Legal understanding of the object
Regardless of what stage of construction a building is at, the construction of which is not completed, it refers to real estate, since the Civil Code of Russia (Article 130) directly states: everything that has an integral physical connection with the land refers to real estate.
However, in domestic legislation there is neither the very concept of such an object nor its precise definition. In practice, an understanding of this term has developed that simultaneously corresponds to all of the listed characteristics:
- this is an immovable object, the construction of which is at any stage: from the construction of the foundation and first floor to work related to the installation of windows, doors, communication structures in a completed house;
- the building is a so-called capital (long-term) construction object: i.e. kiosks, stalls and other temporary structures do not meet the definition;
- The construction process of such a building is suspended for various reasons until a specific date (or without specifying a date in case of objective impossibility) due to subjective factors: lack of funds, force majeure, changes in market conditions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QPUVIBIE0gQ
However, the Town Planning Code and other regulations do not directly indicate what can be considered a capital construction project. Therefore, at the theoretical level, difficulties in definition still exist.
The regulatory framework, which contains some grounds for interpreting the concept of an unfinished construction project, is as follows:
- Civil Code.
- Town Planning Code.
- Instructions on the procedure for preparing reports on capital construction.
Based on these documents, we can give the following definition: this is an immovable construction project that is not completed from a technical point of view: i.e. the construction of the building and/or installation of life support systems has not been completed in whole or in part, which excludes the possibility of living in it, organizing non-residential premises and any other type of operation.
What does the tax office see in this?
As soon as, when checking the procedure for conducting cash transactions, the tax inspectorate sees the issuance of funds to the head of the company for reporting and the return of this money in a day or two to the cash desk of the enterprise, then it is considered that the enterprise thus stores excess cash.
Tax authorities base their arguments on the basis that:
- money is not spent at all, including on the needs of the enterprise;
- the advance report is not submitted;
- in the application for receiving funds from the cash register (if there is such an application at all) a fictitious purpose is indicated. And the application itself is needed only for formal compliance with the requirements of the Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U.
And even if a zero advance report is submitted, the tax authority will focus on the absence of actual expenditure of accountable money. It is this fact that will serve as the main evidence that the actions of the head of the company have replaced the obligation of the enterprise to keep excess money in a bank account.
Especially if several tens or hundreds of thousands of rubles are “issued” for the report, and this amount increases from time to time. As a result, it is immediately clear that the entire procedure for the return and subsequent issuance of cash for reporting is fictitious!
Moreover, the tax authority may question the actual availability of these funds. After all, very often, in order to avoid paying extra taxes on the income of the founders, the payment of dividends to them is hidden behind the issuance of endless reporting.
In addition, during an on-site audit, tax authorities may consider substantial accountable amounts that the head of the company does not spend at all as income, with all the ensuing problems. Those. calculate personal income tax on this amount! Moreover, there is judicial practice that favors the tax authorities.
Representatives of extra-budgetary funds can do the same when conducting their audit - charge insurance premiums for these amounts.
How to avoid such problems? First of all, you need to find a way to reset the existing infinite sub-report and find a way to avoid it altogether, using completely different operations.
Accounting and assessment of work in progress in construction
Commissioned construction projects belong to the category of fixed assets (this is the company's real estate). At the construction stage, all costs associated with construction are investments in non-current assets. Such costs include:
- construction costs (purchase of materials, payment for contractor services);
- installation costs;
- the cost of purchasing tools and equipment to complete construction work;
- payment of salaries to specialists involved in construction, deductions for insurance premiums;
- payment of rent for land plots on which work is carried out;
- fuel costs for special equipment used during construction.
How to take into account the actual costs of construction in progress? In accounting, account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” serves as an intermediate link; it accumulates the costs of constructing and preparing for commissioning of a real estate property. This account is active, all expenses are carried out by debit turnover.
If there is unfinished construction, in accounting, account 08 is used indicating the subaccount - 08.3. If there are several objects under construction, separate analytics are carried out for each of them. This is necessary to ensure the ability to isolate from the total amount expenses that should be attributed to the original cost of a particular asset.
