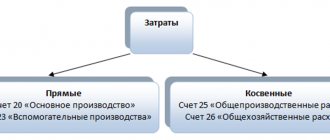
General operating expenses (OCC) are expenses not directly related to production or other core activities. However, they are necessary for the normal functioning of any organization. These are indirect costs that can be distributed between production facilities, types of products and are written off taking into account the method chosen by the organization. The composition of the operational and maintenance work, the accounting procedure, the method of their distribution and write-off, as a rule, are determined by the type of activity of the business entity.
General business expenses in the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations.
Scope of application
Every day, company management is faced with management costs that have nothing to do with production, sales or revenue-generating services. The question arises of how to take them into account correctly. Accounting 26 makes it easy to do this. First, all general business expenses are taken into account in this account, and then written off to the debit of accounts 90 “Sales”, 20 “Main production”, 29 “Service of production and economy” or 08 “Investment in non-current assets”, depending on the direction of the main activity of the enterprise.
Money is leaving
The most active users of account 26 are organizations related to the provision of services: dealers, brokers, forwarders, agents. It can include all expenses and be credited to sales accounting.
Trading companies rarely turn to account 26 in their activities. It is easier for them to assign account 44 “Sales expenses” for their business expenses. They attribute all costs to him.
Organizations engaged in agriculture distribute their general business expenses at the close of the reporting period once a month or quarterly by type of production. The exception is the cost of feed, seeds, raw materials for semi-finished products and materials. At the end of the year they are subject to adjustment to the level of actual costs. Also, if the company’s accounting policy allows this, they can be written off to the debit of account 90 “Sales”.
Construction companies, as well as house-building factories, mechanization departments, factories for the production of building materials 26 use accounting accounts to account for the costs of servicing workers, the costs of organizing work on construction sites, and maintaining administrative and economic personnel. General business expenses at the end of the month are written off to the debit of account 20.4 “Costs of construction and installation work.” Factories and house-building plants distribute them according to the types of services provided and products produced. And the mechanization departments are proportionally divided between the services provided to third parties and the construction and installation work performed.
Note! In budget accounting, the purpose of account 26 will be completely different. There it will be off-balance sheet. Budgetary institutions take into account property transferred for free use in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 157N dated December 1, 2010.
Construction
What is considered OCR?
According to the Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts (pr. 94n of the Ministry of Finance), the following can be legally classified as OMR:
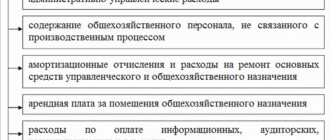
- remuneration for the AUP of the central office with contributions to the Funds;
- depreciation of fixed assets, intangible assets used in the management process;
- rental payments if buildings for non-industrial purposes are used under a lease agreement;
- expenses for maintaining non-industrial buildings, including payments to utility services;
- labor protection costs;
- payment for business trips of the AUP;
- entertainment expenses;
- office, banking, expenses, auditor services, etc.
Regulatory acts currently do not contain an exhaustive list of environmental protection measures. The main feature that allows costs to be classified in this category is the fact that they are not directly related to the production of goods, work or provision of services.
On a note! When deciding whether to consider expenses general production or general economic, for example, if an organization has a branch, it is advisable, in addition to the ratio of its costs directly to the production process, to evaluate such a factor as the participation of the responsible persons of the branch in the production of products (management of the organization as a whole). In certain cases, the territorial distance of the division (branch) from the company’s central office plays a role.
Account characteristics
What activities can be classified as general business expenses:
- cash payments to employees of the administrative and economic apparatus who do not bring direct income to the company: directorate, accounting department, secretariat. Account 26 reflects wages, bonuses, vacation pay and other incentives paid by the company;
- insurance premiums paid by the company from the earnings of employees of the administrative and economic apparatus, subject to payment to the budget of the Russian Federation;
- depreciation of intangible assets and fixed assets acquired for the needs of the administrative and economic apparatus;
- rent, except for profit-generating premises: production workshops, retail premises, etc.;
- costs of repairing operating systems not related to production activities;
- expenses associated with the provision of consulting and information services;
- costs of materials that will be used for management needs;
- entertainment expenses;
- staff development;
- security of premises;
- recruitment;
- subscription to periodicals;
- software;
- telecommunications, communications, internet;
- business trips of administrative and economic staff.
To account for general business costs, enterprises use a full or partial journal-order form. They reflect information on payroll, consumption of materials, the total amount of wear and tear on the operating system, enter transcript sheets containing various financial expenses, etc.
Note! Payment for services rendered for the maintenance of general business personnel is all 26 accounts.
