Reasons for downtime
The provisions of Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation distinguishes three types of downtime:
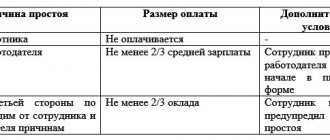
| View | Causes |
| Due to the employer's fault | Temporary suspension of the organization's activities by executive authorities, crisis at the enterprise, violation of contracts with contractors, lack of orders |
| Due to the employee's fault | Violation of safety requirements or labor discipline, theft or damage to equipment, etc. |
| Due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties | Disasters, accidents, natural disasters, fires, etc. |
Simple is also divided into several subclasses:
- Short-term: occurs only for a few days and usually affects one work shift.
- Long-term: lasts for weeks. Initially, work may not be available to a limited number of workers, but then the scale expands to the entire team.
- Local: only one department or several people from it are not working.
- Massive: labor activity throughout the organization has been suspended.
Definition of the term "simple"
According to Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (LC RF), downtime is a temporary stoppage of a company’s work, the reasons for which may be problems of an organizational, technical, technological or economic nature. Thus, the problems due to which you can declare downtime can be different:
- a sharp or gradual drop in demand for a manufactured product;
- shortage of components;
- equipment malfunction, etc.
Also, during a crisis period, an employer may encounter economic difficulties that impede the operation of the enterprise.
How to apply for a simple one: step-by-step instructions
“The first thing an employer needs to do when downtime occurs, regardless of fault, is to issue an appropriate order, indicating in it the reasons for suspending the activities of an enterprise or an individual team,” says N. Komova, an expert at the magazine “Human Resources and Personnel Management of an Enterprise.”
The algorithm of actions in this situation looks like this:
- The employee notifies the manager about equipment malfunctions and other problems that interfere with the implementation of activities. If it is determined that the equipment broke down due to the fault of the manager (for example, untimely replacement of consumables, unless another responsible person is appointed), this is indicated as the reason in the order.
- The employer collects documents confirming the need for downtime and issues an order. It can concern the entire team or individuals. They must be familiarized with the document upon signature.
- If the work of the entire production is suspended, the manager notifies the Employment Center about this (Article 25 of the Federal Law “On Employment”).
- Idleness reports are filled out. They are needed to determine specific days when work was not performed at the enterprise or department.
There is no unified form of an order for downtime, but it must necessarily reflect the following information:
| Top part | Middle | End |
| Name of organization, title of document | The essence is simple | Responsibilities of the accountant and HR employee in this situation |
| Date of preparation | Name of the unit where there is no activity, period indicating the start and end date and time | FULL NAME. and signature of the general director, as well as persons familiar with the document |
Order on duration of downtime
The beginning and end of downtime must be recorded. The manager must issue an order on the duration of the downtime and its payment. Reflect losses from downtime in the act.
Example of downtime design
On January 14, 2015 at 8.00 the driver of the organization Yu.I. Kolesov discovered that the car he was supposed to use for the trip was faulty. Kolesov drew up a memo about the downtime.
Director of the organization A.V. Lvov issued an order regarding the duration of the downtime and its payment.
The occurrence of downtime, as well as the amount of losses from it, the members of the commission recorded in the report.
How is downtime due to the employer's fault paid?
Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation clearly regulates that the downtime period must be paid in the amount of at least 2/3 of the average earnings of employees. If the problem arose due to reasons beyond the control of the parties, then remuneration is calculated based on 2/3 of the salary or tariff rate.
If production is suspended due to the fault of employees, downtime is not subject to payment.
When calculating the average salary, it is necessary to be guided by the norms of Art. 139 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- It is necessary to take into account all types of payments accrued to employees: bonuses, increasing coefficients, bonuses (including one-time ones) received over the last 12 calendar months.
- An enterprise’s internal regulations may provide for its own procedure for calculating average earnings, if they do not worsen the situation of employees and do not contradict the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Let's look at an example of calculating payment for downtime if the manager is to blame:
SDZ x 2/3 x number of days of downtime = total amount payable.
How was the payment calculated to Martynov V.P.:
971.67 x 2/3 x5 = 3238.90 rub. – the total amount to be paid for 5 days of downtime.
