Accounting
Marina Dmitrieva
Leading expert - professional accountant
Current as of March 6, 2020
Starting in 2021, a new method of forming a work record book has been introduced—electronic. However, it is also possible to prepare a paper version at the same time. Find out how to take into account paper work book forms in our material.
Free form
Issue employment record forms to employees free of charge if:
- an emergency occurred (fire, flood), as a result of which the employees’ work books were damaged;
- The work record form was spoiled by an employee of the organization responsible for personnel records during the initial filling.
This is stated in paragraphs 34 and 48 of the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2003 No. 225, and the letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated August 6, 2010 No. 12-3/10/2-6752 (in relation to work books that were lost in fires in July–August 2010).
Situation: is it possible not to charge an employee for a work book form?
Yes, you can.
But such a condition must be enshrined in a local regulatory act of the organization (for example, in the Labor Regulations or in the order of the manager).
In addition, this operation will have taxation specifics.
When calculating income tax (or a single tax when simplifying the difference between income and expenses), the cost of the form cannot be taken into account to reduce the tax base (clause 16 of article 270, clauses 1, 2 of article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For the purpose of calculating VAT (if the organization pays this tax), the issuance of work books and inserts, including on a gratuitous basis, is recognized as a sale of goods. Therefore, you need to pay VAT on such a transaction (subclause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of VAT accrued on the cost of the form donated free of charge does not reduce the tax base for income tax (clause 16 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This procedure is confirmed by the Ministry of Finance of Russia in letters dated August 16, 2013 No. 03-03-05/33508, dated November 27, 2008 No. 03-07-11/367.
With regard to the deduction of personal income tax from the cost of a work book issued to an employee free of charge, the following must be taken into account.
If an organization issues a work book to an employee free of charge, then he has income in kind, from which personal income tax must be withheld (clause 1 of Article 210, subclause 1 of clause 2 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 27, 2008 No. 03-07-11/367). At the same time, the work book is transferred to the employee free of charge. This basis allows us to conclude that a gift agreement has been concluded between the employee and the organization. Such an agreement can be concluded either orally or in writing. This is stated in paragraph 1 of Article 572 and Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, providing an employee with a work book free of charge can be qualified as a gift. Income in the form of gifts is exempt from personal income tax in an amount not exceeding 4,000 rubles. for the year (clause 28 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Similar clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 1, 2010 No. 03-04-06/6-106.
Issuing a form to an employee without experience or an insert for it
In connection with the transfer of ownership from the employer to the employee, a VAT tax base arises. The tax billed by the supplier is deductible. The obligation to pay tax does not arise if the enterprise is not a VAT payer. The moment the VAT base arises is the day the work book is opened.
Example of issuing a form ⇓
The company Novost LLC hired employee V. without work experience. The acquisition cost after VAT was 100 rubles. The following entries were made in the accounting of Novost LLC:
- The cost of the completed form is included in the expenses: Dt 91/2 Kt 10 in the amount of 100 rubles;
- The accrual of VAT is reflected: Dt 91/2 Kt 68/1 in the amount of 18 rubles;
- The form was written off based on the certificate: Kt 006 in the amount of 100 rubles;
- The cost of the form is reflected in income: Dt 73/3 Kt 91/1 in the amount of 118 rubles;
- The amount of debt is withheld when calculating wages at the request of the person: Dt 70 Kt 73/3 in the amount of 118 rubles.
The moment of accounting for enterprise expenses is determined when costs arise - the purchase of forms. The amount of payment for the forms received is taken into account as part of income when a debt arises to the enterprise.
Accounting and taxes
Situation: how can an organization take into account the acquisition and issuance of a new work book to an employee under the general regime?
The procedure for accounting and taxation of transactions related to the provision of work books to employees is not regulated by law.
The right of an organization to charge an employee a fee for issuing a work book is provided for in paragraph 47 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225.
In accounting, the cost of purchased work books can be taken into account as part of:
- materials on account 10 of the same name (as assets used for management needs (clause 2 of PBU 5/01)) with subsequent write-off to other expenses;
- goods on account 41 “Goods”.