In the accounting of public sector employees, construction in progress is reflected in account 10611. In the Instructions from the Order of the Ministry of Finance dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n, account 10600 is designated as an account for accounting for investments in non-financial assets, it is generalizing. With the help of analytical accounts, the type of assets on the formation of which money is spent is clarified (fixed assets, intangible assets, etc.).
Work in progress is the construction contractor's costs for unfinished work performed in accordance with the construction contract. Work in progress in a construction organization includes unfinished work on objects of cost accounting from the beginning of the contract. The general contractor's work in progress consists of the costs of construction and installation work performed in-house, as well as the cost of work performed by subcontractors accepted by the general contractor.
One of the most difficult issues that arise during process costing is the assessment of work in progress. Work in progress has a lower cost than the cost of finished goods, and the presence of work in progress inventories at the beginning and end of the reporting period does not allow us to determine the cost of finished goods by dividing total costs by total production volume.
Work in progress (WIP), according to the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n, includes: products (works) that have not passed all stages (phases, redistributions) provided for by the technological process ; incomplete products that have not passed testing and technical acceptance.
Press service of the Interregional Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. 3 for the Belgorod Region
As in accounting, in tax accounting expenses are divided into direct and indirect (Clause 1, Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, these are completely different concepts.
If in accounting, direct costs are understood as those expenses that are directly (in particular, without distribution) included in the cost of production, then in tax accounting, direct expenses are understood as all expenses that are included in the tax cost of products.
The taxpayer independently determines in the accounting policy for tax purposes a list of direct expenses associated with the production of goods (performance of work, provision of services) (clause
Production in accordance with clause 63 of the Accounting and Reporting Regulations includes: products (works) that have not passed all stages of the technological process and incomplete products that have not passed testing and technical acceptance, as well as unfinished work not accepted by the customer.
Unfinished products also include fully completed products that have not passed the tests required by the technology.
The volume of work in progress is determined by inventory or documentary method.
Accounting for work in progress
Work in progress (WIP) represents parts and assembly units that have not been fully manufactured, as well as products that have not been accepted by technical control. The composition of unfinished goods includes: parts and semi-finished products of our own production, subject to further processing or assembly, incomplete products that have not passed testing and technical acceptance, correctable defects.
Uncorrectable defects, materials in workshops that have not been processed, parts, assembly units and products on canceled orders, etc. do not apply to production.
Correct assessment of work in progress is important for accurately calculating the cost of manufactured products, as well as for ensuring the safety of unfinished parts and products.
In accounting, the actual value of costs in work in progress is the value of the debit balance in accounts 20 “Main production” and 23 “Auxiliary production”.
— know its quantitative expression (number of parts, assembly units, products by stages of the technological process);
- make its valuation.
To more accurately determine the amount of work in progress, an inventory is carried out, usually at the end of the year.
- in a single unit - according to actual costs incurred;
— in mass and serial production: according to standard (planned) production costs; by direct cost items; at the cost of raw materials, materials and semi-finished products.
A publishing and printing organization uses a stamp to cut blanks of a certain shape from paper, which are then folded into brochures.
Chapter 1. Economic essence and methodology of accounting for work in progress
Unfinished objects in the amount of costs incurred for their construction are taken into account on account 08 under subaccount 3. The account is active. Expense transactions are reflected in debit transactions. All amounts accumulated during the construction period are written off against the loan upon commissioning of the asset. Typical wiring:
- Contract work accepted by the customer – D08.3 – K60.
- D19 – K60 - reflects the amount of accrued VAT.
In the balance sheet form approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, the cost of unfinished construction is shown as part of fixed assets. Line 1130 is intended for this (section 1 in the reporting form asset). Additionally, a breakdown of the cost of unfinished objects is compiled.
If you decide to sell the unfinished building to third parties, VAT is charged on its value. The tax base is the size of the price reflected in the contractual documentation. The transaction is formalized by a purchase and sale agreement. The proceeds received are accounted for in the period in which the asset was transferred to the buyer on the basis of the act. Profit is shown by the date of registration of ownership rights by the party acquiring the object.
The sale will be accompanied by the preparation of the following corresponding records:
- D62 – K91.1 – posting confirming the recognition of income from the transaction for the sale of unfinished construction;
- D91.2 – K68 – reflects VAT accrued on the contract price;
- D91.2 – K08.3 – the cost of an unfinished asset that is being sold is taken into account.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The disadvantage of the current taxation scheme is evident for simplifiers. They will have to include the entire proceeds in the tax base, which will significantly increase the value of the tax liability.
