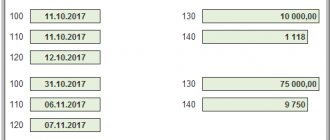
If the tax agent does so, then in the situation under consideration there should be no sanctions against him for failure to withhold personal income tax from the premium. — What about one-time bonuses for labor results: for example, for concluding a large contract on especially favorable terms for the company or for early delivery of a large project, etc.
But there are payments, the grounds for which are listed in clause 28 of Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, if such a payment does not exceed 4,000 rubles, then it is not subject to personal income tax. Recipients of the information are the tax authorities that carry out accounting of the organization or individual entrepreneur or are located on the territory of the location of separate divisions with workplaces.
When paying bonuses based on the results of work for the month, which are part of the salary, the date of actual receipt of income is recognized as the last day of the month for which the bonus was accrued.
Is the award subject to personal income tax?
Premium payments can be divided into two types: labor and non-labor, according to Art. 191 and 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, both types of payments are equal to wages and are taxed at 13% , like any income of an individual, but some differences still exist.
Labor
Labor bonuses are payments accrued to an employee for quality work, special achievements in the performance of direct duties, high professional qualities, etc. The tax on this type of material incentive is taken on the day when the payment is made , and it does not matter whether it is issued in cash or transferred to a bank account (Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The only exceptions are payments that are included in the list provided for by PRF Resolution No. 89 - these are funds of international and all-Russian significance paid to a person for outstanding achievements.
You can find out more about whether a bonus is subject to personal income tax and when it is not withheld from wages here.
Other types
Non-labor accruals include bonuses in honor of anniversaries and holidays, financial assistance to the employee, material remuneration in honor of the founding of the organization, etc. Near-labor material support for employees, although not related to wages, is subject to taxation, like any income of an individual.
Only those types of non-work incentives are exempt from taxation, the amount of which is no more than 4,000 per year (Article 217, paragraph 28 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But in order not to “deduct” personal income tax, the payment should be “linked” to a specific date or holiday, and also paid under a gift agreement (clause 2 of Article 574 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Under what conditions is a premium recognized as an expense?
As is known, labor costs include any accruals to employees in cash and (or) in kind, incentive accruals provided for by legislation, labor and (or) collective agreements (Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, paragraph 2 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly states that labor costs include accruals of an incentive nature, including bonuses for production results. Bonuses are included in labor costs if the following conditions are simultaneously met:
- the bonus is provided for by an employment agreement (contract) and (or) a collective agreement, or a local regulatory act (regulations on remuneration, regulations on bonuses for employees), provided that the employment contracts contain a reference to this act (Article 255, paragraph 21 of Art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The corresponding clarifications are given in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/12/16 No. 03-03-06/3/7522 and dated 06/03/14 No. 03-03-06/4/26582 (see “The Ministry of Finance recalled under what conditions remuneration paid to employees at the end of the year, may reduce taxable profit” and “The Ministry of Finance announced when the cost of bonuses for holidays can be taken into account when calculating income tax”). At the same time, it is important that the document establishes specific indicators taken into account when assigning a bonus, the procedure for determining the bonus, the conditions for paying the bonus, etc. This is stated in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 04/01/11 No. KE-4-3/5165 (see “The Federal Tax Service recognized bonuses, the amount of which was provided only in the bonus order, as a labor expense”).
Compose HR documents using ready-made templates for free
- a bonus (regardless of its name) is paid for labor performance, that is, for production results, professional excellence, high achievements in work, etc. (Clause 2 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 22, 2016 No. 03-03-06/1/42954, see “Non-production bonuses do not reduce taxable profit”). It does not matter whether such a bonus is periodic or one-time, whether it is in the nature of wages or is an incentive not included in the salary. This means that as part of expenses, you can take into account both a one-time bonus for special achievements in work or for performing certain work, and a bonus for vacation, if these payments are correctly established in the relevant local acts and employment contracts;
- there is a document confirming that the employee fulfills the bonus conditions established by the organization (memo, justification calculation, etc.). If the bonus is paid based on the results of work in each month, then it should be obvious that in each month the employee fulfills the production indicators for which it is awarded: actual time worked, the amount of material assets created, the amount of income received through labor, etc. (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 04/01/11 No. KE-4-3/5165, see “The Federal Tax Service recognized bonuses, the amount of which was provided only in the bonus order, as a labor expense”).
