Workers hired to perform seasonal work (according to Article 293 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) have the same social guarantees as full-time employees. They have the right to sick leave, vacation and vacation compensation upon dismissal. An employment contract is concluded with seasonal employees for a period of work, which usually does not exceed 6 months according to generally established rules, but in some industries a longer duration of seasonal work is possible. Most often, workers from agriculture, road transport and construction infrastructure, geological exploration, etc. are hired for seasonal work.
Labor guarantees for seasonal workers
Labor relations between an employer and a seasonal worker are regulated by the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. An employer engages a citizen in seasonal work by concluding a fixed-term employment contract with him. The period of validity of the agreement is determined in accordance with weather and climatic conditions affecting the execution of work.
A sample employment contract with a seasonal worker can be downloaded here ⇒ Employment contract with a seasonal worker.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides seasonal workers with the following labor guarantees:
- paid days of rest according to Art. 295 Labor Code of the Russian Federation;
- payment for the period of absence from work due to temporary incapacity for work on the basis of sick leave;
- payment of severance pay upon dismissal due to reduction.
When engaging an employee in seasonal work, the employer sets a work schedule and fixes it in local regulations and an employment contract. The period of work of a seasonal worker during the reporting period should not exceed the standards established by the production calendar.
If the period of work of a seasonal employee exceeds the established norms, the employer will calculate and pay an additional payment for overtime:
- in the amount of 150% of the hourly tariff rate for each hour of overtime (the first 2 hours);
- in the amount of 200% of the hourly tariff rate for each hour of overtime (subsequent hours).
Additional payment is also provided for attracting a seasonal employee to work on weekends, holidays, and night hours (from 23:00 to 06:00).
What kind of work is considered seasonal?
Seasonal work is distinguished from other work modes by a number of features:
- labor is bound by natural and climatic conditions;
- workers are employed for a specific period rather than the entire calendar year;
- a period (season) has a certain duration.
The duration of seasonal work, as a general rule, is set at less than 1⁄2 years, but may exceed this period. Lists of works lasting more than six months and their maximum duration may be established by industry and interindustry agreements of federal significance.
All features of seasonal work and labor relations associated with them are discussed in Chapter. 46 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Lists of work, which by default are classified as seasonal, are contained in a number of documents adopted quite a long time ago, but still used in practice (Lists of seasonal work approved by the post of the NKT of the USSR from No. 185 of 10/11/32; approved by post Council of Ministers of the RSFSR No. 381 dated 04/07/91; approved by resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 498 dated 04/07/02).
Examples of seasonal work: clearing and removing snow and ice, gardening work, seasonal work on the production of thermal energy (work can last over six months, depending on the fuel season).
Clue! Temporary work differs from seasonal work in that it is not related to natural conditions and lasts strictly up to 2 months (Article 59 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, work during the season can last less than 2 months or exceed this period. The main criterion for difference is dependence on natural conditions.
How many days of vacation for a seasonal worker?
According to Art. 293 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to provide a seasonal employee with paid leave at the rate of 2 working days for each month of work . This means that, after working a full calendar month, a seasonal employee can go on vacation for 2 days; after working for 2 months, he can take a vacation for 4 days, etc.
In general, the minimum period of continuous work at the enterprise for taking leave is 6 calendar months. However, this requirement does not apply to persons hired to work under a fixed-term employment contract.
A seasonal employee can take a vacation for 2 days after continuous work for the 1st calendar month. In exceptional cases, by prior agreement with the employer, leave may be granted earlier - after 2 weeks of work. In this case, the rest period will be 1 day.
We emphasize that seasonal workers are subject to the general provisions of labor legislation, in accordance with which an employee can take leave without pay, regardless of the period worked at the enterprise.
Let's look at an example . 07/01/2021 Dubkov S.D. got a job at Sadovod LLC. Dubkov’s employment contract was drawn up taking into account the following provisions:
- the contract period is from 07/01/2021 to 10/01/2021 (3 months);
- Dubkov is involved in the work of harvesting apples.
On August 1, 2021, Dubkov took a 2-day vacation (from August 7 to August 8).
