Tax authorities constantly check taxpayers. When submitting declarations, tax officials conduct a desk audit. To ensure that transactions are correctly reflected by the buyer and seller, the Federal Tax Service may arrange a counter-inspection. Another type of audit is an on-site tax audit. The most common types are desk and field tax audits. We will describe below what tax inspectors check during an on-site audit, how to prepare documents for an audit and pass the audit without negative consequences.
The Federal Tax Service organizes an on-site tax audit to find out whether the taxpayer complies with the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and other legislative acts on taxes and fees.
There is a myth that companies do not audit the first three years. Actually this is not true. In most cases, the Federal Tax Service is really interested in companies and individual entrepreneurs that have been operating for more than three years. But if market newcomers conduct activities that raise suspicion, inspectors may come with an inspection in the first year of operation.
What is an on-site tax audit?
The Tax Code does not contain a clear definition of the term “on-site tax audit”. But from the provisions of Articles 82, 88 and 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation it follows that an on-site tax audit (VTA) is a tax control event that is characterized by two main features. Firstly, during such an audit, the correctness of the calculation and payment of one or more taxes for a certain period is studied (while within the framework of the “camera chamber” only the data of a specific declaration are examined). Secondly, during the VNP, inspectors may be present on the taxpayer’s premises.
What is an exceptional case
As already mentioned above, according to paragraph 6 of Art. 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, extension of the inspection period to 6 months is possible only in exceptional cases. Subp. 4 clause 2 of the Grounds specifically defines only one such case - when the company being inspected has 10 or more separate divisions.
If you are planning to open a separate division, find out useful information from the materials:
- “Registration of a separate division in 2021 - 2020 - step-by-step instructions”;
- “We are opening a separate division under the simplified tax system”.
In other circumstances, exceptional cases depend on the specific situation. Clause 2 of the ruling of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated November 9, 2010 No. 1434-О-О states that the tax authority independently assesses the feasibility of extending the control measure.
However, sometimes tax officials abuse this opportunity and receive lawsuits in response. The resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District dated 04/01/2013 No. A43-17631/2012 shows that the reasons for the extension given by inspectors are not always convincing not only for the taxpayer, but also for the arbitrators.
Grounds for on-site tax audit
Such checks have long been of an exclusively planned nature. Candidates for this activity are selected by the Internal Revenue Service based on risk criteria. Some of them are publicly available and are given in the order of the Federal Tax Service dated May 30, 2007 No. MM-3-06 / [email protected] Let us list the main criteria.
The tax burden. Those who have it below the industry average fall into the “red” zone. The values of this criterion are published annually on the Federal Tax Service website. For more information, see “Tax burden: how to calculate it in order to compare it with the industry average” and “Which tax burden will not raise suspicions: indicators for assigning audits have been updated.”
Determine the likelihood of an on-site tax audit and receive recommendations on the tax burden
Share of VAT deductions. The following criterion for selecting applicants for verification is applied here: the amount of deductions is 89 percent or more of the VAT accrued for 12 months.
Average monthly salary per employee. Those at risk are taxpayers whose rate is lower than the industry average in the region. Data on the average salary level by type of activity should be published on the websites of territorial bodies of Rosstat and the Federal Tax Service for the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
Profitability of activities . Those who are 10 percent or more below the industry average may receive an inspection. Data for comparison can be found on the Federal Tax Service website.
The ratio of expenses and income. Taxpayers whose growth in expenses outpaces their growth in income will be included in the audit plan. Also suspicious are situations when income falls faster than expenses, or income falls while expenses rise.
Unprofitability of activities. The attention of inspectors will be drawn to organizations that show losses over two or more calendar years.
Conducting activities through a chain of counterparties. In this case, controllers will assess whether there was a reasonable economic or other reason for using intermediaries.
Conducting activities with high tax risk. In particular, attracting shell companies, disabled workers, etc. is risky.
Check the counterparty for signs of a shell company, bankruptcy and the presence of disqualified persons
Also see “How to check the reliability of a counterparty using the TIN or OGRN or on the tax website” and “How to check whether a potential counterparty is located at the legal address.”
