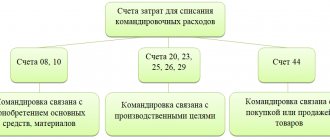
Sending an enterprise employee on a business trip begins with an order from the director. The employee is informed about this, and if an agreement is reached, the order is transferred to the accounting department (the order of operations at different enterprises may be different).
The accounting department issues a travel certificate (based on the director’s order). These documents are not prepared in the standard configuration of 1C 8.3 “Enterprise Accounting 3.0”.
In the 1C program, registration of a business trip begins with the issuance of money to the account.
Issuance of travel money
For accrual and payment, go to the “Bank and Cash Office” section and select “Cash Documents”.
Our team provides consulting, configuration and implementation services for 1C. You can contact us by phone +7 499 350 29 00 . Services and prices can be seen at the link. We will be happy to help you!
You will see a list of previously created documents for the receipt or issuance of funds from the cash register. Click on the “Issue” button.
Now you can proceed to filling out the document itself. There is nothing complicated here. First of all, select the value “Issuance to an accountable person” in the “Type of transaction” field. Please note that when you change the values in it, the structure of the document details also changes. That is why, when creating a cash withdrawal document, first indicate the type of transaction.
We will leave the accounting account as default. Next, we will indicate the employee who needs to accrue travel allowances in 1C. To the right, let's select the organization and division in which he works. In the “Amount” field we will indicate that for this business trip our employee will receive an amount of 15,000 rubles.
In our configuration, accounting for DDS items is configured for additional analytics, so this field can also be filled in. For convenience, we will indicate in the comments that the money was issued for a business trip. This will make our search easier in the future.
If you need to edit the details of the printed form, expand the section of the same name. In our case, all the displayed data came here automatically when selecting an employee.
After carrying out the document, we will be able to see from the formed movement that now the amount of 15,000 rubles is listed on Gennady Sergeevich Abramov. The debt will be written off from him after he reports on the amounts spent.
Let's supplement our video instructions on the cash register in 1C:
Travel expenses within normal and above normal limits
Expenses reimbursed by the employer to an employee during a business trip (Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) are reflected in the reporting of insurance premiums.
According to clause 2 of article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 12 of clause 3 of art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses during a business trip are not subject to insurance contributions and personal income tax if they:
- Do not exceed 700 rubles for each day of a business trip within the Russian Federation;
- Do not exceed 2,500 rubles for each day of a business trip outside the Russian Federation.
If the employer sets daily allowances in a larger amount than specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, then he will need to withhold personal income tax from the excess amounts and charge insurance contributions.
To display expenses on a business trip within normal limits in 1C ZUP 3, you must enter an accrual with the following settings (Fig. 7):
Rice. 7.1. Setting spending within normal limits
Rice. 7.2. Setting spending within normal limits
The accrual is carried out by the document “Income in kind” (Fig. 8):
Rice. 8 Expenses during the business trip are within the normal range in the document “Income in kind”
To reflect expenses for a business trip period in excess of the norm in 1C ZUP 3, you must enter an accrual with the following settings (Fig. 9):
Rice. 9.1 Setting up excess spending
Rice. 9.2 Setting up excess spending
The accrual is carried out by the document “Income in kind” (Fig. 10):
Rice. 10 Expenses in excess of the norm in the document “Income in kind”
The calculation of insurance premiums for travel expenses accrued in excess of the norm is carried out in the document “Calculation of salaries and contributions”.
Let's set up the calculation of travel allowances in 1C:ZUP
Let's set up 1C:ZUP for the correct calculation of travel allowances in 1C:ZUP.
We provide a guarantee for services! from 2,600 rub./hour
To learn more
Support for travel allowance accounting in 1C:ZUP
Support for your work in 1C, regular consultations, assistance with settings and troubleshooting
from RUB 700.
To learn more
Advance report
Advance reports that are needed to write off the debt for an advance received from an employee are also located in the “Bank and Cash Office” section.
We will fill out the header of the document as standard, as we did earlier. On the “Advances” tab in the tabular section, add a line and select the previously created cash disbursement document. As you can see, 1C 8.3 allows you to report on several advances issued to the same employee at once. This is done by adding additional rows to this tabular part.
We have indicated what the employee is accountable for for his/her daily allowance. Now we need to reflect what documents and for what amounts he provided. This can be done on the “Payment” tab.
In our case, the employee provided two tickets and a check for hotel accommodation to the accounting department. The total amount was 12,500 rubles. After the document is processed in 1C, the debt to our organization will be reduced only by this amount. Let's look at the wiring:
It turns out that the employee was given an advance in the amount of 15,000 rubles, but he reported only 12,500. It follows from this that he still has a debt, but in the amount of 2,500 rubles. In this case, by mutual agreement, he can either provide the missing checks for this amount or return the money.
The difference can be returned, for example, when calculating salaries. The employee can also bring this amount to the cashier.
In the event that an employee, on the contrary, did not meet the amount given to him and spent more, such a difference can be paid to him in the same way as the travel allowances themselves through the cash register.
See also the video on advance reports in 1C 8.3:
What is Smartway and why does an accountant need it?
Smartway is a business travel solution that completely replaces a business travel agency. The company gets access to all the tools for planning trips and purchasing tickets directly, without intermediaries.
It will become more convenient for an accountant to work with documents on business trips. The Smartway service will help the accounting department in arranging business trips.
- Accountants will have online access to supporting documents in their personal account.
Smartway itself will generate reporting documents and save acts, invoices and tickets.
