Last modified: January 2021
Work beyond the established duration is always the employer’s offer and not always the right of the hired personnel to refuse. Preliminary agreement with employees or an order by order depends on the status of the workers and the circumstances of their involvement. A distinctive feature is the payment of overtime work at an increased rate, the minimum amount of which is strictly fixed by labor legislation, and the maximum is not limited by any limits.
Methods of recording working hours
This is the period during which the work team performs duties. At the same time, he complies with the PVTR, as well as the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Traditionally, enterprises and organizations adhere to the 5/2 regime. The number of hours in 5 days does not exceed 40. In a number of areas of work activity, a shift schedule or working day (part-time) is established.
The employer has the right to independently establish the operating hours of a particular company. He takes into account the specifics of her work. All details are documented. This is the schedule, time and specifics of the work.
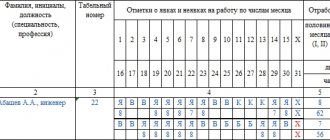
Working hours are recorded in the form of a daily report maintained by the enterprise. It indicates the number of working hours worked by the person, and also specifies unforeseen circumstances. For this purpose, an output schedule is generated. This is a special document that reflects the information:
- number of shifts at night;
- hours beyond normal;
- certificates of incapacity for work;
- days off for hired personnel;
- business trips of employees.
REFERENCE: employers have the right to independently choose a methodology related to monitoring the work process, but in such a way that this does not occur in violation of the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Replacement of compensation for additional rest
Employees have the right to replace additional overtime pay during rest periods on the basis of Art. 152 TK. The additional rest time must correspond to the number of overtime hours. For example, an employee worked 4 hours above the standard. The right to additional rest should be granted to the employee in the amount of 4 hours. In this case, overtime is paid at a single rate.
Additional rest time is not paid in any way and is provided by order of the employer.
If an employee has earned a whole day of rest, it is reflected in the working time sheet using the letter code “НВ” or the digital code “28”. These codes indicate an additional day off without pay.
What is overtime work?
Overtime work according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is carried out at the initiative of the employer. It includes overtime in addition to the normal working hours and shifts.
Involvement of hired personnel in work is possible only with the consent of the person, in writing. In Art. 99, paragraph 3, the legislator listed cases when such a need arises:
- the work needs to be completed: the process was delayed due to technical problems;
- equipment restoration;
- replacing an employee: absent or ill.
Without the consent of employees, they can be involved in additional work, but only in extreme situations. For example, there was an accident at work, another emergency, a catastrophe, or circumstances of indefinable force.
Typically, overtime activities are performed before and after regular time. The condition for attracting a person to such work is the decision of his boss. If a citizen himself remains after a shift to finish his business, without proper registration, this is not considered activity beyond the norm. Delay at work for 2 or more hours is not paid. This provision follows from the Letter compiled by the Ministry of Labor in 2021 under N14-2/B-149.
Regular work without additional hours on a holiday or a day off also cannot be considered overtime. These days are paid according to Art. 152, part 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Overtime is limited by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. For example, it cannot exceed four hours in total for 2 days in a row, or 120 hours over 12 months. For example, a person was late for 3 hours on Monday. On Tuesday he cannot work more than 1 hour after the end of the working day.
REFERENCE: Involvement in additional work beyond that established is legal and without the desire of the person. The provision of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is established by Art. 99, part 3.
Results
Calculations for time worked in excess of standards is a technically complex process that is not entirely clearly supported methodologically, so it should be additionally organized:
- determine the form for calculating the rate for 1 hour (for example, enter it into an employment contract);
Read more about drawing up an employment contract in the article “Unified form TD-1” .
- establish an internal company standard for calculating additional payments for overtime hours, in accordance with the norms of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and clarifications of the relevant departments.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Overtime work with the consent of the employee
Processing according to the Labor Code occurs with the consent of the employee. It is important to document this fact. There are 2 options:
- The employee agrees by signing the order for overtime work.
