The activities of any commercial organization are aimed at obtaining economic benefits, which can be realized through a variety of legal means and in connection with this, additional costs may arise in the form of postage. Indeed, despite the widespread use of new technologies, many organizations remain supporters of conventional mailing methods, both on the sending and receiving side.
The costs incurred when using postal services have such a feature as reasonableness, and documented evidence. Accounting is carried out on a separate account: 44 or 26. Let's look at how to select an account for postal expenses and their accounting.
Selecting an account when accounting for postage costs
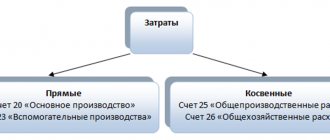
Postal costs cannot be directly attributed to the cost price, so they must be accounted for on a separate account, and the following are important: type of activity and direction of postal expenses: (click to expand)
- marketing research – debit account 26
- in other cases - to the debit of account 44
| Trade | Regardless of whether it is a wholesale or retail company, sales costs are considered distribution costs and are not included in the cost of goods. They are collected at count 44 |
| Production activities | These expenses relate to administrative or general business expenses, are accounted for on account 26 and can be written off to the financial result. Expenses for the sale of finished products are classified as commercial, accounted for on account 44 |
| Non-production companies, except trading (brokerage, dealer companies, etc.) | Information on expenses relates to the main activity, therefore account 26 is used |
| Trade and production activities | Account selection is made independently |
Accounting for postal expenses should be enshrined in the accounting policies and working chart of accounts. Costs that are included in postage must necessarily be related to sales for the purpose of including selling costs.
Examples of advance reports from life
Fill out the “Advances” tab:
It must be said that this tab is not displayed in any way in document postings, but is only available for the AO-1 printed form.
Fill out the “Products” tab (we bought a bunch of everything and put it on ten):
Here are the postings for this bookmark:
We fill out the “Payment” tab (we pay off the debt to suppliers, or pay an advance):
Here are the wiring:
Examples of filling out the “Other” tab.
Payment for communication services:
Payment for newspaper advertisements:
Write-off of daily allowance and debt for travel tickets:
Payment for some services (immediately charged to 26):
By the way, on the “Products” and “Other” tabs there is a checkbox “SF”, if you check it, then the received invoice will be entered on this line:
Moreover, it will be linked directly to the expense report:
After filling out the “Advance report” document, all that remains is to print it:
We're great, that's all
By the way, subscribe to new lessons...
Sincerely, Vladimir Milkin (teacher at the 1C school of programmers and updater developer).
How to help the site: tell (share buttons below) about it to your friends and colleagues. Do this once and you will make a significant contribution to the development of the site. There are no ads on the site, but the more people use it, the more energy I have to support it.
Click one of the buttons to share:
| Subscribe and receive new articles and treatments by email (no more than once a week). Join my group on VKontakte, Odnoklassniki, Facebook or Google+ - the latest processing, error corrections in 1C, I post everything there first. | ||
| Learning to enter acquiring transactions | table of contents | Learning to work with corporate cards |
Accounting for renting a box at the post office
The organization has the right to choose when receiving correspondence:
- by postal address
- poste restante
- using the cells of a subscription mailbox
Expenses for the use of a subscription box in accounting are reflected as part of expenses for ordinary activities (administrative expenses associated with production and sales) and they are recognized in the tax period in which they were generated, regardless of the fact of payment when using the accrual method; when using the cash method, the amount for rent is included in expenses upon payment. In most cases, the fee is paid several months in advance, which is counted as a prepayment.
An example of accounting for expenses for a subscription box
Alpha and Omega LLC rents a mailbox on the basis of an agreement and a transfer certificate for 9 months from April 1, 2021 to December 31, 2021. The payment was made in a lump sum in cash by the accountable person in the amount of 10,620 rubles. (including VAT 18% - 1620 rubles). The organization uses the accrual method. The following transactions have been made in the organization:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The accountable amount was issued from the cash register | 71 | 50 | 10620 |
| A subscription fee has been paid for using the cell | 60 subaccount “Advances issued” | 71 | 10620 |
| Costs for using the cell are written off monthly | 26 (44) | 60 subaccount “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | 1000 |
| VAT on the subscription fee is reflected monthly | 19 | 60 subaccount “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | 180 |
| Acceptance for deduction of VAT on postal services provided | 68 | 19 | 180 |
| Partial prepayment amount credited | 60 subaccount “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” | 60 subaccount “Advances issued” | 1180 |
Filling procedure
Now let's take a closer look at the procedure for filling out the document.
