Regulation No. 148 provides for several types of cash documents. The requirements for their design are different. But one of the details that is always present in such documents is the signature(s). Depending on the type of cash document, the head of the enterprise, the chief accountant, the cashier or persons authorized to do so by the head of the enterprise may (or must) act as signers. Let's look at practical questions and situations related to this topic.
Cash register
According to Regulation No. 373-P, cash transactions - receipt and withdrawal of cash - are carried out from the cash register. The place for their holding (that is, the location of the cash desk) is now determined by the head of the legal entity, an individual entrepreneur (hereinafter referred to as the head).
In accordance with the requirements of the old order, it was the responsibility of the head of the enterprise to equip a cash desk (an isolated room intended for receiving, issuing and temporary storage of cash) and ensuring the safety of money in its premises, as well as when delivering it from a bank establishment and depositing it with the bank. Regulation No. 373-P does not directly stipulate such an obligation. It only indicates that a legal entity or individual entrepreneur ensures the organization of conducting established cash transactions.
Thus, organizations and individual entrepreneurs can equip the cash register premises in 2012 at their own discretion.
Form KO-1
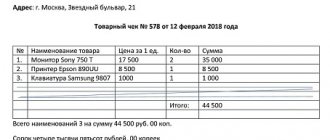
You need to fill out the receipt order in one copy. The form consists of 2 sections. The first is a direct receipt order, and the second is a tear-off slip - a receipt. The latter is issued to the person who deposited the funds. The “Base” line indicates the content of the operation performed. For example, this could be “payment of invoice No. 321 dated February 1, 2017.” The “Including” field shows the VAT amount. The amount is indicated in numbers. If tax is not provided, then you should write “Without VAT”. The “Attachment” field lists the documents that accompany the order. The corresponding account is set depending on the source of funds. The department code is indicated by the operator of separate structural departments of the enterprise. The Debit cell should contain the cash account as planned. The numbering of documents is continuous and is established for one year. The form should not contain numbers written out of order or duplicate codes. OKPO is considered a mandatory requirement. The information is indicated in accordance with the certificate issued by the state statistics body. The name of the organization is indicated in the same form in which it appears in the constituent documentation. If the company has approved analytics codes, they must be indicated in the order. The document contains a “purpose” cell. It is completed only by non-profit enterprises with appropriate funding.
Cash transactions
Cash transactions are carried out by a cashier - a cash register or other employee determined by the manager from among the available workers. The cashier must familiarize himself with his official rights and responsibilities against signature. If there are several cashiers, a senior cashier is selected.
Unlike the old order, Regulation No. 373-P states that the manager also has the right to conduct cash transactions.
Please note that the new procedure for conducting cash transactions, unlike the old one, does not say anything about concluding an agreement with the cashier on full financial responsibility. However, we note that the conclusion of written agreements on full financial responsibility with employees who directly service (use) monetary assets is regulated by the provisions of Article 244 of the Labor Code.
The list of positions and work replaced or performed by employees with whom the employer can enter into written agreements on full individual financial liability for shortages of entrusted property, as well as standard forms of agreements on full individual financial liability, was approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 No. 85. This list contains cashiers, controllers, cashier-controllers (including senior ones), as well as other employees performing the duties of cashiers (controllers).
Stamping
The imprint should be located on the o part of the form and capture the receipt. The legislation does not provide special rules for affixing a seal. In practice, it is customary to place 60% of it on the main part, and 40% on the receipt. Some recommendations are given in Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 88 of August 18, 1998. The legislation also does not establish a specific list of details that must be placed on the operator’s seal. It is advisable to include in the stamp information that was previously considered mandatory:
- Name of the enterprise (full and in Russian), organizational and legal type.
- Location.
- Registration number.
Cash documents
Attention
The forms of cash documents are contained in the All-Russian Classifier of Management Documentation OK 011-93. It was approved by Decree of the State Standard of Russia dated December 30, 1993 No. 299.
As before, cash documents are incoming and outgoing cash orders, payroll, payroll, and cash book.
A cash receipt order (hereinafter referred to as the PKO) is intended for receiving personal money by organizations and individual entrepreneurs. According to the PQS, the following are also accepted:
- balance of cash received on account;
- cash handed over by an authorized representative of a separate unit in the manner determined by the legal entity.
