Transit bank account - what is it?
If we consider the terminology, then this is an account in the currency of another state, which is used to transfer payment for a service or product.
Until 2007, every businessman who conducts business throughout the state gave away part of his profit: in different years this amount ranged from 10 to 50%, depending on legal requirements. To the great joy of entrepreneurs, this percentage is now 0%, thanks to such a banking profile.
This is interesting
To use a transit account, you need to pay a set commission fee and sell on the domestic market a set portion of the currency from the profit received at a fixed exchange rate. Also, one of the conditions for using a bank account is the transfer of part of foreign money into the domestic equivalent, according to the current exchange rate.
At the same time, this is not easy to do: in order to sell/exchange currency, the owner must write a special application, where it is necessary to indicate the amount of the transfer in banknotes. Amounts are redirected to cover losses. This is mandatory for legal entities when establishing business contacts with non-residents of the state. For convenience, insurance companies from other countries also use this method.
What is it for?
So what is a transit bank account and what is it for? It is used so that fiscal (tax) authorities can control the activities of a businessman. It is also an “intermediate point” for currency exchange, according to the exchange rate: that is, first the money is transferred to the transit number, and then only from it to the regular one. This applies to both entrepreneurs and individuals.
It is used for transfers for the following services:
- Transportation of goods to another country;
- Insurance payments;
- Transfer of goods.
You may be subject to commission and administrative fees.
Do you want to start using the money that came to you? Confirm the reality of the transaction by performing identification. To do this, just bring the bank to the tax office:
- Certificate of currency transaction.
- A contract stating the reason for the transfer of finances.
The bank may charge a commission because it is a currency control agent whose services are not free. All tariffs are specified in the agreement for settlement and cash services.
The rules for using accounts are defined in the special instructions of the Central Bank under number 111-I, dated March 30, 2004. The main conditions for transactions with currency within the Russian Federation are regulated by Federal Law No. 173 “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control” (the law came into force on December 10, 2003). Any person who will conduct transactions with dollars or euros must know these rules.
On the issue of the list of questionable transactions
This list is determined by the same Methodological Recommendations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 18. It includes the most typical types of dubious transactions. Each of them is assigned a separate code, provided for by the Regulation of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 375 dated March 2, 2012. The list contains separately:
- Questionable transactions involving money transfers abroad.
- Questionable cash transactions.
Regulation No. 375 contains, among other things, a detailed classifier of signs that may indicate atypical transactions. It is presented as a separate application in the form of a table containing the following information.
| Feature group code | Attribute type code | Description of the characteristic |
Particular attention should also be paid to the MR of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 19 dated July 21, 2017. These are recommendations that were developed and approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation to strengthen control over illegal operations and purposes of legal entities that receive cash using corporate cards.
| Some signs of illegal operations in the building. maps | ||||
| Cash credited to the company's account per week is more than 30% of the total turnover | Receipt of funds from individuals. who were noticed in questionable transactions | We are talking about a legal entity registered no more than 2 years ago or even earlier | The company's account receives amounts greater than 600 thousand rubles. | Cashing out amounts up to 600 thousand rubles. or not exceeding the limits established by the bank |
This list is not exhaustive. It is recommended to study it in detail in the original source. It should be noted that in addition to the named characteristics, standard ones are added. For example, the absence of tax and other generally obligatory payments, etc. The basis for suspicion of fraud may be the identification of at least two or more of the listed signs.
It should be noted that as part of ongoing supervisory measures, cash withdrawals from corporate accounts throughout the week are subject to control. You are allowed to withdraw no more than 100 thousand rubles in one day. A quick withdrawal of cash from several corporate cards by one client, especially at the end of the working day or the morning of the next day, comes under suspicion.
The purpose of MR No. 19 is to minimize such operations, as well as the involvement of credit institutions in them. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation recommends periodic analysis and monitoring of transactions carried out using corporate cards. If signs are identified that indicate a non-standard unusual transaction, information on it should be sent to the appropriate authorities.
