From this article you will learn:
- What does retained earnings mean?
- How is retained earnings formed?
- What can retained earnings be used for?
- What to do with retained earnings when liquidating an LLC
Retained earnings of an LLC represent income received from business activities after taxes - it must be distributed among the participants of the company, taking into account the size of their shares and contributed capital. This concept can mean both additional income and losses incurred by the enterprise. Next we will talk about the intricacies of distributing funds in accordance with the law.
Is it true that retained earnings are net profits?
Retained earnings are truly net profits that (as the name suggests) were not distributed (divided) among the participants/shareholders of the company.
Net profit is considered to be that part of income from sales and non-sales operations that remains after paying taxes. The decision on how to distribute this income rests solely with the owners. Traditionally, the issue of retained earnings is put on the agenda of the annual meeting of the company's owners. The adopted decision is documented in minutes, which are drawn up following the results of the general meeting of participants/shareholders.
For information on how such a document is drawn up, read the article “Decision on payment of dividends to an LLC - sample and order.”
The main ways of spending retained earnings are considered to be in the following directions:
- to pay dividends to participants/shareholders;
- repayment of past losses;
- replenishment (creation) of reserve capital;
- other goals formulated by the owners.
For information about the accounting entries accompanying the accrual, payment and receipt of dividends, read the material “Accounting entries for the payment of dividends”.
Recommendations for reinvestment
As a private investor, make a commitment to regularly reinvest your profits instead of spending your income. Let it not be all the profit, but only 30-40% of it. Even this size of reinvestment can give good results, not to mention the fact that a useful financial habit will be formed.
Some calculations show that on the path to financial independence, it is necessary to reinvest at least half of the net profit. If you can avoid spending your investment income at all, reinvesting it entirely is the fastest way to achieving your financial goals.
Is retained earnings an asset or a liability?
Retained earnings on the balance sheet are, of course, a liability. The value of this indicator indicates the company’s actual debt to its owners, since ideally this profit should be distributed among the participants and invested in the further development of the business.
In fact, the company cannot dispose of retained earnings without the owners making a decision. The loss reflected in line 1370 is also on the passive side of the balance sheet, only this is a negative value, so the number is placed in parentheses.
“How to read a balance sheet (a practical example)?” will help you better understand balance sheet analysis. .
Retained earnings must be reflected on the balance sheet. ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to do this correctly. To do everything right, get trial access to the system and go to the Tax Guide. It's free.
Retained earnings and uncovered losses - what are they?
As mentioned above, retained earnings are the final income received by the company from its business activities, remaining after the transfer of income taxes and not yet divided (not directed to other purposes) by its owners.
Example 1
Voskhod LLC in 20XX received a profit in the amount of 800,000 rubles and paid income tax in the amount of 160,000 rubles. In line 1370 in the balance sheet liability for the year 20XX, Voskhod LLC should reflect 640,000 rubles. This is retained earnings.
The value in line 1370 of the balance sheet may be equal to that indicated in line 2400 of the financial results report if the company had no profits not distributed by the owners at the beginning of the year and no interim dividends were paid during the year.
What can retained earnings from previous years be used for? The answer to this question is in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Our article “Deciphering the lines of the balance sheet (1230, etc.)” .
As for the uncovered loss, this is the excess of the company's expenses over income at the end of the year.
Example 2
In 20XX, Parus-Trade LLC received revenue from the provision of services and other non-operating income. Their total amount was 400,000 rubles.
The costs associated with conducting the main activity (transportation) are equal to 380,000 rubles. Other company expenses (not taken into account for tax purposes) amounted to another 58,000 rubles. Profit tax was assessed in the amount of RUB 4,000. Parus-Trade LLC has no reserve capital.
This means that at the end of 20XX, after the reformation of the balance sheet, an entry of 42,000 rubles will appear in line 1370 in parentheses. (400,000 – 380,000 – 4,000 – 58,000).
An uncovered loss occurs when the company receives an actual loss and there are no financing reserves. The value entered in the liability side of the balance sheet in parentheses will reduce the total for section 3 of the balance sheet.