Filled out by employee
Front side.
So, on the front side of form No. AO-1, the employee must:
- Indicate the company name and OKPO code.
2. Enter the date the document was compiled and assign a number.
3. In the “report in amount” column we enter the amount that the employee spent on the household needs of the enterprise. For example, he was given five thousand rubles, but he spent four thousand. Therefore, in this column he indicates four thousand.
4. We indicate the name and code of the structural unit.
5. After this, indicate your full name. the accountable person, his personnel number and profession (position).
6. Enter the purpose of the advance.
7. On the left side of the table located on the front side of the form, indicate the amount of the amount received from the company’s cash desk (or to a bank card). If necessary, indicate the amount of money issued in foreign currency.
8. We indicate the total amount of funds received.
9. We indicate the amount spent on the business needs of the enterprise.
10. Indicate the amount of the balance.
Reverse side.
11. On the reverse side of the form, in columns 1-6, the employee must list all documents (sales receipts, cash receipts, etc.) confirming the expenses made by the employee, indicating the amounts spent. Documents must be numbered according to the order in which they are listed in the expense report.
Now about what information the employee should enter in the appropriate columns:
- 1 — payment number assigned to the document confirming expenses;
- 2 - date of check;
- 3 — check number;
- 4 - name of the document confirming expenses;
- 5 - the amount of expenses incurred in rubles is entered here;
- 6 - to be filled in if necessary. It indicates the amount of the expense incurred in foreign currency;
- the “Total” line indicates the total amount of expenses.
12. After the employee has filled out the required fields, he must put his signature on the form with a transcript. Next, you need to submit the document to the accounting department. The accountant will check that the form is filled out correctly.
Filled out by an accountant
Front side.
13. After receiving the form, the accountant must ensure that it is filled out correctly. If no errors are found, the accountant makes a note about this in the “report verified” column and signs it.
14. Next, the accountant indicates information about the entered balance/overspending.
After this, the accountant proceeds to further fill out the form.
15. The accountant fills out the detachable part of the form, signs it and gives it to the employee
Reverse side.
16. The accountant records information in columns 7 and 8. The amounts of expenses accepted for accounting are indicated here. Column 9 indicates the numbers of accounting accounts that are debited for the amount of expenses. The amounts indicated by the employee and the accountant must be the same.
After this, the accountant fills out the front side of the expense report.
Front side.
17. On the front side in the right table, the accountant enters the following information:
- balance or overspending of the previous advance;
- the amount of the advance received from the enterprise's cash desk;
- amount of money spent;
- balance or overexpenditure of advance amounts;
- accounting entry - information is taken from the data in column 9, which is on the reverse side.
18. Next, the accountant sends the document to the chief accountant, who also checks it. After checking the expense report, the chief accountant puts his signature on it and sends it to the head of the enterprise for approval.
19. The director approves the document and returns it to the accounting department. After that, it is stored in the company’s accounting department for 5 years. After this period it is destroyed.
possible on our website.
An example of cost accounting for advertising mailings
Alpha and Omega LLC ordered advertising brochures, paid for them and posted them. Half of the booklets were distributed by direct mail, the other half by mail. Postal services are 11,800 rubles. (including VAT - 1800 rubles) The company's revenue for this month amounted to 500,000 rubles. without VAT.
Postage costs for unaddressed advertising are recognized as regulated. The standard will be:
500,000 rub. * 1% = 5000 rub.
The standard is equal to the costs of non-addressed advertising, which means they are taken into account in full - 5,000 rubles. And the postal service accounting will reflect:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| Paid postage for mailing | 60 | 51 | 11800 |
| Reflected VAT presented by the post office | 19 | 60 | 1800 |
| The cost of postal services for unaddressed mailing is reflected as a sales expense | 44 | 60 | 5000 |
| Accepted for VAT deduction | 68 | 19 | 900 |
| The cost of postal services for direct mailing is reflected as sales expenses | 44 | 60 | 5000 |
| VAT written off for direct mailings | 91 | 19 | 900 |
Sample of filling out an Advance report
An advance report from an accountable person is drawn up with the document Advance report, which can be found in the section Bank and cash desk – Cash desk – Advance reports.
In the header of the document you must indicate:
- from - date of preparation of the advance report;
- Accountable person is the individual who provided the advance report.
Let's look further at how to generate an expense report in 1C in different situations.
