The group of movable assets includes all valuables whose parameters differ from the characteristics of immovable objects. One of the specific features of this group is the physical ability to transfer assets to third parties. This means that this group includes all objects that can be easily transported from one location to another. An example of movable property is industrial technical equipment, furniture and household appliances. In this article, we propose to consider the question of what constitutes movable property.
Movable property is all property that cannot be classified as real estate.
What is movable property in simple words
Based on the information in Article 130 of the Civil Code, movable property is considered to be everything that has not been defined as real estate. That is, the bowels of the earth, plots and everything that is installed on them without the possibility of dismantling, maintaining functions and integrity. First of all, this includes buildings, unfinished buildings and other structures. Also real estate is:
- vessels (sailing within the Russian Federation and in the seas abroad);
- space objects;
- aircraft;
- part of the structure where parking spaces for cars are located. One condition must be observed here; the boundaries of this part must be described in accordance with the law on cadastral registration.
Most often, owners of movable property are not required to register it. But, if we are talking about a car, you cannot do without registration. Regarding transactions, they often do not require state registration. An exception may be an item of special value that is in circulation in limited quantities.
Reclaiming property from someone else's illegal possession
To contents
Vindication or vindication claim appeared in antiquity; the concept is literally translated from the Latin “vimdecire” as I declare, I demand. In accordance with Art. 301 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the applicant can only be the legal owner. Art. 302 and 303 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation divide the types of such ownership into bona fide, when the owner did not know that he was violating someone’s rights, and dishonest.
Art. 302 provides for cases of loss of material assets by the owner, or the person to whom they were transferred, loss due to theft, or in another way against the will of the legal owner. The court also establishes compensation for the amount of income that the owner was unable to receive, or the illegal owner received by exploiting the object of dispute. A vindication claim involves the recovery of movable property from the debtor .
However, if the property was divided incorrectly during the divorce of spouses or the liquidation of an organization, then you should first challenge the legality of the transfer of ownership. Recognition of the right to movable property is often difficult, especially if it has not been registered; such cases in most cases remain unresolved.
What are the signs to recognize movable property?
Legislative acts do not contain information about what characteristics movable property has, so it is very difficult to name them specifically. In this case, the characteristics should be determined in contrast to those that the property has, namely:
- permanent location and reference to one area;
- inability to move property without losing its integrity and quality.
For example, it will not be possible to remove a house built on a plot or move the plot itself. Also, communications such as an air conditioning system, water supply or sewerage cannot be considered movable property. The main feature by which property must be distinguished is the ability to be transported without losing its main qualities.
Movable property can be birds, farm animals or pets. In Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation you can find information only about what characteristics real estate has. If other property does not have these characteristics, it is classified as movable.
Why was the plane classified as real estate?
All planes and ships that fly the flag of the Russian Federation are equated to the territory of Russia, that is, they are part of it. This means that Russian laws will apply on board the ship. The same applies to airplanes and ships from other countries of the world. In addition, this property is subject to mandatory registration, which is one of the main features of real estate.
Art. 159.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation - fraud in the field of lending
This crime refers to acts related to obtaining a loan. At the same time, this is also a favorite article of collection agencies. Because only a lazy employee calling debtors by phone would not try to use it to intimidate. We need to look at this article in detail. Let's start with the first part. It is she who defines the crime itself. According to the first part of 159.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, liability is provided for the fact that the borrower steals funds. And he does this by providing information that is not reliable or even deliberately false.
How to commit such a crime? There are several proven methods:
- Providing false information.
- Providing knowingly false information.
Inaccurate information in banking and credit institutions is usually verified using paper and electronic documents. Those. you should have:
- Get a certificate of experience.
- Get a certificate of average salary.
However, these documents should not correspond to the real situation. If you did not do this, therefore there is no crime.
The situation is similar with the second method of committing a crime. There can be a lot of variations here:
- Obtaining a loan using someone else's documents.
- Obtaining a loan using fake documents.
- Providing separate documents with changed information.
For example, some citizens provide the bank with a copy of the Labor Book (work book) and income certificate. It is enough to falsify 1 or 2 of these documents (or copies) and the crime will already be evident. And even in such cases, everything is usually limited to some kind of punishment in the form of a fine and execution. By the way, according to the first part of this article, the sanctions are as follows:
- 4 month arrest.