Among the main reasons for receiving an uncovered loss are:
- obtaining an actual negative financial result from the company’s activities due to the excess of costs over income;
- changes in accounting policies that had an impact on the financial condition of the company (this is directly stated in paragraph 16 of PBU 1/2008, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 6, 2008 No. 106n);
- errors found in the current year, made in previous years, which affected the financial result (subclause 1, clause 9 of PBU 22/2010, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 28, 2010 No. 63n).
Read more about PBU 1/2008 in the material “ PBU 1/2008 “Accounting policies of the organization” (nuances)” .
Increasing the authorized capital of an LLC using retained earnings
If the authorized capital is increased at the expense of the company’s property, its participant does not actually receive funds, goods (work, services) or any other property. Thus, this method of increasing the authorized capital of an LLC does not entail the emergence of income that should be subject to personal income tax.
Let us turn again to judicial practice: there are cases where courts have come to the conclusion that the participants of the company have no income associated with the increase in the nominal value of their shares. This conclusion was considered the only correct one until a company participant exercised any of his property rights, certified by the corresponding share in the authorized capital.
But it is worth noting that this is not the only possible conclusion. According to the position of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, when the authorized capital increases due to retained earnings, an individual receives income at the time of his state registration. These funds should be subject to personal income tax on a general basis (see, for example, Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 22, 2017 N 03-04-06/31351).
This position is supported by clause 19 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which provides for non-taxable income representing the difference between the new and original nominal value of a share in the authorized capital, obtained as a result of the revaluation of fixed assets. At the same time, in Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which defines the list of non-taxable personal income tax income, there is no income resulting from an increase in the nominal value of the participant’s share due to retained earnings of previous years.
If an LLC decides to follow the clarifications of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, it is considered a tax agent for personal income tax, whose responsibilities include: calculating the amount of personal income tax, withholding it from its income upon actual payment, transferring the corresponding amount to the budget (clauses 1, 2, 4 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since in this case the company does not pay the company member any money in the current year, withholding the calculated amount of personal income tax is impossible. Then, according to paragraph 5 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the enterprise must inform the taxpayer and the tax authority at the place of registration in writing about the impossibility of withholding the tax, the amount of the tax itself and the funds from which it was not withheld. This is given until March 1 of the year following the expired tax period in which the corresponding obligations arose. More detailed information on this topic can be obtained in the “Practical manual on personal income tax”.
When increasing the authorized capital of an LLC using funds from retained earnings, an entry is made in accounting to the debit of account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” and the credit of account 80 “Authorized capital” after state registration of changes made to the organization’s Charter. This is required by the instructions for using the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n.
How retained earnings from previous years are displayed
Retained earnings from previous years are accumulated in account 84. The credit balance of this account is transferred to balance sheet line 1370.
Typically, there should be no movement in the debit of the account during the year, since the distribution of profits traditionally occurs at the end of the year after the annual meeting of the company's owners. But there is also a special case when debit 84 needs to be used during the year. To make sure that you did not miss this very transaction, get free access to ConsultantPlus and go to the Typical Situation.
For information on how data on retained earnings is generated for reflection in the balance sheet (final and interim), read the article “Procedure for compiling a balance sheet (example).”
Reserve Fund
The reserve fund is the company’s financial “safety cushion”. It is used to pay off debts, cover losses, buy out shares from participants and bonds from investors, and make transactions.
An LLC is not required to have one, but can create one if necessary. The size of the fund and annual contributions to it, their procedure and the procedure for using the funds of the fund are prescribed in the charter. After making changes to the charter, they must be registered in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (Clause 4, Article 12 of the Law on LLC).
In the balance sheet, the reserve fund is reflected in section III “Capital and reserves” on page 1360, that is, when it is created, part of the profit is transferred to another item of capital. This improves the structure of the balance sheet, because the owners will not be able to withdraw these funds from the turnover of the enterprise. And such an operation is not subject to any taxes. Carry out as follows: debit 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” - credit 82 “Reserve capital”.
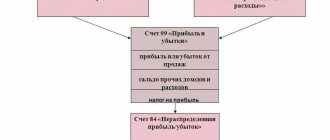
Retained earnings of the reporting year
The credit balance at the end of the year according to accounting account 99 is net profit. But in addition to the financial result, this account also reflects some other indicators. You can learn which ones and how not to make mistakes when making transactions from the Typical Situation from K+, having received trial access to the system.