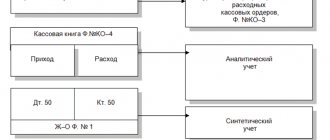
Structure
Everyone knows that the legal currency of Russia is the ruble, but when export relations arise, it is allowed to use other banknotes. For convenience and data recording, intermediate accounts are used. A transit bank account is an example of an accumulating (savings) account, and a person will be able to dispose of the amount only 15 days after receipt.
It consists of the following elements (details):
- a unique number, usually consisting of 20 digits;
- BIC - banking institution code;
- the agreement on opening a transit currency account must contain your data - INN and KPP;
- correspondent bank number (also twenty-digit).
The number is often called a bank identifier, since each group of numbers defines encrypted information. So, the first three digits mean the number of group I. The second two are number II of group. The sixth, seventh and eighth digits determine the currency code. The ninth is the verification number. The next four digits determine which financial institution this account belongs to. The types of institutions are indicated by the next two numbers after them. The last five digits are an internal bank reference point by which the client is identified.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question No. 1: How to determine the incommensurability of the amounts of generally obligatory payments paid and the scale of activity of the payer (bank client)?
We should take as a basis the explanations provided by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in MR No. 18, which clearly states the following. We should proceed from an indicator “close to 0.9% of the debit turnover of the account.” A slight excess of this value is allowed.
It should be remembered that even if the amounts of generally obligatory payments paid turn out to be significantly less than this indicator, this does not mean that the client’s transactions are automatically classified as doubtful. As mentioned above, in addition to this feature, other, additional ones are analyzed and taken into account.
Question No. 2: Only personal income tax is paid from the account. They do not pay mandatory contributions for employees. Is this a sign of a questionable transaction?
Yes, this is one of the additional features that in a certain way characterizes the activities of the organization. They will pay attention to it, but at the same time they will take into account the nuances of the taxation applied to it, as well as its real capabilities in terms of comparability of the volumes of generally obligatory payments and transactions carried out on accounts.
What is the difference between a current account and a transit account?
If we have already figured out why currency numbers are needed, then it is worth deciding on their characteristics and fundamental differences.
To do this, let's take a look at the table with a description:
| Characteristic | Calculated | Transit |
| 1. Purpose | Recording and accounting of performed transactions | Short-term savings of funds in foreign currency |
| 2. Shelf life | Limited by the duration of the contract | 15 days |
| 3. Applications | No restrictions | Used for: profit accumulation; payment of customs duties and duties; converting some part of the profit into foreign currency (10-50%); when paying for services for transporting goods across the border. |
| 4. Difference in account (digit in seventh position) | 0 | 1 |
| 5. Currency control | Not obligatory, as it usually accumulates amounts of money in national currency | Required |
Transaction passport
It is important that you do not exceed the limit of $50 thousand in total for one contract. Even if the contract was initially concluded for a smaller amount, it is necessary to control this limit in order to issue a transaction passport on time, otherwise you will violate currency laws and pay huge fines.
If the contract amount exceeds $50 thousand, then you must obtain a transaction passport from the bank . To do this, you must provide the bank with a completed form of this document and a contract. Other documents may also be required in agreement with currency control.
You can grant the bank the right to fill out a transaction passport form on the basis of an agreement concluded with it, however, the documents and information necessary for issuing a transaction passport must still be provided to the bank within the period prescribed by law.
What is money transit?
The word itself speaks of a certain movement, and in relation to monetary units it is the transfer of a certain amount of money from one account to another. To transfer amounts of funds from a transit number, for example, to pay a state fee, you, as the owner, must issue an order for this operation. This is not necessarily a written notification - the entire process can be carried out through the “Personal Account”. There you need to fill in the details - there are special input fields for them - and indicate the transfer amount, so you will confirm the operation.
Thus, you give permission to write off the specified amount. After this, the report will be available to you.
Supporting documents for the bank
For the bank to transfer money from a transit account to a foreign currency account, legal. the person must prepare:
- Order for transfer from a transit account (taken from the bank).
- Documents confirming the legality of a transaction with foreign currency, for example, a contract or invoice.
Documents must be current at the time of submission. If the bank has questions, it may request additional documents. If the latter requirements do not meet, the bank may refuse the transfer.