Forced downtime must be reflected in the working time sheet in form T-12 or T-13, because it is used to calculate payroll. Opposite the surnames of employees, it is necessary to indicate the letter designation “RP” or the numeric designation “31”, which means the suspension of activities due to the fault of the manager.
The document is filled out by an employee of the HR department or another authorized person, and then transferred to the accounting department.
Payment for forced downtime
The amount of payment for forced downtime depends on its cause (Article 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- if the reason for stopping work is not the fault of the employer or employee, then an amount equal to 2/3 of the employee’s salary is payable, unless otherwise specified in the collective or labor agreement;
- the amount of payments for the period of absence from work due to the fault of the employer is calculated using a special formula. Compensation for downtime is equal to 2/3 of the average monthly salary, including salary, allowances and bonuses. Average earnings are determined in accordance with Art. 139 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Payments for downtime are calculated as a percentage of average monthly accruals to the number of days of downtime using the following formula: (Average daily earnings) x (number of downtime days) x 2/3;
- If the employee’s fault is proven, he is not paid for forced downtime. If the actions of this employee have stopped the activities of other employees, then for them this downtime is classified as downtime for an independent reason and is paid in the amount of 2/3 of the tariff salary.
Watch a video that will tell you about downtime
Example of calculating downtime payment
An example of calculating downtime due to the fault of the employer: gr. Ivanov was in forced downtime due to the fault of his employer from June 1 to June 16, 2017 inclusive, it is necessary to calculate the payments due to him for this event.
Read about whether you can find out your SNILS via the Internet in this article https://otdelkadrov.online/11503-gde-posmotret-nomer-snils-v-kakih-sluchayah-mozhet-ponadobitsya
- Salary gr. Ivanov for a fully worked pay period (12 months before the month of downtime) amounted to 360,000 rubles (30,000 rubles per month), during this period of time he was paid a bonus in the amount of 10,000 rubles, therefore, his earnings for the year amounted to 370,000 rubles.
- Let's calculate the average daily earnings in the billing period from June 1, 2016 to May 31, 2021 inclusive: 370,000 rubles / 248 working days = 1,491.94 rubles.
- Consequently, the payment of gr. Ivanov for forced downtime due to the fault of the employer will be: 1491.94 rubles x 11 working days of downtime x 2/3 = 10940.89 rubles.
It is also necessary to take into account the specifics of including downtime in the length of service when applying for labor pensions. Here, the entire time of a citizen’s official work is taken into account, which includes the total downtime. When applying for an early retirement pension, calculating the length of service does not imply the inclusion of a period of downtime, regardless of its reason.
An example of calculating downtime in the absence of the culprit of the incident: let’s take the initial data of the previous example about gr. Ivanova. The absence of the culprit of downtime involves the payment of 2/3 of the salary without additional charges.
Therefore, the calculation formula will look like this: 30,000 rubles (monthly salary) x 2/3 (calculation rate) / 21 working days (in June 2021) x 11 working days of downtime = 10,476.19 rubles.
About how to view the funded part of the SNILS pension using this link https://otdelkadrov.online/11509-kak-proverit-pensionnye-nakopleniya-po-snils-onlain-cherez-drugie-istochniki
Correct registration of the fact of downtime and the correct calculation of payments in case of forced cessation of work can significantly reduce the financial costs of the employer, because payment for officially registered downtime is almost a third less than the wages accrued to employees during a normal work schedule.
FAQ
Question No. 1. Can I not come to work if my boss declares me idle?
No, this cannot be done if the manager has not indicated in the order the possibility of not visiting the enterprise during the period of suspension of activities. He can also set shorter working hours.
Question No. 2. Does a manager have the right to fire an employee during a long period of downtime through no fault of his own?
No, this is possible only after the organization is declared bankrupt and subsequently liquidated.
Question No. 3. Can a director send employees on leave without pay during downtime?
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Vladislav Ivanovich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in family law. Knows everything about the law.
This is a violation of the law, because Every day of downtime must be paid accordingly, and budget savings through unpaid leaves are punishable under Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, up to the suspension of the organization’s activities.
Most common mistakes
Often, employers do not pay attention to small details that affect the correctness of registration of downtime from a legal point of view, as a result of which, during legal proceedings, the court makes a guilty decision against them, even if the fault for suspending the company’s activities lies with the employee.