Reflection of previously issued accountable amounts in the advance report
October 17 Druzhnikov G.P. brought an advance report for previously issued accountable funds in the amount of 30,000 rubles.
If the employee was previously issued funds, they should be indicated on the Advances tab.
This tab can only be filled in by selecting documents using the Add button. Advances to accountable persons may be issued in the following documents:
- Issuance of monetary documents type of transaction Issuance to an accountable person, for example, if tickets or gasoline coupons were purchased by the Organization and transferred to an accountable person.
- Cash withdrawal type of operation Issue to an accountable person, if the accountable funds are received from the cash register.
- Write-off from a current account type of transaction Transfer to an accountable person, if the accountable person paid through a corporate card, or the accountable funds were transferred to his personal card.
In our example, Druzhnikov G.P. an advance in the amount of 30,000 rubles was previously issued.
If advances have not been previously issued, then this tab is not filled in, and reimbursement of expenses to an employee made from personal funds for the needs of the organization is recommended by Accounting Expert8 through account 73.03 “Settlements for other operations.”
How to prepare an advance report when purchasing materials and inventory items
Let's look at how to conduct an advance report in 1C 8.3 for the purchase of materials and goods using the example of the purchase of stationery by an accountable person.
On October 17, Druzhnikov G.P. provided a report to which he attached:
- check with allocated VAT for the purchase of stationery from Kontur LLC: A4 paper - 5 points at a price of 236 rubles. (including VAT 18%);
If the accountable person has provided primary documents for the purchase of materials, goods or other inventories (MPI), then their list is indicated on the Goods tab.
For inventories for which the employee reported, there is no need to create additional documents Receipt (act, invoice)! The posting of materials and goods to the warehouse purchased by the accountable person is carried out using the Advance report document.
On the Products tab, fill in the name, number of inventories and the amount for which they were purchased, as well as information about the submitted VAT, the supplier and the document on the basis of which VAT can be deducted.
If the accountant has attached an invoice issued to the organization to the Advance Report document, then you need to check the SF checkbox. When posting the Advance Report document, an Invoice document will be automatically created for the amount of VAT entered in the VAT column, which can be accepted for deduction.
If only a primary document is attached (for example, a cash register receipt) in which VAT is highlighted, then the SF checkbox is not checked, while the VAT highlighted in the primary document is indicated in the VAT column.
As a result of posting the Advance Report document, such VAT will be written off as expenses that are not taken into account when taxing profits.
If the accountant has paid the supplier for the goods, and there has been no delivery, the goods have not arrived at the warehouse, and there is only a receipt for payment, then it is necessary:
- The acquisition of goods and materials should be formalized through the Receipt document (act, invoice) when they arrive at the organization. In this case, nothing is indicated on the Products tab of the Advance Report document;
- indicate payment to the counterparty on the Payment tab.
See also Receipt of materials in 1C 8.3: step-by-step instructions
Daily and travel expenses in the advance report
Let's look at how to reflect daily allowances and business trip expenses in the advance report using the following example.
On October 7, July Druzhnikov G.P. was sent on a business trip to Sochi for 6 days.
Daily allowances in the Organization in accordance with the Regulations on Business Travel are paid at the rate of 700 rubles/day, in total - 4,200 rubles.
On October 17, the employee provided a report to which he attached:
- railway ticket (Moscow-Sochi) in the amount of 4,000 rubles. (including VAT 18% - 120 rubles);
- railway ticket (Sochi-Moscow) in the amount of 5,000 rubles. (including VAT 18% - 130 rubles);
- receipt and SF for hotel accommodation in the amount of 9,440 rubles. (including VAT 18%).
Travel expenses (including daily allowances issued to an employee) are indicated on the Other tab.
Daily excess allowances are subject to personal income tax (clause 3 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2 of article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The following standards have been established for 2021:
- business trip within the Russian Federation - 700 rubles. in a day;
- business trip outside the Russian Federation - 2,500 rubles. in a day.
On the Other tab, the data of the primary document is entered (this can be external documents such as checks, tickets, acts, invoices, or internal ones, such as an Order). The name of the costs and their amount, as well as information about the submitted VAT, the supplier and the document on the basis of which VAT can be deducted.
If the accountant has attached an invoice issued to the organization to the Advance Report document, then you need to check the SF checkbox. If, instead of the SF, documents are attached that correspond to the characteristics of the strict reporting form (SRF), for example, tickets, then you must additionally check the SRF checkbox. When posting the Advance Report document, an Invoice document will be automatically created for the amount of VAT entered in the VAT column, which can be accepted for deduction.