Regulatory framework for foreign exchange transactions of enterprises
The development of legislation on the regulation of foreign exchange transactions was initiated by Decree No. 213 of November 19, 1991, which laid the foundations for the liberalization of foreign economic relations between Russia and foreign countries. Later, in October 1992, the Federal Law “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control” was adopted. He defined the rules of the “game” not only in the foreign exchange market, but in the activities of international enterprises and companies, and also indicated the functions and role of regulatory services.
The law stipulates that payment for goods or services by non-residents must be made within 30 days. The regulation also provides for the provision of information about the recipient and sender of funds, as well as the details of the transfer being carried out.
The regulatory document states that domestic organizations can open a foreign currency account only if they have permission to do so from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. At the same time, it is the Central Bank that considers whether it is necessary to open an additional account for a business entity in one of the foreign banks, because in this case it must provide a report on the flow of funds at certain periods.
Purchasing currency
An organization has the right to purchase foreign currency only through an authorized bank (Article 11 of Law No. 173-FZ of December 10, 2003).
To purchase foreign currency, draw up a payment document (clause 3.1 of Bank of Russia Instruction No. 138-I dated June 4, 2012). A single form of payment document is not established by law. As a rule, banks have the necessary forms. In the payment document, before the text part in the “Purpose of payment” detail, indicate the type of transaction code from the list of currency and other transactions (clause 3.2 of Bank of Russia Instruction No. 138-I dated June 4, 2012). When purchasing currency, indicate the currency transaction code 01 030 (Appendix 2 to Bank of Russia Instruction No. 138-I dated June 4, 2012).
For information on purchasing foreign currency for an employee’s business trip, see How to record non-cash purchases of foreign currency for a business trip abroad.
To reflect the currency purchase transaction in accounting, you can use account 57 “Transfers in transit.” This is possible if the issuance of a payment document to the bank for the purchase of currency does not coincide with the date of its receipt in the foreign exchange account. However, if the debiting of rubles from the account, their sale and crediting of currency occur on the same day (this can be determined from bank statements), then account 57 need not be used.
When transferring rubles to purchase foreign currency, make the following entry:
Debit 57 (76) Credit 51 – money was transferred to purchase foreign currency.
Reflect the receipt of purchased currency to your current account as follows:
Debit 52 Credit 57 (76) – currency is credited to the foreign currency account (based on the bank statement).
Capitalize the received currency at the official rate in effect on the date the money is credited to the organization’s foreign currency account. In this case, make entries in the accounting registers both in the currency of settlements (rubles) and in the currency of payments.
This procedure follows from paragraphs 4–6, 20 PBU 3/2006, paragraph 24 of the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting and the Instructions for the Chart of Accounts (accounts 52, 57, 76).
The exchange rate at which the bank buys it usually differs from the official one. If the currency is purchased at a higher price than the Bank of Russia rate, another expense arises from the currency purchase operation (clause 11 of PBU 10/99). If cheaper - other income (clause 7 of PBU 9/99).
Most banks will have to pay a commission to purchase foreign currency. In accounting, include this amount as part of other expenses (paragraph 7, paragraph 11 of PBU 10/99).
An example of recording a foreign currency purchase transaction in accounting
Alpha LLC entered into a foreign trade contract. To execute it, Alpha needs US dollars. There is no money in the organization's foreign currency account. Therefore, on January 30, Alpha instructed the bank to purchase the necessary currency ($1,000). To do this, we drew up a settlement document and transferred 31,000 rubles to purchase foreign currency.
On February 2, the bank bought foreign currency at the rate of 30.50 rubles. per dollar and credited it to the organization’s foreign currency account minus a commission in the amount of 200 rubles.
The US dollar exchange rate on February 2 (conditionally) was 29.70 rubles. for a dollar.
The organization's accountant made the following entries in the accounting records.
January 30:
Debit 57 Credit 51 – 31,000 rub. – money is transferred to purchase foreign currency.
February 2:
Debit 52 Credit 57 – 29,700 rub. (1000 USD × 29.70 rubles/USD) – currency is credited to the organization’s foreign currency account;
Debit 91-2 Credit 57 – 200 rub. – commission fee is withheld by the bank;
Debit 91-2 Credit 57 – 800 rub. (1000 USD × (30.50 rubles/USD – 29.70 rubles/USD)) – reflects the difference between the currency purchase rate and the Bank of Russia rate;
Debit 51 Credit 57 – 300 rub.