Which errors are the most “popular”:
| Error | Rationale | Consequence |
| The order does not indicate the need for employees to be present at workplaces during downtime | Downtime refers to working time, not rest, so employees are required to be present on the territory of the organization | Some employees believe that declaring downtime is grounds for going on “unscheduled leave,” but by law this is considered absenteeism |
| Issuance of an order by an unauthorized person | The document is drawn up only by the head of the enterprise or the person performing his duties during absence | The court declares the order invalid |
| Transfer of an employee to another position without his consent | acc. from Part 2 Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, this is only possible during downtime due to insurmountable circumstances | Reinstatement of an employee to his previous position by court decision, imposition of an administrative fine on the employer |
Conclusion
Forced downtime at work must be properly documented and paid, otherwise the employer, if the fault lies with him, may be held administratively liable. There is no specific list of documents, but the most important thing that must be mandatory is an order, because
on its basis, the time of suspension of activities is determined and the wages of employees are calculated.
Many Russian employers will face forced downtime for reasons beyond their control in 2021, or more precisely due to the spread of the new coronavirus infection. It is still unknown when the pandemic situation will be resolved; all workers and employers need to be prepared for different situations, including the announcement of a suspension of the enterprise.
The government is already promising tax holidays, but it is important to organize your work activities correctly so as not to fall under sanctions.
In this article we will understand how downtime is paid for reasons beyond the control of the company and the employee due to coronavirus, and how to arrange downtime.
Career
Many enterprises are forced to make decisions to suspend work - this is the most relevant way to reduce personnel costs. However, it must be justified before labor inspectors, that is, provide documentary evidence of the duration of the downtime, the reasons why it occurred, and indicate which of the workers was forced to suspend work. The legislation does not say what documents need to be drawn up, how to introduce idle time at the enterprise and terminate it, so the HR employee may have questions. How to announce downtime to employees? What time is considered downtime? How to document downtime? How to correctly calculate and pay for it? Labor legislation provides for the concept of “downtime” - this is a temporary suspension of work for reasons of an economic, technical or organizational nature (Article 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Downtime can affect one employee, a group of employees, or all employees of a particular department or enterprise as a whole. Suspension of the work of an enterprise can occur for various reasons. The Labor Code provides for simple: - through the fault of the employee; - due to the fault of the employer; - due to circumstances beyond the control of either the employee or the employer. If the downtime is caused by equipment breakdown or other similar reasons that make it impossible to perform further work, the employee is obliged to inform the employer about this. Since the legislator has not established the form of such notification, it can be made either orally or in writing. The employee’s duty is considered fulfilled at the moment when he reports the downtime to his immediate supervisor. Failure by an employee to fulfill his duties is a violation of labor discipline and entails disciplinary liability. If, as a result of the employee’s failure to notify the employer about the start of downtime, the latter suffers property damage, the employee may also be held liable. To properly document downtime, you need to know its reasons: the calculation of the employee’s wages depends on them. Payment for downtime is provided for in Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: - if the downtime occurred due to the fault of the employee, then the downtime is not paid; - if the downtime occurred due to the fault of the employer, then the downtime is paid in the amount of at least 2/3 of the employee’s average salary, which is calculated in accordance with Resolution No. 922. Since Art. 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to provide employees with work stipulated by the employment contract, to provide them with equipment, tools, technical documentation and other means necessary for them to perform their labor duties; failure by the employer to fulfill this obligation will lead to downtime through the fault of the latter. ——————————— Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2007 N 922 “On the specifics of the procedure for calculating average wages.”
Example 1. Calculation of wages for downtime that occurred due to the fault of the employer: Khramov S.N. did not work on January 13 and 14 due to breakdown and untimely repair of equipment. His salary is 20,000 rubles. per month. In addition, for the period from January 1, 2008 to December 31, 2008, he was paid a year-end bonus in the amount of 40,000 rubles, as well as monthly bonuses in the total amount of 36,000 rubles. and remuneration for overtime work in the amount of 16,000 rubles. The employee worked in full for the billing period of 250 days. We will calculate the amount of compensation for downtime. The total amount of the employee’s earnings, taking into account bonuses for the year, was: 20,000 rubles. x 12 months + 36,000 rub. + 40,000 rub. + 16,000 rub. = 332,000 rub. Average daily earnings were: RUB 332,000. / 250 days = 1328 rub. Compensation will be: 1328 rubles. x 2 x 2/3 = 1770.67 rubles;
- if the downtime occurred due to circumstances beyond the control of either the employee or the employer, then the downtime is paid in the amount of at least 2/3 of the tariff rate, salary, calculated in proportion to the downtime. This means that this calculation of wages does not take into account various allowances and surcharges to tariff rates or official salaries, bonuses, remunerations and other payments taken into account when determining average earnings.