Failure to provide explanations or documents to the Federal Tax Service. We are talking, in particular, about the refusal to provide documents on requests that were sent within the framework of the “camera chamber”.
Also see “The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate requires documents: which requests need to be answered and which can be ignored” and “The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate has requested data on a counterparty or transaction: when is this legal, and what will happen if the request is not answered.”
Receive requirements from the Federal Tax Service and send the requested documents via the Internet Connect
"Migration" between tax inspectorates. The risk zone includes organizations that, since their creation, have changed their legal address two or more times with a simultaneous change of the Federal Tax Service.
The special regime officer is approaching the maximum indicators. Taxpayers using special regimes may be included in the audit plan if two or more times in a year they approached the maximum indicators (revenue, cost of fixed assets, number of employees, etc.), which entitle them to preferential tax treatment. For these purposes, an “approximation” is considered to be a difference between the actual and limit value of a parameter of less than 5%.
Amount of professional deduction. Entrepreneurs on OSNO can become candidates for an on-site audit if the amount of the professional tax deduction on the declaration is more than 83% of the amount of income.
Extension of verification
The basis for extending an on-site tax audit to four and (or) six months may be:
- the organization being inspected belongs to the category of the largest;
- obtaining during an audit information that indicates the presence of tax offenses in the organization, but requires additional verification;
- force majeure circumstances in the territory where the inspection is carried out;
- the presence of separate divisions within the audited organization;
- failure to submit (untimely submission) by the organization of documents necessary for the inspection to conduct an on-site inspection.
This is stated in paragraph 4 of Appendix 2 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 25, 2006 No. SAE-3-06/892.
Other circumstances are determined in each specific case. In this case, the need and period for extending the inspection are determined based on:
- the duration of the period under review;
- volumes of analyzed documents;
- the number of taxes for which an audit has been ordered;
- the number of activities that the organization engages in;
- ramifications of the organizational and economic structure of the organization;
- complexity of technological processes;
- other circumstances at the discretion of the inspectorate.
This is stated in subparagraph 6 of paragraph 2 of Appendix 4 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 8, 2015 No. ММВ-7-2/189.
To extend the period of an on-site inspection, the inspectorate that conducts it must send a reasoned request to a higher tax authority. Based on this request, the head (his deputy) of the higher tax authority will decide to extend the on-site inspection or refuse such an extension.
This procedure is provided for in paragraph 3 of Appendix 4 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated May 8, 2015 No. ММВ-7-2/189.
Deadlines for conducting on-site tax audits
As a general rule, an on-site audit lasts two months. This period begins to run from the day following the date on which the decision of the head of the Federal Tax Service (his deputy) to order an inspection is dated (clauses 2 and 5 of Article 6.1, clauses 6 and 8 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For example, a review that started on October 6th should end on December 6th. However, in practice, GNPs often take a much longer period of time.
This is due to the fact that the verification period can be suspended or extended. And if the extension of an audit is not such a frequent occurrence, since it requires the intervention of higher authorities, then the Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service uses the suspension of audits very actively. As a rule, a decision on suspension is made when requesting documents from counterparties, including banks, as part of “counter” checks (subclause 1, clause 9, article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
You can find out how much taxes the counterparty paid and check its financial condition in the “Kontur.Focus” service. Connect to the service
REFERENCE
The following circumstances are also reasons for suspending the GNP: conducting an examination; requesting information from foreign government bodies within the framework of international treaties; the need to translate into Russian documents submitted by the taxpayer in a foreign language (Clause 9 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The on-site inspection may be “frozen” for six months, or even for 9 months (in the case of requesting documents abroad). It must be remembered that each suspension and renewal requires the execution of a separate decision of the head of the Federal Tax Service or his deputy. During the suspension of the GNP, inspectors cannot carry out control activities on the territory of the taxpayer, nor send him new requests for the submission of documents (clause 9 of Article 2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What inspectors are allowed to do during the suspension period
During a break in the audit process, the tax authority may send requests to third parties to obtain information about the taxpayer in the manner prescribed by Art. 93.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Such actions do not contradict the Tax Code, since they are carried out outside the taxpayer’s territory. Confirmation of this thesis can be found in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/05/2011 No. 03-02-07/1-156.