In our example, all VAT presented can be deducted.
See also Registration of a business trip in 1C 8.3 Accounting step by step
Services and other costs in the expense report in 1C 8.3 using the example of postage costs
Let's look at how to fill out an advance report in 1C for the purchase of postal services using the following example.
On October 17, the employee provided a report to which he attached:
- KKM check for payment of postage in the amount of 354 rubles (including VAT 18%);
All expenses of an accountable person that do not have a material form are taken into account on the Other tab.
On the Other tab, you enter the data of the primary document, the name of the costs and their amount, as well as data about the submitted VAT, the supplier and the document on the basis of which VAT can be deducted. Here it is also necessary to show the postage stamps that were used and reflected in accounting as monetary documents.
If the accountant has attached an invoice issued to the organization to the Advance report document, then you need to check the SF checkbox. If, instead of the SF, documents are attached that correspond in their characteristics to the strict reporting form (SRF), for example, tickets, then you must additionally check the SRF checkbox. When posting the Advance Report document, an Invoice document will be automatically created for the amount of VAT indicated in the VAT column. This amount of VAT can be deducted.
If only a primary document is attached (for example, a cash register receipt) in which VAT is highlighted, then the SF checkbox is not checked, while the VAT highlighted in the primary document is entered in the VAT column. As a result of posting the Advance Report document, such VAT will be written off as expenses that are not taken into account when taxing profits.
Payment to the counterparty in the advance report
Let's look at how to fill out an advance report in 1C for payment to a counterparty using the following example.
On October 15, the employee provided a report to which he attached:
- bank order for Internet payment in the amount of 1,534 rubles.
An employee's advance report for the transfer of an advance or payment to a counterparty is drawn up on the Payment tab.
On the Payment tab, enter the counterparty and the amount paid by the accountable.
Accounting for postage expenses for payment of dividends
JSCs can use postal orders to transfer dividends to shareholders. Such expenses do not relate to expenses that reduce the tax base for income tax; they are not activities aimed at generating income, because they are paid out of net profit, which means that postage costs must be covered from net profit.
Costs associated with informing shareholders are included in non-operating expenses when calculating income tax. In terms of accepting the costs of reducing the tax base, the situation is similar to that with the payment of dividends by mail.
Strict reporting forms can also serve as confirmation of an organization's expenses for postal services when paying in cash, along with cash receipts.
Advisor to the State Civil Service of the Russian Federation, II class Ya.Ya. Chometz
General information
The 1C advance report must be drawn up after the funds are transferred to the reporting employee. This way you can track expenses and immediately prepare accompanying documents. At the same time, they determine the purposes for which the allocated money will be directed. For example:
- Purchasing goods that the company needs.
- Payment to suppliers.
- Travel expenses.
The AO is written by the employee himself and encloses documentation indicating that he was given money. The accountant then enters this information into the utility’s database.
Accounting for postal expenses for individual entrepreneurs
The expenses of an individual entrepreneur can be presented as, for example, sending 3-NDFL by mail. When calculating personal income tax, an individual entrepreneur has the right to professional deductions based on documented expenses, moreover, carried out to generate income. Thus, postage expenses may be the basis for a professional deduction when calculating personal income tax.
Prepayment for the use of a mailbox is taken into account in the same way as other advances issued
Important! An individual entrepreneur independently determines expenses for activities aimed at making a profit in the same way as organizations in accordance with Chapter. 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Advance report in 1C 8.3 accounting step by step
Organizations regularly issue accountable funds to their employees.
Employees spend this money on business needs - travel expenses, postal expenses, purchase of office supplies, fixed assets. The document that reflects the expenses of accountable persons is called an advance report. How to make an advance report in 1C 8.3 Accounting step by step? How to arrange daily allowances in an advance report in 1C 8.3? We will answer these questions in the article. "BUCHSOFT" REPORTING VIA THE INTERNET Test and send reports to funds and inspections online! Fast connection. If you find it cheaper, we'll give you your money back!
An advance report is prepared for each employee to whom money has been issued against the report. It consists of two sections.
In the first one you can see:
- the amount of debt at the time of drawing up the report either from the organization to the employee (overspending), or from the employee to the company;
- how much money was issued according to the advance report;
- the total amount of expenses according to the advance report;
- balance of debt due to the accountant.
In the second section, you can see in detail what the accountant spent the money on. You can make an expense report in 1C 8.3 in 4 steps.
