The article describes the KBK for monetary penalties - fines in 2021 for failure to comply with the norms of the tax code, the code of administrative offenses and codes that indicate payments for failure to comply with road safety.
Individuals and enterprises sometimes violate the law unintentionally, but in any case, non-compliance entails punishment in accordance with the Code of Administrative Offenses and the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Before paying penalties, you must fill out a payment slip indicating the BCC for the fine. The code will tell the recipient what kind of payment it is and will help to credit the money to the appropriate budget in a timely manner.
What documents are approved by KBK-2020
The BCC applicable in 2021 is covered by two current regulatory legal acts:
- Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 29, 2019 No. 207n “On approval of codes (lists of codes) of the budget classification of the Russian Federation related to the federal budget and budgets of state extra-budgetary funds of the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as Order No. 207n). This document replaced the order of the Ministry of Finance of the same name dated 06.06.19 No. 86n, which became invalid as of January 21, 2021.
- Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 06.06.19 No. 85n “On the procedure for the formation and application of budget classification codes of the Russian Federation, their structure and principles of purpose.”
The codes that were used in 2021 were regulated by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 06/08/18 No. 132n.
Results
In order to understand what kind of KBK 18211603010016000140 this is and what tax should be paid on it, you must first understand the essence of the requests received from the inspectors. At the same time, you should know that under this code in 2021, the taxpayer will pay various fines for violating tax laws. For example, a fine of 200 rubles. - no matter what tax in 2021 according to KBK 18211603010016000140 - tax authorities have the right to impose on a company that:
- submitted reports on paper, but should have done this using telecommunications;
- did not hand over documents in response to the tax authorities’ demands.
And from 2021, a separate BCC will be introduced for each of the violations listed in the article.
For more information about what other powers the tax authorities have during an audit, read the article “Tax audit - what is it and what is the procedure?” .
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 29, 2019 No. 207n
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/08/2018 No. 132n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
BCC for other tax sanctions
The changes affected the codes that are used to pay fines imposed under Chapter 16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In 2021, there was one common code for all sanctions. And in 2020, different BCCs are provided for different sanctions (see Table 1).
Table 1
KBK for payment of tax sanctions for certain types of violations
| Type of tax sanction | 2020 | 2019 |
| For the submission of documents by the tax agent, containing false information (Article 126.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 1608 140 | 182 1 1600 140 |
| For failure to provide the information required for tax control (Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 1607 14 | |
| For gross violation of the rules for accounting for income and expenses and objects of taxation, bases for calculating insurance premiums (Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 1605 140 | |
| For violation of the established method submission of a tax return, calculation (Article 119.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 1603 140 | |
| For failure to submit a tax return, calculation of insurance premiums (Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 1602 140 |
KBK 18211603010016000140: what is the 200 ruble fine for and what is the tax in 2021
So, KBK 18211603010016000140 - transcript 2021 - what tax is the fine paid with it? Please indicate this code only when transferring penalties in 2021 for the following violations:
- For late submission of an application for tax registration or generally working without registration with the Federal Tax Service (Article 116 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Failure to comply with the method of submitting a tax return (Article 119.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) is for which a fine of 200 rubles is imposed under KBK 18211603010016000140.
We will tell you in what form you need to submit tax returns in the article “Procedure for submitting tax reports via the Internet .
- When the managing partner submits financial statements of the partnership with unreliable data (Article 119.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Gross violation of tax accounting rules is grounds for a fine under Art. 120 (clauses 1 and 2) of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
“How to maintain tax accounting registers (sample)” will tell you how to organize accounting of income and expenses for tax purposes without errors .
- Violation of the procedure for using pledged or seized property (Article 125 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Failure to provide information necessary for tax control (Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If, for example, you do not provide the primary information during a counter-inspection of the counterparty by the tax authorities, then you will face a fine of 200 rubles. for each document not presented (clause 1). And if the tax agent does not submit personal income tax calculations on time (clause 1.2), then this is also a reason for a fine (that’s why the fine is 1000 rubles according to KBK 18211603010016000140 ).
For more information on how tax authorities should conduct a counter audit, read the article “Features of conducting a counter tax audit .