When reforming the balance sheet, it is written off to accounting account 84 (Dt 99 Kt 84) and constitutes retained earnings at the end of the reporting year.
Read about the reformation procedure in the material “How and when to reform the balance sheet?”.
In order to separate the indicators of retained earnings of the current (reporting) year from last year’s, some accountants allocate separate lines 1372 and 1372 in the balance sheet, which respectively reflect the retained earnings of the reporting period and previous years.
The use of retained earnings is the prerogative of the company's owners. And highlighting this financial indicator for different years in the balance sheet is primarily convenient for them. But it is worth keeping in mind that the retained earnings of the past year cannot be fully distributed without taking into account the company’s previous operating results.
IMPORTANT! It must not be allowed that the value of the company’s net assets, after transferring retained earnings of the reporting year for the payment of dividends, becomes less than the size of the company’s authorized capital even if there is a reserve fund. The caution applies to cases where uncovered losses were recorded in previous years. The decision to cover last year's losses from retained earnings of the reporting year is made exclusively by the owners of the company.
But retained earnings for previous years can be distributed by the participants/shareholders of the company not only at the end of the year, but at any time. The main thing is to hold a thematic meeting of all company owners and approve the appropriate decision.
Does an LLC have the right to make incentive payments to employees from retained earnings and how to formalize this, and are they taken into account when calculating the average salary? The answer to this question was prepared by labor inspector in the Nizhny Novgorod region V.I. Neklyudov. Get free trial access to the ConsultantPlus system and get acquainted with the official’s point of view.
Receive professional advice from accountants and lawyers
The best way to avoid making mistakes when making calculations and paperwork is to entrust the process to an accounting company with extensive experience. PROGRAMS 93 LLC has been providing professional advice to individual entrepreneurs and organizations for many years, tackling even the most complex issues.
Call the number listed on the website or fill out the feedback form so that we can:
- Tell us more about our services;
- Find out your needs and goals in order to offer the optimal solution;
- Orient by cost and timing;
- Explain how to start cooperation.
Remember that it is easier to keep your accounting records correctly right away than to correct mistakes later!
Retained earnings: calculation formula
According to general accounting data, retained earnings are a company's net profit after taxes that can be distributed to the company's owners.
Based on global financial practice, retained earnings (hereinafter referred to as RR) are calculated using the following formula:
NPk = NPn + PE – Div,
Where:
NPk - NP at the end of the reporting year;
NPn - NP at the beginning of the reporting period;
PE - net profit remaining after accrual of income tax;
Div - dividends paid in the reporting year based on the NP of previous years.
If you do not have the NP value, then to calculate the NP you can use the following scheme:
- first calculate profit before tax (to determine it, calculate operating profit, which is defined as the difference between operating income and operating expenses);
- then subtract depreciation and interest costs from operating profit;
- Subtract tax from the resulting profit value.
To find out whether it is possible to see the amount of operating profit in the accounting statements, read the article “Which line is operating profit reflected in the balance sheet?”
Interest capitalization
A special case of reinvestment is the capitalization of interest received on a bank deposit. During capitalization, the accrued interest is added to the base amount of the deposit, and from the next interest period the rate is valid for the increased amount. In this case, the so-called compound interest formula works, ultimately allowing the investor to receive increased income compared to a deposit without capitalization. However, when choosing a deposit with capitalization, you need to carefully compare the rates. As a rule, banks specifically set rates on such deposits several percent lower.
Another important point is the frequency of capitalization. It can be annual, quarterly, monthly or even daily. The most profitable for the investor is daily capitalization. Every day, income is added to the deposit amount at the rate of “annual interest rate/365”. The very next day, both the deposit amount and the accrued interest will be higher than the previous day.
Indicators for investors
When analyzing the financial condition of a company, investors pay attention to the use of retained earnings. If NP accumulates and is not put into circulation, this state of affairs should seem to suit investors, since they can count on significant dividends.
However, without investment in its activities, the company stops growing, and its income not only does not increase, but may also decrease (due to a drop in competitiveness, high wear and tear of equipment, and for other reasons related to the lack of investment). So a company that accumulates profits but does not invest in its activities cannot be attractive.
