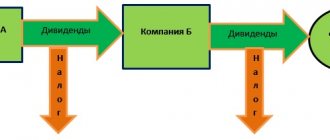
Must pay
According to the current provisions of fiscal legislation, VAT payers are all organizations and individual entrepreneurs that apply the general taxation system.
Consequently, if an economic entity pays income tax, then it will have to pay value added tax to the Federal Tax Service. Please note that the legal form of the economic entity does not matter. The following are required to pay the fee: LLCs, NPOs, public sector employees (from entrepreneurial activities on OSNO), and individual entrepreneurs. The only condition is the general taxation regime and the absence of legally formalized rights to exemption from payment of the encumbrance.
It is worth noting that this is not only about Russian organizations. Foreign companies operating in our country are also required to calculate and pay this fee.
Let us repeat that state and municipal institutions that use OSNO are also considered VAT payers. However, only income-generating activities are considered taxable. VAT is not calculated on activities financed through budget subsidies, grants and investments.
VAT rate for individual entrepreneurs
The basic VAT rate for both organizations and individual entrepreneurs is 18%. However, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for a reduced rate of 10%, applied to types of goods and services established by law (for example, children's goods, medicines, food products, printed materials and transport services). The zero VAT rate is used mainly when exporting goods or services. Accounting for VAT at a 0% rate has its own characteristics and requires a package of documents regulated by Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
[B=63] If for 3 calendar months the amount of revenue (not income, namely revenue) from the sale of goods (excluding excisable goods), works or services in the aggregate turned out to be less than 2 million rubles, then by virtue of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation an individual entrepreneur may be exempted from fulfilling the duties of a VAT payer, even if he applies the general taxation system. At the same time, he no longer needs to keep VAT records, but he also loses the right to highlight tax in invoices. This, as a rule, is unprofitable for those entrepreneurs who work with individual entrepreneurs and organizations that pay VAT. After all, in this way all transactions take place without the right to provide a tax deduction.
Tax benefits
Officials have provided a number of benefits for VAT payers. In simple words, this is a list of transactions that are exempt from value added tax (Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). These operations should include:
1. Benefits that can be applied to all categories of taxpayers:
- providing loans;
- provision of goods worth up to 100 rubles for advertising purposes;
- free transfer of goods, works, services within the framework of charity.
2. Transactions that are not recognized as subject to VAT taxation:
- the place of implementation of such an operation is not recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation (export);
- sale of land plots and shares in them;
- other operations specified in clause 2 of Art. 146 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- import of goods into the territory of the Russian Federation that are not subject to VAT, according to Art. 150, pp. 1.1 clause 1 art. 151 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
3. Operations that can only be used by certain categories of taxpayers indicated in paragraph 1 of Art. 56 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- educational services of non-profit organizations and certain other operations;
- medical services, except cosmetic, veterinary, sanitary and epidemiological;
- banking operations, except for operations related to collection activities;
- insurance activities of insurers carried out by non-state pension funds.
Please note that the taxpayer has the right to refuse some benefits. The refusal is legal only in relation to non-taxable transactions named in paragraph 3 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. To refuse, you must submit a corresponding application to the Federal Tax Service.
When VAT taxpayers are government agencies
The current version of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain norms according to which state and municipal bodies are VAT payers (Article 143 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, there is a list of actions during which state and municipal institutions can be recognized as such:
- if the institution does not act on behalf of a public legal entity, but acts as an independent economic entity (Article 125 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- the action is carried out in one’s own interests, and not as a performance of the functions of a public legal entity.
Such conclusions are contained in paragraph 1 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 2014 No. 33.
If you rent state property or bought real estate from the municipality, you are the one who is required to pay the tax, since you are the tax agent. ConsultantPlus experts explain with examples how to correctly calculate the amount of tax and reflect it in accounting and tax accounting. Get a free trial and proceed to the Typical Situation.
Don't have to pay
Legislators have designated a circle of persons who are exempt from calculating and paying value added tax. So, only two groups of economic entities are not recognized as VAT payers:
1. Organizations and entrepreneurs applying special tax regimes (STS, Unified Agricultural Tax, UTII, PNS). It is worth noting that the exemption applies only to those types of activities that are taxed under special regimes. For example, when combining the main taxation system and the special regime, a fee will have to be calculated. But only within the framework of activities taxable under OSNO.
