
- In accordance with the procedure established by the Federal Law, provide compulsory social insurance for employees.
- Compensate for harm received as a result of their performance of work duties.
Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation: questions and answers
Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to the basic rights and responsibilities of the employer in the process of labor relations with employees. Let's consider the questions that arise when applying this article.
How can an employer influence employee behavior?
By requiring an employee to fulfill all the rules established specifically for him (job functions) and for the entire team (internal labor regulations, labor protection requirements), the employer has the right to:
- encourage him for a responsible attitude towards his duties or for some special achievements in work;
- punish for violations.
Encouragement can be expressed in different forms (Article 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For example, in the form:
- gratitude;
- diplomas;
- awards;
- gift;
- incentive payments.
The use of incentives can have either a systematic form, based on an internal regulatory act, or a one-time form, determined by individual orders of the manager.
Punishments are a consequence of violations:
- disciplinary nature, in which disciplinary liability occurs (Article 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- associated with causing damage to the employer and entailing financial liability (Chapter 39 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The possibility of applying punishments is regulated quite strictly by law, requires compliance with certain rules when issuing them and is limited by a time frame.
What are works councils according to Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation?
Since May 2013, after the Federal Law “On Amendments to Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation” dated May 7, 2013 No. 95-FZ, additions to the text of the article, another right of the employer appeared - to form production councils. This body, which can be created by any employer except an individual employer, is advisory (consultative), formed on a voluntary basis from representatives of the most qualified and active workers.
The goals of its creation are to develop proposals on the following issues:
- optimization of processes of the employer's core activities;
- introduction of new technologies and equipment;
- increasing the level of qualifications of personnel and their productivity.
All necessary aspects related to the formation and process of work of this body are established by the employer by its internal regulations. It should include the following provisions:
- about the powers of the council and the range of tasks it solves;
- the procedure for convening and possible current operating procedures;
- the number of council members and the composition of employee representatives in it.
The right to create a works council, established by Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation , is applied with comments regarding its competence: it includes exclusively issues of improving production activities, but not functions related to the process of managing the activities of the employer or representing the interests of employees. The employer is obliged to communicate the result of consideration and implementation of proposals developed by the council to its participants.
What are the rights of an employer in the field of special assessment of working conditions?
The rights of the employer in the field of special assessment of working conditions are established by Art. 4 Federal Law “On special assessment of working conditions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 426-FZ and include the possibility of:
- requirements to substantiate the results of the special assessment;
- carrying out an unscheduled procedure for assessing working conditions;
- requirements from the organization carrying out the special assessment for documents confirming its competence to conduct such an assessment;
- appealing the results of a special assessment if you disagree with them.
What are the responsibilities of the employer in terms of organizing the labor process?
The employer must provide each hired employee with the opportunity to perform exactly those functions that are specified in the employment agreement and job description. The requirement to perform other work is prohibited by law (Article 60 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and becomes possible only as a temporary measure (Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) either with the consent of the employee or without it (in emergency situations).
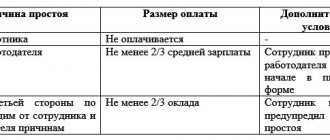
The ability to perform the work must be technically ensured by the employer (by providing the necessary tools, equipment and other means), if this follows from the essence of the assigned work. If it is impossible to carry out a labor function due to the lack of necessary technical means, the blame for the employee’s downtime lies with the employer, who is obliged to pay for the time of such downtime (Article 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Conditions for performing work functions must be as safe as possible for the employee. In this regard, the employer has responsibilities (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- to identify harmful and dangerous factors in the workplace;
- informing the employee about these factors and safety measures;
- provision of special protective equipment and training in their use;
- demonstration of safe operation techniques using the provided technical equipment;
- training in emergency behavior and first aid techniques.
The employer must take care of ensuring the work and rest schedule, as well as the sanitary and domestic needs of people. In particular, it is important to comply with:
- the required length of rest periods (Articles 108–111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- duration and frequency of regular vacations (Articles 115, 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- cleanliness in work areas and regularity of their cleaning (Article 209 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- measures of protection from cold and excessively high temperatures (Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- conditions for regular comfortable eating and sanitary and hygienic procedures (Article 223 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Another obligation of the employer related to the organization of labor is the need for compulsory social insurance of employees and the payment of related payments aimed at:
- for the formation of a future pension;
- provision of a minimum amount of free medical services;
- payment of sick leave and benefits related to maternity;
- prevention of accidents at work.