- Fine 120 thousand (or according to another calculation scheme).
- Compulsory, corrective, forced labor.
- Restriction of freedom (24 months).
Deprivation of liberty is not even observed here. It is important to understand that qualification is not always carried out only according to 159.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. If you didn’t forge anything and didn’t ask your employer to forge papers for the bank, then you don’t have to worry about threats from collectors. If you forge something, then be prepared for a more serious punishment.
The qualifying feature for the second part of the current article is the existence of a preliminary conspiracy and a group of persons. This is exactly the case when you persuaded someone at work and together falsified documents. Here the punishment is more serious:
- Imprisonment (4 years upper limit).
- Fine up to 300,000 rubles.
By the way, if someone used his official position, he faces a more serious punishment. Because this is a part 3 qualification. Here the sanctions will be tougher:
- Up to 6 years in prison (combined with fines and restrictions on freedom).
- Fine up to half a million rubles (minimum 100).
- Forced labor.
If you have done the same thing that is qualified by the third part, but on an especially large scale or with participation in an organized group, then the punishment will be even more serious. Namely:
- Up to 10 years in prison (combined with a fine of up to 1 million rubles).
- Restriction of freedom.
We must understand one more very important thing. The fact is that a large size is at least 1.5 million rubles. And a particularly large one is already 6 million rubles.
It must be said that there is quite a bit of practice on such crimes. Because it is still necessary to prove that the falsification was committed intentionally and with a selfish component. Moreover, amounts of this size are not accessible to ordinary citizens purely technically. Therefore, collectors who begin to scare all debtors without exception are simply mistaken. In order to attract a debtor under 159.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, it is necessary to prove that he falsified the data in the loan application. Or simply provided information that was not reliable. Was not reliable at the time the loan was issued. And given the fact that banks now use scoring systems and check a potential borrower on all bases, the likelihood of falsification is extremely low. Therefore, almost every case under such an article can be examined under a microscope.
It is most likely that crimes committed on a particularly large scale under this article will be the most attractive to criminals. Because in all other situations it simply doesn’t pay off. If you are interested, you can familiarize yourself with the judicial practice under 159.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. There are not so many cases in the Russian Federation under this article, but they still exist.
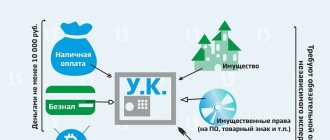
Types of movable property
In some countries, the civil code is so different that the same things can apply to movable and immovable property. Article 1205 of the Civil Code states that the ownership of things should be determined by the law of the party where it is located. But, if an item is on the road, for example, it is transported by plane, ship or car, the termination or emergence of rights to it is determined by the law of the party from which it was sent.
The law defines especially valuable movable property in relation to budgetary and federal institutions that are under the support of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation, this includes:
- objects with a cost above 350,000 rubles;
- other property that is necessary so that the services can fully and efficiently take measures in the event of emergency situations identified by the charter of their activities. The book value of these items per unit must exceed 100,000 rubles. This includes personal protective equipment, weapons, robotic equipment, power machines and machine tools, computer equipment, office equipment, remote-controlled systems, tractors, as well as other special vehicles;
- objects that are alienated in accordance with the procedure established by regulations and laws of the Russian Federation. Including valuable museum collections, as well as documents that are in state ownership and on the balance sheet of museum funds of the Russian Federation.
There are several types of property, about which lawyers have many controversial situations, this includes the following:
- air conditioners, alarm systems, payment terminals, ATMs, advertising banners;
- vehicles;
- electrical network, water supply, cable communication lines, sewerage;
- improvement items installed in leased premises;
- leasing objects and for delivery to tenants;
- property that was received during the reorganization or contributed to the authorized capital;
- items that have previously been used by others;
- modernized facilities.
Federal property and structure of federal authorities, local governments
Federal property is state property managed by the federal agency Rosimushchestvo. The agency's scope of activities includes responsibilities for the provision of public services and law enforcement functions of land relations.
