What is inventory
This term refers to the verification and calculation of fixed assets listed on the balance sheet of the enterprise. In turn, fixed assets include all the property of the company that is used to carry out its activities. In particular, these are: equipment, machinery, instruments, transport, buildings and structures, etc. One of the main features of an object, in order to classify it as a fixed asset, must be the period of its use: at least one year, as well as a certain minimum value threshold (which is established at the legislative level and changes over time).
Reasons for verification actions
The reasons for inventory activities can be very different: upcoming annual reports on accounting and taxes, a change in financially responsible employee, theft, theft, other abuses of the organization’s property, the upcoming transfer of fixed assets to a tenant or a new owner.
In addition, property inspection is carried out during the reorganization of the company and its impending liquidation, as well as in force majeure circumstances (fires, floods, accidents, etc.). Inventory can be carried out both on a voluntary basis and compulsorily, both one-time and regularly, and its duration can vary from several hours to several days. At large enterprises, inventory is carried out separately for each structural unit.
* * *
In conclusion, we note that the changes made to the inventory list (form 0403087) and the statement of discrepancies (form 0404092) are related to the provisions of federal standards that came into force on January 1, 2021.
[1]Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n “On approval of forms of primary accounting documents and accounting registers used by public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state (municipal) institutions, and Guidelines for their use."
Budgetary organizations: accounting and taxation, No. 2, 2018
What goals are set and what results can be
Based on the above, it is not difficult to understand the main goals and objectives of this event.
- First of all, this is a certification that all fixed assets credited to the organization’s balance sheet are safe and sound, there are no surpluses or shortages, and that all factual data fully corresponds to what is reflected in the documents.
- Thanks to the inventory, management gets the opportunity to get a real picture of the enterprise’s property, as well as to carry out timely write-off of fixed assets (broken, obsolete or lost).
- This procedure also has a disciplinary nature: knowing about its implementation (especially if it is carried out regularly), materially responsible employees perform their job duties with greater care and reliability, avoiding negligence and deliberate violations.
Changes in the order of reflection of inventory results in accounting registers
Troshina O., magazine expert
By Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 17, 2017 No. 194n, amendments were made to Order No. 52n[1].
The essence of the amendments is the addition of the forms “inventory list (matching sheet) for objects of non-financial assets” (form code 0504087) (hereinafter referred to as inventory list (f.
0403087)) and the “statement of discrepancies based on inventory results” (form code 0504092) (hereinafter referred to as the statement of discrepancies (f. 0404092)) with new information. We will talk about what information is now reflected in these forms in the article.
Inventory list (matching statement) for objects of non-financial assets (form 0504087)
To reflect the results of the inventory of non-financial assets carried out by the institution (hereinafter referred to as NFA), an inventory list is used (f. 0403087). The following changes have been made to this register:
Column numberIndicator nameNote
| Actual presence (condition) (indicators columns 5 – 9) | ||
| 5 | Price (estimated value) of the inventory item | When taking inventory of material assets for sale, the price of the product or product is indicated |
| If a surplus is identified, the estimated value of the object is reflected | ||
| 8 | Status of the accounting object (this column indicates information about the condition of the property as of the inventory date, taking into account the assessment of its technical condition and (or) the degree of involvement in economic turnover) | In relation to fixed assets, the following is indicated: “in operation”, “requires repair”, “is under conservation”, “does not meet operational requirements”, “has not been put into operation” |
| In relation to material inventory items, the following is indicated: “in stock (for use)”, “in stock (in storage)”, “inadequate quality”, “damaged”, “shelf life has expired” | ||
| In relation to objects of unfinished construction, the following is indicated: “construction (acquisition) is underway”, “the object is mothballed”, “construction of the object is suspended without conservation”, “transferred into ownership of another public legal entity” | ||
| 9 | Target function of the asset (this column indicates information about possible ways to involve inventory objects in economic circulation, use them to obtain economic benefits (extract useful potential) or, if this is not possible, about ways to dispose of the object) | In relation to fixed assets, indicate: “commissioning”, “repair”, “mothballing of the facility”, “retrofitting (retrofitting)”, “write-off”, “disposal” |
| In relation to inventory items, indicate: “use”, “continue storage”, “write-off”, “repair” | ||
| In relation to unfinished construction objects, the following is indicated: “completion of construction (reconstruction, technical re-equipment)”, “mothballing of an unfinished construction object”, “privatization (sale) of an unfinished construction object”, “transfer of an unfinished construction object to other economic entities” | ||
| Inventory result (indicators columns 13 – 18) | ||
| 13 | Quantity (indicates the number of inventory items for which a shortage was identified according to accounting data) | |
| 14 | Amount (this column reflects the cost of the item for which a shortage was detected) | Determined by multiplying the indicator in column 13 by the result of dividing the indicator in column 12 by the indicator in column 11 |
| 15 | Quantity (indicate the number of inventory items for which surpluses have been identified) | |
| 16 | Amount (this column reflects the cost of an unaccounted object identified during the inventory) | Determined by multiplying the indicator in column 15 by the indicator in column 5 |
| 17 | Quantity (shows the number of inventory items for which the institution’s commission has determined that they do not comply with the conditions for recognition of assets for accounting purposes) | |
| 18 | Amount (indicates the value of objects that do not meet the criteria for classifying an object as an asset) | Determined by multiplying the indicator in column 17 by the result of dividing the indicator in column 12 by the indicator in column 11 |
| 19 | Note (information is indicated that is not reflected in other columns of the form) | Information is provided on accounting objects in respect of which a shortage has been identified, and the number of accounting objects that have retired within the limits of natural loss norms is indicated. This column also indicates information about the reasons (grounds) for changing the status and (or) target function of the accounting object from the previous inventory |
* When forming an accounting policy, the institution independently determines the method of indicating the status of an accounting object by its name and (or) code.