Education
Composition of general business expenses
Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n clearly establishes that account 26 in accounting is used to reflect general business expenses (OHR).
Such expenses of an enterprise include some types of expenses that cannot be attributed to the main production, but without which the implementation of the main activities would become impossible or problematic. The following types of costs are attributed to accounting account 26 (for dummies):
- Remuneration of management personnel, as well as taxes and insurance premiums accrued on the salaries of administrative and managerial personnel.
- Fixed assets, intangible assets, which are used to ensure the work of the enterprise administration. As well as depreciation charges for such property.
- Material supplies (stationery, fuels and lubricants, spare parts) that are purchased for management, ensuring the operation of the farm and the AUP.
- Payment of rental and leasing payments for property purchased directly for the needs of the company administration. For example, renting office space.
- Information, consulting, legal and other support services of third-party organizations and firms that are used in the company’s activities as auxiliary.
For exceptional types of activities, account 26 can include not only general business expenses, but also expenses for core activities. For example, the activities of brokerage companies. Such features should be described in detail in the accounting policies.
Closing
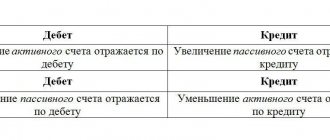
To determine active or passive account 26, you need to pay attention to how costs are reflected on it. They are distributed as a debit and written off as a credit to the cost accounts for the main production. Thus, account 26 in the accounting department is active. It closes monthly. All balances are transferred to the cost of production. The balance at the end of the period should be zero.
There are two ways to form costs:
- At actual cost (full).
- Direct costing or at reduced cost.
An enterprise can use only one method in its activities, which must be fixed in its accounting policies. It will not be possible to change it. Closing the account 26 will depend on the chosen method.
If the organization uses the formation method at actual cost, then in this case general business expenses will be closed to account 20 “Main production”. If the company has service or auxiliary workshops that provide services to third parties, then the costs must be divided between accounts 23 “Auxiliary production” and 29 “Service production and facilities”. The procedure for writing off and distributing general business cost bases must also be reflected in the accounting policy. The accounting entry in this case will look like this:
Dt20 (23, 29) - Kt26
How to close the 26th account if the company has chosen the direct costing method. Everything is very simple. General business expenses when working at a reduced cost will be taken into account in account 90.2 “Cost of sales”. Wiring sample:
Dt90.2 - Kt26
In accounting, problems sometimes arise with writing off general business expenses. Why is account 26 not closed? Most likely he has an opening balance, which he shouldn't have. There are several reasons that, by eliminating them, can solve this impossible question:
- First of all, you need to check the accounting policy settings in the accounting program. It should indicate the method of cost formation at the enterprise, as well as information on how general business costs are distributed.
- The second possible reason may be incorrect analytical accounting for general business expenses. You should check the correctness of the distribution of costs by type of item, as well as by division of the company. Most likely, an error will be discovered in the details of the operations performed.
The accountant closes the month
. What to do if there was no revenue during the reporting month. There is also a way out. You need to create a sale for 1 kopeck and send it to a fake counterparty. After this, you can close general business expenses from account 26 to account 20 “Main production”. After this, all that remains is to manually reverse the extra penny at the end of the year.
An example of how to close account 26 manually by posting:
Dt26 - Kt02 - depreciation on fixed assets has been accrued.
Dt26 - Kt10 - inventories are written off.
Dt26 - Kt70 - wages accrued to the administrative and economic apparatus.
Dt26 - Kt68 (69) - insurance payments have been calculated.
Dt20 (21, 29, 90) - Kt26 - costs have been written off.
Important! If general business expenses are taken into account in tax accounting as indirect, then temporary differences invariably arise. They must also be written off by postings.
Structure of OCR in the table
A complete list of expenses for general business needs with examples:
| Main categories | Compound | Examples |
| Administrative and management expenses | Salaries of management personnel, secretariat, accounting, personnel department and legal department. Insurance premiums and other charges on the earnings of the AUP. Representation expenses of the organization. Expenses for business trips and business trips. Payment for postal services, telephony, internet, communications, etc. Security services. | The official salary and bonus of the director of the organization, insurance premiums for the reporting month. Payment for postage stamps for sending business correspondence. |
| Repair and depreciation | Costs of an economic entity for the repair of non-production equipment. Depreciation charges for fixed assets and intangible assets not involved in the production cycle. | Repair of the CEO's company car. Depreciation for office premises of the AUP and accounting department. |
| Material support | Acquisition of inventory and intangible assets to meet general economic needs. | Purchasing computers for the secretary. Purchasing specialized software for accounting. |
| Rent | Payment of rent for AUP. | Calculations of monthly rental payments for the office of the organization's directorate. |
| Budget payments | Taxes, fees, contributions. | Payment of fiscal payments to the budget of the Russian Federation. |
| Other | Consulting, information, audit services. | Payment for external audit control. |
How does account 26 correspond with other accounts?