There is a widespread opinion among tax inspectors that it is also not forbidden to interrogate witnesses during this period. They summon such persons to the inspection without formally violating the law. However, the legality of this approach is controversial and causes repeated complaints from taxpayers.
It is also worth noting that the on-site inspection can first be extended and then suspended. You can do the same steps in reverse order. There are no violations of the law. Confirmation of this can be found in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the city of Moscow dated February 21, 2008 No. 16-27.
Example
A week before the end of the 2nd month of the on-site audit of Omega LLC, the tax inspectorate suspended it for 2 months to request information from the counterparties of this company. After the suspension period expired, the following decisions were made:
1. The tax office has decided to resume on-site tax audits.
2. The regional department of the Federal Tax Service decided to extend the on-site inspection to 3 months.
The decisions of the tax authorities are quite legitimate.
Procedure and rules for conducting on-site tax audits
As already mentioned, first the management of the Federal Tax Service makes a decision on ordering an inspection. It can only be accepted by the inspectorate with which the taxpayer is registered. The decision shall indicate data on the control event. For example, for what taxes and for what period will the audit be carried out, and who exactly is included in the audit team.
IMPORTANT
The Tax Code does not require that the taxpayer be given a copy of the decision to order an audit. However, the form of the decision provides for the transfer of a copy of it to the inspected organization or individual entrepreneur (Appendix No. 5 to the order of the Federal Tax Service dated November 7, 2018 No. MMV-7-2 / [email protected] ). And tax authorities, as a rule, hand over this document.
Next, the inspectors specified in the decision proceed directly to control activities. Namely: they send requests for the submission of documents; carry out seizures, inspections, examinations, interrogations and perform other necessary actions.
ATTENTION
During the audit, the composition of the inspectors may change, but only if appropriate adjustments are made to the decision to order an audit.
On the last day of the GNP, a certificate is drawn up. It specifies the subject of the inspection and its timing. The certificate is presented to the taxpayer (clause 15 of Article 2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The right of the Federal Tax Service to an on-site inspection
It is legally determined that the right to conduct an on-site tax audit has the tax authority to which the taxpayer belongs territorially. Although there are exceptions that apply to the largest taxpayers and separate divisions.
Also important are the date of registration as a taxpayer with a particular tax authority and the date of amendments to the accounting register.
Thus, if, when changing location, the corresponding changes are not made to the Unified State Register of Legal Entities in a timely manner, then an on-site tax audit will be carried out by the tax authority at the previous location. If such a situation arises due to the fault of the tax inspectorate in connection with violation of registration requirements and deadlines, then an on-site tax audit will also be carried out by the inspectorate at the old place of registration (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated May 29, 2013 No. A65-25327/2012).
Other Federal Tax Service Inspectors do not have the right to order inspections of taxpayers located outside their jurisdiction. Thus, the tax authority, which only registers real estate and transport, but not the taxpayer himself, cannot assign the latter an on-site tax audit.
According to what criteria does the Federal Tax Service select taxpayers to conduct an on-site audit, ConsultantPlus experts told. Get a free trial and learn from authoritative content.
How is an on-site tax audit carried out?
As a general rule, it is carried out in the office (on the territory) of the taxpayer. An exception is made for situations where the company cannot allocate premises for inspectors. In this case, the inspection is transferred to the location of the tax inspectorate (clause 1 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In practice, the most common event carried out within the framework of the GNP takes place in absentia mode - inspectors send requests for documents via telecommunication channels (TCC) or by mail. And the taxpayer being audited (or his counterparty, including a bank) sends a response to the Federal Tax Service.
Receive requirements and send requests to the Federal Tax Service via the Internet for free
During an on-site inspection, witnesses may be interrogated, including current and former employees of the taxpayer (Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the employer does not have the right to be present during such interrogations (Decision of the Supreme Court dated June 16, 2020 No. 301-ES20-8110).