- Submission by a tax agent of documents with false information (Article 126.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Failure to appear at a tax violation case as a witness (Article 128 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Refusal to assist in conducting a tax audit or issuing a knowingly false conclusion, being an expert in any field or a translator (Article 129 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Silencing important information, provided that you have information that you should have reported to the tax authorities (Article 129.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Failure to submit information about controlled transactions or submitting them with incorrect data (Article 129.4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Violations that banking organizations can commit: opening a current account for a businessman or company without the necessary documents, violation of deadlines for the execution of payment orders for the payment of taxes, illegal continuation of transactions on the taxpayer's current account, failure to fulfill the obligation to submit account statements to the tax authority, violation of the rules for working with electronic money (Articles 132, 133, 134, 135, 135.1, 135.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For each of these articles, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for different amounts of fines for the taxpayer. The smallest fine is 200 rubles. - this is a penalty for violations under Art. 119.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and 126 (clause 1).
This is for 2021. For the KBK for these violations for 2020, see the next section.
What to do if instead of the BCC valid in 2021, the old one from 2021 was indicated? The answer to the question was given by ConsultantPlus experts. Get trial access to the system and move on to the Ready-made solution.
Codes for administrative fines
There are also innovations under the Code of Criminal Procedure for administrative fines, which are imposed under Chapter 15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation for tax-related violations.
In 2021, separate codes should be used for some fines, but in 2021 one general BCC was used (see Table 2).
Fill out payments in the web service for individual entrepreneurs for free
table 2
KBC for payment of administrative fines for tax-related violations
| Type of administrative fine | 2020 | 2019 |
| For violation of deadlines for submitting a tax return, calculation of insurance premiums (Article 15.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 1605 140 | 182 1 1600 140 |
| For failure to provide (failure to report) information, necessary for tax control (Article 15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 1606 140 | |
| For violation of the registration deadline in the tax authority (Article 15.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) | 182 1 1603 140 |
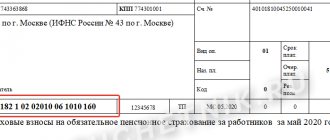
How to enter KBK 18211603010016000140 into a payment order - sample
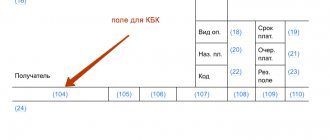
A payment document for the payment of fines for tax offenses is drawn up in the same manner as for any tax payment. It provides a special field .
To pay the fine, you must send a payment slip to the bank indicating KBK 18211603010016000140 in 2021 or another required code in 2020. A sample payment order for 2021 can be downloaded from the link below.
What codes to use in 2021 when paying fines for past periods
Since budget classification codes approved by Order No. 207n are in effect from January 21, 2021, the previous values do not apply from that date. This means that, regardless of the period to which the payment relates, it is no longer possible to use outdated BCCs.
EXAMPLE. Let’s say that in January 2021 the company pays a fine for a gross violation of the rules for accounting for income and expenses committed in 2021. The amount of the fine is reflected in the decision made following the tax audit in December 2021. In the payment order, the accountant must reflect the BCC in force in 2020, namely 182 1 1605 140.
Please note: errors when filling out payment slips can be eliminated if payment documents are generated automatically. Some web services for submitting reports (for example, “Kontur.Extern”) allow you to generate a payment in 1 click based on data from the declaration (calculation) or the request for payment of tax (contribution) sent by the inspectorates. All necessary data (recipient details, current BCC, account numbers of Federal Treasury departments, codes for payer status) are promptly updated in the service without user participation. When filling out a payment slip, all current values are entered automatically.
Decoding KBK 18211603010016000140 (2019–2020)
Our readers - practicing accountants - often receive letters from the tax office demanding the payment of a certain tax or fee. This happens if the taxpayer violated the law and did not transfer any payment to the budget on time in full. In this case, tax authorities are required to indicate the name of the tax for which the claims arose, its BCC (for example, BCC 18211603010016000140) and a number of other information.
For information on how a demand for payment of taxes and fees should be formalized, read the materials in the section “Request for payment of taxes and fees” .
But the document that instructs the company to pay according to BCC 18211603010016000140 raises the most questions - what was the fine for in this case and what does this BCC mean?