The inventory list (f. 0504087) is signed by the chairman and all members of the commission of the institution carrying out the inventory after the responsible person(s) have provided an explanation of the reasons for the discrepancies (if any) and the conclusion of the commission of the institution on the results of the inventory.
Example 1:
Based on the results of the inventory carried out in the budgetary institution by the commission, it was revealed that, according to accounting data, the following objects are taken into account and are actually in a certain state:
- carpentry equipment that has not been put into operation and is subject to additional equipment;
- plywood in the amount of three sheets, of inadequate quality - subject to write-off;
- an unfinished construction project is a non-residential building that was previously mothballed and is currently under construction.
In particular, the inventory list (f. 0403087) will reflect the following information:
Name of the non-financial asset objectActual presence (condition)According to accounting dataNote
| Quantity | Accounting object status | Asset objective function | Quantity | ||
| 2 | 6 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 19 |
| Carpentry equipment | 1 | Not put into operation | To be retrofitted | 1 | |
| Plywood | 3 | Poor quality | To be written off | 3 | It fell into disrepair as a result of a pipe break in the warehouse |
| Non-residential building | 1 | Construction is underway | 1 | Removed from conservation, construction completed |
Statement of discrepancies based on inventory results (f. 0504092)
The statement of discrepancies (f. 0504092) is filled out in order to summarize the information:
- about deviations from accounting data identified during the inventory;
- about accounting items for which it has been established that they do not comply with the conditions for recognition of an asset.
This statement is compiled for the responsible person(s) at the place where the inventory is carried out by the institution’s commission, indicating:
Column numberIndicator nameCompliance with inventory data (form 0504087)
| 1 – 4 | Object information | Columns 1 – 4 |
| 5 | Accounting account number (code) | Box 10 |
| 6 | Book value (amount) per unit of accounting object | The result of dividing the indicator in column 12 by the indicator in column 11 |
| 7 | The price (estimated value) of an inventory item, indicated when taking inventory of goods (price of goods), when identifying surpluses - the estimated value of the item | Box 5 |
| 8 – 15 | Inventory result | |
| 8 | Number of inventory items for which a shortage was identified according to accounting data | Box 13 |
| 9 | Sum | Box 14 |
| Determined by multiplying the indicator in column 8 by the indicator in column 6) | ||
| 10 | The number of inventory items for which a discrepancy was identified within the limits of natural loss norms according to accounting data and actual availability | |
| 11 | The amount of inventory items for which a discrepancy was identified within the limits of natural loss norms | |
| Determined by multiplying the indicator in column 10 by the indicator in column 6 | ||
| 12 | Number of objects exceeding accounting data | Box 15 |
| 13 | Sum | Box 16 |
| Determined by multiplying the indicator in column 12 by the indicator in column 7 | ||
| 14 | The number of inventory items in respect of which the institution’s commission established their non-compliance with the conditions for recognition of assets for accounting purposes | Column 17 |
| 15 | Sum | Column 18 |
| Determined by multiplying the indicator in column 14 by the indicator in column 6 |
The statement of discrepancies based on the inventory results (f. 0504092) is signed by the chairman and all members of the commission of the institution carrying out the inventory.
Example 2:
Based on the results of an inventory carried out in a budgetary institution, the commission identified objects (wooden models) - 2 pieces, valued at 5,000 rubles, book value 12,000 rubles - that do not belong to fixed assets.
The inventory list (f. 0403087) will reflect the following information:
Name of the non-financial asset object Actual presence (condition) According to accounting data Inventory results
| Does not meet the conditions of the asset | |||||||
| Price (estimated value) | Quantity | Amount, rub. | Quantity | Book value, rub. | Quantity | Amount, rub. | |
| 2 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 11 | 12 | 17 | 18 |
| Wooden models | 5 000 | 2 | 10 000 | 2 | 12 000 | 2 | 12 000 |
In the statement of discrepancies (f. 0504092) the specified objects will be reflected as follows:
Name of the non-financial asset object According to accounting data Inventory results
| Book value per unit, rub. | Price (estimated value) | Does not meet the conditions of the asset | ||
| Quantity | Amount, rub. | |||
| 2 | 6 | 7 | 14 | 15 |
| Wooden models | 6 000 | 5 000 | 2 | 12 000 |
* * *
In conclusion, we note that the changes made to the inventory list (form 0403087) and the statement of discrepancies (form 0404092) are related to the provisions of federal standards that came into force on January 1, 2021.