(31,000 rubles – 1000 USD × 30.50 rubles/USD – 200 rubles) – the balance of unspent money is returned.
How to open a transit currency account
For organizations that are involved in export or import operations, or are in partnership with non-resident firms, opening a foreign exchange office is a prerequisite.
List of documentation:
- a completed form where the client automatically gives his consent to the creation and activation of the number;
- a notarized copy of the statutory documents of the enterprise or company;
- card with a corporate stamp imprint and sample signatures;
- a decision with a notary’s seal on the foundation (legal registration of the legality of work in the business sector) of a business entity.
You must fill out an application in which you indicate that you need to conduct transactions in foreign currency. In addition to the application, you must show additional extracts and certificates that determine the status of the person (the company’s statutory documents).
note
Important information: upon activation, the account is immediately opened to convert profits into national currency.
Once you have prepared a list of documents for opening, you need to take care of the evidence that the currency that comes in has legal sources of origin. The bank will also have to make sure that your enterprise (firm) has qualified personnel to carry out financial transactions required by the practice of using currency and transit accounts.
After this, after some time, the financial institution will evaluate the prospects and make a “verdict”. Please note that the above list of documents is not final: the bank may change it by adding or deleting items, depending on internal policies and other factors.
Example 2 Signs indicating an unusual transaction according to the classifier, with assigned codes
The classifier is presented by the Regulation of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 375. It begins with group No. 11. This code is assigned to general characteristics, on the basis of which we can say that “laundering” of illegal income is carried out.
Group No. 11 includes, for example, the sign with code 1101. Its description: the confusing and strange nature of the transaction without economic justification and legal purpose.
Also included in this group is the attribute with code 1106. Its description: refusal of the client (his authorized representative) to comply with the requirements of the credit institution to present documents and information requested as part of its fulfillment of AML/CFT requirements.
How to close a transit account
As stated earlier, it opens along with the main one and is needed to identify the currency that is received by the client. Money is not stored on it 24/7 - in the future it can be transferred to a regular card. You can close it in the same way as a bank account.
After a business entity no longer needs to use this account, he needs to close it. This happens after filing:
- applications for closing, according to the form;
- amounts on the balance sheet.
According to the norms of Russian laws, an agreement between an entrepreneur and a banking institution can be terminated if there is mutual agreement or an objective requirement of one of the parties. Closing is considered valid from the moment the client or his authorized representative submits a special application for termination of the contract.
The rest of the money can be received immediately in cash or in the form of a transfer. After completing the closing procedure, you must notify the tax service about this as soon as possible (for late notification you will receive a fine of 1,000 rubles or more). To avoid problems, you must write about the closure within 7 business days. The main thing is to warn them about your plans in time.
Case Study
Let's imagine that a certain company received foreign exchange earnings in the amount of $13,000.0. In addition, one of the founders made a contribution to the authorized capital, the amount of which amounted to USD 7,000.0.
At the time of crediting resources, the rate was 55.0 rubles per 1 US dollar. Then the company decided to sell $3,500.0. At the time of withdrawal of funds from the account, the rate rose to 57.0 rubles, and upon sale it was equal to 56.0 rubles. For the transactions performed, the bank's commission amounted to 50.0 US dollars.
In this situation, the accounting department made the following entries:
1) Dt 52
Kt 62 – 13,000.0 US dollars / 715,000.0 rubles, crediting of funds;
2) Dt 52
Kt 75 – 7,000.0 US dollars / 385,000.0 rubles, founder’s contribution;
3) Dt 57
Kt 52 – USD 3,500.0 / RUR 199,500.0, sale of foreign currency;
4) Dt 92
Kt 52 – USD 3,500.0 / RUB 196,000.0, sale of foreign currency;
5) Dt 51
Kt 91 - 3,500.0 US dollars / 196,000.0 rubles, crediting funds from the sale of currency;
6) Dt 91
Kt 52 – 50.0 US dollars / 2,850.0 rubles, service fee written off;
7) Dt 91
Kt 57 – RUB 3,500.0, taking into account exchange rate differences.