First of all, let’s figure out what the meaning of KBK is 18211603010016000140. To administer budget revenues, each type of payment has a special code - KBK (budget classification code). It must be indicated in each payment order for the payment of funds to the budget, as well as in tax reporting sent to the Federal Tax Service, Social Insurance Fund and other government agencies.
The full list of codes is contained in the KBK classifier (in 2019 - this is the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/08/2018 No. 132n, from 01/01/2020 - dated 11/29/2019 No. 207n). This is where you need to look for the decryption 2019-2020 KBK 18211603010016000140.
According to the classifier (in the current version) indicating KBK 18211603010016000140 - decoding for which the fine is in 2021 - 2021 - the taxpayer must transfer the fine for violation of tax legislation under the following articles of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: 116, 119.1, 119.2, 120 (paragraphs 1 and 2) , 125, 126, 126.1, 128, 129, 129.1, 129.4, 132, 133, 134, 135, 135.1, 135.2. That is, in 2021, BCC 18211603010016000140 is the same for several types of fines.
ATTENTION! From 2021, the BCC for fines under these articles is different (see Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 29, 2019 No. 207n).
Let's take a closer look at what these articles of the code are and what fines are paid under them.
Do you have any questions about filling out payment forms? Ask them on our forum. On this thread, for example, you can clarify what to do if you sent a payment order indicating the wrong BCC.
How can an organization pay a fine?
Typically, legal entities pay fines from their current account. To do this, bank payment orders are issued separately for each fine.
Payment order is a document that is created to transfer money from the sender's bank account to the recipient's account.
But there are other ways to pay an organization’s fines for which no one will be punished. The main thing is to pay within 60 days and fill out the details correctly so that the money does not go elsewhere.
These are the methods:
- In cash at the bank's cash desk, at the post office or self-service terminal. You must have with you all the orders that need to be paid. Or pre-printed receipts.
- Bank card - employee’s personal or corporate card:
- through your personal account or bank application;
- on the website of the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate, State Services;
- through an ATM;
- Through payment systems WebMoney, Yandex.Money, QIWI, etc.;
In the last two cases, you will need to enter the recipient's details separately for each fine. For a fleet with a lot of cars and fines, this is labor-intensive and will have to spend a lot of time.
- Through special services for automatic control of fines of organizations, for example, such as, the service itself finds all fines and allows you to pay them in one click.
Check the organization's fines
Legislative regulation
Responsibility for failure to fulfill tax obligations is established at the legislative level using the main document in force in the fiscal system of the Russian Federation - the Tax Code.
Specific penalties for land tax are not allocated - they are the same for different categories of payers and are divided only by a specific type of offense.
In particular, Art. 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which provides data
measures. It is worth considering that in addition to this type of liability, which applies to all categories of payers, some of them (namely individual entrepreneurs and legal entities) are subject to more severe measures within the framework of criminal legislation established by the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
In the event of particularly serious offenses in the tax sphere, these types of liability may be applied to these categories of payers. The most important requirement in this case is the presence of compelling reasons for their use.
In some situations, criminal liability can also be established for individuals, but the amount of debt must be very large, which in practice is quite rare.
Fines for late submission of declarations
Filing tax reports based on the results of economic activities for the past period is one of the main responsibilities of all taxpayers without exception. For each fiscal obligation, in addition to specially approved reporting forms, there are also established deadlines for their submission. If an organization or individual entrepreneur violates them and does not send documents to the Federal Tax Service on time, they will be forced to pay a fine.
Thus, a fine for late submission of reports to the tax office is understood as a financial penalty that is paid by a business entity to the budget due to its failure to comply with the norms of the current fiscal legislation.
General requirements for preparing and filing tax documentation
According to Art. 80 of the Tax Code of Russia, a tax return is a statement of a business entity, which records data on objects of taxation, recorded income by sources of their formation, expenses incurred, fiscal benefits, calculated tax payments, as well as other relevant information that is the basis for the accrual of a certain type tax and payment to the budget.