An expense cash order (hereinafter referred to as RKO) is used to issue cash on account for expenses associated with the activities of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur.
The issuance of cash in the form of wages, scholarships and other payments is carried out according to cash settlements, payroll statements, and payroll statements.
A cash book is maintained to keep track of cash coming into and out of the cash register.
In contrast to the previously existing procedure, Regulation No. 373-P mentions maintaining a book of accounting for funds accepted and issued by the cashier (hereinafter referred to as the cash book). Thus, it reflects transactions involving the transfer of cash between the senior cashier and cashiers during the working day. Entries in this book are made at the time of transfer of cash.
However, Regulation No. 373-P does not say anything about maintaining a log of registration of PKOs and RKOs. Let us recall that, according to the old procedure, in this journal, incoming and outgoing cash orders or documents replacing them must be registered by the accounting department before being transferred to the cash desk.
What do tax authorities pay attention to during an audit?
Previously, banks were authorized to verify compliance with cash discipline rules. However, since 2012, this competence has been transferred to representatives of the Federal Tax Service, who, during an on-site inspection, can control:
- correct accounting of cash in the cash register;
- information recorded on the fiscal memory of the cash register by printing reports;
- any documents related to the execution of cash transactions (receipt and expense orders, cash register reports, cash book);
- timely issuance of cash receipts to customers.
Preparation of cash documents
The following persons can draw up cash documents in accordance with Regulation No. 373-P:
- Chief Accountant;
- an accountant or other employee determined by the manager in agreement with the chief accountant (if available) by issuing an administrative document;
- – manager – in case the chief accountant and accountant are absent. The basis for drawing up cash documents are:
- – payroll statements;
- – pay slips;
- – statements;
- – accounts;
- – other documents.
The listed papers must be attached to cash documents.
As before, corrections to cash documents are not allowed.
Who has the right to sign cash documents
According to Regulation No. 373-P, cash documents are signed by:
- cash receipt order - chief accountant or accountant, and in their absence - manager, cashier;
- expense cash order - the manager, as well as the chief accountant or accountant, and in their absence - the manager, cashier.
The cashier must have:
- sample signatures of persons authorized to sign cash documents;
- a seal (stamp) containing (containing) details confirming the conduct of a cash transaction.
If the manager conducts cash transactions and draws up cash documents, then he also signs the cash documents. In this case, sample signatures of persons authorized to sign cash documents are not drawn up.
Methods for preparing cash documents
Cash documents, cash book, cash book can be prepared in two ways:
- on paper;
- using technical means designed for processing information, including a personal computer and software.
In this case, cash documents are printed on paper.
Operator actions
When issuing funds for expense orders, the cashier must check:
- Availability of required signatures and their compliance with the samples.
- Equality of amounts indicated in words and numbers.
- Availability of documents provided in the form.
- Compliance with full name in the order information provided by the recipient.
After this, the operator prepares the required amount and hands over the payment document to the person receiving it. In the order, the recipient must indicate the number of rubles (in words) and kopecks (in numbers). The person also signs and dates it. The operator must count the prepared money. In this case, the recipient must see how the cashier does this. The subject who accepted the funds also recalculates them under the supervision of the operator. If this is not done, the recipient subsequently cannot make a claim to the cashier for the amount issued. After this, the operator must sign the payment document.
Cash acceptance
Regulation No. 373-P describes the procedure for accepting and issuing cash in more detail. As before, the cashier is responsible for accepting cash into the cash desk of an organization (individual entrepreneur). Upon receipt of the PQS, he checks:
- the presence in the document of the signature of the chief accountant or accountant, and in their absence, the presence of the signature of the manager and its compliance with the existing sample;
- correspondence of the amount of cash entered in numbers with the amount of cash entered in words;
- availability of supporting documents listed in the PQS.
Cash is accepted by sheet, piece by piece and in such a way that the cash depositor can observe the actions of the cashier.
Then the cashier checks the amount indicated in the PQS with the amount of cash actually received.
If the amount of money deposited corresponds to the amount specified in the document, the cashier signs it, the receipt for the PKO and puts a stamp on it confirming the cash transaction. To confirm the receipt of cash, the depositor is issued a receipt for the PKO.
