Off-balance sheet account meaning
Keeping records of inventory items that have been accepted for storage until they become the property of the enterprise should be carried out using off-balance sheet position 002. If we consider off-balance sheet accounts in general, the essence of their purpose is to reflect the category of goods, according to which the organization does not have ownership rights, i.e. they are received for use for a certain period of time. In this case, we can talk not only about the designated products, but also about conditional rights and obligations.
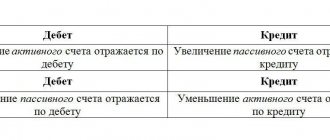
Balance sheet position 002 is active, and therefore, when products are received, their amount is reflected on the debit side, and relocation or disposal on the credit side. In this case, the cost of incoming working capital should be reflected in accordance with the documents attached at the time of delivery. If it is not indicated, then the assessment should be conditional or reflected in quantitative terms.
Account 02 – typical transactions:
- D 20 (25, , 26, 44, 91) K 02 - depreciation was accrued on fixed assets used for production purposes (general production; auxiliary production; for management or general economic needs; in trading companies; for leased objects).
- D 02 K 01 – reflects the write-off of depreciation accrued during the operation of the fixed assets.
- D 02 K 83 - reflects the increase in the company’s additional capital due to the depreciation of fixed assets.
- D 02 K 84 - reflects the restoration of depreciation accrued in previous periods.
- D 02 K 91.1 – reflects the write-off of depreciation upon disposal of fixed assets.
- D 83 K 02 – additional depreciation accrual due to revaluation of fixed assets is reflected.
Types of current assets accounted for off-balance sheet
In this case, enterprises and organizations reflect those goods that for some reason are unable to be reflected on the corresponding balance sheet accounts:
- this may be a situation where the received product turns out to be defective, damaged or does not meet the agreed parameters specified in the terms of the contract, and therefore must be returned to the seller;
- if the ownership of the purchased products passes after the purchase price is paid, and not at the time of delivery;
- if the specified values are taken into account under the pledge agreement;
- if the specified category of goods has already been paid for by the enterprise, but the supplier for some reason did not have time to transport the order from the warehouse;
- when goods and materials are received under an exchange agreement, by mistake.
Depreciation of fixed assets in accounting and tax accounting
During use, OSs lose their value due to wear and tear. Depreciation is the inclusion by fixed assets of their value over a certain period of time in finished products, works, and services.
Fixed assets in accounting and tax accounting have different criteria for classifying objects according to their value.
In addition, not all methods of calculating depreciation can be used in tax accounting. For this reason, there may be discrepancies in the amount of depreciation in accounting and when determining taxes.
For tax accounting purposes
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that fixed assets will be objects with a long service life and a price of 100,000 rubles and more.
Depreciation of fixed assets is calculated based on the original cost and the depreciation rate, which is determined based on the period of operation of the object.
Objects priced below 100,000 rubles must be shown in accounting as materials, so their price is immediately included in the cost of finished products.
The same objects that are defined as basic in tax accounting must be depreciated either linearly or nonlinearly.
The first of them involves determining the depreciation rate based on the useful life. The depreciation rate per year is calculated by dividing the unit by the useful life and multiplying by 100%. This method can be applied in tax accounting to all fixed assets.
Attention! The nonlinear method is applied only to operating systems whose application period does not exceed 20 years (group 1-7). Depreciation is determined based on the residual value of the object and the depreciation rate, which is determined for each group based on the period of use of the asset.
For accounting purposes
PBU establishes that fixed assets in accounting include objects with a price of 40,000 rubles or more. Subjects have the right to charge objects with a price less than the established criterion as expenses as materials. For objects that are priced as fixed assets, depreciation charges must be calculated.
In this case, companies and individual entrepreneurs have the right to use one of certain methods:
- Linear - by multiplying the original cost by the depreciation rate calculated based on the useful life.
- Declining balance method (non-linear) - by multiplying the residual value by the depreciation rate calculated based on the useful life.
- Proportional to the number of remaining years of use - the initial cost is multiplied by a coefficient defined as the number of years of use of the OS by the sum of the number of years of use.
- Proportional to the volume of products produced - the initial cost is multiplied by the number of products produced and divided by the planned volume of products that can be produced at the facility for the entire period of its use.
You might be interested in:
08 accounting account - “Investments in non-current assets”
Typical entries for balance sheet item 002
As for standard accounting records for the movement of inventory items, here we can highlight:
- Dt 002 and Kt of the corresponding position - receipt of valuables for storage;
- Dt ... and Kt 002 - write-off of inventory items due to their return to the supplier;
- Dt 002 and Kt... - products received with special conditions for the transfer of ownership;
- Dt ... and Kt 002 - write-off of valuables that were accepted under special conditions;
- Dt 002 and Kt ... - accepted goods and materials due to failure to fulfill obligations under the pledge agreement;
- Dt... and Kt 002 – sale of values accepted under the pledge agreement.
Which account is intended to reflect VAT?
In order to reflect transactions related to VAT in transactions, a separate subaccount 02 is opened to the main account 68 - “VAT calculations”. It is he who participates in the transactions drawn up when calculating value added taxes, and other subaccounts are used for actions with other taxes.
Correspondence from 68.02 also involves 2 accounts - 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets” and 90.3 “Value added tax”. The first account is responsible for the input tax accrued for purchased goods, services or work performed, and the second is used to reflect the tax payable to the budget on goods sold, services or work provided.
Reflection of off-balance sheet transactions with the supplier
Accounting for the designated category of goods under item 002 in the case of a supplier is carried out in a situation where the ownership of them has already transferred to the buyer.