Usually the interrogation takes place within the premises of the Federal Tax Service or on the territory of the taxpayer. Inspectors can enter residential premises only with the consent of the residents (clause 5 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This restriction also applies in the case of an interrogation at the witness’s home (letters from the Ministry of Finance dated 02/20/18 No. 03-02-08/10690 and dated 09/01/20 No. 03-02-08/76651).
ATTENTION
The head of the organization can also be questioned as a witness (resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Volga-Vyatka District dated May 17, 2018 No. F01-1539/2018).
Also, when conducting an on-site inspection, inspectors have the right to inspect the premises and territory of the taxpayer, carry out an inventory and seize original documents and other items (Clause 13 of Art., Art. and Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is also permissible to confiscate flash drives, disks, computers or laptops (Decision of the Supreme Court dated July 10, 2019 No. 305-ES19-11972).
At the initiative of the inspection, within the framework of the GNP, it is possible to appoint examinations, as well as attract specialists in various fields (Articles and Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, police officers can participate in the on-site inspection (clause 1 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT DURING CORONAVIRUS
Activities that require personal contact between inspectors and taxpayers, witnesses and other persons must be carried out based on the sanitary and epidemiological situation in the constituent entity of the Russian Federation. At the same time, it is necessary to comply with the rules established in the region for the use of personal protective equipment (Federal Tax Service order No. BS-7-2 / [email protected] , see “Tax officials have resumed inspections and surveys”).
When working remotely, it is necessary to exchange electronic documents with employees Start exchange
Results
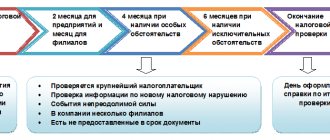
Established in Art. 89 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the period of an on-site inspection (2 months) can be extended to 4 months: if a large taxpayer is being inspected, a natural disaster has occurred on the company’s territory, there are several separate divisions in the structure of the person being inspected, and in some other cases.
In exceptional cases, the period of an on-site inspection may be extended to 6 months: if the company being inspected has 10 or more separate divisions and in other cases at the discretion of the tax authorities, taking into account specific circumstances.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows for the suspension of an on-site inspection with its subsequent continuation. During this period, tax officials are required to leave the taxpayer’s territory; they cannot seize documents and items, or carry out a number of other procedures, the right to which arises only during the period of an on-site inspection.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to prepare for an on-site tax audit
It is almost impossible to prepare in advance, since the plan for carrying out these events is not published in open sources. Taxpayers will learn about the upcoming GNP directly from the inspectors. (In practice, inspectors send the decision to schedule an inspection along with the first request for the provision of documents on the TKS, or convey this decision to the manager or representative of the company personally).
However, you can take some preventative measures to help you pass the audit with minimal losses for your business. In particular, the correct nomenclature of cases and organization of office work will help reduce the time for searching and preparing the requested documents. For more information, see “Storage periods for accounting and personnel documents in an organization in 2021: table.”
It is also advisable to take care of issues of legal (including lawyer) assistance in advance in case employees and management are called for interrogation. Employees should be aware that the company provides legal counsel. And in his absence, they have the right to refuse to testify on the basis of Article 51 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation. Or they can report only information that is publicly available (posted on the company’s website, sent to contractors, etc.).
It would be a good idea to make it a rule to annually conduct a mini-audit of tax obligations with the invitation of third-party specialists. A fresh look at the documents and the accepted accounting procedure will allow you to correct errors, avoiding additional charges during the audit.
Finally, it is advisable to independently carry out the same work that the Federal Tax Service does, that is, carry out a risk analysis of its own activities. This will reduce the likelihood of ordering an on-site audit (if it is possible to eliminate suspicious, in the opinion of tax authorities, circumstances of the activity), or prepare in advance arguments and documents confirming the correctness of calculation and payment of taxes.
IMPORTANT
The Business Risk Control service allows you to quickly learn about events that may raise suspicion among tax authorities. He keeps under control all risk factors related to reporting, taxes, requirements and registers of the Federal Tax Service. For more details, see “Business Risk Control: How to Avoid Account Blocking and Fines for Missed Reporting.”