Example 2. Calculation of wages during downtime, which occurred due to circumstances beyond the control of either the employee or the employer. Let's take the conditions from example 1, only the downtime occurred due to the fault of the energy supply organization, which turned off the power. We will calculate wages for downtime (in this case, bonuses and rewards will not be taken into account): 20,000 rubles. x 2/3 = 13,333.34 rub. Now let’s determine the employee’s remuneration for days of downtime. In January 2009 there are 16 working days, of which 2 days are downtime. The amount of payment for downtime days will be: RUB 13,333.34. / 16 days x 2 days = 1666.65 rub.
Documentation Regardless of the reasons for the downtime, it must be documented. In accordance with Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to keep records of the time actually worked by each employee. To process such accounting data, the State Statistics Committee of Russia has developed unified forms N T-12 and N T-13. These unified forms for recording working hours and settlements with personnel for wages are used by legal entities of all organizational and legal forms and types of ownership, except for budgetary institutions. Depending on the reason for the downtime, an alphabetic or numeric code is indicated in the lines of the form: - due to the fault of the employer - “RP” or “31”; - due to the fault of the employee - “VP” or “33”; - for reasons beyond the control of the employee and the employer - “NP” or “32”. ——————————— Approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated 01/05/2004 N 1 “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording labor and its payment.” However, the legislation does not specify either a document or, accordingly, a unified form by which downtime would be introduced or terminated in an organization. In this regard, enterprises most often issue an order in any form, but with the most detailed information about the reasons for downtime. The reasons for downtime in a crisis situation may be the absence or reduction of orders, short supply of raw materials, delayed financing, late payments from customers and much more. A detailed description in the order of the reason for the downtime serves as confirmation that the employer is not to blame for the current situation, which means that employees are paid for downtime according to the most favorable scheme for the employer, that is, at least 2/3 of the official salary, calculated in proportion to the downtime. In addition to describing the reasons for the downtime, the order must indicate the start date and end date of the downtime. If everything is simple with the start date, then the end date, as one might assume, is needed to calculate wages for employees. If for some reason the downtime did not end by the date specified in the order, then the downtime can be extended with an additional order and vice versa. Also, do not forget to indicate in the order whether downtime has been declared for the entire company or for individual employees. Here is a sample order for declaring downtime.
Can an employee not be present at the workplace during downtime? At the legislative level, downtime is not limited in any way - a day, two, a month... In other words, downtime at an enterprise can be quite long, so the question very often arises: should an employee be present at the workplace? Labor legislation and other regulatory documents related to labor relations do not indicate that during the period of work stoppage in the organization, employees may be absent from the workplace during their working hours, and presence at the workplace is their direct responsibility in accordance with Art. 91 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Working time is the time during which an employee, in accordance with the internal labor regulations and the terms of the employment contract, must perform labor duties, as well as other periods of time that, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, relate to working hours. We can conclude that the employer has the right to allow employees not to go to work during the downtime period. This decision must be reflected in the order declaring downtime, which employees are familiar with upon signature. Such downtime, when employees may not go to work, is in practice called forced leave. Despite the fact that forced leaves are not provided for by law, their provision does not contradict the law if they are paid according to the rules for paying downtime. Since downtime, as a rule, brings certain losses (the employee does not perform his job function, but he is paid), many companies send employees on leave without pay, which is a gross violation of labor laws. Attention! If employees appeal the legality of granting such vacations, the organization will be obliged to pay them for the time of these vacations (Article 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, for violation of labor legislation, the labor inspectorate may hold the organization administratively liable in the form of a fine in the amount of 30,000 to 50,000 rubles. Here is a sample order declaring downtime (with the right of employees not to go to work).