The main functions of the Federal Property Management Agency in the established powers:
- implementation of the only state policy in the field of property and land relations;
- implementation of the owner's powers within the limits and as it must be determined by federal legislation regarding the property of federal state unitary enterprises and government institutions, shares (shares) of joint-stock (economic) companies and other property treasury entities of the Russian Federation
- differentiation of state-owned property, including land, property of the Russian Federation, property of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and property of municipalities;
- implementation of the powers of the owner of the debtor's property - a federal state unitary enterprise, performing bankruptcy procedures;
- protection of property and other rights and legitimate interests of the Russian Federation in the event of management of federal property and its privatization on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad;
- introduction of accounting of federal property and maintaining a register of federal property.
Current, operational management of public utilities must be carried out by structures that are especially created for this purpose, created from professionally trained personnel. The functions of such management structures in municipalities are performed by local government bodies. They were created for broader purposes and to solve at least two problems: political (power) and economic rule, and it is not always possible to separate these tasks precisely.
Communication lines, water supply and sewerage
These objects are considered one of the most controversial. Sometimes lawyers try to argue that they should be classified as movable property, which would subject them to benefits. According to the law, electricity and water supply networks are located in the premises, but they are only part of the building, which is not subject to state registration. Despite this, each of the objects is real estate.
According to the law, a building is a single volumetric system containing engineering and technical support items. Any of the functional items, especially elevators and heating radiators, cannot be removed without causing great material damage.
This means that each of these properties must be subject to property taxes. Speaking of cable lines, these are movable objects. The law states that engineering infrastructure facilities must be registered. This includes cable crossings, above-ground buildings and below the ground floor. Cable lines are also classified as preferential property.
Characteristics of real estate
The legal concept of real estate implies the presence of the following properties:
- in fact, they are land plots and areas on which deposits are located;
- strong connection with the earth. This means the presence of design or other features due to which real estate objects occupy a stable position due to contact with the surface of the land plot. These can be the root system of trees in a garden or forest, as well as the foundation or piles under a building or structure;
- the impossibility of moving an object in space without causing disproportionate damage to its purpose. It is this characteristic that distinguishes between temporary structures (stalls and pavilions), which are included in the list of movable items, and stationary buildings and structures. If a non-capital object can be taken away on a truck, then this cannot be done with a capital one. Even rare cases of moving buildings are associated with the fact that during this, they cannot be used for their intended purpose (to house offices or businesses).
There are also derived features. They are associated with the need to register ownership of real estate.
Transport
There are almost never any problems with road transport. These objects have all the characteristics of movable property, which are indicated in Article 130 of the Civil Code of Russia. As mentioned above, the only exceptions are airplanes, watercraft, space rockets and other objects such as satellites and the ISS. They are subject to mandatory state registration.
But most companies do not have this property on their balance sheet and this will most likely never happen. Other vehicles are not subject to property tax. The tax is imposed only on vehicles that were accepted on the balance sheet as main vehicles before January 1, 2013.
Pledge
To contents
Banks offer loans secured by movable property . Thus, the acquired property will be considered a guarantee of payment, or the already acquired property ensures the receipt of funds. Registration of a pledge of movable property takes place on the website www.reestr-zalogov.ru after which it is not subject to sale to third parties.
Seized property
Foreclosure of pledged property may be carried out pre-trial. In this case, the pledgee is notified by the notary. Sale is possible ten days from the date of delivery of the notice, unless other conditions have been stipulated between the pledgor and the pledgee. The deadline for fulfilling an obligation secured by a pledge of movable property may occur earlier, however, with a greater risk of loss in price due to the urgency of the sale.
Leasing object and for rent
According to Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, movable objects that will be leased are exempt from property tax. This preferential right can be used either by the lessee or the lessor, it depends on whose balance sheet the fixed asset is indicated on.
It is also worth understanding that the decision on who will put the leased asset on the personal balance is decided jointly by the lessee and the lessor. If this property ends up on the balance sheet of the lessor, he will have to pay property tax. The same applies to the second party to the agreement. Benefits can also be used when transferring property for temporary use. It relates to fixed assets and will be displayed in accounting as a material value or investment.
Modernized facilities
Fixed movable assets that were placed on the balance sheet before January 1, 2013 are subject to reconstruction or modernization. According to the Ministry of Finance, benefits should not apply to these objects. This position is explained by the provisions of PBU 6/01, which states that the fixed asset must be accepted for reporting at the original price.