What must an employer observe when paying for work?
The employer's responsibilities for remuneration are in fact much broader than those specified in Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (non-discrimination in payment for work of equal value, meeting deadlines, complete payment of wages), and require compliance (Articles 135, 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- a remuneration system developed and approved by the employer;
- the procedure for notifying the employee about the formation of the total monthly payment amount;
- forms of issuing money convenient for the employee (cash at the place of work or by bank transfer to the bank specified by the employee);
- frequency of payments at least 2 times a month with an interval of 2 weeks between them;
- dates established for the payment of wages by internal regulations.
Regarding payment terms, the following options are possible:
- wages are paid in advance (on the previous working day), the deadline for which, established by internal regulations, falls on a day off (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- vacation pay is paid in advance (at least 3 calendar days before the start of the vacation) (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment dated December 21, 2011 No. 3707-6-1);
- Sick leave is paid on the salary payment date closest to the calculation made (10 calendar days are allotted for it) (clause 1 of Article 15 of the Federal Law “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” dated December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ) ;
- directly on the day of dismissal, all amounts not received by the employee before that day are paid (Article 140 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Failure to comply with the 2-week interval and established deadlines may result in the following for the employer:
- administrative fine for failure to comply with the requirements of labor legislation (Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
- payment to the employee of monetary compensation for the delay (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- transfer of vacation at the request of an employee who did not receive vacation pay on time (Article 124 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the need to pay the employee for the time of suspension of work resulting from a delay in payment of wages (Article 142 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- criminal liability for a manager who caused a delay due to personal interest (Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
How should an employer communicate information with employees?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges the employer to promptly provide employees (their representatives) with information:
- necessary for the development of a collective agreement;
- reflected in internal regulations;
- which is a response to requests regarding violations of labor laws;
- necessary for employee participation in the management of the organization.
Since a collective agreement is the result of a bilateral agreement, employee representatives participating in its creation on behalf of the collective must be fully aware of all the necessary information associated with this document.
Internal regulations are created for the purpose of employees’ compliance with their provisions, so familiarization with them is a fairly important step in the process of bringing the necessary information to the attention of employees and occurs against signature. Failure to comply with the requirements of these documents, subject to compliance with the familiarization procedure, entails disciplinary liability for employees.
Legislatively, the right to monitor compliance with labor legislation is assigned to trade unions (Article 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), which can act for these purposes in various forms - from authorized persons to labor inspectors. A fairly wide range of powers granted to them allows them to quickly identify violations and demand that the employer eliminate them. The employer has a period of 1 week (Article 370 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), during which he must:
- consider the requirement;
- take measures to eliminate the violation;
- inform the body that contacted him about the results of consideration of the appeal and the measures taken regarding it.
The right of employees to participate in the management of the organization is provided for in Art. 52 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. To implement it, a mutual exchange of information is necessary (Article 53 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), in which the parties receive information of the following nature:
- employer - in terms of taking into account the opinions of employees when creating a collective agreement and internal regulations, receiving proposals for improving the work of the organization;
- employee - in relation to changes in the structure of the organization, production technology, prospects for the development of the enterprise.
Can workers be tested with a lie detector?
Today, when applying for a job or in the process of working, a lie detector test is relevant. This device has proven itself well in establishing the truth in clarifying various issues.
- working with money, assets, reputation of the organization;
- positions of accountants, lawyers, cashiers, bank employees, etc.
Is it legal to use a polygraph? Regulations do not directly indicate the need to use a lie detector or a ban on its use. In any case, if you decide to test an employee with a polygraph, you must follow an important rule.
If the employee himself does not object, then he must sign a document to this effect. If the employee is against it, then he has the right to refuse and then it is illegal to conduct an inspection. Dismissal due to failure to pass a background check is unacceptable. If this happens, the injured party has the right to go to court with a claim to restore justice.
Is it permissible for a boss to yell at a subordinate?
The rights and responsibilities of the employer and the staff of the organization intersect, since the activities of the enterprise always rely on their interaction. However, does a manager have the right to shout at a subordinate? Such precedents often occur, especially in stressful situations, business problems, employee mistakes, etc.