- there is an order to pay the bonus (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
All of the above is relevant both for those taxpayers who are on the OSNO and for those who pay a single tax under the simplified tax system. After all, the “simplified people” who have chosen the object of taxation “income minus expenses” take into account labor costs according to the rules of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (subclause 6 of clause 1 of Article 346.16 and clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Keep records, prepare and submit income tax and VAT reports
As for non-production bonuses (in connection with retirement, for a birthday or anniversary, for a holiday, including professional ones), they are not taken into account when taxing profits on the basis of paragraph 21 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This conclusion is confirmed in letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia (for example, dated 04.24.13 No. 03-03-06/1/14283, dated 03.20.13 No. 03-04-06/8592, see “The Ministry of Finance clarified the procedure for taxation of one-time benefits when employees leave for retirement” and dated 02.21.11 No. 03-03-06/1/111, see “A one-time payment upon retirement of any employee is not taken into account in expenses”). A similar approach is followed by courts of various instances (see, for example, Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 03/01/11 No. 13018/10, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated 03/05/13 No. A81-1945/2012, East Siberian District dated 05/02. 12 No. A74-2038/2011, Northwestern District dated 09.07.09 No. A56-20637/2008 and Volga District dated 10.17.06 No. A65-3412/2006-SA2-41, resolution of the Arbitration Court of the North Caucasus District dated 15.04. 15 No. Ф08-894/2015).
Note that the ban on writing off non-production bonuses also applies to “simplified” workers, since, by virtue of the direct indication of paragraph 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, such taxpayers, when accounting for expenses, act according to the rules of paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. And this norm, in turn, does not allow taking into account the expenses specified in Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Keep records, prepare and submit reports according to the simplified tax system in the web service
Reflection of the bonus in personal income tax
When filling out reporting documents, you should take into account the types of bonuses that were paid to the employee, the period of their accrual, as well as some nuances that distinguish the following features of bonuses:
- a one-time payment cannot be defined by the concept (wages), since this type is not systematic and refers to non-labor incentives; in the 2-NDFL certificate it is reflected in a separate code, as a payment made from the profit of the organization or revenues of a targeted nature.
In 6-NDFL it should be written as a separate block from the salary, and the date of tax withdrawal must coincide with the date of direct payment of the bonus or dated the next day after the money is transferred to the person, but no later - order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation MMV-7-11/450 (more on that , how to reflect the bonus in 6-NDFL separately from the salary, read in a separate material). - In the middle of the month - in certificate 2 it is written with a code based on the direction of the payment and its relation to wages; in calculation 6 it is recorded in the same way as a one-time payment, that is, taking into account the date of payment.
- The monthly bonus is a systematic payment and is fixed in the employment agreement in the form of a monthly bonus payment, therefore it is classified as wages and is written in 2-NDFL under a code that corresponds to payments from the main accounts, not the target ones.
Important! In 6-NDFL it does not need to be written in a separate block (it is written together with the salary); such a bonus is dated, like the salary, on the date of the last working day of the month.When entering salary into calculation 6, the date of salary payment and tax calculation is considered to be the last day of the month, because according to the law, taxes are not calculated from an advance payment, the same rule applies to the monthly bonus.
- At the end of the month - it is reflected in the reporting documents, depending on the direction of payment, because such a bonus can be either monthly (being remuneration), or one-time or periodic (for special merits, etc.), therefore it is recorded in certificate 2 with a code corresponding to the purpose of the money paid.
