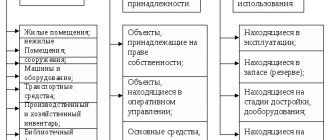
Fixed assets are buildings, structures, equipment, furniture, etc., the useful life of which for accounting purposes is more than a year and the initial cost is from 40,000 rubles. At the same time, in tax accounting, fixed assets in 2016 must have a minimum value of 100,000 rubles. Since 2016, the limit on the cost of fixed assets has been increased from 40,000 to 100,000 rubles (clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which means tax differences may arise in accounting. If an object costs more than 40 thousand, but less than 100 thousand, in accounting, fixed assets expenses will be written off during its service life by calculating depreciation, but in tax accounting, this object is not classified as fixed assets.
The procedure for recording transactions related to fixed assets in accounting is regulated by PBU 6/01. The accounting unit for fixed assets is an inventory item. When purchasing a particular item of property related to fixed assets, the company reflects it as a debit to account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. Next, commissioning takes place (Debit 01-Credit 08), at this moment an inventory card for the asset is created (form OS-6). From this moment, the property is on the organization’s balance sheet, and from the month following the month the OS was put into operation, depreciation begins to accrue on it.
Introductory information
Starting from January 2021, low-value fixed assets are reflected differently in accounting and tax accounting.
Maintain tax and accounting records of fixed assets according to the new rules
In tax accounting, a new version of paragraph 1 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is used, according to which fixed assets are recognized as means of labor with an initial cost of over 100 thousand rubles. Accordingly, cheaper objects are not classified as fixed assets, and their cost is written off as current expenses. Let us recall that this distinction applies to property that was put into operation on January 1, 2021 and later (see “Changes to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: the cost of depreciable property and fixed assets has been increased, and a new revenue limit has been introduced for the payment of quarterly advances on income tax ").
Accounting rules allow the recording of fixed assets, the initial cost of which does not exceed the established limit, as part of inventories. The limit is 40 thousand rubles (clause 5 of PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”). This means that objects up to 40 thousand rubles can be taken into account in one of two ways: either as fixed assets or as inventories. As for property worth 40 thousand rubles or more, there is no choice for it - in any case, it is reflected as a fixed asset.
For clarity, we have compared in the table the rules according to which, starting from 2016, fixed assets should be taken into account in tax and accounting.
How do the fixed asset accounting rules in force in NU and in accounting compare?
| Initial cost of the object | How to reflect in tax accounting | How to reflect in accounting |
| up to 40,000 rub. | write off as operating expenses upon commissioning | The organization has the right to choose one of two ways: — include in the inventory and write off as current expenses upon commissioning; — include in the OS and depreciate |
| from 40,000 rub. up to 100,000 rub. inclusive | write off as operating expenses upon commissioning | include in the OS and depreciate |
| over 100,000 rub. | include in the OS and depreciate | include in the OS and depreciate |
The popularity of mobile OSes versus desktop ones, Apple's problems, the successes of Samsung and the Chinese
Microsoft's main concern right now is the mobile market. The problem is that mobile devices are gradually replacing desktop PCs:
After a slight adjustment in June, StatCouner again recorded a record volume of traffic from mobile devices in July. Smartphones and phablets alone already generate 44.75% of traffic, compared to 37.15% for the same period last year.
StatCouner has been observing this growth for a long time, and the key question is: at what point will it slow down. It is already obvious that mobile devices will take at least half of the traffic. However, they can move much further, significantly narrowing their “living” space for Microsoft, as well as for a number of other companies, including hardware companies.
What makes the situation worse for Microsoft is that it actually failed to enter the mobile market itself. Yes, there is a seemingly successful line of Surface tablets, but look at the picture above: what kind of traffic is generated by the stalled tablet market and how smartly smartphones and phablets are moving forward.
All of Microsoft's attempts, from the ridiculous story with the Kin smartphones in 2010 to the already quite solid Lumia line, ultimately ended negatively.