IMPORTANT!
These conditions apply only to transactions carried out on the territory of the Russian Federation. If an economic entity imports goods, works, services from abroad, then it automatically becomes a VAT payer in relation to import transactions.
2. A number of economic entities whose activities are related to the preparation and holding of the FIFA World Cup (2018), as well as the Confederations Cup championship in 2021. Such provisions are outlined in Article 143 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Please note that for this category of subjects, exemptions apply to all types of transactions performed both on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad.
Electronic services of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation to help individual entrepreneurs when calculating VAT
The Tax Service of the Russian Federation has developed several useful online services for entrepreneurship. They are very helpful in running a business, speed up processes and save personal time.
Checking the correctness of invoices
The electronic service of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation is designed to speed up and simplify the verification of the details of its suppliers or recipients when issuing invoices for generating VAT reporting. It makes it possible to clarify online all the data on received and issued invoices. You will save a lot of time at the control stage of filling out VAT accounting documents: purchase and sales books, as well as financial accounting journals.
For now, the “Counterparty Verification” service is operating in test mode. But its importance is obvious, given the requirements of tax inspectors for the expanded declaration of VAT transactions since 2015.
Using this service you can find out online:
- whether the organization or private entrepreneur is registered in the register of taxpayers (USRN);
- what status the counterparty is in: active or, according to the Federal Tax Service, does not have this tax status (and does not pay VAT);
- correct or incorrect TIN is indicated;
- does the gearbox comply, etc.
The input data must be entered strictly according to the system requirements (spaces, date form, etc.), otherwise the service will generate an error. You can enter one company at a time or as a list.
The Federal Tax Service is interested in making paying taxes convenient
Steps when using the invoice verification service:
- Correctly enter the counterparty's data into the control fields of the electronic form. All fields, oh, must be filled out. When checking a legal entity, it is recommended to indicate the checkpoint to obtain data on a specific branch.
- Click the check button.
- To clarify the transaction for the selected date, you need to fill in the appropriate field, in this case the period will be checked, including 6 days before and after.
- If the service gives an error in the details of the counterparty, you first need to check the accuracy of the entered numbers.
- But if the data matches what is indicated in the invoice, and the resource reports an error, in this case you need to inform your supplier about the need to check and correct his data.
- If the system indicates an error in your credentials, you need to contact online services technical support. Maybe it's just a glitch in the program. In order for your electronic record to be quickly checked, it is recommended to attach a scanned copy of the TIN certificate. Such applications are considered first.
The result of the check “3-The checkpoint does not correspond to the TIN specified in the request (the date may or may not have been indicated)” means that the counterparty’s TIN is indicated correctly, and the checkpoint corresponds to the format and the indication of such a checkpoint will not be an error when submitting a declaration and office verification.
Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation
https://www.nalog.ru/
UKEP is an important tool for private business
The presence of an enhanced qualified electronic signature is necessary for document management in modern conditions. UKEP is developed using cryptographic means taking into account all personal security requirements. The UKEP certificate for business is confirmed by the FSB of the Russian Federation. Any documents certified by such an electronic signature have full legal force.
Electronic document management is a modern requirement
Tax legislation requires VAT payers to ensure electronic interaction with the Federal Tax Service within 10 days from the date of registration. All VAT reporting documents are submitted only through EDI. To do this, you need to obtain a qualified electronic signature key certificate and enter into an agreement with an electronic document management operator.
To obtain UKEP, it is enough to contact any of the accredited certification centers; their current list for each city of the Russian Federation can be found on the government services portal.
The package of documents required for obtaining a UKEP certificate for a private entrepreneur includes:
- passport;
- TIN;
- SNILS;
- extract from the Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs;
- statement.
Having a qualified electronic signature is a prerequisite for working with government service portals, the Interdepartmental Electronic Interaction System, submitting reports to tax authorities, sending banking and other documents via the Internet, performing state and municipal functions and when performing other legally significant actions.
Public services
https://www.gosuslugi.ru/
VAT office of an Internet company
There is a specialized service for Internet companies that are required to register with the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation as VAT payers on electronic services. These include individual entrepreneurs who provide paid online services: access to music, movies and games, sale of domain names and hosting, etc.