In calculation 6, if the bonus received at the end of the month is monthly and is included in wages, it is recorded and deducted in trade union organizations no later than the last day of the month (along with the salary).And if this incentive is not included in the payment of labor under an employment contract, then the procedure is prescribed in a separate block, and it is fixed if you transfer personal income tax when the payment of money is withheld, on the same day we record the deduction of the tax and the next day (no later) we record the date of transfer of the tax to budget.
- The annual and quarterly bonus is included in the report in accordance with the nuances provided for by the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated January 24, 2017 No. BS-4-11/1139; here, when filling out 2-NDFL, the same code is used as for the monthly bonus.
Workers employed under an employment contract receive not only a salary, but also bonuses. However, here there is an interaction between labor and tax laws. Read our articles about whether such incentives are taxable, as well as how director bonuses are paid and what documents are needed for this.
When is it paid?
Considering that the results are calculated at the end of the quarter, that is, in the first days of the next month, you must follow the following rules for transferring funds to an employee:
- the bonus is provided separately from the salary;
- frequency of provision – once every three months;
- The maximum transfer period is the 15th of the next month.
As practice shows, a quarterly bonus is a good stimulator for the work of subordinates. Especially if the size of the incentive significantly increases the amount of income, depending on the total salary.
Labor type incentive codes
Several years ago, incentives in reporting certificate 2 were recorded under code 2000, as salary (in cases where this type of bonus is fixed in the employment contract as systematic, that is, related to wages) or under code 4800, which denotes additional or other income of an individual faces.
But today, bonuses are reported in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Tax Service order No. ММВ-7-11/633 dated November 22, 2016, which provided separate codes for bonuses.
Payment to an employee for special labor merits, which cannot be paid from the organization’s income or target accounts, is registered with code 2002, and one-time, anniversary and other types of bonuses are recorded under code 2003.
Possible benefits for employees
Tax inspectors and police officers do not have many privileges. High wages, as well as the opportunity to enjoy privileges, depend on length of service and rank.
So, for example, a tax officer with the rank of tax police colonel and above has the right to receive 15 square meters of additional living space. Taxpayers have the right to free medical care and provision of medicines at the expense of the Department.
Taxpayers can relax in sanatoriums and boarding houses that are under the jurisdiction of the Tax Police Department and receive compensation for the funds spent. Taxpayers have the right to receive tax benefits when carrying out real estate purchase and sale transactions.
Tax service employees are entitled to a 50% discount in payment for housing and communal services.
Tax employees can receive an interest-free loan for organizing construction and economic needs.
How to correctly calculate the date of personal income tax withholding?
The calculation of the tax date on the premium directly depends on its type and the principle of payment. If this incentive is money of a systematic nature, as specified in the labor contract, then the date of actual payment and withholding of personal income tax will be considered the last day of the month, and the day of crediting the money to the state budget will be fixed as the next one.
When to withhold personal income tax from the premium? If the bonus payment is of an anniversary, holiday nature, or is paid for certain merits of the employee, then the dates of actual receipt and withholding of tax will be considered the day when the money arrived in the person’s account (for cases where the bonus was transferred to a bank account).
Reference! If the financial award is given in cash, then the day of actual receipt and deduction of the tax will be the date when the cash was taken from the bank, and the date of entry into the state budget should be fixed the next day after the person received the bonus (in both cases).
Annual or quarterly incentives, as already described above, are dated differently: the date of actual receipt should be written as the last day of the month in which the person received the bonus; the date of deduction of personal income tax should be considered the number indicated in the order for calculating the bonus as the date of payment, and the day of transfer to the budget will be the next number.
Calculation example
Citizen Yusupova works at an enterprise where in the last quarter of 2021 she worked 48 days instead of the required 56 and received the following salary amounts:
- October – 58,970 rubles;
- November – 60,200 rubles;
- December – 59,900 rubles.
In connection with the successful end of the year, the management of the enterprise decided to pay all employees a quarterly bonus in the amount of 45% of income. For citizen Yusupova, the calculation formula will be as follows:
- Establishing total income for the quarter: 58,970+60,200+59,900 = 179,700 rubles.