Moreover, what ultimately happened with Lumia is difficult to understand. Why, when, at what stage and who in the company’s management decided to put an end to this line, and, therefore, put Windows Mobile under severe attack is a mystery.
Of course, MS, given its colossal resources, will clearly not give up the battle for mobile devices and is now simply preparing to announce a certain new line of smartphones, now, most likely, under the Surface brand. However, is the corporation really so confident in it that it shut down devices that were selling up to 10 million per quarter?
However, Microsoft is far from the only ones who are planning or even already having problems. For example, Apple. In July, the company summed up the results of the next quarter and again announced a decrease in income.
The first time Apple did this was in April of this year, now the situation has repeated itself again, and Tim Cook is already suggesting that the next reporting period may turn out to be “so-so.”
Revenues are declining due to decreased demand for all key Apple devices. First of all, this concerns iPhone smartphones, which form the lion's share of the corporation's financial revenues. Over the last quarter, Apple was able to sell “only” 40 million devices compared to 47.5 million in the same period last year.
The compact and more affordable iPhone SE, shown in March, not only did not help increase sales of Apple devices in quantitative terms, but also seemed to harm in terms of income, since some users preferred this cheaper model instead of the iPhone 6S and 6S Plus.
As a result, there is every reason to believe that the iPhone SE will not have subsequent models, just as the iPhone in a plastic case with the letter “C” in the name did not have them. Thus, Apple’s second attempt to enter a more affordable price category turned out to be a failure.
In addition to the iPhone, iPad sales are falling. Here, however, the two iPad Pros presented last fall and this spring managed to slow down this decline. Mac sales are also falling, and income from the “Other” category, which, among other things, includes the Apple Watch smart watch, is also declining. Their second version will be released in the fall, but it is already obvious that the Watch is unlikely to ever bring in the same money as the iPhone or even the iPad, although high hopes were placed on them.
The main horror of Apple at the moment is that their flagship product for this fall - iPhone 2021 (the name is unknown, it’s not a fact that there will be a number “7”) differs very slightly in terms of design from the 6S and is minor, not major renewal, as previously happened in even years. This means that Apple can then announce failures for another four quarters until the release of the anniversary iPhone 2021.
The company's fans even believe in the latest device, released ten years after the presentation of the first iPhone, as a salvation from all troubles. According to rumors, the iPhone 2021 should have an “edge-to-edge screen,” a touch-sensitive Home button, and a new design with an OLED display to boot.
It's funny, but these rumors could further harm sales of the model coming out this year. And that same miracle display in 2017 can eliminate frames not from the entire front side of the device, as fans dream, but only from its side edges, as Samsung has been doing for the second year in its flagships. Moreover, it will supply displays for Apple.
By the way, it is the Korean Samsung, together with an armada of Chinese companies, that now act as the locomotive thanks to which Android, having dealt with all other systems, began to push iOS out of the market. In July, Android reached 65.17, up 0.64% from the previous month. The share of iOS, on the contrary, fell by 0.75% over the month.
Thanks to the success of the flagship Galaxy S7 and budget Galaxy J, Samsung feels great financially, actively pushing Apple even in the USA.
At the beginning of August, the Korean giant demonstrated the Galaxy Note 7, its most sophisticated gadget, occupying the highest level in price categories. It is noteworthy that our SGN7 with 64 GB of permanent memory, despite its threatening price tag of 65 thousand, will cost a thousand less than even the most affordable iPhone 6S Plus, which has only 16 GB of memory. And this despite the fact that the new Galaxy Note has a larger screen, more RAM, and even a proprietary stylus included.
In turn, the Chinese are even more impressive. For example, Xiaomi alone, which only recently announced its first laptops, is about to enter the smartwatch market. Before that, she showed the largest phablet and rethought the Mi Band bracelet, adding a built-in display.
Along the way, Xiaomi presented its first smartphone with a dual camera and an OLED display, and these displays are also made in China by Chinese companies. An entry-level VR gadget has just been announced, and a presentation of the flagship Mi Note smartphones is scheduled for the second half of August. And all this in just a few months from just one Chinese company.