On the “VAT Office of an Internet Company” resource, you can independently check whether you need to register; to do this, you just need to pass a three-minute test. You can submit an online application for registration, submit declarations and use all legal forms for conducting online business.
Released, but must pay
Now we have figured out who pays and who is exempt from paying value added tax. It's quite simple. If you are an individual entrepreneur or an organization using OSNO, and your activities are not related to the preparation and holding of the World Cup, then you will have to pay a fee. It would seem that all other companies and merchants are exempt from paying the additional fee. But everything is not quite as we would like.
Officials determined that some entities who are not VAT payers are still required to pay tax, but under exceptional circumstances. It turns out that even the special regime does not provide a 100% guarantee of exemption from the “additional fee”. Let's determine what these circumstances are.
Mandatory payment of VAT is provided for the following cases:
- A company or individual entrepreneur carries out operations to import goods, works, and services.
- An economic entity is a tax agent for value added tax. Read more: “How a tax agent calculates and pays VAT.”
- The company, individual entrepreneur, issued an invoice to the buyer with the allocated tax amount.
- An organization or individual entrepreneur acts as a participant who conducts general affairs in a simple partnership.
- The entity acts as a concessionaire under a concession agreement or as a trustee under a property trust management agreement.
IMPORTANT!
If the subjects meet the above conditions, then they are automatically recognized as VAT payers.
Checking the declaration before sending
VAT returns are submitted electronically. After receiving them, the tax office processes the documents. When checking declarations, compliance with control ratios is analyzed, and the data of buyers and sellers is compared.
If the tax office reveals errors, this will entail negative consequences for the company. The company that committed the violation will have to at least pay a penalty or fine. To avoid such risks, it is better to check the declarations yourself before sending. In particular, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- the correctness of the rate in the primary documents and bank statements entered into the accounting database;
- availability of invoices, as well as mandatory details of these documents;
- correctness of VAT distribution (if separate VAT accounting is maintained);
- correct completion of the declaration form itself.
If possible, it is recommended to regularly reconcile invoices with invoices of counterparties to avoid discrepancies and errors in the purchase or sales ledger.
A special case
Quite often there are cases in which a company acts as a tax agent or commission agent for a certain type of service. In simple words, the company reissues received invoices. What to do if the end consumer - the recipient of the reissued invoice - is not the payer of the fee. For example, the final recipient is a company using the simplified tax system.
In this case, services are re-invoiced without VAT; simplified workers are not recognized as VAT payers.
It is worth noting that if the commission agent includes his commissions in the cost of services, then it is necessary to take into account the tax on this commission when creating an invoice. But in this case there is no need to allocate a fee.
Who pays VAT on advances
Individual entrepreneurs who are VAT taxpayers, by virtue of paragraph 1 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, must charge tax on advances received. Therefore, if an individual entrepreneur has received an advance payment under a contract against a future delivery, he must charge VAT. The tax base in this case is the amount of the prepayment, and VAT is calculated at calculated rates of 10/110 or 18/118, depending on the object of taxation (goods or services sold). This procedure is provided for in paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
A prerequisite for such an operation is the issuance of an advance invoice. The supplier is obliged to do this within 5 days from the date of receipt of the advance amount in the bank account. The procedure for issuing an advance invoice is regulated by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
There are situations when the transaction is canceled and the seller must return the advance received to the buyer. In this case, he must also deduct VAT on the advances that were returned to him. To do this, VAT is reversed in the purchase book and this operation is necessarily reflected in the accounting entries and tax return.
It is important to note that since an advance payment can be received in one reporting period, and the main operations for this transaction take place in another, the status of a VAT payer may change for an individual entrepreneur. For example, he can switch to the simplified tax system. By virtue of Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, entrepreneurs on the simplified market do not pay VAT. Therefore, if an individual entrepreneur has charged VAT on advances, and then switched to a preferential tax regime, after which there was a direct sale of a product or service, then he has no legal grounds for deducting the VAT already paid to the budget. However, there is also no obligation to charge VAT on the amount of goods and services sold.
Calculation of the amount of VAT included in the cost of inventory items
Materials used to carry out both taxable and tax-exempt transactions are inventory items subject to write-off as expenses related to taxable and non-taxable transactions (section 1.4 of the article), or capitalized to support the activities of the relevant departments (Table 2 ).