Thus, the seller reflects these values deposited in 41 accounts. Once they are returned to the warehouse and remain the property of the supplier. In this case, account 002 will not be used for accounting records.
Thus, the receipt of goods for storage, as well as their return, is reflected in the following transactions:
Dt 002
Kt 002
Accounting for off-balance sheet transactions with the buyer (postings, examples)
In practice, there are cases when the buyer does not have the right to capitalize designated categories of goods as part of maintaining accounting records. This can happen when the delivered products turn out to be of poor quality, defective or in insufficient quantities.
Results
Having analyzed the state of account 02 for Debit 02 - Credit 02 , you can judge the amount of accrued depreciation when using and disposing of fixed assets of the enterprise.
Postings according to Kt 02 accrue depreciation on an asset. With the help of correspondence with Dt 02, the amount of the residual value of the property is determined - both those used in the future in the production process and those disposed of for various reasons. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Reflection of VAT in transactions when selling goods
In this case, the correspondence with the account 68.02 will include the account 90.3. Since the tax is payable from the organization to the budget, account 68 will be credited to the posting and it will look like this:
Dt 90.3 Kt 68.02 - VAT charge on sales
If the buyer makes an advance payment, the seller is also obliged to issue and transfer to him an invoice within 5 calendar days, which shows the amount of tax. This action is necessarily reflected in accounting when using account 76.VA “Calculations for VAT on advances received”, and the posting will look like this:
Dt 76.VA Kt 68.02 - VAT is charged on the advance payment transferred against future supplies
After the goods are shipped or in the event of a refund of the advance payment, the seller will deduct the tax previously accrued on the prepayment. The posting is as follows:
Dt 68.02 Kt 76 VA - value added tax accrued on the advance is accepted for deduction
Typical correspondence
In practice, the account in question often corresponds with the following lines of the plan.
By debit:
- 01 – “OS”;
- 02 – “AOC”;
- 03 – “Investment contributions to assets of a material nature”;
- 79 – “On-farm calculations”;
- 83 – “Additional capital.”
By loan:
- 02 – “AOC”;
- 08 – “Investment funds in non-current assets”;
- 20 – “Main production process”;
- 23 – “Auxiliary production”;
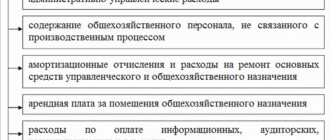
- 25 – “General production costs”;
- 26 – “General expenses”;
- 29 – “Serving business areas”;
- 44 – “Implementation costs”;
- 83 – “Capital of added value”;
- 91 – “Other income and expenses”;
- 97 – “Costs relating to future periods.”
Application of depreciation and calculation procedure
The legislation related to the features and procedures for calculating depreciation has undergone several changes. It is assumed that if the beginning of the actual use of an object does not coincide with the moment of its acceptance into the accounting system, then accrual starts exclusively from the month that follows the period of the beginning of actual use.
As for the end of accrual of AOC, it can be determined taking into account certain provisions of the law, as well as in the event of reorganization of the enterprise.
OS upgrade
The main feature of modernization is that its result changes the original characteristics of the OS object. As a result, its cost, period of use, etc. change. When accounting for expenses, it is advisable to open a sub-account on account 08, in which to collect all costs incurred for modernization.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 08 | 10 | Material costs written off for modernization |
| 08 | 23 | Auxiliary production costs written off |
| 08 | 60, 76 | A third-party contractor was involved in the modernization |
| 08 | 70 | The salaries of employees involved in the work were written off for modernization |
| 08 | 69 | Social contributions of employees were written off for modernization |
| 01 | 08 | Increased OS cost due to modernization costs |
Sale
When selling, proceeds are recorded in the amount established by the contract. In this case, expenses must include sales costs, as well as accrued depreciation. All transactions are shown in account 91.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 62 | 91 | Reflected revenue from the sale of operating systems |
| 91 | 68 | Determined VAT on the sale of fixed assets |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | The original cost of the object is transferred |
| 02 | 01/Disposal | Depreciation calculated over the operating period is transferred |
| 91 | 01/Disposal | The residual value is transferred to other expenses |
| 91 | 60, 76 | Costs for preparation for sale, dismantling, delivery, etc. are indicated. |
| 19 | 60, 76 | The amount of VAT for delivery, dismantling, etc. services has been determined. |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
| 91 | 99 | The financial result of the sale of the OS is reflected |
Liquidation
Liquidation of an asset can be carried out in a situation where it is no longer profitable to use it and it is not possible to sell it. In this case, the decommissioned OS can be disassembled, and the resulting materials can be used for other purposes.
| Debit | Credit | |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | The original cost of the object is transferred |
| 02 | 01/Disposal | Accrued depreciation is transferred |
| 91 | 01/Disposal | Residual value is transferred |
| 19 | 68 | The tax amount was restored based on the residual value |
| 91 | 60, 76 | Expenses include the costs of hiring a third party for the disassembly operation |
| 19 | 60 | VAT charged by the contractor has been taken into account |
| 10 | 91 | Materials received during disassembly of the OS object were capitalized |
Accounting account 01 is the active account “Fixed Assets” and reflects information about the organization’s fixed assets (Fixed Assets), their value and movement. The account belongs to the non-current assets section of the approved Chart of Accounts.
Specifics of use
Account 02 is intended to record materials about depreciation accumulated during the use of fixed assets. The amount that was accrued is displayed in the corresponding transactions. There are several types of objects for which depreciation is not calculated:
- elements related to the housing stock (residential buildings, dormitories, apartment property);
- external improvement;
- forestry;
- Men at work;
- plots of land;
- environmental management;
- fund of library value, museum, artistic values;
- models of layouts and other aids located in offices and scientific laboratories;
- architectural and cultural monuments.