Definitely, the manager should not allow the following moments in his work:
- screaming and lashing out at subordinates;
- insults to employees and personal attacks;
- threats of dismissal for any reason;
- attempts to show the employee his insignificance by shouting and insults, etc.
Legislation protects the honor and dignity of a person, but in the case of an unreasonable cry from an employer, it is quite difficult to defend oneself.
In addition, the problem will worsen when filing complaints and applications with inspection and control authorities, as well as the court. That is why it is advisable for an employee to collect the maximum number of evidence, testimony of witnesses, and only then go to court. If the problem can be ruled out, then you should try to talk with your boss face to face and resolve the conflict.
If the situation becomes systematic, the management of the organization communicates in a similar way with all employees, it is advisable to file a collective complaint. However, it is often easier for an employee to find a new job and quit if possible. This will save nerves and effort.
Can an employee be forced to work 2 weeks upon dismissal?
The legislation does not actually establish the obligation to work 2 weeks before dismissal. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines the need to notify management that an employee is going to resign of his own free will.
The rest is at the discretion of the employer and he has several options:
- immediately sign documents to terminate the employment relationship and release the employee;
- Give yourself time of up to 2 weeks to find a new employee, during which the employee remains in place and transfers matters.
The legislation provides for cases when an employer does not have the right to leave an employee for 2 weeks.
This is relevant when the quitter does not have the opportunity to continue working. For example, when enrolling in a university, etc. In other cases, management has the right to leave the employee in place for 14 days. As a result, the employer's rights must be enforced, as is the case with employee guarantees.
In a situation where they are violated, the employer or his representatives have the right to appeal to the court or other responsible authorities. However, the employer cannot abuse his position and the rights granted by law. He must comply with the requirements of the law and not contradict them in local acts.
Can cameras be installed in the workplace?
Installing CCTV cameras in the workplace is popular today. However, employees do not always agree with this decision of management and wonder whether it is legal.
An employer has the right to install cameras at the enterprise if certain conditions are met:
- It is unacceptable to install cameras in places that are not directly for work. For example, in toilets, showers, etc.;
- the employee must be warned about the installation of the camera by written notice;
- local regulations indicate the need to install a video surveillance camera;
- The employee is explained the basis and reason for the installation, for example, the need to monitor the safety of inventory items, etc.
If all the rules are followed, then installing cameras is legal and possible.
The employer does not have the right to carry out visual control where the employee is not required to engage in work activities.
What conditions must be taken into account in an employment contract?
- Installation information . This section touches on aspects directly related to the subjects of labor relations - the employer and the future employee. Additionally, a number of information regarding the conclusion of the contract are indicated here.
- Place of work . This section should indicate information about the immediate place of work of the future employee and the name of the employer. If a citizen is hired to work in one of the branches of the employing company, his address must be indicated in the contract.
- Labor function of the employee . The concluded agreement must necessarily describe the main tasks that will be assigned to it. Important! The employer can determine the title of the position independently, but only in cases where the work is not related to harmful and dangerous industries, that is, it does not imply the payment of any benefits or compensation.
- Start date of work duties . It may differ from the date of conclusion of the agreement. If a specific day is not specified in the contract, the employee is obliged to go to work on the day following the signing of the agreement.
- Contract time.
- The procedure for remuneration and its conditions . The text of the document must describe the employee’s salary, wage scale, as well as all possible bonuses, allowances and additional payments. The maximum salary is not limited, with the exception of certain categories of employees whose remuneration is directly determined by the legislative acts of the Russian Federation. The minimum size cannot fall below the minimum wage established by law. This section also stipulates the terms and methods of payment of wages.
- Schedule of working hours and rest . This clause includes conditions relating to vacations, days off and non-working holidays, and other nuances relating to the employee’s right to rest.
- Working conditions and additional guarantees . This condition must be included in the employment contracts of employees working in hazardous industries or in hazardous working conditions.
This is important to know: How to correctly draw up an employment contract with an employee: sample 2021
Some working conditions are not initially required to be included in an employment contract, but they may become so if certain legal aspects arise in a particular situation. Such nuances may include a probationary period, full or partial financial liability, etc.
Types of claims for court
Claims may be resolved based on certain individual characteristics:
- For a procedural task.
1.1. Declaratory actions are actions that declare something invalid.
1.1.1.1. Negative declaratory actions.
1.1.1.2. Affirmative declaratory actions.
1.2. Enforcement lawsuits are lawsuits that seek to collect a debt.
1.3. Conversion lawsuits are lawsuits asking for a divorce.
1.4. Preemptive claims. This definition is used if no one has yet infringed on individual rights, but such a risk exists.