Connect to the “Business Risk Control” service
Desk inspection
As part of a desk tax audit, the inspectorate can only control the period for which the organization filed a declaration or calculation, including an updated one (clause 1 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that if an organization has submitted a VAT return to the inspectorate for the second quarter of 2015, then as part of a desk audit of the submitted declaration, the inspection can check the correctness of the calculation of this tax only for the second quarter of 2015. At the same time, to carry out the inspection, the inspection has the right to use data from other reporting periods.
Situation: is it possible to cancel the inspection decision based on the results of a desk audit? Based on the results of the inspection, the inspection made conclusions that were not related to the period for which the declaration (calculation) was submitted.
Answer: yes, it is possible, in terms of those conclusions that relate to periods that are not subject to desk audit.
As part of a desk audit, the inspection can only control the period for which the organization filed a declaration or calculation (clause 1 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Deviation from this period will be a violation on the part of the inspectorate. Therefore, the inspection decision based on the results of the desk audit is subject to cancellation in that part of the findings that relate to periods not subject to inspection. In arbitration practice there are examples of court decisions confirming the legitimacy of this conclusion (see, for example, the decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated February 17, 2009 No. 1437/09, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated October 21, 2008 No. F09-7599/08-S2 , East Siberian District dated August 27, 2007 No. A58-6343/06-F02-5686/2007, Northwestern District dated March 5, 2007 No. A56-16972/2006).
Results of on-site tax audit
As already mentioned, the GNP ends on the day the corresponding certificate is drawn up, which is handed over to the taxpayer (clauses 8 and 15 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This document starts the procedure for recording the audit results.
All identified violations are recorded in a report, for the preparation of which the tax authorities have two months (Clause 1 of Article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The prepared act with all attachments is presented to the taxpayer for signature (clause 2 of article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It makes no sense to refuse to sign an autograph, since signing this document does not mean agreement with the facts stated in it. On the contrary, the taxpayer’s signature on the act will not allow inspectors to make changes and additions to it in the future. After signing, one copy of the act is transferred to the taxpayer (clause 5 of Article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
ATTENTION
If the taxpayer avoids receiving the report, the document is sent by mail and is considered delivered on the sixth day from the date of sending (paragraph 2, paragraph 5, article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From the moment the act is received, the time allotted for drawing up written objections (if any) begins to flow. The taxpayer has exactly one month to prepare and send them to the Federal Tax Service (Clause 6 of Article 100 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Objections can be prepared both for the act as a whole, if the person being inspected does not agree with all the inspectors’ conclusions, and for its individual parts.
REFERENCE
Submitting written objections is a right, not an obligation, of the taxpayer. There are no fines or other negative consequences for the absence of this document.
The taxpayer's written objections with attached documents, as well as the audit report with all attachments form the tax audit materials. They are submitted for consideration by the head of the Federal Tax Service or his deputy (clause 1 of Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Review of materials is an open event, to which the head of the company or another representative of the taxpayer must be invited (clause 2 of Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Violation of this rule entails the unconditional cancellation of the decision made based on the results of the GNP (clause 14 of Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
During the review of the inspection materials, the head of the Federal Tax Service (his deputy) once again examines all the data specified in the act, as well as objections, if any. In this case, the taxpayer has the right to provide additional explanations, including written ones. Therefore, when going to the hearing, take with you blank sheets of paper and writing materials. And if you give oral explanations, make sure that they are reflected in the review protocol. Failure to provide the taxpayer with the opportunity to give clarifications or explanations directly during the consideration of the case is another gross violation that entails the unconditional cancellation of the decision made (Clause 14 of Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Submit a complaint against the decision of the Federal Tax Service through the EDF operator Submit for free
Based on the results of the review, a decision is made. It can either be final - on bringing to responsibility or refusing to do so, or intermediate - on the appointment of additional tax control measures. In the first case, in the text of the decision to bring to justice, the Federal Tax Service must analyze in detail all the arguments that the person being inspected brought in his defense (both in objections and in the process of considering materials), indicating for what reasons they are accepted or not accepted (clause 8 Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the second case, the decision indicates exactly what additional measures should be taken and for what purposes. In this case, only three actions are permissible: examination, interrogation, and requesting documents from the taxpayer or third parties. And the purpose of such control is to collect additional evidence to confirm or refute the facts stated in the act. Therefore, the Federal Tax Service cannot look for new violations within the framework of additional measures. The duration of additional events is limited to one month. It cannot be extended.