A more correct way of reflection is to take books into account as materials. The fact is that the sale of work books for ordinary organizations is not the main activity. Organizations provide themselves with such forms on a contractual basis for a fee (clause 46 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225). In this case, work record forms can be purchased directly from the Goznak association, as well as from distributors that meet the requirements of this association (clauses 2 and 3 of the Procedure approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 22, 2003 No. 117n).
Therefore, account 41, which summarizes information on the availability and movement of inventory items purchased as goods for sale, and account 90 “Sales,” which summarizes information on income and expenses associated with ordinary activities, are more convenient to use for distributors of labor books.
Other organizations that purchase forms of work books and inserts for them for their own needs (for subsequent issuance to employees) can account for these forms in account 10.
Simultaneously with the posting of work record forms, reflect on account 006 “Strict reporting forms” in conditional valuation (clause 42 of the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225).
When you receive the forms, please make the following notes:
Debit 10 Credit 60 – work books have been capitalized;
Debit 19 Credit 60 – reflects the amount of VAT presented by the supplier;
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” Credit 19 – the amount of VAT presented by the supplier is accepted for deduction;
Debit 006 – work record book forms are accepted for accounting.
If an organization charges a fee for issuing work books, the transaction is reflected in account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other transactions.” If an organization deducts payment for a work book form from an employee’s salary, use account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”.
The issuance of work books and their inserts to employees of the organization is recognized as the sale of goods. Therefore, VAT must be paid on such a transaction. This conclusion follows from the provisions of subparagraph 1 of paragraph 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is confirmed in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 30, 2015 No. 03-07-11/55714, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 23, 2015 No. GD-4-3/ [email protected] In this case, the employee pays the organization the cost of the work book including VAT (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 26, 2007 No. 07-05-06/242 and dated June 13, 2007 No. 03-07-11/159).
In accounting, operations for issuing work books and their inserts to employees and receiving payment for the forms are reflected in the following entries:
Debit 50 (51, 70) Credit 73 – the cost of the issued work book was reimbursed (including VAT);
Debit 73 Credit 91-1 – income is recognized in the amount of payment received for the work book form (including VAT);
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” - VAT is charged on the reimbursement of the cost (sale) of a work book by an employee (if the organization is a tax payer);
Debit 91-2 Credit 10 – the cost of work books transferred to an employee of the organization is written off.
When transferring work books and their inserts to employees free of charge, make the following entries in accounting:
Debit 91-2 Credit 10 – the cost of work books transferred free of charge is written off;
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” - VAT is charged on the free transfer of work books to employees (if the organization is a tax payer).
You can write off the work book form (the insert for it) on the day it is issued to the employee. In this case, the date of issue should be considered not the day of dismissal of the employee, but the day when the work book is opened on the basis of Part 4 of Article 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Credit 006 – forms of work books (inserts for them) have been written off.
Advice: there are arguments that allow an organization not to pay VAT on the issuance of a work book (its insert) to an employee. They are as follows.
Firstly, the work book (the insert for it) does not have the characteristics of the goods defined in paragraph 2 of PBU 5/01 and article 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Secondly, providing work books to employees who do not have work experience is the responsibility of the organization established by labor legislation (Part 4 of Article 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Thirdly, the amount of payment for the form charged to an employee should not exceed the amount of costs for its acquisition (clause 47 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225).
Since, by issuing work books to employees, the organization does not pursue the goal of making a profit, such operations cannot be considered as entrepreneurial activity (sale of goods, work, services) (Article 2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). A similar point of view is reflected in the decisions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated October 1, 2003 No. A26-5317/02-28 and dated March 2, 2007 No. A56-44214/2006. Consequently, the issuance of work books (free of charge or for a fee) is not a sale. This means that such an operation is not subject to VAT (subclause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If, when filling out, you spoiled the work book form (the insert for it), make the following entries in accounting:
Debit 91-2 Credit 10 – the cost of damaged work books has been written off;
Debit 19 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for VAT” – VAT previously accepted for deduction has been restored;
Debit 91-2 Credit 19 – the restored amount of VAT is written off;
Credit 006 – forms of damaged work books (inserts for them) have been written off.