Fiscal documents are prepared and submitted by enterprises and individual entrepreneurs separately for each tax obligatory for these entities, unless otherwise provided by the current law. So, for example, according to the provisions of Art. 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a business entity must not submit to the Federal Tax Service declarations (calculations) for those types of fiscal obligations from the payment of which it is exempt in connection with the application of a special taxation regime to it in terms of economic activities, the implementation of which involves the use of tax benefits, or assets, involved in carrying out such activities.
The documentation is drawn up in paper format or in electronic form with its subsequent transmission via telecommunication channels through the payer’s personal account or using an electronic signature through the EDS.
The declaration must be sent along with the documents attached to it in order to comply with the requirements of the Tax Code of Russia. They can be provided electronically.
According to the EDI, reporting is submitted by the following categories of taxpayers:
- business entities with an average number of personnel for the previous calendar year of 100 or more people;
- newly registered companies (including through reorganization) with a staff of 100 or more people;
- other entities that are tax payers, the submission of declarations for which is provided exclusively in electronic form (for example, VAT reports).
For companies that need to file returns electronically, the easiest way to do this is through a service accounting company.
Citizens who themselves calculate and transfer income taxes to the state budget (individual entrepreneurs on the general taxation system, lawyers, notaries, etc.), individuals who have received taxable income (from the sale of real estate and transport, rental of housing and cars, winnings in casino or lottery, etc.), as well as tax residents who earned income outside the Russian Federation, based on the results of the calendar year, are required to prepare and send a 3-NDFL declaration to the NI at the place of registration.
You can report to the Federal Tax Service in person, send documents by mail or via the Internet.
Submission deadlines
According to Art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taxpayers must, in the manner established by the current law, submit declarations (calculations) to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration in cases where this is established by the current legislation.
The obligations of taxpayers to prepare and submit reports and calculations on current taxes and fees are provided for in Part II of the Tax Code of Russia in the context of each of them, and failure to submit a declaration on time is an offense that entails the imposition of financial sanctions.
The deadlines for submitting reports on the vast majority of fiscal obligations are regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, the annual profit declaration is submitted by business entities no later than March 28 of the year following the reporting year.
As for the 3-NDFL report, as a general rule, it was necessary to report on income received for 2021 before April 30, 2020. This deadline does not apply to cases of filing a document in order to obtain a tax deduction.
Let us note that the administration of local and regional taxes and mandatory payments, as well as the regulation of the deadlines for filing mandatory reports on them, falls within the competence of the authorities of the subject or municipality. Accordingly, these individual rules will apply exclusively in the territory of a specific region (for example, land and transport fees, etc.).
Amount of penalties for late submission of a tax return
Submitting a declaration in violation of the deadlines is included in the category of non-compliance with the procedure for submitting mandatory reporting. The amount of penalties for all companies and entrepreneurs in these cases is regulated by uniform provisions and calculated using the same algorithm.
So, according to paragraph 1 of Art. 119, late submission of tax reports entails a fine of 5% of the amount of tax indicated in the report as the amount payable to the budget for each full and partial month. In this case, the size of the limit amount of financial liability should not exceed 30% of the amount of the payment not paid on time. The lower limit of sanctions is 1000 rubles.
The absence of accruals in the reporting period does not relieve the taxpayer from financial responsibility - in this case, he will have to pay a minimum fine for failure to file a return of 1000 rubles.
Violation of the reporting method also falls into this category. In this case, we are talking about the largest taxpayers and companies with an average number of employees of 100 or more people who are required to submit reports electronically.
A taxpayer is not exempt from paying a fine for a declaration even if:
- the tax was paid to the state budget on time and in full;
- There is no estimated amount of fiscal liability to be paid.
For the above cases, the law provides for the withholding of the minimum amount of financial sanctions - 1,000 rubles. (Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 N 57, paragraph 18).
Financial liability for untimely payment of insurance premiums is calculated using the same principle. In this case, the amount of the fine is also 5% of the volume of unpaid payments calculated for payment over the last three months. The fine limits are similar: minimum 1,000 rubles, maximum 30% of the calculated amount.
In addition to tax legislation, liability for violation of deadlines for filing declarations is also regulated by the Administrative Code. So, according to Article 15.5, this offense is punishable by a warning or a fine in the amount of 300-500 rubles.