- Packages of supporting documents can be downloaded or received by email in PDF or Excel format. And the originals are sent by mail.
- There are convenient settings for a group of companies. In the service you can choose which company to issue invoices to. If you need different legal entities to pay for different services on the same trip, Smartway will issue invoices to different companies.
- The accountant will immediately see which employee made or changed the reservation.
Accounting for entertainment expenses
Representation expenses include:
- Official receptions, both for representatives of other organizations, officials of the taxpayer organization, and members of the board of directors and others, regardless of the venue;
- Transport provision for the delivery of these persons to the place of official reception and back;
- Buffet service during negotiations;
- Translation services during the official reception.
The list is closed and entertainment expenses not included in it are not taken into account in income tax.
Representation expenses do not include organizations:
- Entertainment;
- Recreation;
- Prevention or treatment of diseases.
Important! Representation expenses of a non-profit organization at the expense of targeted financing are not taken into account in income taxation.
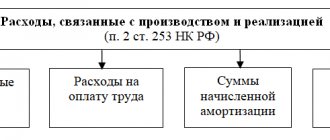
Entertainment expenses are included in other expenses in an amount not exceeding 4% of labor costs for the reporting period. When representative expenses exceed the norm, a permanent difference arises.
Important! Expenses must be economically justified and documented.
Typical entries for hospitality expenses
| Dt | CT | Wiring Description |
| 26 | 71 | Payment of entertainment expenses by the reporting person |
| 26 | 60 (76) | Services of third parties are included in entertainment expenses |
| 90.08 (20, etc.) | 26 | Write-off of representative expenses |
Write-off of travel expenses: postings
Based on the supporting documents received from the employee and attached to his advance report, travel expenses are written off by posting:
- D26,20,44-K71 - travel tickets, daily allowance, accommodation without VAT;
- D19-K71 – posting is done if VAT is included in their cost.
If an employee on a business trip purchased goods for sale, materials for the company, an entry is made:
- the employee incurred expenses, posting: D41.10-K60;
- VAT is reflected on the basis of received invoices (or UPD): D19-K60;
- travel expenses are reflected, posting: D60-K71.
When purchasing fixed assets, the postings will be as follows:
- D08-K60 - OS purchased,
- D19-K60 — VAT included,
- D71-K60 - employee expenses are reflected.
It often happens that companies pay for travel to and from their business trip from their current account, booking air and train tickets in advance: for many this is cheaper and more convenient. In this case, the wiring is as follows:
- D60.76-K51 – the ticket price has been paid including the fee,
- D19-K60.76 – VAT reflected,
- D20,26,44-K60,76 – the fee for issuing a ticket is reflected,
- D50.3-K60.76 – the ticket was received by the company’s cash desk,
- D71-K50.3 – ticket issued to a posted worker.
After submitting the advance report with attached electronic tickets and boarding passes, the following entry is made:
- D 20,26,44-K71 – the cost of the ticket has been written off.
Business trip by personal transport in 1C Accounting 8
When traveling short distances, for example to a neighboring city, posted workers can use their own car for the trip. Let's look at how a business trip using personal transport is reflected in 1C Accounting 8th edition. 3.0.
The director of Veda LLC went on a business trip by personal transport for 2 days. The daily allowance established at the enterprise is 500 rubles. per day. The employee was given a cash advance in the amount of 5,000 rubles from the cash register. for travel expenses. The employee's expenses were: accommodation 1500 rubles, gasoline costs 2035 rubles. (55 l * 37 r)
Upon returning from a business trip, the employee submitted an advance report with the necessary documents attached (hotel bills, gas receipts).
Business trip by personal transport in 1C Accounting 8 ed. 3.0
In the 1C Accounting program 8th edition. 3.0 a business trip using personal transport is documented with the following documents.
First, you need to reflect the issuance of cash to the posted employee. To do this, the program draws up a document “Issue of funds” with the transaction type “Issue to an accountable person.” You can find it on the “Bank and cash desk” tab in the journal of cash documents.
According to the document, a posting is generated: Dt 71.01 Kt 50.01
Next, you need to fill out an advance report. This document can also be found on the “Bank and cash desk” tab in the “Cashier” section.
In the expense report, you need to select an accountable person, a warehouse, indicate the purpose and number of documents attached to the expense report.
Three tabs will be filled in the document: Advances, Goods and Other.
On the “Advances” tab, you must select the document with which the money was given to the accountable person. In our example, money was issued from the cash register, so we select the “Cash Withdrawal” document and select the one we need from the list.
On the “Products” tab, it is necessary to reflect the purchase of gasoline by the accountable person. Here we indicate the document, item, quantity, amount, supplier.
On the “Other” tab we indicate the remaining expenses associated with the business trip. In our example, these are per diem and housing costs.
The following transactions will be generated according to the document:
Dt 10.03 Kt 71.01 – 2,035 rub. (payment for gasoline)
Dt 26 Kt 71.01 – 1,500 rub. (accommodation)
Dt 26 Kt 71.01 – 1,000 rub. (daily allowance)
Next, gasoline must be written off as an expense. This can be done using the “Demand-invoice” document. Located on the “Production” tab.
According to the document, a posting will be generated: Dt 26 Kt 10.03
And the accountable person must return the balance of the unused amount to the cashier. To do this, based on the advance report, we create a “Cash Receipt” document. The document is filled in automatically.
In this way, you can reflect a business trip using personal transport in 1C Accounting 8th edition. 3.0. About filling out an advance report when traveling on a business trip not on personal transport, ed. 3.0 see here in edition 2.0 here
Get the full course on 1C Accounting 8th edition. 3.0