As for reconstruction and modernization, we are talking only about adjustments to the previously formed value. This means that reconstruction and modernization cannot change the date of putting the fixed asset on the balance sheet. If the property was registered in 2012 or earlier, the property is taxed according to general principles.
Registration of an object as a sign of real estate
Article 131 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides that ownership and other proprietary rights to real estate are subject to state registration. The question arises: does property belong to real estate if the rights to it are not registered?
In the commented letter, the tax authorities indicated that in this case it is necessary to take into account the conclusions contained in the Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated 04/07/2016 in case No. 310-ES15-16638. The court noted that a thing is immovable either by virtue of its natural properties, or by virtue of a direct indication of the legislation that such an object is subject to the regime of immovable things. At the same time, state registration of the right to a thing is not a prerequisite for recognizing it as real estate. Similar explanations are contained in the Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated September 30, 2015 No. 303-ES15-5520.
Based on this, tax authorities provided the following algorithm of actions to identify the grounds for classifying a property as real estate.
First of all, you need to establish whether there is a record about the object in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. If there is, then such an object is recognized as real estate.
If there is no entry in the Unified State Register of Real Estate, you need to check whether there are grounds confirming the strength of the connection between the object and the ground and the impossibility of moving the object without disproportionate damage to its purpose. For example, in relation to capital construction projects, documents of technical accounting or technical inventory, permits for construction and (or) for putting the facility into operation (if necessary), design documentation, expert opinions or other documents that contain information about the relevant characteristics are subject to examination. objects, etc.
Tax officials also drew attention to the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated September 24, 2013 No. 1160/13, which states that, within the meaning of civil legislation, rights can be registered only in relation to those things that, having signs of real estate, are capable of acting in civil circulation as individual objects of civil rights.
Previously used property
Enterprises often purchase movable assets that were previously used by other organizations. This means that each of these objects was previously accounted for as a fixed asset on the balance sheet of the former owner.
Therefore, you need to figure out whether the current owner will be deprived of rights to benefits. Most likely, each of the specialists from the financial department will give a negative answer. There are no restrictions in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for objects that were previously used by another enterprise. This means that second-hand property will qualify for the tax exemption, just like any new property.
Improvements in the rented premises
Every tenant sooner or later begins to improve or change the premises he rented. Sometimes, one of the improvements may be included in the database of objects subject to property tax. It all depends on what kind of improvement it is - inseparable or separable.
In the latter case, it can be successfully disassembled or transferred to another location in such a way that this does not affect the quality and appearance of the product. This will also mean that this improvement is recognized as movable property and will not be subject to tax. An inseparable improvement is a capital investment in a rental property. The funds spent on this are taken into account in the initial price of the premises.
Following from this, this improvement will be associated with the object as a whole and will be classified as real estate. As a result, the tenant will have to pay property taxes throughout the entire lease term. In legal practice, there are cases where landlords did not agree with such conditions.
Sometimes you can come across the opinion that an inseparable improvement should be equal to a separable one and, as a result, excluded from the tax base. In most cases, the argument is made that the tenant is not the owner of the improvement. In this regard, he does not have the opportunity to register with the Federal Tax Service at the location of the property he rented and submit a property tax return.
Methods for assessing property value
To contents
Every property is unique, so valuation uses several methods that can most accurately determine the value. Such a procedure can be carried out during the liquidation or bankruptcy of an organization, the division of common property between family members, and the calculation of tax on inheritance received.
Market or comparative approach
Value is determined based on recent equivalent transactions and industry ratios. Thus, the cost of a car can be the average for the region, and the cost of a real estate object can be the average for the area in which it is located.
Income approach
The calculation is based on an analysis of income generation opportunities. In this case, profit is capitalized; it is not distributed among holders of shares or other rights, but is spent on reproduction and increasing fixed capital. Then they resort to discounting cash flows, which means that the value of the object will increase by the amount of payments received. This method is used when investing.
Cost-effective approach
Most often used for real estate valuation. The amount of necessary investments is calculated, depending on the wear and tear of the object; it cannot exceed the cost of replacing the object with a new one. For example, no buyer would agree to buy a house that needs to be renovated if the same funds could be used to build a similar one.