Is sick leave paid during downtime? Temporary disability benefits for the period of inactivity are paid in the same amount as wages are maintained during this time, but not higher than the amount of benefits that the insured person would receive according to the general rules (clause 7 of Article 7 of Law No. 255-FZ). This means that the benefit amount will be no less than 2/3 of the average earnings or official salary (tariff rate). When calculating benefits in accordance with clause 7 of Art. 14 of Law 255-FZ, it is necessary to take into account the provisions of the Regulation on the specifics of the procedure for calculating benefits for temporary disability, pregnancy and childbirth for citizens subject to compulsory social insurance. Let us remind you that, according to the general rules, the amount of the benefit depends on the length of the employee’s insurance period (60, 80 or 100% of average earnings), on the reasons that led to the disability (illness or injury, the need to care for a sick family member, etc.), and not may exceed the maximum amount established by the law on the FSS budget for the next financial year (in 2009 - 18,720 rubles). Thus, the accountant needs to compare the amount of the benefit, which is determined according to the rules for paying for downtime, with the amount of the benefit, calculated according to the general rules, and pay the employee the smaller amount. ——————————— Federal Law of December 29, 2006 N 255-FZ “On providing benefits for temporary disability, pregnancy and childbirth to citizens subject to compulsory social insurance.” Approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 15, 2007 N 375. If downtime occurred due to the fault of the employee, temporary disability benefits for this period are not accrued (clause 1 of Article 9 of Law N 255), since downtime due to the fault of the employee is not paid.
What is simple
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation has such a concept as forced downtime due to independent reasons. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, payment for downtime in 2021 is made differently depending on whose fault it occurred.
Based on Art. 72.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, downtime is a temporary suspension of the activities of an enterprise for the following reasons:
- economic;
- technological;
- organizational;
- or of a technical nature.
Downtime happens, which is quite obvious, either through the fault of one of the parties to the labor relationship, the employer or employee, or for reasons beyond their control. These include various force majeure and emergency circumstances, such as an epidemic or pandemic.
Data
The economic crisis of the entire country led to disruptions in the work of more than one enterprise. So in one year, starting in December 2008, more than 200 thousand employees were sent to it, their duration also varied. And many enterprises did not want to pay and justified this fact as being beyond their control.
So, at the beginning of 2009, the Chelyabinsk Regional Court issued a ruling in which it designated this position as unlawful and illegal. According to it, the crisis situation of the country’s economy is not considered an indicator of the organization’s inability to fulfill its responsibilities to its employees.
It is not surprising that during periods of crisis in our country, labor inspectors have a lot of work to do. Multiple violations are identified, and they are followed by administrative penalties. More often than others, they are fined for making payments below the required full 2/3.
Downtime due to coronavirus
Experts from government agencies agree that forced downtime due to coronavirus in 2021 cannot be blamed on the employer. Employers cannot control the situation with the development of the pandemic; they cannot influence the epidemiological situation and prevent the spread of coronavirus.
Therefore, downtime due to coronavirus refers to downtime for objective reasons independent of the parties.
The pandemic can be classified as an emergency, because because of it, a state of emergency has already been practically introduced in European countries, and a non-working week and a strict self-isolation regime have been declared in Russia.
How is downtime paid for objective reasons?
Downtime due to force majeure is paid based on salary. With piecework wages based on the tariff rate. To determine the amount of payment, you need to take the tariff rate calculated for the month, divide the salary by the number of working days in the month. Then you need to multiply this figure by 2/3 and the number of days of downtime.
The Labor Code separately regulates the work of creative workers, artists, singers, actors, etc., working in the media, film and television studios and participating in the creation and performance of performances and concerts. The time during which they do not participate in the creation and performance of concerts, theatrical productions, and other works cannot be considered idle time. Accordingly, payment in accordance with Art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is not carried out. Such cases may be provided for in the local regulations of the organization, in which case payment is made in accordance with its provisions.
What to consider when registering downtime
When formalizing the suspension of activities, employers must take into account the following provisions, based on established judicial practice:
- a separate official order must be issued to introduce a downtime regime in an organization. Otherwise, downtime is not considered and all employees are paid in full;
- the employer can establish a larger amount of payment for downtime in a collective agreement or other LNA;
- payment according to art. 157 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is carried out only for the period when the employee did not fulfill the duties assigned to him in the employment contract. If an employee with piecework wages performs work of a different qualification, his work is paid according to the rates and payment systems accepted by the employer.