Upon completion of additional measures, the above procedure is repeated: an additional act is drawn up, the taxpayer provides his written objections (if any) and all materials undergo a new review by the Federal Tax Service.
IMPORTANT DURING CORONAVIRUS
The taxpayer (his representative) may participate in the consideration of audit materials through telecommunication channels or video conferencing channels. To do this, you must submit to the TKS inspection an application to ensure such participation and copies of documents proving your identity and confirming your authority. If the taxpayer does not send such an application (or a request to postpone the consideration of the case), then the tax authorities will be able to consider the audit materials without his participation (clause 3 of the Federal Tax Service order No. ED-7-2 dated March 20, 2020 / [email protected] ).
How will the on-site inspection end?
On the last day of the audit, tax officials draw up a certificate of the audit and hand it over to the taxpayer. Over the next two months, they issue an on-site inspection report. To prepare an act for a consolidated group of taxpayers, 3 months are allotted for drawing up an act. The report and the documents attached to it are also handed over to the taxpayer.
If the person being inspected has objections, he has the right to send them to the Federal Tax Service for consideration within a month. See the objection form here. If no objections are received, tax officials begin to review the case materials and make a final decision.
Does it make sense to submit clarifications after completing the review? Find out here.
Read more about the procedure for processing tax audit results in the section of the same name.
What happens if the deadline for delivery of the act is missed?
Nothing. It will not be possible to use the tax authorities’ violation of the deadline for delivering the audit report to turn its results in their favor. In itself, the delay in delivery of the act is not a basis for canceling the decision on the inspection, since it does not relate to significant violations of the procedure for considering its materials (clause 14 of Article 101 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This is also confirmed by the courts (see the resolution of the 9th Arbitration Court of Appeal dated December 16, 2013 No. 09AP-40446/2013 in case No. A40-76732/13, which was upheld by the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated April 9, 2014 No. F05-2601/ 2014).
27.01.2021Is it possible to take into account interest on a loan received to buy back shares?
The joint-stock company decided to reduce the authorized capital by repurchasing part of its own shares. For this purpose, the organization executed a loan agreement. In this regard, she had a question whether the JSC has the right to take interest under such an agreement into account in income tax expenses.
27.01.2021Rosreestr taught how to pay less taxes
If you are in doubt about how accurately the cadastral value of your property is determined, you can check it. And if it was assigned incorrectly, then correct it. Rosreestr gives its recommendations on how to do this. He claims that reducing the cadastral value has become easier than it was before.
27.01.2021Employees should always be notified of the start of vacation.
Rostrud requires that companies comply with Article 123 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and always notify employees of the start date of vacation.
27.01.2021How do I report the value of movable assets in Section 4 of my property tax return?
The Federal Tax Service, by its order dated December 9, 2020 No. KCH-7-21/ [email protected], approved a new form of property tax declaration. It includes a section in which information about movable property must be reflected. The new declaration form will begin to apply on March 14, 2021. At the same time, tax officials plan that they will be able to report for 2021 on the company using a new form.
27.01.2021Where are dividends reflected in financial statements?
The financial statements are affected by both accrued and paid dividends. Some features need to be taken into account when indicating interim dividends, as well as dividends paid in kind and not paid on time. Let us remember in what forms of financial statements dividends are reflected.
27.01.2021Tax authorities may assess additional taxes based on your work notes and records.
Tax authorities can determine the amount of revenue, wages, and actual expenses based on any information, not just accounting and tax accounting documents.
27.01.2021SZV-STAZH report in 2021
The deadline for submitting the SZV-STAZH form for the past year is March 1, 2021. However, fund inspectors can already accept the companies’ personal reporting.
