Suspension of a company's activities (temporary downtime) occurs for various reasons:
- due to the fault of the employee or employer;
- under the influence of external circumstances.
Over the past few months, organizational leaders have increasingly decided to issue downtime orders amid the spread of coronavirus.
The list of unforeseen circumstances includes: failure by the counterparty to fulfill its obligations, revocation of a license, exposure to natural forces. During downtime, the enterprise or one of its divisions does not function, but the employee is required to be at the workplace. Absence of personnel is allowed only if the employer indicated this in the order.
Legislative regulation
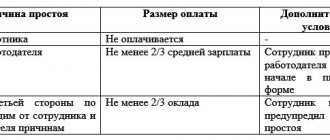
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not have a separate chapter devoted to this term. It is not clear whether this period should be classified as working time or rest time. In Art. 72.2 provides a meager definition that downtime is a “temporary suspension of work.” It can have different reasons - it is important whose fault the malfunction occurred:
- Employer;
- Employee;
- Due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties.
Downtime caused by an employee has no legal consequences and is not regulated by law. But the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the responsibility of the employer for dishonest attitude towards their duties, which caused disruptions in production, and also establishes additional rights for employees for this period.
In practice, it is difficult to prove whose actions caused downtime at work. Here's a simple example: sales figures have decreased. On the one hand, the employer may refer to a drop in demand, but on the other hand, this may be caused by illiterate business practices and negligence. Courts, as a rule, take the side of workers if management has not ensured maximum production capacity.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not regulate the permissible downtime due to the fault of the employer, which frees his hands. In fact, he can repeatedly extend this period until the reasons that caused the failure are eliminated. The main thing is that the required documents are completed on time.
How to create an order
The suspension order is drawn up in the form approved by the organization. There is no legally established or recommended form.
The document includes information:
- justification for stopping work. Specify one of four reasons: economic, technological, technical or organizational in nature, without being more specific;
- moment of beginning;
- end moment. If it is difficult to determine the exact moment, write “until the causes are eliminated”;
- a list of employees or departments to which the order applies;
- payment order;
- It is permissible to indicate whether employees go to work during a specified period or can stay at home. The period is working time, so personnel must be at their workplaces. Absence without permission is equivalent to truancy. But if there is no need for employees to be present, the organization has the right to separately indicate in the order that employees are not required to be at the workplace during this period.
The employees who are affected by the order familiarize themselves with it by signing it.
Reasons for suspension of work
The main factors include:
- Economic. These are common difficulties caused by financial crises within the country and in production itself, and a lack of material and raw materials. Responsibility lies with the employer, since there is a business risk.
- Technological. May be caused by the reorganization of the working mechanism and the introduction of new production methods.
- Organizational. A common example is a change in the form of an enterprise in the event of a division, merger or reorganization.
- Technical. These include equipment upgrades that require employee training, or equipment breakdowns. Technical reasons can be a consequence of the actions of both the employee and management. If the employee’s guilt is proven, then payment for downtime is not provided.
The legislator does not single out force majeure circumstances (emergency situations, disasters) as special reasons, but in fact they relieve the employer of blame and change the formation of wages during this period.
The employee was forced to go on leave without pay for the duration of the downtime
From Art. 128 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation it follows that leaves without pay are divided into those that the employer can provide to the employee, and those that he is obliged to provide. But in both the first and second cases, the basis for granting such leave is the employee’s initiative and his voluntary expression of will. The possibility of sending an employee on leave without pay at the initiative of the employer, although based on the employee’s application, but due to circumstances related to the activities of the employing company, is not provided for by labor legislation.
On June 27, 1996, the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation gave clarification No. 6 “On leaves without pay at the initiative of the employer,” in which it indicated that such leaves can only be provided at the request of employees for family reasons and other valid reasons. “Forced” leaves without pay at the initiative of the employer are not provided for by labor legislation.
How is an employee's time paid?
Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 157 established the norm on the minimum wage for employees during the suspension of activities. In this case, the calculation procedure depends on the reasons that led to it. Guaranteed payment for downtime due to the obvious fault of the employer is 2/3 of the employee’s average earnings. It includes not only the tariff rate, but also allowances, bonuses and other required payments.
An example of such a calculation - let the salary be 20,000 rubles + a guaranteed monthly bonus of 50% of the tariff rate. The calculation for 5 days looks like this: (30000/29.3) * 5 (days) * 2/3 = 3412.97 rubles.
In the event of force majeure, payroll changes and payment for downtime due to circumstances beyond our control will be 2/3 of the salary. For employees working at a tariff rate, there is no difference, but in production most often they set a small salary, and decent wages are formed through incentive bonuses. Therefore, managers try to prove their innocence in causing difficulties so that downtime is paid at a lower rate.