At the same time, the employer should take into account that no matter how long the pandemic situation lasts, payment must be made. An employee cannot be forced to take unpaid leave. You may consider switching to remote, remote work.
Crises and production failures often occur even at large enterprises. This may occur due to circumstances beyond people's control or result from management negligence.
The law provided for the possibility of registering downtime at the enterprise in such cases in order to preserve jobs after the restoration of the usual work regime. How to register downtime due to the fault of the employer and what employees should do during this time - these issues require detailed study.
- Legislative regulation
- Reasons for suspension of work
- How is an employee's time paid?
- Procedure for registration of downtime
- Responsibilities of the employee
Social guarantees for employees during downtime
According to the Labor Code, downtime due to the fault of the employer is not a basis for refusing to fulfill the social guarantees enshrined in legislation.
Some facts
After the employer becomes aware of the forced downtime, he needs to issue an order which will specify the following points: the start date of the stoppage of work; positions and names of employees whose work was suspended; indicate the amount of wages during downtime; indicate the employee responsible for the forced downtime. After issuing the order, the employer must familiarize each employee of the organization with this document.
The management of the enterprise retains the following responsibilities:
- Calculation and accrual of benefits for sick leave (sick leave), pregnancy and childbirth.
- Providing additional leave in the same manner and under the same conditions as during normal working hours.
- Inclusion of the time of suspension of labor activity in the employee’s total length of service (taken into account when calculating the amount of the pension).
- The downtime period and its reasons are not subject to indication in the employee’s work book.
- The right to go on annual paid leave is retained, regardless of downtime (in accordance with the approved vacation schedule).
- Retention of the employee’s workplace as determined by the employment contract or local regulatory legal acts.
The only “downside” of downtime for employees is that this period is not taken into account when calculating length of service for early retirement.
Legislative regulation
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not have a separate chapter devoted to this term. It is not clear whether this period should be classified as working time or rest time. In Art. 72.2 provides a meager definition that downtime is a “temporary suspension of work.” It can have different reasons - it is important whose fault the malfunction occurred:
- Employer;
- Employee;
- Due to circumstances beyond the control of the parties.
Downtime caused by an employee has no legal consequences and is not regulated by law. But the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the responsibility of the employer for dishonest attitude towards their duties, which caused disruptions in production, and also establishes additional rights for employees for this period.
In practice, it is difficult to prove whose actions caused downtime at work. Here's a simple example: sales figures have decreased.
On the one hand, the employer may refer to a drop in demand, but on the other hand, this may be caused by illiterate business practices and negligence. Courts, as a rule, take the side of workers if management has not ensured maximum production capacity.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not regulate the permissible downtime due to the fault of the employer, which frees his hands. In fact, he can repeatedly extend this period until the reasons that caused the failure are eliminated. The main thing is that the required documents are completed on time.
Reasons for suspension of work
The main factors include:
- Economic. These are common difficulties caused by financial crises within the country and in production itself, and a lack of material and raw materials. Responsibility lies with the employer, since there is a business risk.
- Technological. May be caused by the reorganization of the working mechanism and the introduction of new production methods.
- Organizational. A common example is a change in the form of an enterprise in the event of a division, merger or reorganization.
- Technical. These include equipment upgrades that require employee training, or equipment breakdowns. Technical reasons can be a consequence of the actions of both the employee and management. If the employee’s guilt is proven, then payment for downtime is not provided.
The legislator does not single out force majeure circumstances (emergency situations, disasters) as special reasons, but in fact they relieve the employer of blame and change the formation of wages during this period.
How is an employee's time paid?
Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Art. 157 established the norm on the minimum wage for employees during the suspension of activities.
In this case, the calculation procedure depends on the reasons that led to it. Guaranteed payment for downtime due to the obvious fault of the employer is 2/3 of the employee’s average earnings.
It includes not only the tariff rate, but also allowances, bonuses and other required payments.
In the event of force majeure, payroll changes and payment for downtime due to circumstances beyond our control will be 2/3 of the salary. For employees working at a tariff rate, there is no difference, but in production most often they set a small salary, and decent wages are formed through incentive bonuses.
Therefore, managers try to prove their innocence in causing difficulties so that downtime is paid at a lower rate.
If during this period the employee goes on sick leave, then he is not provided with temporary disability benefits. When sick leave begins before the suspension of production or ends after it, the calculation is made for the days actually worked.
