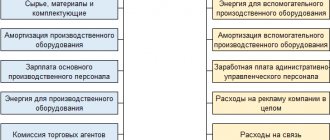
Depreciation means transferring the cost of fixed assets (FP) and intangible assets (IA) to the cost of work, services, as well as products manufactured by the enterprise as they wear out. To understand clearly what this is, let’s turn to economic terminology and start with the OS.
OS - means of labor (material assets) involved in the production process. These are, for example, buildings, transport, overpasses, tools, equipment.
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
Important! OS (structures, tools, etc.) retain their natural shape, are used in the main activity, and have a service life of more than a year.
Various operating systems, for example, tools or the same equipment, participate in a number of production cycles. For the most part, they retain their natural shape for a long time. Gradually, OSs lose their consumer properties, cost and require repair, or even replacement. Taking this into account, the cost of tools, equipment, their repair or replacement is transferred equally to the cost of production. Here we are talking only about the products in the production of which these operating systems are involved, and their standard service life. This transfer is the depreciation of the OS.
What is the purpose of accelerated depreciation?
For certain reasons and under specific conditions, fixed assets are depreciated at an accelerated pace. Then special depreciation rates are applied, and the cost of the operating system is transferred to the final product faster than usual. That is, their formal wear seems to be accelerating.
Thus, the main goal of the process is to accelerate the equal distribution of the value of tangible assets. All increased accruals go to compensate for costs during the service life. This stimulates investment and has a positive effect on the distribution of modernization expenses and the pace of enterprise development.
When accelerated depreciation becomes beneficial to a company
The main obvious advantages of acceleration are as follows:
- quick write-off of OS;
- thanks to the use of special coefficients, a reduction in the tax base and, accordingly, a reduction in the amount of taxes payable;
- tangible replenishment (compensation) of one’s own expenses;
- use of acceleration in leasing, which reduces costs.
Important! The use of accelerated depreciation and the corresponding coefficients must be economically justified and not run counter to the norms of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Restrictions on the use of the coefficient
The same operating system may meet several criteria, which imply the use of a number of increased (or, as they are often called, accelerated) coefficients. As stated in paragraph 5 of Art. 259.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , out of the total number of permissible coefficients, only one of them is allowed to be used.
Important! The taxpayer is obliged to record in the accounting policy which acceleration factor from among the possible ones it will apply.
Methods for calculating depreciation
Russian accounting standards today are represented by PBU 6/01. This provision identifies four commonly used methods for calculating depreciation (Am):
- Linear. Am is accrued equally throughout the service life, starting from the initial cost (HC) and ending with the residual value. Current residual article = NS - SNA, where SNA is the total accumulated depreciation of fixed assets.
- Reducing balance (or accelerated). Am for the period = residual value * corresponding %. Am is accrued on the balance at the beginning of the year.
- Write-off of items based on the sum of numbers of years of useful life (hereinafter abbreviated as SPI).
- Write-off is proportional to the volume of products (work). Accrual is based on a specific natural indicator.
Am is accrued in one of the named ways for a group of identical fixed assets, and during the entire SPI of objects of this group.
Methods for calculating depreciation in accounting
An enterprise has the right to use any accrual method that suits it. Usually, when choosing, they start from the ratio of profits and expenses. When choosing the optimal accrual option, most enterprises advocate reducing the difference between the accounting and tax accounting components and bringing them closer together. Therefore, when depreciating fixed assets, preference is given mostly to the linear method. It is suitable when profits flow evenly during the SPI period.
Methods for calculating depreciation in tax accounting
The amount of depreciation that is calculated for taxes is determined independently by the payer each month. The methods and procedure for calculation are established by Art. 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Accrual is made:
- Nonlinear method - by depreciation group (subgroup).
- Linear method - according to the object.
The payer can choose any of them and record it in the accounting policy.
Important! You can change the selected accrual method once every 5 years and only with the beginning of a new tax period.
The linear method should always be applied to those operating systems that are listed in paragraph 3 of Art. 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, regardless of which method the payer has chosen and enshrined in its policy.
Clause 5 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
If an organization during any calendar month was established, liquidated, reorganized or otherwise transformed in such a way that, in accordance with Article 55 of this Code, the tax period for it begins or ends before the end of the calendar month, then depreciation is calculated taking into account the following features:
clause 1, depreciation is accrued by the liquidated organization for the month (inclusive) in which the liquidation is completed, and by the reorganized organization - for the month (inclusive) in which the reorganization is completed in accordance with the established procedure;
Clause 2 depreciation is accrued by the organization established as a result of reorganization from the 1st day of the month following the month in which its state registration was carried out.