If during this period the employee goes on sick leave, then he is not provided with temporary disability benefits. When sick leave begins before the suspension of production or ends after it, the calculation is made for the days actually worked. The employer is responsible for failure to pay compensation during downtime. In this case, he faces a fine and possible loss of his position.
The downtime order was issued by an unauthorized person
The order to declare downtime must be signed by the appropriate person (the head of the organization or another authorized person). If an order is issued by an unauthorized person, the declaration of downtime may be considered illegal.
Arbitrage practice. As the Khabarovsk Regional Court emphasized in the appeal ruling dated July 20, 2012 in case No. 33-4009/2012, the director of the organization is not authorized to issue an order for downtime after the introduction of bankruptcy management. In such a situation, only the bankruptcy trustee can do this.
Procedure for registration of downtime
If reasons arise that lead to a disruption in production, the employee can inform management, both orally and in writing, about the start of downtime due to the fault of the employer and the inability to continue working. The management itself can initiate registration of downtime, but is reluctant to do so, thereby increasing its costs.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Article 91 gives the employer the obligation to keep a log of hours worked by each employee in the approved form. It must indicate downtime. .
Step by step procedure:
- The employer issues an order on downtime, indicating the start date, a list of employees whose work is suspended and their responsibilities, and the salary amount for this period.
- The downtime order is handed over to employees for review against signature.
- If the enterprise has completely stopped production, then within 3 days the management reports this to the employment service.
- An appropriate note is made on the working time sheet.
The employer may offer affected employees to temporarily transfer to another position while maintaining average income or to take a vacant position with higher or similar qualifications.
Example of an order:
If management does not begin the registration procedure, then employees can draw up a collective act of downtime in free form, outlining the reasons and circumstances of the incident. It is transferred either to the board of directors of the enterprise or to a trade union organization.
Act template:
Drawing up documents when idle
A certain procedure for registering downtime.
An act on the beginning of downtime can be issued both for the entire structural unit and for the entire organization as a whole, taking into account the circumstances that caused the downtime. This act is drawn up by officials of the organization.
When drawing up the act, it is advisable to have the participation of management, representatives of the trade union and the workforce of the enterprise. But the composition of the commission is determined depending on the reasons for the downtime.
For example, if the cause is a breakdown of equipment, the chief engineer or other technical employee should be involved, who must establish the cause of the breakdown and the time frame for its elimination. Or if the reason is the lack of raw materials for production, the head of the supply department and an economist are involved. The law does not define a standard form for registering a downtime act.
Downtime should be formalized by an act in any form using the mandatory details established in domestic office work. It is imperative to indicate the reasons that led to the suspension of work.
Example of a downtime order
04/11/2016 MILKMAN LLC ORDER
Moscow
No. 22-k
About enterprise downtime
Having studied the circumstances of the downtime and its reasons specified in the Act on downtime of the enterprise dated 04/11/2016 No. 2, guided by Art. 113 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the norms of the Collective Agreement for 2021.
I ORDER:
- Approve the Act on the downtime of the enterprise dated 04/11/2016 No. 2;
- Consider the time 8:00 on April 14, 2016 as the beginning of the plant’s downtime;
- Set the downtime period from 8:00 04/11/2016. until 24:00 04/30/2016;
- Approve a list of activities during downtime and overcoming its consequences;
- Allow the employees of the enterprise not to go to work during downtime, except for the head of the supply department E.K. Romanyuk, the head of production S.I. Konovaluk, the head of the personnel department A.G. Stetsenko, to go to work every day on working days and mark their arrival at work and leaving work;
- Head of the HR Department Stetsenko A.G. familiarize the employees of the enterprise with the order before the start of downtime and ensure that downtime is recorded;
- The HR department will promptly inform employees about the resumption of work, the person responsible is the head of the HR department A.G. Stetsenko;
- The accounting department of the enterprise, according to time sheet data, pays for downtime in the amount of two-thirds of the employees' tariff rate. Responsible - chief accountant Tretyakova M.T.;
- Approve measures to overcome enterprise downtime. Responsible - Head of the Supply Department Romanyuk E.K.;
- Control over the implementation of this order is assigned to the head of production Konovaluk S.I.;
Reason: Act on business downtime dated April 11, 2016 No. 2.