- Right of action.
2.1. Business situation claims.
2.2. Claims affecting the family branch of law.
2.3. Claims affecting the labor branch of law.
2.4. Property claims.
- Type of interest.
3.1. Personal claims.
3.2. Class action lawsuits.
3.3. Claims for the protection of the general public.
The type of claim is reflected in the statement of claim. The statement of claim to the court for each type of claim has its own characteristics and individual points that must be completed.
Legislative regulation
All labor relations are subject to the jurisdiction of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The rights and obligations of the employer, as a party to labor relations, include the materials of Art.
22. The text of the article contains a list of the employer’s powers, which is very convenient for use in practice.
And in case of violation of rights or failure to fulfill prescribed obligations, it is easy to trace the legislative basis for protecting your interests.
IMPORTANT! The list is quite complete, but not exhaustive; the article explains within the framework of which the employer’s responsibilities arise and how his rights are limited.
Procedure for filing a claim in court - deadlines
The period for consideration of a claim is the period of time that the law gives the court to consider the problem of the claim and make a fair verdict on it.
The time frame for consideration of a claim in court is regulated by the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation and its already mentioned Article 154. According to its first paragraph, the maximum period for consideration and resolution of a claim is up to 2 months from the date of acceptance of the application. If the statement of claim is sent to the Magistrates' Court of the Russian Federation, then the minimum period there is 1 month.
But the law also provides for the suspension of time limits for trial proceedings.
Exactly 5 days are given to consider the claim for acceptance or refusal.
Claim proceedings can take a long time.
If the established period ends on the day of a holiday, the period will automatically be extended until the first working day.
The timing of the trial is not affected by the nature of the case and the branch of law that was violated. Time limits include the time to accept the statement of claim, conduct the first trial, and conduct proceedings until the final decision of the court. Also, the time period for consideration of a case by the courts includes the period of time that the court deliberated before the final verdict.
Responsibilities of the employer
The employer's responsibilities can be divided into groups depending on to whom these obligations arise.
What is the employer obliged to do as a subject of legal relations?
As a party to labor law, the employer must comply with and fulfill the following obligations:
- Strictly follow the labor laws currently in force in the country.
- Comply with the standards prescribed in various regulatory documents on labor legislation:
- regulations;
- local documents;
- federal laws, regional and municipal regulations;
- collective agreements;
- individual employment contracts;
- additional agreements.
Responsibilities of the employer to state regulatory authorities
These responsibilities cannot be attributed to those that arise directly before employees, however, their compliance is aimed at organizing favorable work for hired personnel. So, the employer, in relation to management and control bodies, is obliged to comply with all instructions issued by the federal executive authorities exercising state supervision and control over the proper implementation of the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Responsibilities of an employer to its employees
By hiring employees, the employer takes on a fairly large number of obligations. There are many of them for the reason that they must guarantee respect for the rights of employees, which are also enshrined in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 21). They can be reduced to several groups, differing in the principle of actions taken:
- responsibilities related to compliance with Labor Code standards in relation to employees;
- responsibilities related to the organization, protection and remuneration of labor;
- responsibilities regulating the preparation of working documentation;
- Responsibilities for providing work with everything necessary.
Let's consider some of the obligations of the person providing the work, listed in the corresponding list from Art. 22 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- The employer must provide the hired employees with the work specified in the agreements.
- By providing the opportunity to work, the employer is obliged to provide a workplace, equipment, materials, raw materials, special documentation, tools and other factors that will be necessary for full-fledged activities within the framework of the employment agreement.
- The organized conditions and principles of compliance with labor safety must meet the requirements established in labor legislation for this industry.
- Remuneration for work of equal value should be equal.
- Differences in pay must be determined by objective factors provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: qualifications, length of service of the employee, level of job responsibilities, their number, etc.
- Payment of remuneration for labor must be made within the terms established by the collective agreement or individual contracts, if they do not contradict the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Employees must be provided with rest as a break for meals, days off in accordance with regulations, annual leave, etc.
- For categories of workers provided for by law, a special labor regime must be provided: for example, reduced working hours, light work, etc.