When calculating income tax, the costs of purchasing forms of work books (inserts for them) can be taken into account. Such costs are economically justified and are associated with activities aimed at generating income (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 26, 2007 No. 07-05-06/242, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 23, 2015 No. GD-4-3/ [email protected] ). These expenses reduce the tax base for income tax at the time of issuing a work book (insert to it) to an employee of the organization (clause 2 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Include the amount of reimbursement by the employee for the issuance of a work book as part of income subject to taxation.
If the amount of compensation is equal to the cost of the organization to purchase the form, the profit is zero. Consequently, the organization does not pay income tax (Article 247 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If an organization does not charge an employee for a work book form (for example, in the case of mass loss of books, damage or incorrect initial filling), it will not be able to take into account when calculating income tax either the costs of its acquisition or the VAT accrued on the gratuitous transfer ( Clause 16, Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). As a result, due to differences between accounting and tax accounting, a constant difference is formed, with which the permanent tax liability must be calculated (clauses 4 and 7 of PBU 18/02):
Debit 99 Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - reflects the permanent tax liability.
In addition, when transferring a form free of charge, personal income tax must be withheld from an employee (Article 1, 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Its market value is recognized as the employee’s income (clause 1 of Article 210, subclause 1 of clause 2 of Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This is confirmed by the Russian Ministry of Finance in a letter dated November 27, 2008 No. 03-07-11/367.
Accounting entries when purchasing forms
Accounting for transactions for the purchase of work books is carried out using account 76 when purchasing by bank transfer. When registering, you must have an invoice issued by the seller. Work books purchased by an enterprise cannot be classified as goods. The reason is that the document is not intended for further resale.
Accounting for the movement of forms is mainly carried out by entries on account 10. A number of enterprises use account 41, which does not correspond to the position that there are no signs of the goods. When registering, an entry is simultaneously made to account 006, intended for accounting for BSO. Off-balance sheet accounting allows you to have information about the presence of the required number of documents on record.
| Purpose of the operation | Account debit | Account credit |
| Payment for forms has been made | 60 (76) | 51 |
| Posting of forms is reflected | 10 | 60 (76) |
| VAT from the supplier is included | 19 | 60 (76) |
| Forms accepted for off-balance sheet accounting | 006 |
In the future, when accounting for the movement of the form and funds to pay the cost, account 73 is used, to which subaccount 3 “Payments for work books” is opened.
Accounting for work records
Work books are documents of strict accountability, therefore the legislation defines the procedure for their recording and storage (section VI of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225).
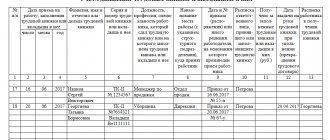
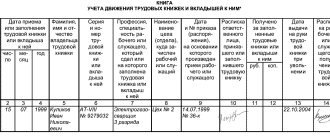
Each organization is required to maintain special books for recording work records. The first of them is a receipt and expenditure book for recording work book forms and the insert into it (Appendix 2 to the resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated October 10, 2003 No. 69). The second is a book for recording the movement of work books and inserts in them (Appendix 3 to the resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated October 10, 2003 No. 69).
The receipt and expenditure book for accounting of work book forms and the insert in it is maintained in the accounting department of the organization. Make entries in it immediately after receiving the forms from the distributor. In the book, be sure to include information about all transactions related to the acquisition and use of purchased work books and inserts in them, indicating series and numbers. And also enter information about the cost of the forms.
The organization's personnel service should keep a record of the movement of work books and inserts in them. But if there is no such service, then this responsibility is usually assigned to the accounting department. In this book, enter information about the date the employee was hired, his last name, first name, patronymic, series and number of the work book and insert, position, place of work, as well as details of the document on the basis of which the employee was hired.
All sheets in both books must be numbered, laced, certified by the signature of the head of the organization, and also sealed with a wax seal or sealed.
This procedure is established in paragraph 41 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225.
Advice: joint stock companies and LLCs have the right not to use a seal. But for now it’s better not to give up seals. The explanation is this.
On April 7, 2015, the Law of April 6, 2015 No. 82-FZ came into force. Articles 2 and 6 of this law provide that joint stock companies and LLCs now have the right (and not the obligation) to have a seal. The company reflects information about the presence of a seal in the charter.