According to Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 24, 2021 No. 03-05-06-01/17081, unfinished objects that have been registered fall into the category of taxable property. The value of such assets is included in the overall property tax base. For individuals, the norm was introduced in 2015 (Article 401 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the payer of property tax is an individual, then the cadastral or inventory value is taken as the basis for taxation (Article 402 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In Art. 403 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for a number of tax benefits for pensioners, disabled people, persons with state awards and participants in military operations (a complete list of persons entitled to take advantage of the benefit is given in Article 407, paragraph 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is not possible to reduce tax by applying benefits in relation to trade, administrative facilities and expensive assets (with a price of 300 million rubles or more).
For legal entities, tax obligations on buildings under construction arise after the facility is ready. Exemption from property tax will be relevant until the company begins to use the asset for its intended purpose and stops investing in its construction or improvement.
If construction is carried out by the customer using borrowed resources, then the cost of the constructed objects in tax and accounting will differ. The tax value will be used when calculating depreciation deductions and income tax; the accounting value is needed to derive property tax liabilities (if the cadastral valuation is taken as the basis).
Typical wiring
In accounting for enterprises that are not part of public sector business entities, the following standard correspondence for accounting for unfinished construction projects can be used:
- The acquisition of unfinished property is reflected in accounting by placing the object on the balance sheet and reflecting the debt to the seller - D08.3 - K60. The same entry also shows the costs of paying for the services of third-party organizations entrusted with completing construction and putting the asset into operation.
- D01 - K08.3 - work in progress in construction in accounting passes to the status of completed, the facility is put into operation. This operation is carried out if there is a certificate of verification of the readiness of the object.
If the unfinished building is sold to third parties, the following set of transactions is drawn up:
- income is reflected through the debit of account 62 and credit of other income account 91.1;
- VAT must be charged on the cost of the asset being sold, this amount is shown in debit 91.2 and credit 68;
- when selling, it is necessary not only to show income, but also to close the amounts accumulated in the investment account in fixed assets; this is done using posting D91.2 - K08.3.
Registration of an unfinished construction project
In the recent past, unfinished buildings could not be classified as real estate. Russian laws did not allow this. It was believed that the object had not acquired a finished appearance, which means that it was nothing less than just the sum of building materials and human labor spent on the work.
The situation changed with the introduction of amendments to the Civil Code. More specifically, new amendments have appeared to Article 130, which states that any building that, as a result of certain circumstances, remains unfinished due to the suspension of construction is real estate, which means you can register it as your own property.
The owner of the building, who has become the owner by registering it with the relevant government agencies, can perform the following operations:
- sell;
- give;
- pass on as an inheritance;
- exchange;
- pledge against cash.
Perhaps the main condition for successfully registering the right to an unfinished building is the presence of two most important documents - the right to own the land territory on which the building is located, as well as permission to carry out construction and installation work. Plus, before you begin the registration procedure, you must:
- Have a contract in hand with a construction and installation company.
- Visit the Cadastral Chamber and register the unfinished building.
- Complete a technical inventory of the facility in accordance with all rules.
- Take the collected package of documents to the authorities responsible for registering real estate construction projects.
There is one more change regarding the rules for registering unfinished and long-term construction. Previously, the owner could register ownership of such an object only if he intended to carry out some transactions with it (sale, exchange, etc.). Now this condition has been removed from the list of mandatory ones. Thus, ownership can be claimed even if the owner does not intend to complete the transaction.
Registration of an unfinished property, as well as any other type of real estate, is a very troublesome matter. But it is not difficult to carry out this operation from start to finish if you know what actions need to be taken and what documents are needed. It is worth noting that an unfinished property is a very specific category of real estate, so the list of papers for its registration is much wider.