It corresponds with other accounts in the chart of accounts, both in debit and credit. Basic debit entries:
Dt26
Dt26
Correspondence with loan accounting accounts:
Kt26
Correcting errors in accounting
The use of automated accounting greatly simplifies accounting. Errors are not uncommon in specialized accounting programs. Why account 26 is not closed:
- Check the accounting policy settings in the software product. Follow the prompts that the program gives, or contact the developers.
- Check that transactions are recorded correctly in the special program. In most cases, errors lie in misgrading (for example, an accountant made a mistake in the details or nomenclature).
- Check the dates of registration of transactions. For example, in the 1C software, the dates of registration of a business transaction play a key role in the formation of accounting data.
To avoid mistakes, systematically create the turnover sheet and check the accounting card 26.
Postings
Which entries are most often used in accounting when writing off general business expenses:
- Calculation of depreciation of fixed assets for administrative and economic needs - Dt26 - Kt02.
- Costs associated with OS repairs by the organization itself or with the involvement of third-party specialists - Dt26 - Kt10 (60, 76).
- Depreciation was accrued for intangible assets (intangible assets) for administrative and economic needs - Dt26 - Kt05.
- The costs of renting premises that are not commercial or industrial are reflected - Dt26 - Kt76 (60).
- Costs for audit, information, consulting services - Dt26 - Kt76 (60).
- Expenses for training employees of the administrative and economic apparatus - Dt26 - Kt76 (60).
- Taxes written off - Dt26 - Kt68.
- Salary of administrative and economic personnel - Dt26 - Kt70.
- Insurance premiums - Dt26 - Kt69.
- Conducting official receptions, business meetings and negotiations, transport support - Dt26 - Kt71 (60, 76).
As can be seen from the example entries, all general business expenses are reflected on Dt26, and according to Kt26 they are written off to cost and sales.
A business meeting
Accounting for general business expenses based on an example
Synthetic accounting of general business expenses during the month is carried out in correspondence with the accounts:
| Dt 26 Kt 02 | Depreciation of equipment used for administrative and economic needs has been calculated. |
| Dt 26 Kt 05 | Depreciation was calculated on intangible assets used in the administrative and economic sphere |
| Dt 26 Kt 10 | Raw materials, supplies, and household equipment used in the administrative and economic sphere have been consumed |
| Dt 26 Kt 21 | Semi-finished products of our own production were released for administrative and economic purposes. |
| Dt 26 Kt 43 | Part of the finished products is used for our own administrative and economic needs |
| Dt 26 Kt 60 (76) | Costs for the services of suppliers and contractors are reflected on the basis of acts for the general economic needs of the enterprise |
| D 26 Kt 70 | Accrued wages for general business personnel |
| Dt 26 Kt 69 | The amounts of insurance payments to extra-budgetary funds related to the remuneration of general business personnel were included in expenses. |
| Dt 26 Kt 71 | In accordance with the advance report of the accountable person, entertainment expenses were written off |
| Dt 26 Kt 97 | A share of deferred expenses is written off to general business expenses |
Example
During the month, the architectural and design bureau incurred the following expenses.
The salary of employees performing design work amounted to 500,000 rubles.
The salary of the administration - the director of the organization and the accountant - amounted to 120,000 rubles.
The amount of insurance payments to funds related to administration salaries amounted to 36,240 rubles.
Depreciation of equipment for geological exploration amounted to 25,000 rubles, depreciation of a laptop and multifunctional device, which the accountant uses in his work, amounted to 5,000 rubles.
The cost of consumables for the multifunctional device purchased for the administration amounted to 6,000 rubles.
During the month, the following transactions are generated on account 26:
- Dt 26 Kt 70 - 120,000 rub. — salaries of the director and accountant were calculated.
- Dt 26 Kt 69 - 36,240 rub. — the amounts of contributions to the director’s and accountant’s remuneration funds are expensed.
- Dt 26 Kt 02 — 5,000 rub. — depreciation of the laptop and multifunctional device has been calculated.
- Dt 26 Kt 10 - 6,000 rub. — consumables for a multifunctional device were used for the needs of the administration.
Subscription to electronic publications
Situation: how to reflect in accounting the costs associated with subscriptions to electronic periodicals?
Accounting for expenses for periodical electronic publications depends on the type of contract.