- The citizen draws up a corresponding application and addresses it to the head of the company. There is no strict, unified application form: it is written randomly, by hand.
Overtime at work is established by the Labor Code. In particular, the law in Art. 99, part 2 defines situations when people are involved in working overtime:
- There is a need to perform, complete certain work that could not be done due to objective reasons (for example, technical). Failure to complete the work has adverse consequences for the company. For example, death, damage to property, threat to human life.
- Work of a temporary nature associated with the repair work of mechanisms, their restoration in cases where their downtime will cause workers to be unemployed.
- Production at the enterprise does not allow interruptions: a person who does not show up for work must be replaced.
REFERENCE: the boss is obliged to familiarize certain categories of employees who have the right to refuse such work against signature.
Tax principles
Additional pay accrued for overtime work should be subject to general taxation. That is, personal income tax must be withheld from the amount received. If the employee is a resident of the Russian Federation, calculate personal income tax at a rate of 13%.
If the recipient of the additional payment is not a tax resident of Russia, then apply the already increased personal income tax rate - 30%.
Insurance premiums from amounts for work in excess of the standard will also be calculated and paid to the budget. Apply the same tariffs as for regular types of accruals (salaries and other remuneration for labor).
Keep in mind that for some categories of policyholders in 2020 the right to reduced rates was canceled (pharmacies on UTII and organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system). It should also be remembered that the limits on insurance coverage have been increased for 2021. Now the limit on compulsory pension insurance is 1,115,000 rubles, and on temporary disability and maternity - 865,000 rubles.
This type of surcharge should be included in labor costs when calculating the amount of corporate income tax. State employees can exercise this right only in relation to funds from income-generating activities.
Overtime work without the employee's consent
Art. 88, part 3 establishes that in extreme cases an employee is required to work overtime:
- Prevention of accidents, disasters, elimination of their consequences.
- Elimination of the consequences of an accident at the enterprise.
- Elimination of circumstances under which engineering systems, transport, and communications stopped working.
- Martial law has been introduced throughout the country, cases that threaten the life and health of people (fires, tornadoes, floods, etc.).
What does overtime mean? These are a person’s working hours, which are summed up when he is at his place of work after the end of the day or shift.
REFERENCE: in these situations, the consent of the trade union body is not required. Refusal to perform work entails drawing up a special act. The employee is subject to disciplinary liability.
How is overtime pay for piece workers calculated?
Citizens who work piecework are paid for each part produced. Overtime pay for piece workers depends on how many parts they produce outside of normal working hours, as well as on the length of overtime work. Cash is paid without taking into account one and a half or double premium.
Example: Kurochkina A.N. works at the factory. She works piecework. For each part made, she is paid 400 rubles. On 03/09/2019 she worked 4 hours outside of school hours, producing 5 parts during this time: 2 pcs. - for the first 2 hours and 3 pcs. — for the remaining 2 hours. Payment depends on the number of parts produced and on the time worked above the norm. Therefore the calculation is:
(400 rub. × 1.5 × 2 pcs.) + (400 rub. × 2 × 3 pcs.) = 1200 rubles + 2400 rubles = 3600 rubles.
Who should not be required to work overtime?
According to the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, certain categories of employees cannot be involved in overtime work:
- pregnant women (Article 99);
- minor citizens (under 18 years of age);
- certain categories of employees (Article 268, the list is prescribed by the Decree of the Russian Government in 2007, N252);
- Art. 348.8, part 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: athletes, if the provision on not involving this category is spelled out in the collective regulations, in local acts;
- employees of the enterprise, if a student agreement is in force (Article 203, Part 3);
- other workers whose restrictions are usually prescribed by medical requirements: for example, drivers due to health conditions.
Special procedure for recruitment
- The employee's consent in writing.
- There are no contraindications to overtime work due to medical requirements.