At the same time, paragraph 41 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225, continues to apply. This by-law requires the sealing of labor record books. Rostrud recalled this in a letter dated May 15, 2015 No. 1168-6-1.
Therefore, we recommend that you continue to use printing when maintaining work records.
One more thing. To refuse seals, be sure to make changes to the charter of your organization.
It is worth noting some features for organizations and entrepreneurs of Crimea (Sevastopol). Until January 1, 2015, such employers kept books of employment records in accordance with Ukrainian legislation (clause 2 of article 2 of the Law of October 14, 2014 No. 299-FZ). Since January 1, 2015, they have been keeping records of work books in forms approved by Russian legislation (clause 1 of article 2 of the Law of October 14, 2014 No. 299-FZ). In the new form of the book for recording the movement of work records, it is necessary to enter information only about newly hired employees into the organization.
There is a special situation with those employees in Crimea (Sevastopol) who have been working for a long time. Such people have work books that are reflected in the old accounting book, and there are movements in these books after re-registration. Where to reflect these movements?
The legislation does not regulate the issue of transition from one form of book to another. And this has never happened in practice before. Taking this into account, there are two possible solutions.
1. Open a journal using the “Russian” form, where you can make entries only for newly hired employees. At the same time, entries will continue to be made in the “Ukrainian” journal upon dismissal of employees who were recorded in it. After some time, the old journal will close and it can be archived.
2. A new journal is opened, into which unclosed entries from the old one are transferred in chronological order.
This position is supported by Rostrud specialists in oral explanations.
An example of registration of work record books
E.V. Ivanova is getting a job for the first time, so the organization issued her a work book.
Accountant V.N. was appointed responsible for personnel records. Zaitseva.
Zaitseva drew up a work book and made entries in the income and expenditure book to record the forms of work books and inserts in them and the book of accounting for the movement of work books and inserts in them.
Situation: how to certify work record books if the organization does not have a wax seal?
If the organization does not have a wax seal, the work record books can be sealed (clause 41 of the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225). The seal is easy to make. Bring the ends of the fastening thread you used to stitch the magazine to the inside of its back cover. Place them between two squares of white paper and glue the squares together. Attach the seal to the inside of the cover and place the usual round seal of the organization or personnel service on it so that part of the stamp extends onto the cover. And do not forget to make a certification about how many pages in this book are laced, numbered and sealed. Place your signature and date next to it.
Advice: joint stock companies and LLCs have the right not to use a seal. But for now it’s better not to give up seals. The explanation is this.
On April 7, 2015, the Law of April 6, 2015 No. 82-FZ came into force. Articles 2 and 6 of this law provide that joint stock companies and LLCs now have the right (and not the obligation) to have a seal. Information about the presence of a seal is reflected in the company's charter.
At the same time, paragraph 41 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225, continues to apply. This by-law requires the sealing of labor record books. Rostrud recalled this in a letter dated May 15, 2015 No. 1168-6-1.
Therefore, we recommend that you continue to use printing when maintaining work records. Do this until changes are made to the bylaws.
One more thing. To refuse seals, be sure to make changes to the charter of your organization.
Basic norms in document flow
At enterprises, work books are recorded as strict reporting forms (SSR). Despite the prevalence of the document in retail, the only legal way to purchase is to purchase BSO forms from legal representatives of Goznak. The enterprise was organized on the basis of a federal institution and has been a joint-stock company since 2014. The company produces products marked with state marks, including work books.
In the document flow, responsible persons are guided by the Rules approved by GD dated March 16, 2003 No. 225 (hereinafter referred to as the Rules). To make entries, a journal is used - a receipt and expenditure book for recording forms and inserts.
Sample accounting book 2021
Responsibility
For the absence of labor records or their incorrect registration, the labor inspectorate may fine the organization (entrepreneur) and its officials.
In this case, the amount of the fine will be:
- for officials (for example, a manager) – from 1000 to 5000 rubles;
- for an entrepreneur – from 1000 to 5000 rubles;
- for an organization – from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
And for repeated violation you face the following:
- for a manager (official) – a fine in the amount of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles. or disqualification for a period of one to three years;
- for an entrepreneur – a fine in the amount of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles;
- for an organization – a fine in the amount of 50,000 to 70,000 rubles.