How to make an advance report in the BukhSoft program
Answers to common questions
Question No. 1: Can the delivery of documents from the counterparty via a freight forwarding company be attributed to postal expenses and on what account should they be accounted for? (click to expand)
Answer : The organization has the right to attribute these expenses to postal expenses and reflect them on account 44 because it has to do with implementation.
Question #2 : How are stamps counted for any form of mail?
Answer : In accounting, the cost of purchased stamps is taken into account as part of administrative expenses (account 26 or account 44) only after they are used for dispatch. Stamps must be accounted for as an independent asset if they were purchased using a separate invoice and, before being written off as expenses, are reflected in account 50 of the “Cash Documents” subaccount. When affixing stamps by mail, the sender pays for the postal service and reflects the postage costs in full (according to invoice 26 or 44).
How to create an expense report in 1C 8.3 Accounting?
In the expense report journal, right above the list of documents, find the “Create” button and click it.
The document number is assigned automatically after recording the expense report. If necessary, you can enter your own value in this field. The date is also filled in automatically and corresponds to the current one. You have the right to correct this value as well.
Select the reporting person in the appropriate field. After that, pay attention to the bottom of the window. There are fields for recording the purpose of the advance, as well as the number of documents confirming the expenses.
The “Destination” field may contain, for example, the following information:
- business trip to Nizhny Novgorod from 07/01/2018 to 07/04/2018;
- household expenses;
- postage;
- and so on.
Remember that you can create new documents in 1C 8.3 by copying old ones. This should be done in the case when the new document almost completely repeats the data of any of the previously created expense reports. Otherwise, such an action often leads to errors when the accountant forgets to delete or correct this or that line.
Now you can proceed to filling out financial indicators.
Postings under the simplified tax system
The services of banks are used by all organizations and entrepreneurs carrying out economic activities.
Most of the services are provided by credit institutions on a paid basis; the fee for such services is called a bank commission. In order to attract clients, financial institutions are constantly expanding their range of services, offering not only financial intermediation, but also software products in the form of personal accounts with a set of accounting functions and reporting forms.
The most popular services of credit institutions include:
- settlement and cash services for ruble and foreign currency accounts;
- remote management of settlement operations through a client bank;
- currency control;
- accepting and issuing cash;
- cash collection;
- SMS notifications about payment transactions;
- acquiring operations for accepting card payments;
- issuance and servicing of payment cards;
- factoring operations;
- provision of bank guarantees.
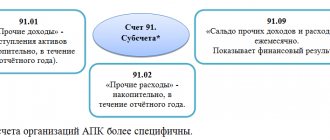
In accounting, expenses associated with servicing in credit institutions are classified as other expenses (clause 11, paragraph 6 of PBU 4/99 “Expenses of the organization”) and are reflected in account 91.02 “Other expenses and income.”
From the point of view of accounting entries, the list of the most common bank services can be divided into two types of operations: not subject to VAT and subject to VAT.
Let's look at the accounting entries for each type of transaction.
Bank services: transactions without VAT
Operations for opening and servicing a current account, cash transactions (except for collection), making payments, issuing a bank guarantee, servicing a bank client and others listed in clause 3 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not subject to taxation.
Services of credit institutions without VAT should be reflected in correspondence with the cash account:
Dt 91.02 Kt 51, 52, 55, 57.
Bank transactions for services without VAT:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Commission for execution of payment order | ||
| Commission for RKO in March | ||
| Fee for using a bank client | ||
| Commission for execution of payment in foreign currency | ||
| Acquiring fees | ||
| Refund of erroneously charged commission |
If an organization deposits funds in excess of the cash limit to a bank for crediting to a current account independently, without involving collectors, then the service for receiving and recounting cash is not subject to VAT.
Delivery of proceeds to the bank, postings:
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Cash deposit to current account (revenue) | ||
| Cash conversion fee | ||
| Cash acceptance fee |
A banking offer called “salary project” has become quite popular, which allows organizations to save accounting time on issuing wages, shortens and simplifies the procedure for paying wages.
Many credit organizations charge a commission within the framework of a salary project for transferring funds to employee cards; this type of commission is not subject to VAT. The accounting entry when paying for servicing a salary project:
Dt 91.02 Kt 51.
Postings to the bank for services subject to VAT
Banking products not specified in clause 3 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are subject to VAT at a rate of 18% in the general manner.
The peculiarity of these banking services is that it is necessary not only to pay for them, but also to obtain primary documents confirming the fact of their receipt.