You can correctly calculate the amount of the fine using online calculators that are posted on specialized resources. They make it possible to select the type of document, indicate the date of its actual sending and the amount of calculated tax, and then calculate the penalties to be paid to the budget.
To ensure that reporting is submitted on time, the easiest way is to outsource accounting. In such companies, liability is insured and fines will no longer be your concern.
Penalties for failure to provide a zero report
As mentioned earlier, the amount of financial liability for failure to submit a tax return is calculated as a percentage of the amount of the tax payment accrued for payment to the budget. In this case, the fine payment cannot be less than 1000 rubles. Since a business entity must always report to the inspectorate, failure to submit even a zero report is also an offense and is punishable by paying a penalty. In this situation, it is 1000 rubles.
Responsibility for failure to submit interim reports
According to current legislation, a number of taxes require taxpayers to provide reports not only on the results of the tax period, but also on the results of each reporting period - mandatory interim data. First of all, we are talking about income tax (clause 1 of Article 289 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), which should be reported quarterly or monthly.
At the same time, according to the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation (clause 17 of Resolution No. 57 of July 30, 2013), failure to comply with the deadlines for filing interim reports should be punished not under clause 1 of Art. 119 (5% of the amount of payment not transferred to the budget, min 1000 rubles, max 30%), and according to clause 1 of Art. 126 of the Tax Code of Russia, that is, a penalty of 200 rubles, because such a violation is regarded as failure to provide documents and information provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for tax control and verification of the validity of the tax base.
Sanctions for late filing or failure to provide 3-NDFL
Basically, the calculation and withholding of taxes on the income of individuals is carried out by tax agents - employers, financial and insurance companies, banks, etc. As for income received without their participation, the responsibility for declaring it rests with the individuals themselves.
As a general rule, such income includes income from the sale of real estate and vehicles before the expiration of the minimum period of ownership of the specified property (3 years for cars, 5 years for real estate), income from the rental of real estate and vehicles, lottery and casino winnings, income , received outside the Russian Federation, income from the professional activities of notaries, lawyers, gifts received from non-close relatives, etc.
The requirements for drawing up the 3-NDFL report are regulated by the Tax Code of Russia. The tax register must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service by April 30 of the year following the reporting year. “Zero” reporting by entrepreneurs is also submitted within the same period. If, according to the calculated data, tax payable to the budget has not been accrued, untimely sending or failure to submit a document threatens the violator with payment of a fine for failure to submit 3-NDFL in the amount of 1,000 rubles.
If documentation has not been submitted according to which the individual has obligations to the budget, such a violator will have to pay a penalty in the amount of 5% of the amount calculated in the document for each month of delay (full and incomplete), but not more than 30% in total.
Moreover, if, along with failure to submit reports, the tax was also not paid by July 15, the individual faces a fine of 20% of the amount of the fiscal payment. This penalty applies only if the Federal Tax Service itself has established non-payment. If, before receiving a notification from the inspection, a person has independently made the obligatory payment, the grounds for collecting this penalty will be exhausted.
Correctly filling out a payment order for a traffic police fine
It is important to fill out the details correctly - an error in even one number will lead to the money going to the wrong place. The payer will consider the fine paid, but in fact there will be a delay in payment. As a result, the debtor will have problems with the bailiff service: from an additional fine to blocking the company's current account.
The procedure for processing payment orders for a traffic police fine is regulated by Appendix No. 2 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 107n dated November 12. 2013
The list and description of payment order details are in Appendix 1 to the Regulations of the Bank of Russia dated June 19. 2012 N 383-P
The table below contains important points for filling out a payment order indicating the contents of the details.
| Field no. | Props name | Contents of the props |
| 101 | “08” (Organization or individual entrepreneur making payments to the budget system) | |
| 18 | Type of operation | “01” (payment order) |
| 21 | Payment order | 5 |
| 22 | Code | UIN identification number (indicated in the line “Resolution”) |
| 24 | Purpose of payment | “Fine for an administrative offense in the field of road safety” number and date of resolution |
| 104 | KBK | 188 1 1601 140 |
| 105 | OKTMO | OKTMO code of the municipality to which the traffic police department that issued the fine belongs |
| 106 | Basis of payment | “0” |
| 107 | Taxable period | “0” |
| 108 | Document Number | “0” |
| 109 | Document date | “0” |
| 110 | Payment type | “0” |
Statute of limitations
To bring an entity to justice and apply penalties to it, the law sets a deadline during which this can be done.