The provisions of this paragraph do not apply to organizations changing their legal form.
Under what conditions is it permissible to use accelerated depreciation (list of situations)
Important! Accelerated depreciation is applied only to a limited range of assets that are characterized by rapid wear and tear. Their list is determined by Art. 259.3 Tax Code of the Russian Federation .
For all operating systems from the list, the so-called acceleration coefficient is applied (K = up to 2 or K = up to 3). Details of the OS list are given below along with the odds sizes.
Increasing coefficients for fixed assets used in aggressive environments
An aggressive environment is understood as an environment that can negatively affect surrounding materials and structures and cause their destruction. Under its influence, the wear and tear of the OS accelerates. A striking example is the interaction of an OS with a toxic substance.
Under these circumstances, it is permissible to use K = no more than 2. This norm does not apply when using a non-linear technique in relation to objects 1, 2 and 3 of depreciation. gr.
In fact, acceleration can also be used when depreciating objects that, according to their intended purpose, should not be used in an aggressive environment. If the documentation contains a note about the possibility of such use, then it is usually used when there is an excess of the standards stated in the documents.
Important! The use of an increased coefficient applies only to those objects that are exposed to an aggressive environment. The remaining fixed assets are subject to depreciation in the usual manner, without acceleration.
Depreciation of fixed assets used in scientific and technical activities
All objects participating in this activity are subject to accelerated depreciation with the participation of K = up to 3. The concept of “scientific and technical activity” (hereinafter abbreviated as NTD) is explained by Art. 2 Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 127 dated August 23, 1996. Nevertheless, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, referring to the norms of Art. 262 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, also includes research and design developments.
Accelerated depreciation of leased objects (+example)
In the case of leasing, the established coefficient cannot exceed 3. For example, Tekhnika LLC, under a leasing agreement, received equipment classified as 4 depreciation. gr. The validity period of the contract is 3 years. The balance holder (tenant) determined the SPI = 6 years. By agreement of the parties, a coefficient of 2 was established. It is assumed that the equipment will be written off within 3 years of leasing.
Features of accelerated depreciation during leasing:
- When the lessee changes, the lessor continues to charge depreciation.
- If the entire enterprise is comprehensively recognized as a leasing object, then depreciation is charged on all fixed assets. The exceptions are those OS that relate to 1, 2 or 3 depreciations. group.
For your information, the new lessee has the right to change the amount of increase for the property that was transferred to him from the previous lessee.
conclusions
Accelerated depreciation helps enterprises write off fixed assets faster, as well as cover their own expenses at an increased rate.
Also, this measure allows you to reduce the amount of taxes paid, which has a beneficial effect on the amount of income and profit.
However, reckless use of this write-off method can lead to violations of tax legislation (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This accrual method can also be applied to fixed assets that are leased, thereby reducing costs.
Depreciation acceleration factor
This multiplier appears exclusively in accruals that are made using the reducing balance method described above. This is evidenced by clause 19 of PBU 6/01. Its value ranges from 2 to 3, depends on the type of OS, and is determined in accordance with the provisions of Art. 259.3 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These are some kind of limits that cannot be exceeded.
Factor up to two
In practice, it occurs most often, especially in relation to OS objects with which they work:
- in an aggressive environment,
- with increased shifts;
- agricultural organizations of industrial type;
- SEZ participants.
This also includes objects:
- high energy efficiency;
- from among the main technological equipment;
- included in 1-7 depreciation. gr. and made under an investment agreement.
Factor up to three
Used less frequently than the previous multiplier, and only for OSs that:
- are the subject of a leasing (rental) agreement;
- used in scientific and technical documentation;
- participate in the extraction of oil and gas in a new subsoil area located within sea waters;
- involved in the water supply and sanitation industry.