- Establishing the average monthly profit: 179,700/3 = 59,690 rubles.
- Multiplying the amount of payments by the premium percentage: 59,690 * 45% = 26,860 rubles.
- Calculation of the limit bonus amount: (26,860 / 56) * 48 = 23,022 rubles.
Thus, based on the results of the last quarter of 2021, citizen Yusupova will receive a quarterly bonus in the amount of 23,022 rubles.
Reflection of the award
Previously, in the 2-NDFL certificate, bonuses received for special achievements in work in section three were recorded under code 2000, like salaries, and incentives on anniversaries and holidays were recorded under code 4800.
Today, for bonus payments, two separate codes are used, that is, the salary remains under the code 2000, we write it separately in the lines of paragraph 3, and we designate the bonus as 2002, if it is an incentive for work, and we write it under the number 2003, if it was issued in honor of the holiday.
In paragraphs 4 and 5 of this certificate, the income data is summarized, that is, the bonus is reflected separately only in paragraph three.
What it is
The legislation does not contain a clear definition of what a quarterly bonus is.
Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation includes this concept as part of the more general concept of “wages” with the caveat that this is an incentive payment. The term “quarterly” indicates the frequency of payment - for how many months the amount is accrued: once a quarter. Incentive payments are the right of the employer, that is, the company has the right to decide to establish additional financial incentives for employees or not. The company has the right to independently determine the calculation procedure, frequency of payment and grounds for incentives. Moreover, if additional payments are recorded in the internal documents of the organization, the employer no longer has the right not to pay them unreasonably.
An exception is made by employers whose activities are regulated by federal regulations, for example, cash payments to civil servants are established by Federal Law No. 79-FZ of July 27, 2004 and orders of individual departments issued in its implementation; quarterly bonuses to civil servants are not provided for in the federal law.
Is the bonus recorded on the payslip?
Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the employer is obliged to show the employee all accruals on the payslip; the bonus must also be recorded in this document.
The form of the sheet is developed and approved by the organization, taking into account all types of payments, under the item “accrued”, where the names of payments are indicated, there should be a line “premium”, in the fifth column its amount should be reflected, in paragraph 2 - the amount of personal income tax that was withheld.
A bonus is a very strong incentive for every employee, but the main thing when paying this remuneration is to correctly display it in the documents, so that the good intention to please and reward the employee does not lead to additional expenses in the form of a fine for the employer himself.
Why do tax workers receive low salaries?
Today, the prestige of working as a tax official is falling. The sector suffers from a shortage of personnel; many workers cannot withstand the workload and quit. In addition, the unenviable financial situation of tax service employees.
Since 2006, there have been no salary increases for tax officials. And although in the same 2021 it was planned to increase salaries by 15% , this innovation remained on the verge of the project. As of today, no changes are expected, since salaries for the public sector are quite large.
How to calculate
Companies independently choose the strategy and procedure for how the quarterly bonus is calculated. In internal regulations, the employer has the right to link the calculation to a fixed amount or to the employee’s salary.
Calculation from the amount of earnings
With this method of calculating material incentives, the calculation takes into account:
- employee salary;
- actual time worked in the accounting quarter;
- What percentage of income is the quarterly payment?
The calculation is made using the formula:
P = ZP × 3 × PP / KDK × KOTD,
Where:
- P - amount of payment;
- ZP - monthly salary of the employee;
- 3 - number of months in a quarter;
- PP - bonus percentage established in the regulation;
- KDK - number of working days in the billing quarter;
- KOTD - the number of days actually worked in the billing quarter.
From salary
Let's look at an example of how to calculate a quarterly salary bonus: an employee has a salary of 50,000 rubles and his employer has established a quarterly additional financial incentive in the amount of 10% of earnings for the billing period. If an employee works fully in the first quarter of 2021, the amount that will be additionally transferred to him will be:
P = 50,000 × 3 × 0.1 / 57 × 57 = 15,000 rubles.