Designs for advertising signs, ATMs, air conditioners and terminals
Whether or not benefits will apply to air conditioners, as well as alarm systems (burglar and fire), depends on the specifics of the installation. Sometimes they are an inseparable part of the technical and engineering support system. In this case, they must be built into a building, a nearby structure, or installed as a separate object.
For example, if an air conditioner is built into the wall and looks like part of the ventilation system of the building, it is classified as real estate and the owner will have to pay tax for it. Also, using this example, we can consider the situation with an alarm system, which is a component of the engineering system.
If each of these objects is installed as an independent object, it can be removed and moved without causing damage to the structure. In this case, this property will be classified as movable and eligible for benefits. Regarding payment terminals, ATMs and advertising structures, these are independent objects; therefore, benefits apply to them.
Art. 159.5 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation - deception on the part of insurers
An equally interesting article that is practically not used. Because insurers have money. But victims usually don’t have them. However, there is practice under this article. According to the first part of this article, you can probably involve employees of any insurance company. And without exception. But as you understand, in reality everything does not work quite as it should. For the first part, there are several signs of a crime committed:
- Fraud in the context of an insured event.
- Fraud regarding the amount of insurance compensation.
- Cheating by any other means.
The criminal does not face anything serious here. Fine up to 120,000 rubles. There is also correctional work and compulsory work. They may be restricted for 24 months or arrested for 4 months. All. This is where all the sanctions end. The second part provides for liability for causing significant damage. It also provides for the qualification of preliminary conspiracy. Here the sanctions are a little stricter:
- Imprisonment (up to 5 years).
- Restriction of freedom.
- Correctional or compulsory work.
- Fine up to 300,000 rubles.
If your official position was used or there is a large amount of damage, then this is part 3. Fine up to half a million rubles. And also imprisonment for up to 6 years. Well, traditional forced labor. If there is a particularly large size or an organized group, then qualify for the 4th part. There is already a prison sentence of up to 10 years. Restriction of freedom and a fine of up to 1 million rubles are also applied. But, as you might guess, part 4 is used extremely rarely. Well, the last one for today is Art. 159.6 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation – actions in the field of computer and information technologies.
Movable objects as authorized capital or received during reorganization
Upon completion of the reorganization process, the company receives by right of inheritance the object belonging to the previous owner. If it is movable, the recipient is legally exempt from paying tax. Any of these items that were received no earlier than 2013 are not included in the tax service database. The same applies to items that the company received as a result of the spin-off.
Organizations that were created after the transition from a unitary enterprise can take advantage of the same preferential conditions. If the new company receives property from a municipal or unitary enterprise, the owner has the right not to pay the state fee. This also applies to movable property that was contributed to the authorized capital in the form of a contribution.
Related posts:
- Leasing - what is it and why is it needed?
- Loan - what is it, how is it different from a loan?
- Types of legal entities - a detailed overview
- Encumbrance - what it is and how it works
- Rent - what is it and how does it work?
- Beneficial owner - his rights, who can...
- Easement - what is it in simple words
- Individuals and legal entities - what are their differences?
How was fraud previously classified?
The first mention in our law of such an act as fraud is found in the Council Code. In those days, fraud was any theft of someone else's property, characterized as:
- Sudden.
- Deft.
- Deceptive.
That was earlier. Now fraud is a much broader qualification. In fact, now fraud is actions related not only to theft. But also with alienation, and sometimes even with legalized (by external signs) transfer of property. The example of black realtors who draw up all the paperwork in such a way that you can’t even dig into it is appropriate here. And fraudulent schemes of this kind were not always obvious to law enforcement agencies.
In addition, the forms of fraud themselves are quite diverse. After all, a citizen can be deceived both by falsifying a transaction and by direct theft of personal data or documents. Fraudsters (for the most part) have in-depth knowledge:
- In laws.
- In information systems.
- In psychology.
- In the order of work and features of office work of state and municipal bodies.
It’s probably easier to list those areas where scammers definitely don’t understand. There are actually very few of them. So little that even in science there are now a huge number of scammers. And I don’t even want to say how many officials with stolen candidate’s papers are still working in our country and have not been exposed. And after all, those citizens who organize such a “conveyor” are also engaged in a kind of fraud. True, to organize the market for scientific titles, the qualifications of fraud are not enough. There, in total, a dozen more criminal articles can be added.