At the same time, a company that does not make a profit and does not pay dividends cannot interest investors at all.
The ideal option for investors is a company that invests the funds remaining after paying dividends in its development. Although the owners may decide not to pay dividends and direct the entire volume of NP into circulation.
Reinvestment
Investors, business owners and shareholders are constantly looking for answers to the questions: “How to increase profits?”, “How to improve financial performance?”
and other similar issues in one way or another related to increasing income from the activities in which they are engaged. Today we will look at the simplest and at the same time effective way to achieve your goals.
Reinvestment is a great way to increase the profitability of an investment project without attracting additional funds.
Reinvestment is the repeated investment of profits after the end of the investment period in the same object. The point of reinvesting is to increase capital as much as possible in the shortest possible time.
The principle of reinvestment or capitalization (recapitalization) is easiest to understand using the example of accruing profit from deposits.
For example, if interest on the deposit body is accrued every month, and you do not withdraw it from the account, nor do you reduce the deposit amount, then next month interest will be accrued on the deposit body and on the amount of interest accrued in the previous period. When the first period ends, the deposit body will increase by the amount of interest accrued during the period.
In common parlance, this operation is called “interest on interest.” In financial mathematics, compound interest is calculated.
Interest capitalization is specified in the terms of the contract.
Reinvestments can be made not only in the same object, but also in any others. This is done in order to increase the number of instruments in the investor’s portfolio and reduce the risk of capital loss.
The main distinctive features of reinvestment are:
- the income received from investments is re-invested in the same asset to increase future profits
- full or partial reinvestment (full - all profits received are sent back into circulation, partial - part of the funds is invested back, part is spent on personal needs)
- cyclical nature of investments (reinvestment occurs from time to time)
- in the beginning, money must work for the sake of money, which means that income at the initial stage will be minimal or there will be no income at all
- the cheapest source of financing.
Fundamental things that directly affect the amount of profit received from reinvestment:
- the amount of initial investment capital
- the duration of the period during which repeated investments are made (the longer the period, the higher the level of profit, and the higher the dynamics of its growth)
- profit level for the reporting period
- expert assessment of the situation in the industry or area where the investment object is located.
Problems solved by capital reinvestment:
- business/production development and expansion
- independence from other sources of financing
- obtaining the maximum possible income, all other things being equal.
Reinvestment in the broad sense of the word can be considered any income from a business invested in the same business (dividends from shareholders spent on the development of the company; profits aimed at expanding the scope of the organization’s activities, and so on).
The amount of income from reinvestment is based on “compound interest”.
We can also conclude that investors use a financial instrument such as reinvestment to increase investment profits as quickly as possible, which is an unconditional plus. However, it is also subject to risks, so it is always necessary to clearly analyze and give a competent assessment and justification of your planned investments.
The disadvantage of reinvestment is that the funds are not withdrawn from circulation; the investor does not use them until the profit from the investment process reaches the required amount. If reinvestments are carried out under an agreement, for example, a bank deposit, the investor most often cannot withdraw them without loss of profit.
Results
There is a separate line in the balance sheet to reflect retained earnings (profit remaining after the amount of income tax or net profit has been withdrawn from it). The figure entered into it corresponds to the amount of the entire net profit accumulated over the years of the company’s activity. During the reporting year, the value of retained earnings in accounting relating to this year can be seen in a separate accounting account. Dividends are paid out of net profit.
Sources: Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 6, 2008 No. 106n
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Accounting entries
Transactions related to dividend income are recorded in accounting using the following entries:
- Calculation of dividends:
- persons not employed in the organization: Dt 84 Kt 75;
- persons employed in the organization: Dt 84 Kt 70;
- Calculation of tax withheld from dividend income (the debited account changes according to the principle of the first point):
- Dt 75 Kt 68;
- Dt 70 Kt 68;
- Dividend payment:
- Dt 75 Kt 50 (51) - to legal entities and individuals from the cash register (from a bank account);
- Dt 70 Kt 50 (51) - to individuals employed in an organization, from the cash register (from a bank account).
- Payment of tax obligations to the budget: Dt 68 Kt 51.