Calculation from a fixed amount
In some cases, employers set a fixed quarterly payment amount that does not depend on the employee’s salary. The amount of actual payment is reduced if the employee has not fully worked all days of the pay period. The formula for calculating the bonus for actual time worked is as follows:
P = FRP / KDK × KOtD,
Where:
- P - premium to be paid;
- FRP - a fixed amount of payment established by regulation;
- KDK - number of working days in the billing quarter;
- KOTD - actual days worked.
Let's look at an example of calculating bonuses for actual time worked. For a citizen with a salary of 50,000 rubles, a fixed quarterly additional incentive of 100,000 rubles has been established. There are 57 working days in the first quarter of 2021. If he works all of them, he will receive the entire bonus. If an employee was absent from work throughout January and missed 17 working days, the amount he will receive:
P = 100,000 / 57 × 40 = 70,175 rubles 44 kopecks.
Salary bonus: when to pay personal income tax and deadlines for 2021
The procedure for transferring personal income tax from bonuses to the budget is determined by letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 04/04/2017 No. 03-04-07/19708. The deadline for paying income tax on premiums to the budget depends on the type of payment.
If the bonus is tied to wages, then such income is considered received on the last day of the month. The date of actual receipt of income in the form of other bonuses (not related to wages) is considered the day of payment of such income.
The deadlines for paying personal income tax on income in the form of bonuses in 2021 are such that the tax should be withheld on the day the money is paid, and paid no later than the next day. Until the release of this document, the Ministry of Finance recommended recognizing bonus payments on the same day as their issuance.
Find out how to reflect various types of bonuses in 6-NDFL from the publication “New explanations of the Federal Tax Service on bonuses: monthly, quarterly, one-time.”
There is liability for late payment of income tax - penalties for each day of delay and penalties in the amount of 20% of the unpaid amount.
Read about the extent of liability for non-payment of personal income tax in the material “What is the liability for non-payment of personal income tax?”
Additional topics:
The concept of the source of payments3-NDFL declaration is submitted upon receipt of income or when applying for the purpose of transferring social...
How to find out KBK tax for 3-NDFL KBK is a budget classification code. KBK codes for...
Dividing bonuses between workers using KTU Task 1 Distributing a collective bonus between employees of the department...
Reducing personal income tax when calculating wages. How to reduce the tax burden on wages if there is a family...
Features of vacation pay in terms of personal income tax, vacation pay, as well as sick leave, must be reflected in the 6-NDFL report...
what are they arguing about:
Tax authorities require companies to pay personal income tax on bonuses on the day they are issued. Organizations are proving that this can be postponed until the payday at the end of the month.
Personal income tax on bonuses: The Ministry of Finance spoke about the deadline for transferring tax for monthly payments
According to paragraph 2 of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the date of actual receipt of income in the form of wages is the last day of the month for which the taxpayer was accrued income for the performance of labor duties in accordance with the employment agreement (contract). The Ministry of Finance believes that the date of actual receipt of income in the form of a bonus paid for the performance of job duties based on the results of work for the month is determined in a similar way. That is, if the bonus is a component of wages, then the date of actual receipt of income is the last day of the month for which the employee was accrued bonuses. Payment of personal income tax to the budget is made no later than the day following the day of payment of income to the taxpayer. This general rule is established by paragraph 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, if the premium for March is paid on April 25, then the date of its actual receipt will be considered March 31, and personal income tax will need to be transferred no later than April 26. To the question of how to fill out 6-NDFL when paying an employee a bonus based on the results of work for the month, the tax authorities answered in a letter dated 04/19/17 No. BS-4-11 / [email protected] (see “The Federal Tax Service reported how to calculate 6-NDFL reflect income in the form of a bonus at the end of the month").
Fill out, check and submit 6‑NDFL and 2‑NDFL via the Internet
About the types of bonuses, also see: “We reward employees correctly: how to arrange bonuses in an organization.”