On August 15, 2021, Dubkov again turned to the management of Sadovod LLC to arrange a vacation for 2 days - from August 20 to 22, 2021. Since Dubkov used 2 days of vacation accrued for July earlier, and for the first 2 weeks of August Dubkov was accrued 1 vacation day, rest days from August 20 to 22 are issued to Dubov in the following order:
- 08.2021 – 1 day of annual paid leave;
- 08.2021 – 1 day of vacation at your own expense.
Dismissal
A fixed-term contract with a seasonal worker is terminated when its validity period expires. You don't need to work 2 weeks. The employer is obliged to warn the employee about this in advance. If an employee himself decides to resign, he also warns the administration of his intention. In both cases, the period is one - 3 calendar days before dismissal (Article 79, Article 296 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The parties are required to do this in writing.
If no notification about the termination of the working relationship has been received from anyone, the employee continues to fulfill his duties, the contract becomes valid for an indefinite period (Article 58 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If an organization is liquidated or an employee is laid off, he must be notified 7 calendar days in advance. Severance pay is calculated as the average wage for 2 weeks. A pregnant employee engaged in seasonal work cannot be fired before the end of pregnancy (Article 261 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Part 2), even if the contract has expired.
A seasonal worker is fired, citing Art. 77 Labor Code of the Russian Federation, part 1, clause 2. Documenting the dismissal in itself is no different from the standard actions of the personnel service in such cases.
Applying for leave for a seasonal worker: step-by-step instructions
Registration of leave for a seasonal employee is carried out in the general manner - based on the employee’s application to the employer.
Below are instructions that describe the features of registering vacation and calculating vacation pay for a seasonal employee.
Step 1. Preparing an application
At the first stage, an employee involved in seasonal work draws up an application for leave and submits it to the employer.
The application is drawn up in the general manner and does not have any special features compared to the application drawn up when applying for leave under a standard employment contract.
The application form is not approved by law; the document is drawn up in free form, indicating the following information:
- name of company;
- Full name, position of the manager in whose name the application is being submitted;
- Full name, position of seasonal worker;
- vacation period (from _____ to _____), number of days (___days);
- basis for granting leave (Article 295 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- date of application.
A sample application form can be downloaded here ⇒ Application for leave for a seasonal worker.
Once completed, the employee signs the document and submits it to the manager for approval.
Step #2. Issuance of an order
Based on the application, the employer issues an order to grant the employee leave.
The order must be drawn up and signed by the manager no later than the day the vacation begins.
After drawing up the document and signing it by the manager, one copy of the order is given to the seasonal worker for review (“Acquainted”, employee’s full name, signature, date).
A sample order can be downloaded here ⇒ Leave order for a seasonal worker.
Step #3. Calculation of average earnings for vacation pay
An employer providing annual leave to a seasonal employee is obliged to pay for days of rest in accordance with the norms of the Labor Code, namely to pay vacation pay in the amount of average daily earnings for each day of rest:
VacationSeason = WedDearSeason*PeriodOpt,
where Vacation season is the total amount of vacation pay accrued during the vacation period; Average daily earnings for the billing period; PeriodOtp – vacation period in calendar days.
When calculating the average earnings of a seasonal worker, the employer takes into account the entire amount of income paid to the employee within the pay period, which generally does not exceed the term of the employment contract, namely:
- salary calculated according to the tariff rate;
- additional payment for overtime, work on weekends, holidays, night shifts;
- awards.
If during the validity of a fixed-term employment contract a seasonal employee was on vacation at his own expense or was absent due to illness, then such periods are excluded from the calculation period. Payment of benefits for the period of incapacity for work accrued on the basis of sick leave is not included in the calculation of the average earnings of a seasonal worker.
Vacation of part-time workers, freelancers and student interns
Leave for combined work is granted to part-time workers simultaneously with leave for their main place of work. Vacation payment is made according to general rules, taking into account wages for part-time positions and at the main place of work (Resolution No. 922 of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007).