So, here is a list of documents that will be needed for registration and entering information into the Unified State Register of Rights:
- description of the object, its design documentation (if such a document is not available, registration will be rejected);
- building permit (usually issued by municipal authorities);
- documents proving the right to a land plot (it is important to formalize them correctly, otherwise the building may be regarded as an unauthorized construction - Article 222 of the Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation);
- technical passport from BTI;
- an estimate indicating the monetary costs of constructing the facility;
- cadastral plan of the land territory;
- documents confirming that the construction of the building has been suspended (about the absence of a contract, conservation act);
- documents confirming that there are no interests of third parties in the case;
- a receipt issued after payment of the state fee;
- statement of intention to register the object.
Having collected the papers, you should carefully review them and make sure that they are in proper form. The registration authority has the right not to accept documents from the applicant if they are drawn up contrary to the standards: for example, if there are inconsistencies in the land contract or in the project documentation. The verified package of documents can be taken to the local branch of Rosreestr personally by the applicant or his authorized representative, who has presented the appropriate confirmation.
The right to carry out operations on unfinished construction is recognized in cases where the following conditions are met:
- There should not be a valid contract agreement for the project.
- The developer is constructing an object for his own needs, and not for third parties.
- The owner has all the necessary documents permitting its construction.
- The owner of the building has a certificate of ownership.
Ownership rights can also be issued for those objects that are at a certain stage of construction and, accordingly, are unfinished.
From the date of execution of the document, the legal right to own it arises (Article 219 of the Civil Code). All actions with the building, the land plot under it and around it can be performed after registration:
- sale (purchase);
- donation;
- exchange;
- provision of collateral against cash or other facilities;
- inheritance.
The documents that certify the legal rights of the owner to the site and building are as follows:
- certificate of ownership (separately for the object and separately for the land plot);
- certificate of inheritance (including lifelong inheritance);
- certificate of the right to long-term (or indefinite) use of the site for construction purposes;
- long-term lease agreement.
Until recently, it was possible to transfer unfinished real estate into ownership only on the condition that the owner intended to carry out some kind of transaction with it in the near future (sell, donate, exchange, etc.).
However, the current version of the relevant federal law (No. 196-FZ) does not impose such requirements. Now you can freely register a house as property without the obligation to further sell it, exchange it, etc.
Due to the specifics of an object whose construction has not been completed, the list of documents submitted for registration is much wider than in the usual case:
- standard application form;
- original passport or other document that confirms identity;
- receipt of payment of state duty;
- documents with the project and construction estimates (technical passport, cadastral passport, accounting documents and others);
- certificate of ownership of the land plot;
- a permit issued by municipal authorities for construction;
- the entire package of constituent documents that confirm the fact of registration and opening of a legal entity;
- documents proving that the building is not the subject of the contract, i.e. the fact that construction work is not currently being carried out at this address (such documents, for example, include an agreement to terminate the contract);
- documents certifying that the building is not under arrest, is not claimed by third parties, and there is no other type of encumbrance (these facts are reflected in the extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate).
Registration of property rights occurs during a personal application to the territorial office of Rosreestr directly by the applicant or his representative, who acts by proxy.
After the appropriate permits have been obtained, agreements have been reached with the contractor, and after the act of suspension of construction work has entered into force, the following documents must be drawn up and signed between the customer and the construction company:
- Certificate of acceptance of completed work (partially completed work) by the customer in the form KS No. 2.
Based on this document, a certificate of work completed is drawn up - it indicates the cost of the work, which the customer is obliged to pay to the contractor within the prescribed period.
- A statement that indicates the name of materials, unmounted equipment, machines, structures that will not be used during the conservation period. The form of the document is free and usually represents a list of specified objects with marks of their quantity and cost.
- A document reflecting a complete list of all work and costs associated with ensuring the integrity and safety of the mothballed facility, additional structures and all structural elements that are an integral part of the unfinished building.
After drawing up and signing the specified documents, the customer must, within no more than 2 calendar months from the day on which the act of suspension of construction work was signed, make payments to the contractor:
- for work completed before conservation in full;
- for all losses that arose in connection with the suspension of work;
The customer is also obliged to ensure, at his own expense, the transportation of building materials and/or equipment to other construction sites, if any (or ensure their safety - by agreement with the construction company).
Knowledge of the legal features of registering ownership of an unfinished construction project allows the customer and contractor to avoid unnecessary risks and be able to defend their interests during legal proceedings.