To reflect expenses for services of credit institutions, subject to VAT, the use of an account for mutual settlements with suppliers is required; most often, account 76 is used for these purposes.
When the bank's services are paid for, the posting is generated in correspondence with the cash accounts:
Dt 76 Kt 51.
When the UPD is received from the bank, a posting is generated in correspondence with the expense account.
Examples of transactions for banking services with VAT are given in the table.
| Banking service | Debit | Credit |
| Service costs under the factoring agreement, including VAT | ||
| Paid expenses under the factoring agreement (statement) | ||
| Expenses for servicing a foreign exchange contract, including VAT | ||
| Paid the bank commission for performing the functions of a currency control agent (bank statement) | ||
| Expenses for collection of proceeds by the servicing bank | ||
| Collection of proceeds paid (extract) |
Accounting for expenses when retailing using the simplified tax system
All company expenses must be:
- economically justified
- documented
- aimed at generating income
Conventionally, the company’s expenses for the simplified tax system can be divided into the following groups:
- expenses for the purchase of goods (excluding VAT)
- VAT presented by the supplier (if the supplier works on the general taxation system)
- expenses for purchasing goods
- costs of selling goods
An additional condition for companies operating on the simplified tax system is that goods purchased for resale must be paid for and sold to customers.
The accounting policy must define one of the methods for valuing purchased goods:
- FIFO method (first of all, expenses for the earliest goods purchased are taken into account)
- based on the average cost of purchased goods
- at the cost of a unit of goods.
Source: //ecoafisha.ru/provodki-pri-usn/
New KOSGU in 2021 in a budgetary institution: application
An examination of the technical condition of the property to determine whether it can be further exploited is reflected in subarticle KOSGU 225 “Works, services for property maintenance.” Water heater diagnostics is one of these services.
Order No. 209n. In addition, specialists from the financial department prepared Methodological Recommendations for the procedure for applying KOSGU and communicated them by letter dated 06/29/2018 No. 02-05-10/45153 (hereinafter referred to as the Methodological Recommendations).
The detailed subarticles of Article 340 of KOSGU can be divided into 3 types:
1. It is easy to notice that the names of subarticles of KOSGU from 341 to 346 practically repeat the names of the analytical accounts of account 105 00 “Inventories” given in paragraph.
118 Instructions, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n. These sub-items were introduced to detail the costs of acquiring (manufacturing) inventories by their groups.
2.
Subarticle 347 of KOSGU was introduced to separate the costs of paying for contracts for the acquisition (manufacturing) of all types of materials, including building materials, for the purposes of capital investments.
Expenses for sending and delivery of correspondence
Power ministries and departments : accounting and taxation,” 2009, No. 1 Almost every institution uses postal services. The institutions of power ministries and departments are no exception. Sending correspondence, parcels, parcels, etc., as well as receiving them using postal services are associated with postage expenses. In this article we will look at the features of reflecting postal expenses in accounting. Postal costs for sending correspondence Features of accounting for the costs of purchasing envelopes and stamps To send correspondence, institutions must have marked or unmarked envelopes and stamps available. Therefore, the most common type of postal costs when sending correspondence are the costs of their acquisition. Let's consider what features should be taken into account when such expenses arise.
Postings according to the simplified tax system
The simplified taxation system (STS, simplified) is a special tax regime applied by organizations and individual entrepreneurs who have submitted an application to the Federal Tax Service for its application and meet the criteria for its application.
ConsultantPlus FREE for 3 days
Get access
The conditions for applying the special regime are established by Chapter 26.2, Part 2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. If they are violated, the application of the simplified tax system will be considered unlawful, with subsequent additional taxes being assessed based on the general taxation system.
Conditions for applying the simplified taxation system:
- the average number of employees does not exceed 100 people;
- the residual value of fixed assets is not more than 150 million rubles;
- annual income does not exceed 150 million rubles.
In addition to these restrictions, there is a ban on the use of a special regime for certain types of activities and if the organization has branches (Clause 3 of Article 346.12 Part 2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Object of taxation under the simplified tax system and tax rates
The Tax Code in this case offers two objects of taxation - “income” and “income minus expenses”. The choice is made when submitting an application to the Federal Tax Service to apply the simplified taxation system. It will be possible to change the object of taxation to another only from the beginning of the next tax period (calendar year) by submitting a new application.
The tax rate depends on the chosen tax base. For the simplified tax system with the object of taxation “income”, the rate is 6%, with the right of constituent entities of the Russian Federation to set a rate from 1 to 6% on their territory.