Because of this activity of the Chinese and the growing strength of Samsung, it is becoming difficult for many manufacturers even in the Android camp. Although statistics show the overall growth of devices running Android, many companies there are starting to have problems due to the onslaught of competitors. It’s not good for Taiwanese HTC, the flagship G5 from the Koreans LG showed a very weak result, the market share of the Indian Micromax is declining, the sales of Xperia from the Japanese from Sony have dropped dramatically:
As for manufacturers who once tried to stay on the market with other OSes, all their attempts have long ago failed. In the statistics, you can see the market shares of WP and WinRT from Microsoft, a whole group of deceased OS from Nokia, the Blackberry system, and the Bada platform from Samsung, which are getting closer and closer to zero. WebOS, which Palm and HP once wanted to make leaders, has already completely disappeared. And Firefox OS and a number of other systems, unfortunately, did not even score hundredths to get at least to the “bottom” of these statistics.
This is how the popularity of mobile operating systems has changed over the past year and month, respectively:
The only thing that is a little curious is Tizen, but to be honest, we doubt that Samsung intends to promote it seriously and, most likely, is simply leaving it as an experiment and (or) insurance in case of an unforeseen deterioration in relations with Google.
When temporary differences occur
For each object that is reflected differently in accounting than in tax accounting, it is necessary to show the difference. This requirement is established in PBU 18/02 “Accounting for calculations of corporate income tax.”
In this case, the difference will be temporary, because at the end of the useful life the initial cost of the object will be written off both in the NU and in the accounting book. Consequently, the discrepancies between both types of accounting will eventually be reduced to zero (read more about this in the article “How to apply PBU 18/02 “Accounting for corporate income tax calculations” in practice)”).
This applies to all fixed assets without exception, the initial cost of which falls in the range from 40 thousand rubles to 100 thousand rubles inclusive. Also, temporary differences appear if in the company’s accounting, objects worth less than 40 thousand rubles are reflected as part of fixed assets, and not as part of inventories.
Amortization of intangible assets
Intangible assets (IMA), unlike depreciation of fixed assets, have a nominal value, but lack physical content. These include:
- copyright;
- reputation of the enterprise (business);
- property rights;
- right of the patent holder;
- expenses of the enterprise for organizational purposes, etc.
They are accepted for accounting (for accrual of transactions) on account “04” at the original cost (the order of deduction is determined by the method of receipt). Accrual and posting are made using the chosen method if the cost exceeds 100 thousand, according to the new regulation, which came into force at the beginning of this year.
What transactions need to be created?
Since when reflecting low-value fixed assets in tax accounting, the initial cost is written off immediately, and in accounting gradually through depreciation, the “tax” profit turns out to be less than the “accounting” profit. This means that the temporary difference is taxable. A deferred tax liability (DTL) arises, which is shown in the debit of account 68 and the credit of account 77. The amount of DTL is equal to the taxable temporary difference multiplied by the income tax rate (20%).
Submit your income tax return online using the new form
When calculating monthly depreciation, on the contrary, the “tax” profit exceeds the “accounting” profit, because depreciation deductions are made in accounting, but in NU they are not. This creates a temporary difference that is deductible. It generates a deferred tax asset (DTA), which is shown in the debit of account 09 and the credit of account 68. The value of DTA is equal to the deductible temporary difference multiplied by the income tax rate.
Example 1
In February 2021, a trading organization acquired a fixed asset with an initial cost of RUB 86,400. and a useful life of 4 years (which is 48 months). In the same month, the facility was registered and put into operation.
In accounting, the object is reflected as a fixed asset. According to the accounting policy, the linear depreciation method is used for accounting purposes. The accountant has determined that the annual depreciation rate is 25% (100%: 4 years). Accordingly, the annual amount of depreciation is equal to 21,600 rubles (86,400 rubles x 25%), and the monthly amount is 1,800 rubles (21,600 rubles: 12 months).