In accordance with the law “On registration of rights to real estate” (clause 2, article 25), registration of ownership of an unfinished construction project begins with registration. To do this, the owner of an unfinished construction project or “unfinished project” must present a permit to carry out construction work.
And also, ownership of the land plot on which these works are being carried out.
If before 2015 a building permit was not required, then starting from March 1 of this year, this document again appeared in the list of required papers. In order to register ownership of an unfinished construction project, you must do the following:
- conduct a technical inventory of the facility;
- obtain permission to carry out construction or construction work;
- enter the object into the cadastral register;
- Take the package of necessary documents to the registration authorities.
Can they be punished for this?
First of all, it is worth recalling that paragraph 1 of Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation punishes an ordinary organization only for:
- for cash settlements with other organizations or entrepreneurs in amounts exceeding those established by the Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3073-U dated 07.1013. cash payment limit – i.e. 100 thousand rubles (in Russian currency) and an amount equivalent to 100 thousand rubles if payments are made in foreign currency. It should be borne in mind that this limit applies to settlements under any civil contracts concluded between organizations and (or) entrepreneurs;
- for complete or partial failure to receive cash to the cash register, any money, not just revenue;
- for violating the procedure for storing available funds. According to paragraph 7, clause 2 of Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014. free cash means cash that exceeds the cash limit established by the enterprise and is actually in the cash register. And such funds should only be stored in a bank account;
- for the accumulation of cash in the cash register in excess of the cash limit established at the enterprise. The exception is the accumulation of funds on days when salaries, scholarships and other remunerations are paid that are included in the wage fund (according to the methodology used to fill out statistical observation forms), and when social funds are paid. On these days, when paragraph 8 of clause 2 of Directive No. 3210-U is allowed to exceed its limit at the cash desk, they also include the day of withdrawal of cash from the bank account to make the specified payments. In addition, it is allowed to store money in excess of the limit in the cash register on non-working holidays and weekends, but only if organizations and entrepreneurs conduct cash transactions on these days.
Among the above violations, there is no liability for violations of the rules for issuing accountable funds.
In particular, this is confirmed by the conclusions made in the Resolution dated March 26, 2014 of the Seventh Arbitration Court of Appeal of the Russian Federation in case No. A67-5875/2013.
The essence of the issue considered in this Resolution was that the enterprise periodically issued, on account to its manager, funds that exceeded the established cash limit. The head of the company did not provide a report on the accountable funds he had previously received.
The tax inspectorate considered this behavior to fall under Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. But the court expressed the opinion that in the actions of the head of the company there are violations only in the procedure for issuing cash on account, but there are no violations, which are provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, i.e. there is no reason to believe that in this way the enterprise accumulated money in excess of the limit and violated the procedure for storing available funds.
Moreover, the Court concluded that cash is free until it is issued for reporting to an authorized person for the purpose of the company’s activities.
Thus, after these funds are issued for reporting, they lose their “free” status, which means that these amounts are not subject to the obligation to store them in the company’s bank account and the punishment provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation does not apply.
However, it is too early to rejoice. The court in the considered Resolution rejected the tax inspectorate only because it charged a violation in the form of accumulation of excess funds by issuing an endless sub-account, but in fact proved that the enterprise did not have the right to issue money to its manager on account without providing a report on previously issued amounts.
But there are decisions in favor of the tax authority. For example, the Decision of the Moscow City Court dated August 14, 2013 in case No. 7-1920/2013. In this case, an infinite sub-account was also identified, i.e. the head of the company handed over the accountable money to the cashier and immediately received it in a larger amount again on account. These transactions were documented with incoming and outgoing cash documents.
The tax authority concluded that the company was violating the procedure for storing available funds. And the court supported this conclusion, citing the fact that:
- cash issued on account was not spent, including on the needs listed in Directive No. 3073-U of the Bank of Russia;
- the head of the company did not submit advance reports, from which the very fact of spending funds and their intended or inappropriate use would be visible;
- the funds “left” the cash register for a short period of time and were returned in full.