For “income minus expenses” the tax rate is 15%, with the possibility of reduction by regional legislation to 5%.
Subjects of the Russian Federation in their legislation can establish a zero rate for newly registered business entities operating in the production, scientific, social spheres or in the provision of consumer services to the population.
Organization of accounting
Organizations are required to keep records of accounting transactions in full in accordance with the Chart of Accounts and accounting standards.
Individual entrepreneurs are not required to keep accounting records and can limit themselves to maintaining tax records; in this case, no accounting entries arise.
A feature of the simplified taxation system is that both income and expenses are taken into account on a cash basis, that is, as payment is made. For the tax register - the book of income and expenses during simplification - paid income and expenses are selected.
Postings under the simplified tax system - “income”:
| Dt 51 Kt 62.02 | Receipt of advance payment from buyer |
| Dt 51 Kt 62.01 | Repayment of the buyer's debt |
| Dt 51 Kt 76 | Fines paid under business agreements |
| Dt 57 Kt 62 | Payment via the site |
| Dt 50 Kt 90 | Payment in retail |
Postings according to the simplified tax system - “income minus expenses”, examples:
| Dt 50 Kt 70 | Payment of previously accrued wages |
| Dt 26 Kt 60 | An act of previously paid rent has been received |
| Dt 51 Kt 60 | Payment for services provided |
| Dt 90 Kt 41 | Cost of goods shipped and paid for |
For tax purposes, when simplified, only expenses incurred and paid are taken into account, that is, if there are documents from the supplier and payment.
For trade, there is an additional condition for including the cost of paid goods in expenses - the goods must be shipped.
When calculating the simplified tax system with the taxable object “income minus expenses,” only those expenses listed in Art. 346.16 ch. 26.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Calculation procedure
The calculation of deductions in connection with the application of the simplified tax system is carried out by taxpayers independently based on the results of the tax period, which is a calendar year. Within it, taxpayers calculate quarterly advance payments and pay them by April 25 for the 1st quarter, by July 25 for the 2nd quarter and by October 25 for the 3rd quarter.
At the end of the tax period, organizations pay tax by March 31, and individual entrepreneurs by April 30. As with any other tax regime, the taxpayer is obliged to organize accounting of settlements with the budget and the procedure for calculating the simplified tax.
Accounting for settlements is kept on accounting account 68.12, the debit of which shows the repayment of tax obligations, and the credit shows the accrual of tax in connection with the simplified tax system. Account balance 68.12 shows the total of settlements for the selected period.
Accrual of simplified tax system, postings:
| Dt 99 Kt 68.12 | Advance payment accrued for 1 sq. |
| Dt 99 Kt 68.12 | Advance payment for half a year has been accrued |
| Dt 99 Kt 68.12 | Advance payment accrued for 9 months |
| Dt 99 Kt 68.12 | Tax accrued for the year |
| Dt 68.12 Kt 51 | Tax paid |
Source: //ppt.ru/art/buh-uchet/provodki-po-usn
Sample act for writing off postage stamps
The act of write-off of goods (form TORG-16) is used to document damage that occurs for various reasons, loss of quality of goods (inventory) that are not subject to further sale. The document is drawn up in triplicate. The write-off act is signed by members of the commission, whose powers are confirmed by the head of the organization. If necessary, the report is drawn up with the participation of a representative of sanitary or other supervision. One copy remains in the accounting department and serves as the basis for writing off losses of inventory items from the financially responsible person; another copy of the act is transferred to the department that made the write-off; the third remains with the financially responsible person. Form TORG-16 was approved by Resolution No. 132 of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1998 and is used if damage or defects are detected in the product. Cash documents" (the value is set by default), Credit Cor. account - account 302.21 "Settlements for communication services" and the necessary analytics.
- The intended purpose is the basis for the cash register.
- Accepted from and Reason - indicate the counterparty from whom monetary documents are received at the institution's cash desk, and the agreement concluded with him.
Rice. 2 1.3. On the Payment Explanation tab (Fig. 3):
- The data necessary for generating accounting records is indicated: Amount, KFO, KPS.
- Monetary document is an element of the Monetary Documents directory, where information about the name, unit of measurement and denomination of the monetary document is indicated.
- Quantity - the number of received cash documents.
- Amount - determined automatically if the nominal value is indicated in the Cash Documents directory, or filled in manually.