Let's say the amount of cash deposited does not correspond to the amount specified in the PQS. In this case, the cashier:
- or invites the depositor to add the missing amount of cash;
- or returns the overpaid amount of cash.
If the depositor refuses to add the missing amount of cash, the cashier returns the deposited amount to him. The cashier crosses out the PQR and transfers it to the chief accountant or accountant, and in their absence, to the manager for registration of the PQO for the actual amount of cash deposited.
If CCP is used
When conducting cash transactions using cash register equipment, upon completion of their implementation, based on the control tape removed from the cash register, PKO is issued for the total amount of cash received. The exception is cash amounts accepted by the payment agent (bank payment agent (subagent)).
In addition to this cash receipt order, the paying agent (bank payment agent (subagent)) issues a PKO for the total amount of cash accepted by the specified person.
Who makes the rules
All aspects related to the rules for conducting cash transactions are determined by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. They are mandatory for all structures, regardless of the chosen taxation system. When conducting cash transactions, legal entities and individual entrepreneurs must be guided by the following standards:
- Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U (dated 03/11/2014).
- Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3073-U (dated 10/07/2013).
If the rules are not followed, violators may be subject to administrative penalties in accordance with Art. 15.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
- Officials and individual entrepreneurs will be fined from 4 to 5 thousand rubles.
- If the violator is a legal entity, the fine will be from 40 to 50 thousand rubles.
According to the standards, the individual entrepreneur or the management of the company independently determines only the timing of checking cash at the cash desk, as well as methods for their safety during transportation and inside the premises where cash transactions are carried out.
Cash withdrawal
According to Regulation No. 373-P, the cashier issues cash directly to the recipient indicated in the cash register (payroll, payroll). To do this, the latter must present:
- or a passport or other identification document;
- or a power of attorney and an identity document.
Preparation for issuance
Having received the cash register, the cashier checks:
- the presence of signatures of the manager, chief accountant or accountant (in the absence of a chief accountant and accountant, the presence of the manager’s signature) and their compliance with the available samples;
- correspondence of cash amounts entered in numbers with amounts entered in words;
- availability of supporting documents listed in the RKO;
- compliance of the surname, name, patronymic (if any) of the recipient of personal money specified in the RKO, with the data presented by the recipient of the document proving his identity.
Important point
The cashier does not accept claims from the recipient for the amount of cash if he has not counted the cash he received under the cashier’s supervision.
Cash withdrawal by proxy
When issuing cash by proxy, the cashier checks:
- correspondence of the surname, name, patronymic (if any) of the cash recipient indicated in the RKO to the surname, name, patronymic (if any) of the principal, which are indicated in the power of attorney;
- compliance of the surname, name, patronymic (if any) of the authorized person indicated in the power of attorney and RKO and the data of the document proving his identity with the data of the document presented by the authorized person.
In the payroll statement (payroll), before the signature of the person entrusted with receiving cash, the cashier writes “by proxy.”
The power of attorney is attached to the cash receipt order (settlement and payroll slip, payroll slip).
It may also be that the power of attorney is issued for several payments or for receiving cash from different legal entities (individual entrepreneurs). In this case, its copies are made, which are certified in the manner established by the manager.
A certified copy of the power of attorney is attached to the cash register (payroll, payroll). The original power of attorney (if any) is kept by the cashier and attached to the cash register (payroll statement, payroll) upon the last cash disbursement.
Issuance of money by cash settlement
When issuing money under cash settlement, the cashier prepares the amount to be issued and transfers this document to the recipient, who indicates the amount received (rubles in words, kopecks in numbers) and signs the cash settlement.
The cashier recalculates the amount of cash prepared for issue in such a way that the recipient can observe his actions, and gives him cash in sheets, piece by piece in the amount specified in the cash register.
The recipient, under the supervision of the cashier, counts the cash he has received piece by piece.
After issuing cash according to the cash register, the cashier signs it.
Issuance of money on account
To issue money for expenses related to the conduct of activities of a legal entity (individual entrepreneur), an employee under the report of a cash register is drawn up according to his written application. It is drawn up in any form and must contain:
- a handwritten note from the manager about the amount of cash and the period for which it is issued;
- manager's signature;
- date.
The accountable person is obliged to present to the chief accountant or accountant, and in their absence, to the manager, an advance report with attached supporting documents. It must do this within a period not exceeding three working days after the expiration date for which the cash was issued on account, or from the date of return to work.