[1]Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n “On approval of forms of primary accounting documents and accounting registers used by public authorities (state bodies), local governments, management bodies of state extra-budgetary funds, state (municipal) institutions, and Guidelines for their use."
Budgetary organizations: accounting and taxation, No. 2, 2018
Source: https://www.audar-press.ru/otrazhenie-v-uchete-rezultatov-inventarizacii
Inventory procedure
In terms of structure, inventory can be divided into three main stages.
The first stage is preparation, during which a plan is developed, the availability of documentation for fixed assets is checked and its content is examined, and a corresponding order is issued on behalf of the director of the enterprise. By means of the above order, an inventory commission is appointed (it can be permanent), which should include employees from different departments, then the financially responsible employee writes a receipt, and the balances of fixed assets are determined using the accounting data.
The second stage is the inventory itself. Here everything is measured and calculated, an inventory list is drawn up, into which all the material assets actually available in the enterprise are entered. At the same stage, an assessment of previously unaccounted for objects occurs, a description of the degree of their wear and condition.
And finally, the third stage : the final one. During this process, the received information is compared with accounting information, deviations are identified, as well as their causes, and a statement of discrepancies is compiled. At the end, preparations are made for entering all detected discrepancies into accounting.
Form and sample filling
form for statement of discrepancies based on inventory results (f. 0504092).
Sample of filling out a statement of discrepancies based on inventory results:
Similar articles
- Collation statement
- Inventory results report (filling sample)
- Transmittal sheet for the bag (form and sample)
- INV-26 statement of accounting of results identified by inventory
Document format and design
Today, the statement of discrepancies can be made in any form or according to a template that is developed and approved within the company. However, many businesses still prefer to use the previously unified form because it is convenient and includes all the necessary fields, rows and cells. The format of the statement must be fixed in the local regulations of the organization.
The statement is made in two copies identical in content, each of which is certified by the signatures of responsible employees. There is no need to stamp the form.
What form is used to fill out the matching sheet?
The forms of matching statements are given in the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88, they can be downloaded on our website:
The matching statement form for budgetary institutions in form 0504092 was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated March 30, 2015 No. 52.
Sample statement of discrepancies based on inventory results
- At the beginning of the document, standard data is filled in: date of formation of the statement, name of the organization, name of the structural unit and information about the financially responsible employee.
- Next comes the main part, which is presented in the form of a table. It contains the name of the inventory object, its inventory sign (number), the unit of measurement in the form of a code and its decoding (pieces, liters, meters, etc.), and the accounting account number.
- Then the table contains data regarding the actual results of the event: first, what is the shortfall. Here you write the book value of the object, information about natural losses (quantity and amount), the price at the time of inventory, loss in excess of the established norm of natural loss, the difference between the price on the balance sheet and the market value (plus or minus).
- Then, if surpluses are identified, information about them is entered: their quantity and cost.
- In conclusion, the document must be signed by the materially responsible employee, as well as the accountant.
What is reflected in the statements
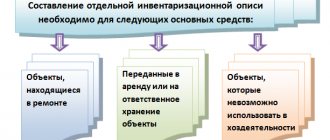
Reports No. 18 and 19 include only those items of property for which deviations were identified. If an organization identifies discrepancies regarding property that does not belong to it (for example, leased property; property received for processing), then data on the results of the inspection for such property are reflected in separate forms.
The amounts of surplus and shortage of inventory items in the matching statements are indicated in accordance with their assessment in accounting. At the same time, if the shortage of inventory items is determined taking into account the norms of natural loss, then in this case it is imperative to attach a calculation of losses within the specified norms. The amounts of the final shortage, taking into account the calculation of losses, are reflected in columns 27-32 of INV-19. The loss of inventory within the established norms is determined after offsetting the shortages with surpluses based on re-grading.
When filling out a document on the results of the inventory of intangible assets, columns 3, 8, 10 are not filled in.
The documents are drawn up in 2 copies and signed by the accountant and the financially responsible person, who confirms with his signature that he agrees with the results. One copy remains in the accounting department, the second is transferred to the financially responsible person. The inventory record is kept for at least five years.
It very often happens that during inventory activities, misgrading is revealed - a simultaneous shortage and surplus of similar material assets. In this case, the shortage can be covered by surpluses. This operation is reflected in the matching statement as an offset. To do this, the financially responsible person must provide the commission with an explanation about the misgrading.
If surpluses and shortages arose due to accountant errors, then the difference between the accounting data and the results of inventory measures is reflected in the corresponding columns 12 to 17 of the column “Adjusted by clarifying accounting entries” of the INV-19 report.
When reflecting shortages and surpluses identified during the audit in accounting, one should be guided by the accounting regulations “Correcting Errors in Accounting and Reporting”, PBU 22/2010, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 28, 2010 No. 63n.