Thus, the head of the company, in the opinion of the court, when registering the excess balance of money as issued on account for business needs, acted fictitiously and actually replaced himself with a credit institution, keeping free funds (i.e., above the limit) at home. As a result, the company and its director were punished on the basis of clause 1 of Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
Why are entrepreneurs not punished for such offenses? Because they do not allow them: unlike a legal entity, an entrepreneur can write off for his own needs at the end of the day all the cash from the cash register, down to the penny! And he doesn’t need to file endless reports. Moreover, Bank of Russia Directive No. 3073-U does not even provide for a limit when issuing cash to an entrepreneur for personal purposes.
The degree of incompleteness of the object
The legislation does not distinguish the degree of incompleteness of construction, therefore, in a general sense, any object is incomplete, starting with the one for which the foundation has just been laid, and ending with one in which the engineering and finishing work necessary to put the building into operation has not been completed.
From the point of view of construction documentation, 4 stages of construction work can be distinguished, at each of which the house is considered unfinished. A description of each stage is given in the table.
| construction stage | completion percentage | what has been done or is being done at this stage |
| initial | 0-15% | The design work and survey work have been completed in full, temporary buildings and auxiliary facilities have been built, a decision has been made on suppliers of building materials and construction equipment |
| average | 16-50% | The supply of building materials, machinery, and equipment has begun and continues; the installation of walls and load-bearing foundations of all floors and roofs has almost been completed; work continues on the installation of internal engineering systems in the building |
| high | 51-75% | All survey work has been completed in full, the supply of equipment, machinery and construction materials continues, the installation of internal engineering systems is more than half completed, finishing work is at the initial stage |
| final | 75-99% | delivery of all construction materials and equipment has been completed in full, finishing work has been completed by more than half, temporary and auxiliary buildings have been built in full, commissioning work is in the initial stage |
It is assumed that the object is fully completed (100% degree of completion) if it is put into operation, which is confirmed by the fact of acceptance by the relevant authorities.
Advantages of our company
]Smart Way[/anchor] has all the necessary specialists for design and assessment activities. We will provide the most favorable conditions for each client, regardless of the complexity of the object or the status of the customer. Our advantages:
- saving time and money, working directly and without intermediaries;
- consulting support at all stages of cooperation;
- involvement of highly specialized specialists in examinations and calculations;
- legal support of transactions with public tax authorities, land plots, assistance in the implementation and management of projects.
For more information about the terms of cooperation, please contact our specialists by calling the numbers listed on the website.
Conservation of the object
A building, the construction of which is unfinished, can be mothballed by decision of the customer of construction work until a certain date (or without specifying it). Such a measure is mandatory provided that a work stoppage is planned for a period of at least 6 calendar months - this is indicated in the Urban Planning Code of Russia.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
- The customer decides to temporarily stop construction and mothball the facility. The fact is reflected in the corresponding order, which contains information on the timing of development of the documentation required:
- for the preservation procedure;
- to organize work on inventory of an unfinished object.
The order form is free, one of the standard forms is presented below.
- Next, the customer notifies the contractor in writing of his decision in accordance with the deadlines specified in the contract.
- It is necessary to obtain a conservation permit from the state environmental assessment, the work of which is paid in full by the customer.
- If necessary, the customer must also send written notifications in advance to various authorities and structures, for example:
- to the fire department;
- to the local traffic police department;
- internal affairs bodies, etc.
- Before carrying out conservation, the customer is obliged to:
- pay the contractor in full for all work completed to date (Article 752 of the Civil Code);
- compensate for possible material damage associated with such a decision (for example, the construction company has already purchased all the necessary materials, and now there is no longer a need for them);
- agree on a further plan of action if the customer proposes conservation for a certain period with further “unfreezing” of construction.
- If conservation is carried out by the developer company (this is the most common case in practice), then a new contract is concluded (or an additional agreement to the original contract), which specifies the start and end dates of conservation, types of work, cost and other essential conditions.
- Convening an inventory commission to evaluate the object and determine the conditions for conservation. This commission includes representatives of all parties to the contract:
- general contractor and subcontractors;
- customer;
- the company that developed the building project.
How can you pay off endless reporting?
Do not set a cash limit
Small enterprises, on the basis of paragraph 10, clause 2 of Bank of the Russian Federation Directive No. 3210-U, have the right not to set a cash limit - and keep as much cash as they want in their cash register and independently decide on the need to deposit it into a current account.