According to the previously existing procedure, accountable persons are also required to submit a report on the amounts spent to the accounting department of the enterprise and make a final payment for them no later than three working days after the expiration of the period for which they were issued, or from the day of the return of these persons from a business trip.
The head of the organization (individual entrepreneur) sets the period during which the advance report must be checked and approved, and the final payment must be made.
The expense report is checked by the chief accountant or accountant, and in their absence - by the manager; approval - leader.
Important point
The procedure for the issuance by a legal entity of cash necessary for cash transactions to an authorized representative of a separate division is determined by the legal entity.
Just as before, cash on account is issued subject to full repayment by the accountable person of the debt on the amount of cash previously received on account.
Salary payment
The amount of cash intended for the payment of wages, scholarships and other payments is established according to the payroll sheet (payroll).
The deadline for issuing cash for these payments is determined by the manager and is indicated in the payroll statement (payroll).
The duration of the period for issuing cash for wages, scholarships and other payments cannot exceed five working days (including the day of receipt of cash from a bank account for these payments). According to the old order, no more than three working days were allocated for the issuance of cash in the form of wages, social security benefits and scholarships (for enterprises located in the Far North and equivalent areas - up to five days), including the day receiving money from the bank.
The senior cashier issues the required amount according to the payroll sheet (payroll) to the cashiers against signature in the cash accounting book or according to the cash register for the period established in the statement.
The cashier prepares the amount of cash to be dispensed and hands the payroll slip (pay slip) to the employee for signature. Then the cashier recalculates the amount of money prepared for dispensing in such a way that the employee can observe his actions. Cash issuance is carried out by sheet, piece by piece in the amount indicated in the payroll sheet (payroll).
The employee, under the supervision of the cashier, counts the cash received by him sheet by sheet, piece by piece, etc. The cashier does not accept claims from the employee for the amount of cash if he has not counted the cash he received under the supervision of the cashier.
On the last day of issuing money in the form of wages, scholarships and other payments in the payroll (payroll), the cashier:
- puts a stamp or makes the inscription “deposited” next to the names of employees who have not been issued cash;
- calculates and records in the final line the amount of cash actually issued and the amount to be deposited and delivered to the bank;
- reconciles the indicated amounts with the total amount in the payroll statement (payroll);
- draws up a register of deposited amounts in any form.
Register of deposited amounts
The register of deposited amounts contains:
- name (company name) of the legal entity (last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the individual entrepreneur);
- date of registration of the register of deposited amounts;
- period of occurrence of the deposited amounts of cash;
- payroll number (payroll);
- last name, first name, patronymic (if any) of the employee who did not receive cash, his personnel number (if available);
- amount of outstanding cash;
- the total amount according to the register of deposited amounts;
- cashier's signature and its transcript;
- additional details.
Registers of deposited amounts are numbered in chronological order from the beginning of the calendar year.
After completing the register of deposited sums, the cashier certifies with his signature the payroll sheet (payroll), the register of deposited amounts and transfers them to verify the correspondence of the entries in the register of deposited amounts with the data of the payroll (payroll) and signing to the chief accountant or accountant , and in their absence - to the manager.
For the amounts of cash actually issued according to the settlement and payroll (payroll) cash register is issued. The cashier puts its number and date on the last page of the payroll statement (payroll).
If the register of deposited amounts is drawn up by the manager, the correspondence of the entries in the register of deposited amounts with the data of the payroll (payroll) is certified by him.
How to arrange the release of funds to an accountable person
If funds need to be issued to an accountable person, this is done on the basis of his written application with the drawing up of an expenditure order.
The accountable person can be any employee of the company who works under an employment contract (possibly under a civil law contract). After approval, the application for the issuance of funds must be endorsed by the head of the company. It is written by hand or using a printing tool.
The application must contain the following information:
- Full name and position of the addressee.
- Full name and position of the reporting person.
- Please provide funds indicating the purpose for their expenditure. The amount must be written in numbers and words.
- The period for which funds are issued.
- Date of application.
- The date the application was signed by the head of the company.
- Signature of the accountable person.
- Director's signature.