Such measures of liability are provided for in parts 1 and 4 of Article 5.27 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses.
No property, no income
If a work book is issued to an employee without paying a fee for the form, then it is generally accepted that the employee received the property free of charge and in this regard he has taxable income (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 27, 2008 No. 03-07-11/367). However, we cannot agree with this opinion.
The fact that the form was the property of the employer is not disputed. But a work book issued for an employee is not a thing. This object does not independently participate in civil circulation - just like a passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation or a diploma of education. Personal documents do not have civil negotiability (Article 129 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The form as such was not transferred to the ownership of the employee. Therefore, there is no need to talk about the transfer of ownership. In connection with the registration of a work book, the employer loses property, but the employee does not acquire it (Clause 2 of Article 209 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
An individual also does not receive any economic benefit from obtaining a work book, since he does not have the legal opportunity to purchase a work book form without going through the employer. That is, Article 41 of the Tax Code cannot be applied to an employee; assessing his benefit (income) in the amount of the cost of the form is unlawful. This means that there is no object of personal income tax taxation.
The employer also does not provide services in the civil legal sense for issuing a work book to an employee, since the norms of economic law do not apply to labor relations (Clause 3 of Article 2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Fulfillment by the employer of the requirements of labor legislation in relations with employees is neither compensated nor gratuitous, because compensation is a category of civil legislation (clause 5 of Article 38, clause 1 of Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Article 423 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
As a result, neither the registration nor the issuance of a work book to an employee is an implementation (resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated October 1, 2003 No. A26-5317/02-28, dated March 2, 2007 in case No. A56-44214/2006). In this regard, the object of VAT taxation does not arise. Therefore, the author cannot agree with the position presented in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06.08.2009 No. 03-07-11/199.
Our reasoning can be supported by drawing a parallel with receiving education at the expense of the budget. Although it is free for a citizen, so far no one has thought of taxing the cost of education or the issued diploma form with personal income tax. Why? Yes, because the legal relations of the parties are regulated not by civil law, but by the Budget Code.
As a result, no additional entries related to the accrual of personal income tax or VAT to the budget are required in the example given.
Storage
Keep work books in the organization as strictly accountable documents and, best of all, in a fireproof safe. If this is not possible, then in a cabinet locked with a key. Give the forms to the person responsible for maintaining work records upon his application, drawn up in any form.
At the end of each month, the employee responsible for maintaining work books must submit to the accounting department a report on the availability of forms and the amounts received for issued work books and inserts, attaching a receipt order. A report on the availability of forms and on the amounts received for issued work books and inserts is drawn up in any form.
This procedure is established in paragraph 42 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225.
An example of issuing work book forms for reporting and preparing a report on the availability of forms and the amounts received for issued work books and inserts
On October 20, the head of the HR department E.E. Gromova, on the basis of her application, was issued the following documents:
- work book form;
- insert in the work book.
On October 21, Gromova submitted a report to the accounting department on the availability of forms and on the amounts received for issued work books and inserts.
Situation: who in the organization should be responsible for recording, maintaining and storing work books?
In a large organization, the personnel department is usually responsible for maintaining work records. At a small employer, due to the lack of an appropriate special unit, accountants, secretaries or other officials can do similar work. The appointment of the person responsible for working with work books should be formalized by order of the head of the organization in free form (clause 45 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225).
When changing the person responsible for working with work books, transfer the work books according to the act of acceptance and transfer of cases. In this case, in the act, indicate not just the number of books, but list their actual composition (names of owners and details). The act must be certified with two signatures - on the one hand, indicate the position and surname of the person who accepted the documents, on the other hand, the person who submitted the documents. If you discover facts about the absence of some work books, draw up an act in which you indicate the reasons for their absence.
Reimbursement of costs for the form
The legislator does not make the issuance of a work book dependent on the payment of a fee for it. This was confirmed by the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation in its ruling dated September 6, 2007 No. KAS07‑416. That is, the employer cannot dictate the condition: “the work book should not be issued to the employee until he pays money for the form.”
When dismissing an employee, settlement with him is made according to the rules of Article 140 of the Labor Code. The application of this article was clarified by the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation in its ruling dated February 21, 2008 No. 74-О-О. Namely: if the employee does not agree with the correctness of the amount accrued to him, the employer is obliged to pay the amount due to the employee in the undisputed part, without delaying the settlement with the dismissed employee until the end of the consideration of the labor dispute that has arisen between them. At the same time, the employer does not have the right to deduct the cost of the form from the employee’s salary (remuneration for labor), since the list of grounds for deduction is closed (Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). But payments upon dismissal may include various compensations - most often for unused vacation (Article 165 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). There are no formal contraindications for deducting the cost of the form from compensation. However, as a result, two employees, one of whom used vacation before dismissal, and the other received compensation for it, will find themselves in unequal conditions, since retention is possible only for the second. This result is discrimination in the world of labor and violates the requirements of Article 3 of the Labor Code: no one should receive any advantages depending on circumstances not related to the employee’s business qualities. The conflict between the by-law and the law is obvious.
On a note
Work book forms are objects of civil law, limited in circulation (clause 1, clause 2 of Article 129 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Meanwhile, the condition on the payment of the form for the employee (clause 47 of the Rules) is contained in the resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation, and not in the regulatory act of the federal executive body, as required by Article 66 of the Labor Code. However, Article 423 of the Labor Code clarifies: pending the bringing of regulatory legal acts in force on the territory of the Russian Federation into compliance with this code, they are applied to the extent that they do not contradict it. We have identified a contradiction. Therefore, in the author’s opinion, deductions for the form are illegal in principle. The purchase of forms by the employer is a non-reimbursable expense due to the requirements of labor legislation, along with labor protection costs. For this reason, you should not initially receive forms on account 10.
The reader may object: by the above-mentioned ruling of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation No. KAS07‑416, paragraph 47 of the Rules was recognized as valid.
However, this court decision was made at a time when Article 66 of the Labor Code was in force in a different wording - it was the Government of the Russian Federation, and not the federal executive body, that was vested with the corresponding powers. In addition, the court analyzed paragraph 47 for conflicts with other rules. And the employer’s right to receive reimbursement of expenses in accordance with the will of the employee is not equivalent to the right to demand it. Example
Flagman LLC purchased, through an accountable entity, 10 work book forms at a price of 177 rubles.
per piece (including VAT - 27 rubles). The employee purchased the forms by proxy. In this regard, the accountant will make the following accounting entries: DEBIT 71 CREDIT 50
- 1770 rubles.
(177 rubles × 10 pcs.) – money was given to the accountable person to pay for work books; DEBIT 60 CREDIT 71
- 1770 rub.
– the advance report with supporting documents was approved; DEBIT 006
- 1770 rub.
– work book forms have been accepted for off-balance sheet accounting; DEBIT 91 CREDIT 60
- 1500 rub.
((177 rub. - 27 rub.) × 10 pcs.) - the costs of purchasing forms from the official distributor are written off;v DEBIT 19 CREDIT 60
- 270 rub.
(27 rubles × 10 pcs.) – VAT presented by the distributor is allocated; DEBIT 68 CREDIT 19
- 270 rub.
– VAT is accepted for deduction; DEBIT 006
— 150 rub. – the form used to draw up the employee’s work book has been written off.
Dismissal
When receiving a work book upon dismissal, the employee must sign a personal card and a book for recording the movement of work books and inserts (clause 41 of the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 No. 225).
Work records and duplicates not received by employees upon dismissal must be kept by the organization until the document is requested by the employee or his immediate family (in the event of the employee’s death). Unclaimed – 75 years. This procedure and storage periods are provided for in paragraph 43 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 16, 2003 No. 225, and the list approved by order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated August 25, 2010 No. 558.
Application of seals and wax seals
If a seal is preferable for the employer, then it must be made using a special device, the procedure for use of which is regulated by GOST 31282-2004.
Such a device must:
- have signs of identification;
- protect the journal from unauthorized changes in its structure;
- ensure protection of the seal from intentional violation of its integrity.