The employer is responsible for failure to pay compensation during downtime. In this case, he faces a fine and possible loss of his position.
Procedure for registration of downtime
If reasons arise that lead to a disruption in production, the employee can inform management, both orally and in writing, about the start of downtime due to the fault of the employer and the inability to continue working. The management itself can initiate registration of downtime, but is reluctant to do so, thereby increasing its costs.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Article 91 gives the employer the obligation to keep a log of hours worked by each employee in the approved form. It must indicate downtime. .
- The employer issues an order on downtime, indicating the start date, a list of employees whose work is suspended and their responsibilities, and the salary amount for this period.
- The downtime order is handed over to employees for review against signature.
- If the enterprise has completely stopped production, then within 3 days the management reports this to the employment service.
- An appropriate note is made on the working time sheet.
The employer may offer affected employees to temporarily transfer to another position while maintaining average income or to take a vacant position with higher or similar qualifications.
If management does not begin the registration procedure, then employees can draw up a collective act of downtime in free form, outlining the reasons and circumstances of the incident. It is transferred either to the board of directors of the enterprise or to a trade union organization.
Responsibilities of the employee
What do employees do during downtime? This issue is resolved individually between them and the employer. The order must reflect the time or schedule of workers’ stay on site. In any case, forced downtime due to the fault of the employer does not constitute additional leave, and employees must be present at production.
The employer may offer them to stay at home, but this fact is documented. Otherwise, missing a day of work will be considered absenteeism and will not be paid. Management sometimes uses a trick and offers to give employees leave without pay. In this case, employees also lose the right to compensation.
The suspension of the enterprise's activities is unpleasant for both sides of the issue. Timely registration of downtime will allow you to maintain long-term relationships with employees and quickly restore production.
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Vladislav Ivanovich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in family law. Knows everything about the law.
Downtime (Article 72.2 of this Code) due to the fault of the employer is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the employee’s average salary.
Downtime due to reasons beyond the control of the employer and employee is paid in the amount of at least two-thirds of the tariff rate, salary (official salary), calculated in proportion to downtime.
Downtime caused by the employee is not paid.
The employee must inform his immediate supervisor or another representative of the employer about the beginning of downtime caused by equipment breakdown and other reasons that make it impossible for the employee to continue to perform his job functions.
If creative workers of the media, cinematography organizations, television and video crews, theaters, theatrical and concert organizations, circuses and other persons involved in the creation and (or) performance (exhibition) of works, in accordance with the lists of works, professions, positions these workers, approved by the Government of the Russian Federation taking into account the opinion of the Russian Tripartite Commission for the Regulation of Social and Labor Relations, for any period of time do not participate in the creation and (or) performance (exhibition) of works or do not perform, then the specified time is not downtime and may be paid in the amount and manner established by the collective agreement, local regulations, or employment contract.
Responsibilities and rights of workers during downtime
While employees are downtime due to the employer's fault, employees may be exempt from the need to visit the place of work. To ensure that absence from work is not regarded as absenteeism, it is necessary to agree with the employer. As soon as this issue is resolved, management will issue an appropriate order.
Attention! Employees must be ready to return to work at any time (upon call from the employer).
In practice, there are often situations when the suspension of the work process “flows” into forced leave. The employer obliges employees to write applications for time off or take leave at their own expense, after which the employees are sent home until the circumstances interfering with the work process are eliminated. Such actions are a violation of the law and are unacceptable.
Watch the video about what employees have the right to during downtime of the enterprise.
Some employers offer employees whose activities are temporarily suspended to transfer to another position (subject to availability of vacancies). The transfer is carried out to a position corresponding to the qualifications and work experience of the employee, or to a lower position (only with the consent of the employee).
Several conditions for transfer during downtime:
- temporary transfer is issued for a period of up to 1 year;
- the employee’s consent to the transfer is mandatory if he is transferred for a period of more than 1 month;
- the salary should not be less than the average salary paid in the previous position.
Read about the sanitary and hygienic characteristics of working conditions in this article https://otdelkadrov.online/11371-osobennosti-sanitarno-gigienicheskoi-harakteristiki-otsenki-uslovii-truda
Thus, downtime at an enterprise due to the fault of the employer must be formalized in accordance with the procedure approved by law.