It is prohibited to issue funds to an accountable person without an application. Except in cases when they are transferred by bank transfer. The issuance of cash without an application from the accountable person, if detected by an inspection, will entail the imposition of an administrative penalty under Art. 15.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
If a director takes money as an accountable person, he writes not a statement, but an order. When drawing up an expenditure order, it must indicate the details of the application or order.
On our website you can view a sample application for the report and download it if necessary.
If the accountable person has not yet returned the amounts previously taken, this cannot be an obstacle to issuing new funds to him.
Cash book
As before, a legal entity (individual entrepreneur) maintains a cash book to record cash coming into and out of the cash register.
The paying agent (bank payment agent (subagent)) in addition maintains another cash book to record the cash he has accepted.
Cashier in the cash book:
- makes records for each PKO (RKO) issued for received (issued) cash;
- verifies the data contained in it with the data of cash documents;
- displays the amount of cash balance at the end of the working day and affixes a signature.
In addition, entries in the cash book are verified with the data of cash documents by the chief accountant or accountant, and in their absence - by the manager and signed by the person who carried out this reconciliation.
The sheets of the cash book (book of cash accounting), drawn up on paper, are bound and numbered before maintenance begins. Moreover, the sheets of the cash book of a separate division are selected and bookleted by a legal entity for each such division.
The certification inscription on the number of sheets of the cash book (cash book) is signed by the manager and the chief accountant, and in the absence of the chief accountant - only by the manager and is sealed with the seal of the legal entity (individual entrepreneur, if any). Note that, according to the requirements of the old order, the cash book was sealed with a wax or mastic seal. As you can see, there is no need to do this now.
Control over the maintenance of the cash book (cash book) is exercised by the chief accountant, and in his absence, by the manager.
Nuances when using technical means
In the case of maintaining a cash book (book for registering funds) using technical means, it is necessary to ensure:
- safety of the data contained in these documents on an electronic storage medium;
- excluding the possibility of unauthorized changes to the specified information.
Attention
Let's say there were no cash transactions during the working day, so there are no entries in the cash book. Then the balance of cash in the cash register at the end of the working day is the amount of the balance withdrawn on the last of the previous working days during which cash transactions were carried out.
At the discretion of the manager, when registering a cash book, each transaction involving the transfer of cash during the working day between the senior cashier and cashiers can be carried out with or without printing a sheet of this book on paper. If the page of the book is
funds are displayed on paper, the signatures of the senior cashier and cashiers are affixed to it. Otherwise, the signatures of the latter are affixed on the sheet using an electronic digital signature or another analogue of a handwritten signature in the manner established by the manager.
As for the cash book sheet, it is printed on paper at the end of the working day in two copies.
The numbering of sheets in the cash book (cash book) is carried out automatically in chronological order from the beginning of the calendar year.
Sheets of the cash book (cash book) printed on paper are selected in chronological order, bookleted as necessary, but at least once a calendar year.
Responsibility for storage
For failure to comply with storage periods for accounting documentation, administrative liability is provided:
| Code of Administrative Offenses | Offense | Fine (thousand rubles) | Who is punished |
| Article 15.11 | Absence of CD during storage periods at the time of the audit | 5–10 | Executive |
| Repeated offense | 10–20 or 1–2 years disqualification | ||
| Art.13.20 | Violation of the rules of storage, packaging, accounting or use | 0,1–0,3 | Citizens |
| 0,3–0,5 | Executive |
In 2021, the State Duma approved amendments to Article 15.15.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The changes affected liability for violations related to budget reporting:
- failure to submit or submission in violation of deadlines – from 10,000 to 30,000 rubles;
- minor distortions of reporting data - from 1000 to 5000 rubles;
- significant distortion of reporting indicators – from 5,000 to 15,000 rubles;
- gross distortion of reporting data - from 15,000 to 30,000 rubles.
Transfer of a cash book sheet by a separate department
A separate division, after displaying the cash balance at the end of the working day, transfers the cash book sheet for the given working day to the legal entity. It must do this no later than the next business day. Moreover, the following is subject to transfer:
- a tear-off second copy of the cash book sheet - if a separate division prepares the cash book on paper;
- a second copy of the cash book sheet printed on paper - if it uses technical means to prepare the cash book. A separate division can transfer a cash book sheet to a legal entity electronically.