In accordance with Art. 113 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, this period is 3 calendar years from the date of commission of the offense. That is, if the deadline for paying tax or submitting a return for the reporting year 2021 is February 1, 2021, then it is from this date that the penalty will begin to be calculated.
This will happen until February 1, 2021, after which the application of punishment will cease.
However, in practice, tax inspectorates file lawsuits to collect debts long before the deadline expires. Therefore, it is unlikely that even ordinary citizens, not to mention entrepreneurs and legal entities, will be able to “wait it out” and avoid liability for violations.
Calculation of the penalty amount and its payment
As already noted, a special formula approved by law is used to calculate penalties:
P = N * k * 1/300* SR, where
P is the amount of the penalty, k is the number of days of delay, SR is the refinancing rate, which is set by the Central Bank of Russia.
As an example, consider a situational problem:
Ivanov I.I., who owns a land plot, did not receive a tax notice in 2021 due to its theft from the mailbox. Payment for 2015 was made late - December 23, 2021. The tax amount was 8.3 thousand rubles. Since the payer had to pay the tax before December 1, 2016, the number of days of delay will be 21 days. The refinancing rate of the Central Bank of Russia in 2021 was at 10%.
Therefore, the amount of the penalty will be:
P = 8300 * 21 * 1/300 * 10% = 58.1 rub.
Thus, the fine will be 58 rubles and 10 kopecks. As for the fine, its amount, depending on the absence or presence of the payer’s fault in non-payment of tax, will be equal to 1660 and 3320 rubles. respectively.
You can also use the online calculator below to calculate the penalty:
The penalty is paid in the same way and on the same day as the land tax, but using a separate payment slip (it will have a different BCC).
Details for debt repayment are sent in a notification from the tax authority or can be obtained there as a result of a personal visit to the inspectorate.
To pay, you can contact any bank or do it non-cash using online banking. A receipt confirming the fact of depositing funds must be kept, as it may be needed in the event of any tax disputes.
A public easement is established in the interests of the public (for example, if it is necessary to establish a passage, passage, or provide access to a watering hole). Do you need to sell a house with land? Our article contains a detailed algorithm for this procedure.
There are several types of survey plans depending on the purpose of the survey procedure. Read more about this here.
KBC for payment of penalties
Penalties are charged for each day of delay. The first day of accrual of penalties is the day following the day of late payment. There is still debate as to whether the day of payment of the tax is considered the last day of delinquency and whether to include it in the calculations, and here the decision remains with the taxpayer. If we are talking about a small amount, it is recommended to charge penalties for the day of late payment. The BCC for penalties depends on the place of sale of the goods:
- goods sold in Russia - 182 1 03 01000 01 2100 110;
- goods from Belarus and Kazakhstan - 182 1 04 01000 01 2100 110;
- goods from other countries - 153 1 0400 110.
***
To understand why it is necessary to make a transfer to the budget upon request with KBK 18211603010016000140, you need to know the content of the claims from the fiscal authorities. It is immediately necessary to take into account that this BCC is used if it is necessary to collect fines for various violations of tax legislation.
If the company incorrectly indicates the code in the order, this will not have any consequences for it, however, to correct the situation, it will have to provide a special statement indicating the correct BCC. There is no need to transfer the amount again; previously transferred funds will be counted towards its repayment immediately, despite the incorrect code.
Similar articles
- Property tax - current BCC for organizations
- KBK fine transport tax 2018
- KBK for personal income tax for employees
- Penalty for failure to provide 6-NDFL
- KBK for organizations and individuals on transport tax
An example of how to fill out a payment form to pay a fine
Initial data:
| Parameter | Meaning |
| Tax | VAT |
| Payment type | Fine |
| KBK | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Period | III quarter 2020 |
| Sum | 1000 rub. |
| Basis of payment | Debt repayment on demand |
An example of how to fill out a payment form for a VAT penalty at the request of the tax authority: