Analysis and sources of increasing the organization's profit
First of all, in order to maximize the profit of an enterprise, you first need not to develop specific methods, but to analyze the market, competitors, customers and much more. Analysis is the basis on which any actions are based to increase the company’s own profit.
Sources of profit in an organization can be:
- reduction in production costs;
- diversification of production;
- implementation of budgeting and financial planning;
- cost reduction;
- opening new markets;
- competitive advantage;
- increasing the volume of products sold;
- sale or rental of unused property;
- introduction of the latest technologies and equipment in production;
- restructuring.
Uncovered loss: definition and reasons for its occurrence
If there is a loss for the current year, the calculation formula will look like this:
- NPk = NPn – U – D, where U is the loss of the current year.
The NPK indicator may be negative if the resulting current loss exceeds the NP value at the beginning of the year. It is in this case that the loss becomes uncovered. Those. uncovered means a loss that occurs when the enterprise receives an actual loss and is unable to cover it with reserve funds (including when funding reserves were not created). The main causes of PE are considered to be:
- Excess of company costs over income due to various reasons;
- Radical changes in accounting policies that significantly affected the financial position of the company;
- Errors discovered in the reporting period from previous years, etc.
If there is a loss, the company carefully analyzes the causes of the phenomenon, since it may be a consequence of a drop in the competitiveness of the products being manufactured, which will require a change in the sales strategy or re-profiling of production, or may be a temporary phenomenon with the infusion of impressive, but slowly recouping investments into production.
Let's look at it with an example.
Ways, methods and ways to increase company profits
Motivating employees is one of the most effective ways to increase profits. It is necessary to show employees that their personal income depends on the profitability of the enterprise. This will encourage them to put as much effort into their work as possible.
The introduction of new technologies and automation of production will lead to the possibility of reducing the number of employees, and accordingly, will reduce wage costs.
The riskiest way would be to increase prices. To use this method, the manufacturer must be confident that customers are willing to purchase the product, even if prices increase.
Another way is to reduce costs. But it is important to understand that reducing costs always leads to a decrease in product quality. Because of this, most buyers may go to competitors. This method is more suitable for mass production.
Factors and reserves for increasing the profit and profitability of a company
There are many factors that can affect profit growth. And it is not always possible to accurately assess the degree of influence of one or another factor.
Factors influencing the amount of profit can be divided into internal and external.
External (uncontrollable) factors include:
- extraordinary events (natural disasters);
- political changes in the country;
- changes in legislation;
- competitors;
- social conditions in the state;
- inflationary processes;
- changes in the banking and financial sector of the economy;
- suppliers and partners;
- buyers.
Internal (controllable) factors:
- financial policy within the enterprise;
- social (trainings and courses for company employees);
- introduction of new technologies;
- release of new products.
Gross profit increase
An increase in turnover inevitably leads to an increase in the gross profit of the enterprise. For this reason, it is important to monitor dynamics and ensure that production volumes are stable. Unsold products lying in the warehouse have a negative impact. To prevent this, you can sell products at discounts.
An analysis of the profitability of products sold will make it possible to understand which products need to be paid special attention to when selling them or removed from sales altogether in order to reduce the costs of their production.
An assessment of fixed assets will allow you to understand whether they generate gross profit. Otherwise, it would be better to sell off unprofitable fixed assets.
Financial indicators (Absolute values, thousand rubles)
The total liquidity ratio (current ratio), which characterizes the overall provision of an enterprise with working capital for conducting business activities and timely repayment of the enterprise's urgent (current) obligations, decreased in the period under review from 1.137 to 0.992, or by 12.71%. The value of the indicator indicates an insufficient level of coverage of current liabilities with current assets and overall low liquidity. This may indicate difficulties in marketing products and problems associated with organizing supplies.
The negative trend in this indicator for the analyzed period reduced the likelihood of repaying current liabilities at the expense of inventories, finished products, cash, accounts receivable and other current assets.
The quick liquidity ratio (quick liquidity ratio), reflecting the share of current liabilities covered by cash and the sale of short-term securities, decreased in the analyzed period from 0.824 to 0.616 (recommended range of values from 0.40 to 1.0) or by 25 ,20%.
The absolute liquidity ratio, reflecting the share of current liabilities covered solely by cash, increased in the analyzed period from 0.0016 to 0.0026 (with a recommended value of 0.30) or by 59.73%. Thus, during the analyzed period, the company slightly improved its ability to immediately repay current obligations using cash.
Chart 4. Liquidity ratios of the enterprise
The coefficient of autonomy (financial independence), which determines the degree of independence of the enterprise from external sources of financing and characterizes the share of equity in the balance sheet, decreased in the analyzed period from 0.581 to 0.522 (recommended range of values from 0.5 to 0.8) or by 10.08 %. A decrease in the value of the coefficient indicates a slight decrease in the financial independence of the enterprise.
The share of borrowed capital in the enterprise's balance sheet increased in the analyzed period from 0.419 to 0.478, or by 13.97%. Thus, during the analyzed period, the company has a tendency to increase the use of borrowed capital.
In this regard, the ratio of total liabilities to equity capital (which determines the amount of borrowed funds attracted by an enterprise per one ruble of equity capital invested in assets) in the analyzed period was 0.225 (the recommended range of values is from 0.25 to 1.0), i.e. increased by 0.19, or 26.74%.
Chart 5. Capital structure indicators
Return on sales, which reflects the share of net profit in sales volume, decreased by 2.50% and amounted to 11.36%, which is a negative trend.
The enterprise's return on equity, which determines the efficiency of using funds invested in the enterprise, in the current period amounted to 13.81% and increased by 32.64%, which is a positive fact.
Return on current assets (reflecting the efficiency of using current assets and showing how much profit a unit of working capital of an enterprise brings) in the current period amounted to 15.22% and increased by 19.91%, which is a positive result of the enterprise.
Return on non-current assets (reflecting the efficiency of using non-current assets and showing how much profit a unit of non-current capital of an enterprise brings) was 13.72% in the current period and increased by 18.69%, which is a positive trend.
Graph 6. Profitability ratios
Main conclusions:
The balance sheet currency of the enterprise for the analyzed period increased by 7,130,349.49 thousand rubles. or by 40.06%, which may indirectly indicate an expansion of economic turnover.
The presence of net profit at the enterprise in the analyzed period indicates an available source of replenishment of working capital.
The company's return on equity is at a fairly high level, which indicates the effectiveness of its activities.
The level of borrowed capital is so high that the enterprise is heavily dependent on debt, which means there is a high risk of its insolvency if interruptions in the flow of income occur.
The repayment period for receivables is decreasing, which indicates an improvement in the business activity of the enterprise.
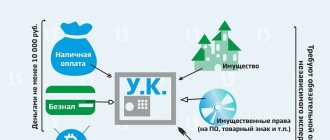
Increasing the authorized capital at the expense of retained earnings
The authorized capital of an enterprise can be increased at the expense of retained earnings. This requires the consent of all participants and the inclusion of a clause on increasing the authorized capital at the expense of retained earnings in the charter of the enterprise. Then you need to submit documents to the inspectorate for state registration of amendments that will be made to the constituent documents of the enterprise, as well as changes to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities.
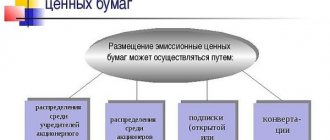
In joint stock companies, the authorized capital can be increased at the expense of retained earnings in two ways:
- additional issue of shares;
- increase in the nominal value of shares.
The procedure for increasing the authorized capital takes place in the following order:
- consent of all shareholders to increase the authorized capital at the expense of retained earnings in one of two ways;
- approval of the decision on additional issue of shares;
- state registration of shares issue;
- placement of shares on the stock exchange;
- providing a report on the placement of shares to the Federal Financial Markets Service;
- registration of a new version of the charter.
Other long-term liabilities
0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Own capital: 10,338,481.48 13,566,016.00 3,227,534.52 31.22 Share capital 697,384.26 697,384.00 -0.26 0.00 Reserves and funds 2,431,053.05 1,247,696.00 -1,183,357.05 -48.68 Additional capital 6,507,893.17 10,729,715.00 4,221,821.83 64.87 Retained earnings 623,775.12,790 120.00 166,344.88 26.67 Other equity 78,375.89 101,101.00 22,725.11 29.00 TOTAL LIABILITIES 17,798,443.51 24,928,793.00 7,130,349.49 40.06Increase in authorized capital due to net profit
The concepts of “net profit” and “retained earnings” are very similar in meaning. The main difference between these definitions is that the term “retained earnings” is used most often when talking about profits that have been accumulated for the reporting year and previous years. The term “net profit” is the profit for the reporting year only.
Based on this, we can conclude that the methods for increasing the authorized capital at the expense of net profit will be the same as if retained earnings were used for this purpose. These methods have already been described previously.
Retained earnings - where can it be used and who makes the decision?
General accountant with 15 years of experience.
Now that I’m retired, in order not to become sour, I study what has changed in the industry and collect materials that are interesting to me.
Each company has the opportunity to continue its production and develop it at the expense of profits.
I hope they will be useful to you in your work - as long as the economy is working, you cannot do without accounting.
If an organization operates at a loss, then soon there will be talk of its liquidation. However, if the profit significantly exceeds the amount required to pay taxes, then management disposes of the rest independently. These funds are called retained earnings, and can be used by the founder at his own discretion, or can be spent on other needs of the enterprise, if any.
Until the founders make a decision on where these funds will be invested, they remain untouchable. Table of Contents For any commercial organization, the main goal is to extract maximum profit from its activities, but not everyone who is going to engage in this business knows how to correctly take it into account and what indicators to pay attention to.
Any company manager is always interested in ensuring the optimal value of the retained earnings ratio, that is, providing himself with funds that can be distributed among the founders or left on the company’s accounts for the purpose of its further development. Retained earnings on the balance sheet is a certain amount of cash that is in the accounts of an organization after it has fully paid taxes to the state budget. In other words, it is simply “net profit” that can be distributed at the discretion of members of the company's management team.
Retained earnings on the balance sheet are a liability, since the value of this indicator shows the presence of the organization’s direct debt to its founders, since ideally this amount is fully distributed among members of the management team and invested in the further development of the business.
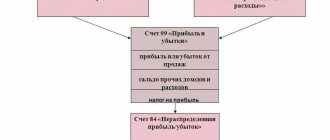
Retained earnings (uncovered loss).
How to use
Line 1370 of the balance sheet reflects retained earnings (uncovered loss) based on the results of the reporting period. The indicator to be entered in line 1370 is calculated on an accrual basis over several years of economic activity.
A company's retained earnings are its net profit (after tax), which has not yet been divided among the participants (shareholders) of the organization. How such profits will ultimately be distributed depends on the decision of shareholders at the annual meeting.
Typically, funds are spent on the following purposes:
- fulfillment of remaining obligations;
- other goals chosen by the owners of the enterprise.
- payment of dividends to shareholders (participants) of the organization;
- formation or increase of reserve capital;
Retained earnings are a liability because they are, in fact, an unfulfilled obligation to the owners of the business. Ideally, the money should be paid as dividends to the owners and used to develop the business. In the same way, a liability is an uncovered loss, which is indicated in parentheses due to its negative value.
Let's look at an example of what constitutes retained earnings and uncovered losses: Indicator Definition Example Retained earnings The final income that was received by the enterprise as a result of business activities remained after taxation and has not yet been divided by the owners or spent on the needs of the business. Pobeda LLC made a profit of 755 thousand in 2021.
rubles Income tax amounted to 125 thousand.
rubles The accountant calculates retained earnings: 755,000 rubles. – 125,000 rub. = 630 tr. This amount will be reflected in line 1370 of the balance sheet. Uncovered loss The excess of an enterprise's expenses over its income at the end of the year. In 2021, Dela Super LLC receives income from production and other non-operating income, in total - 367 thousand.
rubles Costs of production of goods – 335 thousand.
rubles Other expenses that are not taken into account when calculating income tax - 46 thousand.
Measures to increase profits
The main measure to increase profits is profit planning.
Profit planning can be done in three different ways:
- direct account;
- revenue relationships;
- analytical approach.
The first method is the most common in organizations. The essence of the method is that profit is calculated as the difference between the proceeds from the sale of goods and its full cost.
The essence of the second method is to group expenses into fixed and variable.
The analytical method is used as an addition to the direct counting method and is used mainly with a large range of products sold.
Balance (Absolute values)
www.fin-analis.narod.ru – Financial analysis of your enterprise
CONCLUSION ON ANALYSIS OF THE FINANCIAL CONDITION OF THE ENTERPRISE
Enterprise: OJSC "PromInvestGroup"
Analysis period: from 4Q. 2001 1 sq. each 2004
Currency: thousand rubles
Financial condition is the most important characteristic of business activity and reliability of an enterprise. It is determined by the property at the disposal of the enterprise and the sources of its financing.