Subscription to electronic periodicals can be issued:
- an agreement for the provision of paid information services for the provision of a copy of a periodical in electronic form (clause 2 of Article 779 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- a license agreement under which non-exclusive rights to use the electronic resources of the publishing house are transferred (Article 1367 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In the first case, pay for the subscription to the electronic publication in accounting as an advance payment (clause 3 of PBU 10/99). Reflect the advance payment using the following entries:
Debit 60 subaccount “Settlements for advances issued” Credit 51 – advance payment for subscription to an electronic magazine (newspaper) is transferred.
After receiving the issue of the magazine (newspaper) in electronic form, make the following entries:
Debit 26 (44) Credit 60 subaccount “Settlements with publishing houses” – the cost of the next issue of an electronic magazine (newspaper) is written off as expenses;
Debit 60 subaccount “Settlements with the publishing house” Credit 60 subaccount “Settlements for advances issued” - the amount of the advance is offset against repayment of accounts payable.
This procedure is based on the provisions of the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 60, 44, 26), paragraphs 3, 18 and 19 of PBU 10/99.
In the second case, for accounting purposes, intangible assets received for use are accounted for on an off-balance sheet account in the valuation established by the agreement (clause 39 of PBU 14/2007). The chart of accounts does not provide for a separate off-balance sheet account for accounting for intangible assets received for use. Therefore, the organization needs to independently open an off-balance sheet account and consolidate this in its accounting policies for accounting purposes. For example, account 012 “Electronic subscription publications”.
The one-time payment for the granted right to use the electronic publication should be reflected in accounting in account 97 “Deferred expenses” and included monthly in expenses for ordinary activities during the validity period of the license agreement (paragraph 2, clause 39 of PBU 14/2007).
In accounting, reflect the prepayment by posting:
Debit 60 Credit 51 – the cost of the right to use the electronic publication has been paid.
After gaining access to the electronic publication, make notes:
Debit 012 “ Electronic subscription publications ” – the cost of the right to access an electronic publication is taken into account;
Debit 97 Credit 60 – the cost of the right to access the electronic publication is charged to deferred expenses.
Determine the mechanism for transferring future expenses to cost yourself. The following expenses can be written off:
- evenly;
- in proportion to the income received from sales;
- in other ways.
Determine the period for writing off expenses by the period for which access to the electronic subscription publication was provided. The beginning of this period (the beginning of the period of use of the subscription publication) is determined by the format of the software provided. For example, for the Internet version - from the moment the code is activated.
The period of use of the subscription publication is specified in the contract.
The established procedure for writing off future expenses should be fixed in the accounting policy for accounting purposes (clause 4, 8 of PBU 1/2008, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 12, 2012 No. 07-02-06/5).
Monthly during the period of access to the electronic subscription publication, make the following entries:
Debit 26 (44) Credit 97 – part of the payment for using the electronic publication has been written off.
This procedure is based on the provisions of the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 97, 60, 44, 26), paragraphs 18 and 19 of PBU 10/99.
Attention: many write off deferred expenses at a time. They want to understate large profits of the current period or simply out of ignorance. Officials will be fined for this. In some cases, the organization will also suffer. However, you can avoid trouble.
In accounting, reverse the entry that was written off by the RBP at a time. Remember, this can only be done within the year in which the mistake was made.
r />
For example, the Alpha organization received a certificate of conformity for its products valid for five years. The cost of the certificate was 50,000 rubles. According to the accounting policy at Alfa, RBP is written off evenly.
Error!
Debit 20 Credit 76 – 50,000 rub. – the fee for the certificate is taken into account as part of expenses for ordinary activities.
Correctly like this:
Debit 97 Credit 76 – 50,000 rub. – the fee for the certificate is included in deferred expenses.
Monthly:
Debit 20 Credit 97 – 833 rub. (RUB 50,000: (5 years × 12 months)) – deferred expenses are written off.
Here's how to fix the error in this situation:
Debit 20 Credit 76 – 50,000 rub. – the amount previously erroneously included as expenses for ordinary activities is reversed;
Debit 97 Credit 76 – 50,000 rub. – the fee for the certificate is included in deferred expenses.
At the same time, expense the amounts written off for the past months. For example, if three months have passed since costs were accepted for accounting:
Debit 20 Credit 97 – 2500 rub. (3 months × (50,000 rubles: (5 years × 12 months))) – deferred expenses are written off.
Results
General business expenses are written off to the debit of cost accounts 20, 23, 29 if the products are accounted for at full production cost.
If the company determines the reduced cost of production, general business expenses are written off to cost of sales. In the absence of activity and sales revenue, account 91.2 “Other expenses” is included in the postings for writing off expenses. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.