To do this, it is enough to issue an order stating the cancellation (!) of the limit (and not that it is equal to “0”). Without this document, the tax authority will consider the limit to be zero, and any excess of it, even by 1 kopeck, will be recognized as a violation, which should be punished under Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. And then you can “sin” with endless reporting, but still not abuse it!
An entrepreneur can also cancel the limit. But it is much easier for him to do otherwise: at the end of each working day he can completely reset the cash balance in the cash register, taking it for personal needs. And this is not prohibited. Moreover, there are no restrictions on the amount, but only on the condition that the cash order will indicate “for personal needs.”
Draw up an interest-free loan agreement
You can, for example, draw up an interest-free loan agreement. This option is only suitable for organizations. This operation will allow you to close the debt on accountable amounts of the head of the company.
But there are some disadvantages:
- With an interest-free loan, an employee receives a material benefit in the form of savings on interest (clause 1, clause 1, Article 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And this is subject to 35% personal income tax;
- To avoid material gain, you will need to set interest on the loan. But then the company will have taxable income;
- Moreover, a loan will only delay the solution to the problem with endless reporting - after all, the loan will still need to be repaid someday.
It is worth recalling that, according to Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3073-U, loans can be issued only from those funds that were withdrawn from the current account for this purpose. Therefore, in order not to pay extra money, they only make records on paper in the form of an offset:
D account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” subaccount “Provided loans” Account. 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” - the debt on accountable funds has been covered by a loan agreement executed with the debtor.
In fact, the debt on the accountable amount simply changes its form. But first, the accountable amount must be recognized as a debt by the enterprise and the debtor himself. To do this, you should draw up a reconciliation report and sign it.
In addition, the employee's written consent to set off between obligations will be required. After all, there was no actual receipt of the loan, just as there was no deposit of it into the enterprise’s cash register to pay off the debt under another obligation.
And as soon as the debt on accountable funds is closed, you should not be afraid of inflating the paperwork: you need to make another act of reconciliation with the closed debt on account 71, which the debtor must sign. In addition, with the resumption of endless reporting, it is worth waiting until the loan is closed.
Recognize the debt of the accountable person
There is another option for resetting the endless reporting: the organization can recognize the debt of the accountable person and claim it in writing. In this case, the accountable person himself must agree with this debt and enter into an agreement with the company on the gradual repayment of this debt from his salary.
Moreover, Article 248 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows this to be done. In this case, it is even possible to establish an installment plan for repaying the debt if there is agreement between the debtor and the organization.
What does this give? First, it makes perpetual reporting safe because it is officially recognized as debt. Secondly, this amount is gradually returned to the enterprise and is not subject to any taxes or contributions.
But it’s not worth issuing an endless report again until the previous “debt” is repaid. In addition, the reporting person will have to accept some losses from his earnings.
Or you can do it differently: forgive the debt and write it off. But then the reporting person will have taxable personal income tax in the amount of the entire endless sub-account that is registered with him. And from this entire amount you will have to collect 13% personal income tax (clause 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, insurance premiums will have to be charged on the amount of debt forgiven by the enterprise (letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated May 17, 2010 No. 1212–19).
In addition, the organization will not be able to:
- recognize as hopeless;
- and write it off as non-operating expenses!
Conclude a lease agreement for employee property
You can draw up a lease agreement for the employee’s property, so that later “on paper” or actually pay off the endless sub-account using this money. Rent will be subject to 13% personal income tax, but not insurance premiums. Moreover, these payments will go to the expenses of the enterprise.
But it is only necessary that the property be available, transferred by deed to the enterprise and accepted by it for off-balance sheet accounting in account 001 “Leased fixed assets”, and the rental amount should not exceed the current market one.
Rent payments will allow you to gradually close the endless reporting:
D sch. 001 – property rented from an employee has been accepted for off-balance sheet accounting;
D sch. 26 “General business expenses” Account 73, subaccount “Rent of employee property” - reflects monthly rent accruals (if the property is rented from the head of the company),
or
D sch. 97 “Future expenses” To account 73, subaccount “Rent of employee property” - reflects the annual rent. This amount will then be written off monthly as expenses in the amount of 1/12;
D account 73, subaccount “Rental of employee property” Account. 51 “Current accounts”, 50 “Cash” - if actual payments are made. But you need to remember: if real estate is rented from an employee, then you can pay under this agreement in cash only if it is withdrawn from the current account. Not from cash proceeds!