Then the transfer of the cash book sheet on paper can occur in accordance with the document flow rules that are approved by the legal entity.
Cash balance limit
The cash balance limit is the maximum allowable amount of cash that can be kept in the cash register for cash transactions after displaying the amount of the cash balance at the end of the working day in the cash book.
A legal entity (individual entrepreneur) sets such a limit independently by issuing an appropriate administrative document, which must be stored in the manner determined by the manager. At the same time, the bank no longer needs to approve the cash balance limit in 2012. Let us note that previously the cash balance limit was set by the bank, and it was only agreed upon with the managers of the enterprises.
The rules for calculating the cash balance limit are set out in the appendix to Regulation No. 373-P. According to them, when establishing this limit, one can proceed either from the volume of receipts or from the volume of cash disbursements. The last indicator is used in the absence of cash receipts for goods sold, work performed, or services rendered.
So, option one
. The amount of cash receipts for goods sold, work performed, services rendered for the billing period is first divided by the working days of the specified period, and then multiplied by the working days falling on the period of time between the days of depositing the cash received at the bank.
Option two
. The amount of cash issued (with the exception of amounts intended for payment of wages, scholarships and other payments to employees) for the billing period is divided by the working days of this period. Then the result obtained is multiplied by the working days of the time interval between the days of receipt of cash by check at the bank (with the exception of amounts intended for payment of wages, scholarships and other payments to employees).
It should be borne in mind that in both cases the billing period should not exceed 92 working days of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur.
And the period of time between the days of depositing cash into the bank (receiving it from the bank) should not be more than seven working days (if a legal entity or individual entrepreneur is located in a locality where there is no bank - 14 working days). Example
Alpha LLC sells goods in bulk. The organization has a five-day work week with days off on Saturday and Sunday. For the period from October 3 to December 30, 2011 (64 working days), Alpha LLC received RUB 960,000 in cash for goods sold. The time period between the days the organization deposits cash received for goods sold to the bank is seven working days. Based on these indicators, Alpha LLC set the cash balance limit for 2012 at 105,000 rubles. (RUB 960,000: 64 days X 7 days).
An organization that includes separate divisions determines the limit taking into account the cash stored in these structural units. However, if an organization has opened a bank account for a separate division to carry out transactions, then the cash balance limit is set by this separate division in the manner prescribed for a legal entity.
As for bank payment agents (subagents), when determining the cash balance limit, they do not take into account the cash they accepted when carrying out activities in accordance with the Law of June 3, 2009 No. 103-FZ and the Law of June 27, 2011 No. 161-FZ.
Cash over limit
Keeping cash in excess of the limit, that is, free funds, in bank accounts is the responsibility of the organization (individual entrepreneur).
Accumulation of cash in the cash register in excess of the established limit is not allowed, with the exception of days of salary payments, scholarships, remunerations included in the wage fund, and social payments. The specified days include the day of receipt of cash from a bank account for the specified payments, as well as on weekends and non-working holidays in the case of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur conducting cash transactions at this time.
Attention
For a newly created legal entity or individual entrepreneur, the cash balance limit is calculated based on the expected volume of cash receipts for goods sold, work performed, services rendered, or from the expected volume of cash disbursements.
An authorized representative of an organization (an individual entrepreneur or his authorized representative) can deposit free funds directly into the bank. Money can also be deposited, transferred or transferred to the bank account of a legal entity or individual entrepreneur:
- to an organization that is part of the Bank of Russia system, the charter of which grants it the right to carry out the transportation and collection of cash, as well as cash transactions in terms of receiving and processing funds;
- or to the federal postal service organization.
As for a separate division, its authorized representative, in addition to the organizations listed above, can contribute personal money to his legal entity.
Let us note that, according to the old order, enterprises were obliged to hand over to the bank all cash in excess of the established limits of the cash balance in the cash register in the manner and within the time limits agreed upon with the servicing banks.
Important points
The cashier issues funds exclusively to the person whose information is indicated in the order. The latter presents a document confirming his identity. If the issuance is made by power of attorney, it is necessary to check the compliance of the full name. recipient, given in the order, information about the person represented. A document confirming the authority of the actual recipient is attached to the payment form. If several payments will be made under the power of attorney or in different organizations, a copy is attached to the order. The original must remain with the operator who made the last issue.