- Local regulations adopted at the enterprise must be brought to the attention of personnel, which is confirmed by the personal signature of each employee confirming familiarization with them.
- The employee must be registered in accordance with the requirements of the law, therefore the employer’s responsibility is to conclude an employment contract with him.
- The conclusion of a collective agreement and the conduct of collective bargaining also lies on the shoulders of the employer.
- If violations of labor organization and safety are identified, or the employee has reported such violations, the employer must consider these problems and take the necessary measures to eliminate them.
- If an employee is harmed due to the fault of the employer, the latter is obligated to compensate for treatment, as well as compensation for moral damage (within the scope of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
- An employer must provide social insurance for all its employees.
This is important to know: Contract for cadastral works: sample 2021
NOTE! Failure to comply with its obligations for the employer is fraught with administrative punishment - a fine. Penalties are provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as the Tax Code and sometimes the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Expert opinion
Lebedev Sergey Fedorovich
Practitioner lawyer with 7 years of experience. Specialization: civil law. Extensive experience in defense in court.
The most serious violations of their duties may deprive the employer of the right to operate and occupy certain positions for a given period.
Cases for filing a claim
A statement of claim is filed in any case when your rights have been violated or have not yet been, but there is a possibility that they may be violated.
It should also be noted once again that with a claim to the court for a positive result in the form of consent to the proceedings, you should go after going through all previous instances where you were denied.
From the types of claims listed above, we can conclude that the court accepts and examines statements from all areas that surround a person, from divorce to car theft.
The court is the last authority that can translate into reality the right to protect the rights granted by the state.
Of course, before going to court, you need to try to come to an amicable agreement with the person. This can be done in writing. If this fails, then this document will act as an argument that you want and have tried to move towards reconciliation. After drawing up the document, it can be sent by registered mail or given personally to the second subject of the conflict.
What is the employer entitled to?
The rights of the employer extend to a number of actions related to the following labor issues:
- various actions aimed at the dynamics of employment contracts: conclusion, amendment, termination, renegotiation;
- collective agreements and actions related to collective relations;
- employee incentives;
- ensuring the responsibility of working personnel;
- all actions related to internal regulatory documents.
In Art. 22 contains a list of employer rights (also detailed, but not exhaustive).
- The employer has the right to maintain relevant documentation - employment contracts, local acts, collective agreements, regulations, etc.
- The employer is allowed to reward employees by any means for the proper fulfillment of their labor obligations.
- For failure to comply with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the rules stipulated by internal documentation, the employer has the right to hold its employees accountable as provided for by law.
- The employer’s legal right is to demand from its personnel careful treatment of the company’s property, equipment, materials, etc., as well as strict adherence to established labor safety rules and technological processes.
- An employer may be the creator or member of any associations acting to protect the interests of this category.
NOTE! Like the employee, the employer is also protected by law in guaranteeing the observance of his rights, and in the event of their violation, he can apply to defend his interests in the courts.
How to write a statement to the court correctly
The main requirement that the court requests is the form of the statement of claim. The claim MUST be submitted in writing. If you submit a claim electronically, it will be rejected immediately, without considering the problem. To avoid such problems, you must write a statement in writing and send it by registered mail to the district court at your place of residence.
Further, after this main requirement for the rest of the filling out, there are no strict frameworks. But it is better to follow the standard type of filling:
The name of the court in which the claim will be filed. Personal information about the applicant. For a private individual - full name, place of residence according to registration. For a company – the name of the legal entity, place of registration of the company, personal information about the person representing the company. Personal information about the defendant that the applicant knows. Formulation of claims, violations of the second subject, formation of requirements. Formatting the problem. That is, why the demands were put forward, and what the plaintiff relied on when putting them forward. If this concerns finances, then it is required to indicate the amount and make the necessary calculations from which the plaintiff took this amount. A description of attempts to end the conflict independently by peaceful means. If there is documentation confirming this, then it must be attached to the statement of claim. A list of documents is required that can serve as evidence and help in the investigation of the case. Documents and receipts confirming the availability of refusals from other protection authorities.
There is also a detailed sample of a real statement of claim on the Internet and from lawyers, according to which you can draw up your own claim.
If you can’t, then you need to contact a lawyer for advice. There you will tell the situation and together with him will file a claim. He will help fill out the part in which you need to provide a list of laws that the defendant has violated. This part is optional, but a lawyer can fill it out for you.