And then from this money the debt is repaid for accountable amounts, issued by a receipt order with the wording “Debt repayment for accountable funds.” And if rental payments and debt are immediately offset against accountable amounts, bypassing the cash register and current account, then the following posting is made monthly:
D account 73 subaccount “Rental of employee property” Account. 71 “Settlements with accountable persons.”
In this case, it will not be superfluous to periodically draw up and sign with the debtor a reconciliation report for account 71, which will reflect the gradual repayment of the accountable amount.
Payment of compensation to an employee for a car
Instead of renting, you can pay compensation to an employee for using his car in the interests of the company. This will require a compensation agreement and corresponding order.
This option of resetting an endless sub-report is only possible if the employee has a car. Then the compensation paid within the limits of the norms will not be subject to personal income tax (clause 3 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and insurance premiums (clause “and” of part 2, clause 1 of article 9 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009 “On insurance premiums").
True, the amount of the non-taxable compensation limit is not that significant; in particular, when using passenger cars with an engine capacity of up to 2000 cc inclusive, compensation in the amount of 1200 rubles per month is due (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 92 of 02/08/02).
You can look at a sample application for the issuance of funds to report to the director and read the explanations.
What are the costs of opening a coffee shop?
Work of the inventory commission
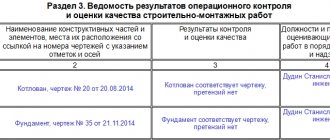
The assembled inventory commission carries out verification work in order to:
- Determining the current state of the construction project, the degree of completion of work according to the developed criteria.
- Detection of construction equipment and communication systems that were transferred to construction, but remained unfinished.
- Determination of facts of overestimation or underestimation of the cost of construction work for the following reasons:
- initial errors in estimate documentation, accounting documents;
- incorrect application of correction factors, with the help of which the cost of work, wages, and other costs is recalculated taking into account current prices on the market;
- inclusion in the general estimate of those items that are not directly related to the work under the contract (for example, repair of equipment, elimination of the consequences of unforeseen failures in the operation of equipment, work on starting up machines, etc.).
The process of recognizing ONS as real estate
The main condition for recognizing such an object as real estate, as noted above, is a completed foundation.
However, there are different interpretations of when the ONS can be considered to have arisen:
- After obtaining a building permit and land ownership.
- After the expiration of the construction contract.
- If the construction is at the conservation stage.
- The facility complies with the standards.
- It received the status of real estate.
- After registering property rights in Rosreestr.
These criteria must be met for an unfinished building to be considered real estate.
Act on suspension of construction
Based on the results of the commission’s work, a corresponding document is drawn up, which is called an act of suspension of construction (form No. KS-17). The document is the main legal confirmation that work will be suspended and the facility itself will be mothballed. It must include the following information:
- name of the object, all its passport data;
- purpose of building construction;
- start date and expected completion date of work (as originally envisaged);
- the full cost of all work, which was initially agreed upon when the parties entered into the contract (estimated cost);
- the estimated cost of work that was actually completed before the date of termination in connection with the decision on conservation;
- the amount needed for conservation and maintenance work until construction resumes.
The act of suspension of construction has an approved, unified form and looks as shown in the screenshot.
Thus, in a legal sense, conservation is not a cessation of work, but its suspension caused by one reason or another. It is provided that the work will be resumed after a certain or indefinite period by the current developer or another company with which a new contract will be concluded.
What is an endless report?
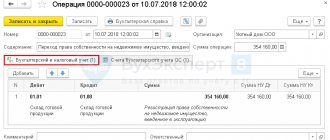
This operation is carried out by many accountants. And it lies in the fact that at the end of the working day, an expense cash order is issued to the head of the company for reporting an amount of cash that exceeds the cash balance, or the amount of money that the manager, who is the founder of the company, simply takes for his needs.
The next day, for example, at the beginning of the day, the amount drawn up for the report is “returned” from the report, and at the end of the working day, a certain amount is written off again. And so every day. This is called endless sub-reporting.