Director (signature) S.I. Dronov
The following have been familiarized with the order:
Head of Human Resources (signature) A.G. Stetsenko (04/11/2016)
Chief accountant (signature) M.T. Tretyakov (04/11/2016)
Head of the Supply Department (signature) E.K. Romanyuk (04/11/2016)
Head of production (signature) S.I. Konovaluk (04/11/2016)
Chairman of the trade union committee (signature) N.I. Savchenko (04/11/2016)
Responsibilities of the employee
What do employees do during downtime? This issue is resolved individually between them and the employer. The order must reflect the time or schedule of workers’ stay on site. In any case, forced downtime due to the fault of the employer does not constitute additional leave, and employees must be present at production.
The employer may offer them to stay at home, but this fact is documented. Otherwise, missing a day of work will be considered absenteeism and will not be paid. Management sometimes uses a trick and offers to give employees leave without pay. In this case, employees also lose the right to compensation.
The suspension of the enterprise's activities is unpleasant for both sides of the issue. Timely registration of downtime will allow you to maintain long-term relationships with employees and quickly restore production.
How to draw up an order to end downtime
There is no approved recommended form of termination order, therefore the employer has the right to proceed from the forms of internal documents adopted by him.
The document should indicate:
- details of the document that declared the suspension;
- the reasons for the introduction and an indication that production activities are being resumed;
- return to work date;
- list of employees returning to work.
All employees called to work are notified and introduced to the document for signature.
How to record on a timesheet
To reflect this period, codes “RP” or “31” are provided. They are suitable if activities have been suspended for 1 or several days. If a person did not work for several hours during a shift, then additional lines can be entered into the timesheet. For example, due to a machine breakdown, a foreman worked only 4 hours out of 8. In this case, the following is written on the report card:
- the first line is the code “I” (“01”);
- second line - number 4;
- third line - code “RP” (“31”);
- the fourth line is the number 4.
If the suspension of activity is due to the fault of the employee, other codes are used - “VP” (“33”), and if the reasons for the downtime are objective - “NP” (32).
Why is it needed?
If a decision is made to temporarily suspend the activities of an individual employee, a division or an entire company, the employer must:
- inform the team or individuals about the situation;
- approve changes to the work schedule;
- determine the payment procedure for such a period.
All these points need to be documented, so an order for forced downtime is drawn up.
IMPORTANT!
In connection with the situation with COVID-19 and the publication of Presidential Decree No. 206 of March 25, 2020 “On declaring non-working days in the Russian Federation,” the employer is obliged to provide employees with paid days off. If it is possible to switch to remote work and the employee does not mind, then an agreement must be concluded. If there is no opportunity to work remotely, and the employer forces you to write an application for leave at his own expense or for a part-time transfer, he is breaking the law, the employee has the right to complain to the State Labor Inspectorate.
The employee is paid for downtime if he gets sick during this period
The question of whether it is worth paying for downtime if an employee is sick until recently led to numerous disputes. Specialists from the Federal Social Insurance Fund of Russia believed that benefits should not be accrued if the employee fell ill during a period of downtime (letter dated March 22, 2010 N 02-03-13/08-2497). However, the courts took a different opinion.
Arbitrage practice. The Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, in Resolution No. 17762/09 dated May 18, 2010, indicated that the legislation in force at that time did not establish the dependence of the payment of benefits on when the employee fell ill (before the start of the downtime or after).
It is interesting that the point of view of the courts did not find support among legislators. From 01/01/2011, amendments were made to the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability due to maternity” (hereinafter referred to as Law N 255-FZ). According to the new edition of Part 7 of Art. 7 of Law N 255-FZ, a temporary disability certificate is paid only if the employee’s illness occurred before the organization declared downtime.
Arbitrage practice. In the ruling of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated January 17, 2012 N 8-О-О “At the request of the Levoberezhny District Court of the city of Lipetsk to verify the constitutionality of paragraph 5 of part 1 of Article 9 of the Federal Law “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” it is stated : p. 5 h. 1 tbsp. 9 of Law No. 255-FZ, which excludes the assignment of temporary disability benefits to the insured person during downtime that occurred during downtime, is due to the intended purpose of this type of insurance coverage and in systemic connection with Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation cannot be considered as violating the constitutional rights of citizens.
Translation during downtime
Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code allows the employer to transfer a subordinate to another position during downtime without asking his consent. But only if the downtime is caused by emergency circumstances (natural/man-made disaster, industrial accident/accident, earthquake, fire, flood, etc.), and for a period of no more than one month. If such a temporary transfer involves performing work of a lower qualification, the employee’s written consent will be required. At the same time, wages at the new place should not be less than the average wage at the previous place of work (where the downtime occurred).
In other cases, the transfer of an “idle” employee to another job is possible only with his written consent (Article 72.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).