Among the most convenient seals, which are provided for by the specified GOST, are film ones. In their structure there are areas where you can record the date of sealing of the document.
The employer should also issue a local legal regulation regulating:
- procedure for using sealing devices;
- the procedure for recording seals (for example, in a separate journal);
- actions of employees upon detection of a violation of the integrity of seals.
As for the use of wax seals, it may look less preferable compared to fillings, because:
- sealing wax can crumble over time (while the magazines in question have a long shelf life);
- sealing wax must be heated using potentially flammable devices before use, and their use in an employer's office may not be advisable.
But if sealing with wax is still chosen, the following should be fixed at the level of local legal acts:
- print format (its content);
- the procedure for using the seal by employees;
- lists of documents that are certified by such a seal.
Registration of pension
To apply for a pension, the employee will need the original work book. It is the work book that is the main document confirming the period of work under an employment contract (clause 11 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 2, 2014 No. 1015).
The employer is obliged to issue the original work book no later than three working days from the day the employee submits the relevant application. In this case, a maximum of three working days after receiving the work book at the Pension Fund branch, the person will have to return the document to the organization. This is stated in Article 62 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The emergence of the need for accounting
The need to keep records of work records does not arise if the employee brings the form for storage at the personnel authority. After employment, a corresponding entry is made in the document with subsequent registration in the accounting journal. In this case, actions are limited to personnel records.
The need for accounting arises when an employee is employed without experience or there is no space in the book to enter text about hiring or dismissal. When maintaining records, a record of transactions accompanying the actions is made:
- Purchase of work books by the enterprise.
- Registration of documents.
- Issuance of the document to the employee.
- Acceptance of a fee equal to the cost of the enterprise's purchase.
A new document is issued after the employee applies to the manager with an application. According to Art. 65 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an organization or individual entrepreneur is required to provide a new form or insert if it is missing or lost by the employee.
You must receive compensation for the provision of your work book. The refusal of the recipient of the document to pay the expenses of the organization or individual entrepreneur for the purchase of the form is not grounds for refusal to issue it. All actions related to the purchase, accounting, and write-off of documents are accompanied by accounting records.
How does destruction occur?
Today in large cities there are many services that are ready to help you get rid of documents for money.
This is not done for free, but quickly and efficiently.
If you have no desire to pay for work that you can easily do yourself, then go for it.
There are two ways to get rid of labor. Firstly, such documents can easily be torn into pieces and set on fire .
As a rule, a similar action is carried out on the territory of the enterprise so that everyone can make sure that the documents are destroyed.
The second method is shredding . A special machine shreds the paper to a state where it is simply impossible to read the contents in it.
The procedure for conducting cash transactions
The issuance of cash from the cash register on account for expenses associated with the organization's activities is carried out according to an expenditure cash order on the basis of an application from an accountable person drawn up in any form. The application must contain a record of the amount of cash and the period for which the cash was issued, the signature of the manager and the date (clause 6, clause 6.3 clause 6 of Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014 “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions by legal persons and a simplified procedure for conducting cash transactions by individual entrepreneurs and small businesses" (hereinafter referred to as the Directive)).
In accordance with paragraph. 2 pp. 6.3 clause 6 Instructions, an advance report on the amounts spent is submitted by the employee within a period not exceeding three working days after the expiration date for which cash was issued against the report. Checking the advance report, its approval by the manager and the final settlement of the advance report are carried out within the time period established by the manager.
Write-off act
The act of writing off the work book is an extremely important document, although there is not a single mention in the legislation of what it should actually look like.
Everyone draws up this act by hand and arbitrarily .
We have derived only a number of rules that should be inherent in this document:
- it must contain the full name of the organization;
- the name of the act itself should be written in large letters in the center;
- We also do not forget to enter the very date when the act was written;
- the act should briefly outline the entire process regarding the write-off of labor;
- the number of written off documents is indicated, as well as the reasons for writing off each one;
- do not forget to list the composition of the inventory and liquidation commissions;
- The document must end with the seal and signatures of all participants in writing off the work books.
It is worth noting that this act is drawn up on A4 sheets, in duplicate . Written with a black or blue pen in the absence of a form.
Act on writing off work books.