- Informing employees that they have the right to refuse an offer made by the employer regarding overtime work (Article 99, Part 5, 259, 264):
- single mothers or fathers with children under 5 years of age;
- persons with disabilities;
- employees raising children with disabilities, caring for family members for medical reasons;
- women with children under 3 years of age, guardians of children under 18 years of age.
Order on extracurricular work
The employer's order and the employee's consent must be in writing. The enterprise can independently choose which document will record the employee’s exit (order, instruction, notification). Don’t forget to also record your overtime hours on your Timesheet.
How to determine the amount of overtime work?
What is the maximum duration of overtime work? According to Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, working hours are 40 hours in 5 days. An employee may work beyond this time, but not more than 4 hours for two days in a row. 120 hours is the maximum for a year.
REFERENCE: the duration worked is reflected in a special document. This is an imperative requirement. The document is abbreviated as T-13.
With a shift schedule
Art. 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that a shift schedule is work activity that is carried out in several shifts. The existence of the schedule is due to the continuity of the production process. If a shift worker works overtime, not on his shift, the day is paid double, or he is given a day off for this.
When recording working hours in total
Overtime work in accordance with the Code and with payment for cumulative working hours is calculated for the period established by the organization. This is a quarter, a year, and also a month.
Accounting is introduced to ensure that the length of time spent at work does not exceed the number of working hours. One week an employee may be at the workplace more than his normal hours, the next week - less. The employer will evaluate his working time after the end of the accounting period. This is a month, quarter or year.
With salary
Based on the provisions of Art. 153. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, overtime work is paid according to the employee’s earnings per hour. For every 60 minutes of overtime, the employer pays one and a half or double the amount. For the calculation, the number of working hours per year is taken as an average. As a result, the average value for the year is displayed. But not the actual number of hours worked per month.
In addition, there is another payment option according to the salary. The actual working hours per month are taken into account. The salary is divided by a person’s work shift in a particular month.
Payment for overtime hours on a shift schedule
Special methods for calculating overtime for shifts have not been established. This raises questions when calculating.
Example 1 (continued)
The employee worked 15 shifts (12 hours) and on his day off, on the last day of the month, he replaced another employee for 1/2 of the shift. In total, he worked 186 hours at a rate of 176 working hours per month. The rate per shift is 2,400 rubles.
Tariff for 1 hour: 2,400 / 12 = 200 rub.
200 × 1.5 = 300 rub. (first 2 hours)
200 × 2 = 400 rub. (subsequent hours)
The question is how to count these hours. The last day of the month was a day off for the employee, that is, overtime is already on schedule - that’s 4 hours, of which 2 are 300 rubles each. and 2 for 400 rubles. How should 6 hours of replacement be counted? 2 for 300 and 4 for 400 or all 6 for 400? There is no clear answer to this question in the laws.
Within the meaning of Art. 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the requirements are the same for any type of overtime payments. If there are no internal company standards, it is better to prefer the option: 6 to 400. This will coincide with the conclusions of the courts in salary disputes.
Thus, the additional payment for overtime will be:
2 × 300 + 8 × 400 = 3,800 rub.
Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: overtime work
Overtime work according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is performed only at the request of the employer. It includes overtime in addition to the traditional working day.
The involvement of hired personnel in work is possible only with their consent, expressed in writing. In Art. 99, paragraph 3, the legislator listed cases when there is a need to work overtime:
- the need to complete work that was delayed due to technical problems;
- work on the restoration of temporary equipment;
- replacing an employee.
REFERENCE: without a person’s consent, he can be required to work additional hours. Overtime work cannot exceed 4 hours on two consecutive days.
How is processing paid?
Payment is regulated by Article 152 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Overtime work is paid according to the rule: the first two hours must be paid at least one and a half times the rate, the next hours at least double the rate. An increased fee may be provided for by local regulations.
In exchange for monetary compensation, additional rest may be provided for a duration not less than the time worked in excess of the norm.
IMPORTANT!
If the working day is irregular (and it must be established by the employment contract), overtime is not paid.