Clause 6, Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Organizations operating in the field of information technology have the right not to apply the depreciation procedure established by this article in relation to electronic computer equipment. In this case, the expenses of these organizations for the purchase of electronic computer equipment are recognized as material expenses of the taxpayer in the manner established by subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 254 of this Code. For the purposes of this paragraph, organizations operating in the field of information technology are recognized as Russian organizations that develop and implement computer programs, databases on a tangible medium or in electronic form via communication channels, regardless of the type of contract and (or) provide services (perform work ) on the development, adaptation and modification of computer programs, databases (software and information products of computer technology), installation, testing and maintenance of computer programs, databases. (As amended by Federal Law No. 213-FZ dated July 24, 2009)
The organizations specified in this paragraph must fulfill the following conditions: (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 213-FZ)
the organization has received a document on state accreditation of an organization operating in the field of information technology, in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation; (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated July 24, 2009 No. 213-FZ)
share of income from the sale of copies of computer programs, databases, transfer of property rights to computer programs, databases, from the provision of services (performance of work) for the development, adaptation and modification of computer programs, databases (software and information products of computer technology ), as well as services (work) for installation, testing and maintenance of the specified computer programs, databases at the end of the reporting (tax) period is at least 90 percent of the total income of the organization for the specified period, including from foreign persons at least 70 percent; (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated July 24, 2009 No. 213-FZ)
the average number of employees for the reporting (tax) period is at least 50 people. (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated July 24, 2009 No. 213-FZ)
When determining the share of income from buyers - foreign persons, income from foreign persons whose place of business is not the territory of the Russian Federation is taken into account. The place of activity of the buyer is defined as the place of actual presence of the buyer in the territory of a foreign state on the basis of the state registration of the organization, and in its absence - on the basis of the place specified in the constituent documents of the organization, the place of management of the organization, the location of the permanent executive body, the location of the permanent representative office , if computer programs and databases, services (work) and property rights provided for in this paragraph were acquired through this permanent representative office, the place of residence of the individual. (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated July 24, 2009 No. 213-FZ)
Documents confirming the receipt of income from foreign buyers are an agreement (copy of the agreement) concluded with a foreign person, and documents confirming the fact of provision of services (performance of work), or a customs declaration (its copy) with marks of the Russian customs authority that carried out the release goods in the customs export procedure, and the Russian customs authority of the place of departure through which the goods were exported from the customs territory of the Customs Union. (Paragraph introduced - Federal Law dated July 24, 2009 No. 213-FZ; as amended by Federal Law dated November 27, 2010 No. 306-FZ)
Features of calculating accelerated depreciation
Accelerated depreciation (Am) is calculated as follows:
Abbreviations: OSOS - residual value of the asset. Using this formula, Am is calculated for a year or a month. For calculation, data is taken for a year or, accordingly, for a month.
Calculation of the amount of accelerated depreciation (example)
Promversiya LLC entered into a leasing agreement for 3 years. Under it, it received equipment with an initial cost of RUR 1,200,000. rub., the service life of which is 6 years. The parties to the agreement reached an agreement on the use of accelerated depreciation with K = 2. The best option in the proposed situation is to write off the operating system during the validity of the contract, i.e. 3 years (SPI = 36 months). Based on these data, we calculate Am per year and per month.
| Data for calculation | Calculation Am per year | Calculation Am per month |
| OSOS = RUR 1,200,000 rub.; SPI=contract term=3 years; K=2 g. | Am (annual) = 1,200,000 / 3 * 2 = 800,000 RUR. rub. | Am (monthly) = 1,200,000 / 36 * 2 = 66,666 RUR. rub. |
Car depreciation calculator
Is it a lot or a little? Let's look at the table of zoning according to the climatic conditions of the regions of the Russian Federation - the Altai Territory belongs to a cold climate. Environmental aggressiveness is high (85 kg of atmospheric emissions per inhabitant).
The number of residents in the region is 700 thousand. Let’s calculate the average annual mileage. 75 364/5=15072.8 km/year. This value corresponds to the coefficient I2=0.89 I1=0.4, Pf=75.4, I2=0.89, Df=5, A2=1.12, A3=1.07, A4=1.050 Let’s calculate the value independently: (I1xPf+I2xDf) xA2xA3xA4=(0, 4x75, 4+0, 89x5) x1, 12x1, 07x1, 050=43, 55% We have obtained the value of natural wear and tear. Let's calculate it in money: 600,000x43, 6/100=261,600 The cost of the car for 2017 will be 600,000-261,600=338,400.
We will calculate the cost taking into account obsolescence in the online appraiser service. It turned out that the market value of the car being valued is 338,400x(1 - 0, 2) = 270,720 rubles.
Useful service life of transport
The indicator depends on the type of vehicle. There are 10 types of transport subject to depreciation. Motor transport includes four categories:
| Group | Useful term | Related transport |
| 3 | 3–5 years | Motor vehicles Passenger cars Freight transport up to 0.5 t |
| 4 | 5–7 years | Special vehicles for people with disabilities Freight transport, vans, tractors, dump trucks Small class buses (up to 7.5 m) Tankers Forestry transport Transport trailers with a load capacity of less than eight tons |
| 5 | 7–10 years | Passenger cars with an engine over 3.5 l Trucks 5–15 tons Passenger transport up to 12 m long Special vehicles Trolleybuses |
| 6 | 10–15 years | Equipment with a load capacity of up to 15 tons Super class buses with a length of 16.5 m |