27.01.2021Inventory is not enough to account for losses from theft
The Supreme Court weighed in on the question of whether conducting an inventory is sufficient to confirm losses from theft of goods. At the same time, he supported the tax authorities and did not allow the organization to include in expenses losses from shortages of goods that were not confirmed by any documents other than those that were drawn up during the inventory.
27.01.2021The employer compensates the employee for the fine: what about the contributions?
If an employer reimburses an employee for a fine, are these amounts subject to insurance premiums?
27.01.2021The bank made a mistake in favor of the client. The Supreme Court dealt with the “irony of fate”
Bank employees, like all people, are not immune to mistakes. Banking equipment, like any other, fails from time to time. Moreover, it is usually the clients who suffer from these errors and failures. In this case, the bank made a “minus” mistake. And tried to turn it into a plus. At first everything went well (especially since the bank’s client also clearly cheated), but the “oil painting” was ruined by the RF Armed Forces.
26.01.2021In what cases can an IT company count on benefits as part of the “tax maneuver”?
From January 1, 2021, IT companies can pay income tax at reduced rates, and insurance premiums at reduced rates. In addition, the transfer of rights to programs developed by them is exempt from VAT. The Ministry of Finance, in letter dated December 18, 2020 No. 03-07-07/111669, considered the features that should be taken into account so that an organization operating in the field of IT technologies can take advantage of these advantages.
26.01.2021How the new FSBU will affect the calculation of the average annual cost of fixed assets
Starting next year, we expect drastic changes in the accounting of fixed assets, and at the same time in determining the average annual cost of fixed assets used in calculating property taxes. Let's figure out what the Ministry of Finance is saying about this.
26.01.2021Is interest on installment payments under a commercial loan subject to VAT?
As a general rule, interest under a loan agreement is exempt from VAT. The installment payment interest received from the buyer is essentially a fee for using borrowed funds. Therefore, they are also not subject to VAT.
26.01.2021Will they create a digital business profile?
The possibility of creating for: confirmed official information about the organization is being discussed. Banks can use this data to optimize work with legal entities. The editors of the magazine "Calculation" commented on this initiative.
26.01.2021How have the powers of tax authorities been expanded in 2021?
Everything that we have observed over the past few years obviously leads to the fact that the Federal Tax Service has taken strict control over all possibilities for optimizing taxation. There is no hope that there will be liberalization of doing business.
26.01.2021How to calculate sick leave for child care in 2021?
An employee can go on sick leave if a child gets sick. In this case, a certificate of incapacity for child care is issued. How to calculate and pay it correctly?
26.01.2021How to indicate the number of “separate” employees when calculating contributions?
From January 1, 2021, information on the average number of employees is provided by contribution payers to tax authorities as part of the Calculation of Insurance Contributions. The Federal Tax Service, in a letter dated January 22, 2021 No. BS-4-11/ [email protected], drew attention to the peculiarity of filling out this data in the Calculation in the case where the organization has separate divisions.
26.01.2021Paying for coronavirus testing of workers: what about contributions?
The employer pays for employees to undergo testing for coronavirus. Are these amounts included in the insurance premium base?
26.01.2021A new fraud scheme related to “remote employment.” How to avoid becoming a victim?
Roskoshestvo has uncovered a new fraud scheme disguised as an offer of remote work, according to the official website of the agency.
25.01.2021How to take into account the costs of purchasing goods for resale when changing the object of taxation to the simplified tax system?
Organizations using the simplified tax system can change the selected tax object.
The Ministry of Finance in letter dated December 31, 2020 No. 03-11-11/116881 drew attention to the peculiarities of accounting for expenses on goods purchased for resale in the case when an organization moves from the taxable object “income” to the taxable object “income minus expenses” . 1 Next page >>
If the KNP act has not been drawn up, how can you find out about its completion?
If 3 months have passed from the date of filing the declaration, and the inspection has not asked you for documents or explanations, or demanded that you make corrections to the reporting, consider that the desk audit ended successfully.
If you need accurate information, contact the Federal Tax Service with a request to inform you about the results of the KNI. The fact that tax officials do not have this obligation does not give them the right to ignore the taxpayer’s request (see, for example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated February 18, 2009 No. A55-10190/2008).