| Name of balance sheet items | 4 sq. 2001, thousand rubles | 1 sq. 2004, thousand rubles | Growth, thousand roubles. | Growth, % |
| Current assets: | 8 481 721,75 | 12 320 451,00 | 3 838 729,25 | 45,26 |
| Cash | 11 693,15 | 18 391,00 | 6 697,85 | 57,28 |
| Short-term investments | 309,42 | 2 309,00 | 1 999,58 | 646,23 |
| Short-term receivables: | 6 347 588,83 | 10 970 791,00 | 4 623 202,17 | 72,83 |
| Accounts and bills receivable | 6 131 614,03 | 7 556 982,00 | 1 425 367,98 | 23,25 |
| Intercompany receivables | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| Other receivables | 215 974,80 | 3 413 809,00 | 3 197 834,20 | 1 480,65 |
| Long-term accounts receivable | 12 317,40 | 78 622,00 | 66 304,60 | 538,30 |
| Inventory: | 1 040 546,65 | 1 239 482,00 | 198 935,35 | 19,12 |
| Raw materials, materials and components | 1 030 875,79 | 1 227 148,00 | 196 272,21 | 19,04 |
| Unfinished production | 1 810,03 | 3 429,00 | 1 618,98 | 89,44 |
| Finished products | 7 860,84 | 8 905,00 | 1 044,16 | 13,28 |
| Other stocks | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| Future expenses | 1 069 266,30 | 10 856,00 | -1 058 410,30 | -98,98 |
| Other current assets | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| Long-term assets: | 9 316 721,76 | 12 608 342,00 | 3 291 620,24 | 35,33 |
| Land, buildings and equipment | 8 029 542,75 | 11 348 925,00 | 3 319 382,25 | 41,34 |
| Intangible assets | 5 382,90 | 0,00 | -5 382,90 | -100,00 |
| Long-term investments | 123 451,03 | 219 956,00 | 96 504,97 | 78,17 |
| Unfinished investments | 1 158 345,08 | 1 039 461,00 | -118 884,08 | -10,26 |
| Other long-term assets | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| TOTAL ASSET | 17 798 443,51 | 24 928 793,00 | 7 130 349,49 | 40,06 |
| Current responsibility: | 7 459 962,03 | 11 360 757,00 | 3 900 794,97 | 52,29 |
| Short-term loans | 170 802,76 | 209 673,00 | 38 870,24 | 22,76 |
| Accounts payable: | 7 287 166,60 | 11 149 301,00 | 3 862 134,40 | 53,00 |
| Bills and bills payable | 5 260 494,75 | 7 604 087,00 | 2 343 592,25 | 44,55 |
| Taxes payable | 620 752,68 | 1 595 815,00 | 975 062,32 | 157,08 |
| Intercompany accounts payable | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| Advances received | 7 668,58 | 63 151,00 | 55 482,42 | 723,50 |
| Dividends payable | 13 524,15 | 2 399,00 | -11 125,15 | -82,26 |
| Other accounts payable | 1 384 726,44 | 1 883 849,00 | 499 122,56 | 36,04 |
| revenue of the future periods | 1 896,40 | 743,00 | -1 153,40 | -60,82 |
| Reserves for upcoming expenses and payments | 96,26 | 1 040,00 | 943,74 | 980,37 |
| Other current liabilities | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 | 0,00 |
| Long term duties: | 0,00 | 2 020,00 | 2 020,00 | 0,00 |
| Long-term loans | 0,00 | 2 020,00 | 2 020,00 | 0,00 |
Development of activities and strategies to increase profits
There are several strategies to increase profits:
- creation of new products. Allows you to expand your circle of clients and expand your business scope;
- cross-selling system. This method is relevant in online stores. When a buyer selects a product, recommendations for a similar product that might interest him pop up;
- system of regular touches. Most businesses notify their customers about discounts or new product releases 2-3 times. If the client does not buy anything after this, then he is added to the list of hopeless ones. But, as the experience of many companies shows, if you notify the client 7-8 times, the percentage of sales will increase significantly;
- educational marketing. The essence of this method is that before you sell something to your potential client, you first need to teach him something useful that will help solve his problems.
Increase store profit
One of the ways to increase a store’s profit is to increase the average check. For example, when a buyer goes to the checkout to order a product, the seller offers him to buy something else at a discount or as related products. Many customers agree to purchase another item at the checkout.
Very often in stores, especially if it is a clothing or cosmetics store, customers come in just to “look”. In this case, the seller should ask “Are you visiting us for the first time?”, and then offer the client an SMS newsletter with information about upcoming promotions or a club card.
As an example: increasing restaurant profits
The main ways to increase restaurant profits:
- Brag. If a restaurant has the best chef or the most talented singer in town, be sure to tell them about it.
- Increase in order cost. When ordering, the waiter can recommend an accompanying dish, for example, if a guest orders meat, then he can recommend a side dish (which turned out to be incredibly tasty today).
- Improvement of employee qualifications. The main thing in a restaurant is its waiters. In fact, waiters are the face of any restaurant. If the waiters are polite and know how to create a cozy atmosphere, then the guest will definitely come back again.
- Positive reviews. The more positive reviews about a restaurant are heard in the city, the more people will want to come there.