Rice. 3 1.4. The cost of damaged postal envelopes was written off KDB 1.401.10.172 KRB 1.201.35.610 120 Expenditure cash order (stock) Certificate of damage to monetary documents Act on inventory results (f. 0504835) Inventory list (matching statement) of strict reporting forms and monetary documents (f. 0504086) Expense cash order (f. 0310002) 1. Receipt of cash documents at the cash desk 1.1. To reflect the receipt of monetary documents at the cash desk of the institution, use the document Receipt Cash Order (stock) in the section Cash - Cash Office of the organization (Fig. 1). Rice. 1 1.2. To correctly reflect transactions and generate primary accounting documents, it is necessary to take into account the following points (Fig.
3.5. The document Expense cash order (stock) generates the following accounting records (Fig. 16): Fig. 16 3.6. After posting the document using the Print button (Fig. 15), you can print the Cash receipt order (f. 0310002) - Fig. 17. Fig. 17 <<- return to the beginning of the article 4. Reports generated based on the entered data 4.1. Incoming and outgoing cash orders with the entry “Stock” are registered in the Cash Order Registration Journal (Fig. 18), which can be generated in the Cash Department section. Rice. 18 4.2. You can analyze the movement of monetary documents on account 201.35 using the regulated register Card for accounting of funds and settlements (f. 0504051) in the section Accounting and reporting - Accounting registers and reporting (Fig. 19). Rice.
The form for the act of writing off goods has the form TORG-16, which was approved by Resolution No. 132 of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation of December 25, 1998 and is used in the event of damage or defects in the product. There are currently no unified forms of primary documents that confirm the write-off of goods on other grounds. If it is necessary to write off products due to lack of market demand or obsolescence, a free form act is drawn up.
The act of write-off indicates all information about the product subject to write-off, namely: its name, article, price, quantity, weight, unit of measurement and reason for writing off this product. The act of writing off goods is drawn up in 3 copies.
AttentionHorns and Hooves” and are subject to write-off stamps and envelopes in the following quantities: - 28 (pieces) stamps of 290 rubles each in the amount of 8,120 (Eight thousand one hundred and twenty) Belarusian rubles - 40 (pieces) stamps of 230 rubles each in the amount of 9,200 (Nine thousand two hundred) Belarusian rubles - 44 (pieces) envelopes of 420 rubles each in the amount of 18,480 (Eighteen thousand four hundred and eighty) Belarusian rubles. Total amount of 35,800 (Thirty-five thousand eight hundred) Belarusian rubles. Reason: log of outgoing correspondence.
Chairman of the commission: Members of the commission: But I don’t understand what the 20 count has to do with it. Stamps are taken into account on 331, these are strict reporting forms. The appearance of postage stamps under the new Rank Plan is maintained on rack 331 Penny documents in national currency. The debit of this account shows the receipt of postage stamps at the cash register of the business, and the credit shows their receipt.
BOARD OF HONOR SEND APPLICATION ADVERTISING NEWS SEARCH ADVERTISING our conditions Please tell me how someone writes off envelopes and stamps. Is it necessary to list where and when each stamp and envelope were used? Belarus << to the list of questions Mandatory. 3 lists are better. The first is when you sign the conferences (just an inventory will do), the second is an inventory of correspondence, which you put in an envelope with the attachments of all letters certified by the head (or better yet, a notary), and finally, the third list to the act of a commission of three people confirming that the conferences are in accordance lists were dropped (in a good way) into the mailbox.
Belarus conferences,,,,, hmm, I don’t know, I got stuck through the “fe”. Belarus Masha 08/10/2012 10:34:01 Is it really illegal to do this or is there a simpler way? Belarus They made fun of you, not entirely successfully. You have d.b. Handbook of 1C:BGU 8 for government institutions Example The government agency “Committee for Technical Supervision for the Osanovsky District” purchased stamped postal envelopes by bank transfer for a total amount of 500 rubles. As a result of damage, part of the envelopes was written off in the amount of 120 rubles. No. Operation Dr Kt Amount (rub.) Document in 1C Primary document Incoming Outgoing Internal 1 Marked postal envelopes have been received at the cash desk of the institution KRB 1.201.35.510 KRB 1.302.21.730 500 Receipt cash order (stock) Agreement, supplier documents Receipt cash order (f. 0310001) 2 Money was transferred for postal envelopes KRB 1.302.21.830 KRB 1.304.05.221 500 Application for cash expenses Application for cash expenses (f. 0531801) Extract from the personal account of the recipient of budget funds (f. 0531759) Appendix to the Extract from the personal account of the recipient budget funds (f.
Writing off stamps and envelopes