In February 2021, the accountant made the following entry: DEBIT 01 CREDIT 08 – 86,400 rubles. — the fixed asset is accepted for accounting.
In tax accounting, the initial cost is completely written off as current expenses. As a result, a taxable temporary difference was created in the amount of RUB 86,400.
The accountant made the entry: DEBIT 68 CREDIT 77 - 17,280 rubles (86,400 x 20%) - IT is reflected.
In the period from March 2021 to February 2023 (48 months in total), the accountant calculates depreciation monthly and makes the following entry: DEBIT 44 CREDIT 02 - 1,800 rubles. - depreciation has been calculated.
In this case, a deductible temporary difference arises in the amount of RUB 1,800. In this regard, a monthly posting is made: DEBIT 77 CREDIT 68 - 360 rubles (1,800 rubles x 20%) - IT is repaid.
At the end of its useful life, it is fully repaid.
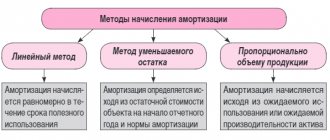
How is depreciation of fixed assets calculated in 2016?
There are several methods for calculating drift. In Russia there are only two methods: linear and nonlinear.
In Ukraine: linear, reduction of the balance, by writing off the cost depending on the volume of work and the sum of the numbers of years of useful use. Most often, depreciation is calculated using a linear method. You cannot change the calculation method more than once every 5 years. In the middle of the period the norm does not change. The new year of use begins on January 1st.
For each group of identical objects, one method and one coefficient are used. Depreciation of fixed assets, how to calculate, is determined by the necessary rules in accounting.
Having a problem? Call a lawyer: +7
— Moscow, Moscow region
+7
— St. Petersburg, Leningrad region
The call is free!
Linear method
In this way, wear is carried out in equal parts. The amount of deductions is written off in each period and appears on the balance sheet. Using this calculation formula, we will find out how to calculate: the annual rate is equal to the ratio of the depreciation rate to 100 percent and multiplied by the original cost. Sample and example of calculation: equipment costs 20,000 rubles. The period for which the accounting department plans to use it is 10 years. This means they expect to write off 2,000 rubles per year.
Equipment will be written off when depreciation charges pay off the cost of the objects.
On the Internet you can download an online calculator and a table for calculating the correct amounts. As well as a course work, cheat sheet or essay, which will describe in detail the calculation of depreciation.
Wiring
Display on synthetic and analytical accounts is mandatory.
Every month there is a date when depreciation is written off. The amount is reflected according to the following entry: Dt 20 Kt 02. It is used for different accrual methods. After the first year of use, the residual value includes the difference between the original cost and depreciation for the period.
Accelerated
The method is regulated by PSB No. 7. Accelerated depreciation attracts investment and increases future revenues and profits. It comes down to the fact that wear is written off faster than it is established in the standards. Thus, the company can receive a tax deferment. And then, when the entire cost is written off, the company's profit increases significantly. As a rule, this technique is used by commercial enterprises. This way they get passive income.
General OS statistics
Finally, let us remind you about the ability of StatCounter to combine statistics for desktops and mobile devices together. This is what the overall picture looks like as of July 2021:
And so it changed throughout the year. As you can see, back in December 2015, all versions of Android managed to bypass the most popular version of Windows and have been noticeably ahead since then.
If we talk about specific figures for the year and recent months, here they are:
- about the author
- Recent publications
Raik
Igor Andreev is the author of articles for ITRew.ru and Our-Firefox.ru. I am passionate about modern technologies, I talk about them in my texts) Follow me — twitter.com
Raik recently posted (see all)
- Why the Galaxy S21 is worse than the S20: six main differences - 01/15/2021
- All smartphones with retractable cameras (list and table) - 12/23/2020
- All the differences between Snapdragon 888 and Exynos 2100 - 12/09/2020
Tell others:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click here to share content on Facebook. (Opens in a new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)