Freelance workers subject to compulsory social insurance receive leave on a general basis. The exception is for employees working outside the state on an hourly basis. Thus, if these employees work on average more than 75 hours per month, they are granted leave at the rate of two days for each month worked. If the total working hours are less than 75 hours per month, then the duration of the vacation will be equal to 15 working days per year.
Students have the right to receive paid leave for the period of practical training in paid positions.
Duration of vacation
to 28 calendar days of vacation annually . But we are talking about employees who work on a permanent basis. In this regard, the question may arise: is it necessary to recalculate the length of leave for a “fixed-term” employee? For example, if a contract is concluded with him for 6 months, does this mean that he should be given a vacation of not 28, but 14 calendar days?
We answer: no, there is no need to recalculate anything . The Labor Code does not contain any guidance in this regard. Reservations are made only for seasonal workers and those hired for less than 2 months - we mentioned them above. All other employees on a fixed-term contract are entitled to a full 28-day vacation.
In accordance with Article 127 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is allowed to provide leave outside the term of the employment contract (vacation with subsequent dismissal). In this case, the day of dismissal will be considered the end date of the vacation. If the leave was provided in advance, then upon dismissal, the share corresponding to the unworked part is deducted from the salary.
Compensation
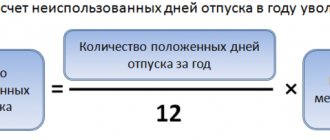
For certain reasons, an employee may not take advantage of the right to go on vacation. Then the employer is obliged to pay him compensation. It is accrued for the number of full months worked by this employee.
A “full working month” subject to compensation is 15 or more days worked. Letter of Rostrud 944-6.
As a result, the employee is accrued 2.33 days of vacation for each month worked . Their cost is paid by the employer.
For short-term and seasonal contracts
In addition to the duration of rest, short-term and seasonal employment contracts differ in the amount of compensation for unused vacation.
For short-term and seasonal contracts, compensation is calculated at the rate of 2 days for each fully worked month.
Another tricky nuance is the actual time worked. An illustrative example is described below.
Example
An employment agreement was concluded for a period of more than two months and a non-seasonal type of work. The contract provides for the opportunity to take vacations. However, the employee took advantage of this opportunity without even working for two full months.
How to calculate the duration of vacation in this case? The period of its actual activity is less than 2 months. Does this mean he is only entitled to rest for 2 days, as with a short fixed-term contract?
No, that's not true. The resolution of this issue is affected only by the terms of the signed agreement. This example does not fall within the exceptions of Art. 115 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, the employee is entitled to a standard period of rest. The number of months actually worked does not matter here.
Fixed-term contract and vacation schedule
When drawing up a vacation schedule for the next year, a specialist may doubt whether to include “urgent” employees in it. Especially if the contract is for a period of less than a year.
The answer is simple - an employee on a fixed-term contract is included in the vacation schedule according to the general rules . Let us remind you that this schedule must be drawn up at least 2 weeks before the end of the year. And if at the time of planning vacations an employee is listed in the company, then it is impossible not to include him in the schedule. In addition, there is always a chance that the term of his contract could be extended. Or that the employee will move from the category of “urgent” to permanent. To avoid a controversial situation regarding your vacation later, it is better to foresee this in advance.
Responsibility
The labor inspectorate may find out about violations during an inspection. Or when the employee himself applies to the inspectorate or court.
For non-payment of compensation, the labor inspectorate may fine:
- organization in the amount of 30,000 to 50,000 rubles;
- official (for example, the head of an organization) - from 1000 to 5000 rubles;
- entrepreneur - from 1000 to 5000 rubles.
Penalty for repeated violation:
- for organizations - from 50,000 to 70,000 rubles;
- officials and entrepreneurs - from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles;
For repeated violations, directors may be disqualified for up to three years.
Additional leave for hazardous working conditions
Despite the fact that, according to Art. 120 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, all annual paid leave due to employees must be provided in calendar days; currently, additional leave for harmful working conditions can be calculated in working days. This conclusion follows from the Resolution of the State Committee for Labor of the USSR, the Presidium of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions dated October 25, 1974 No. 298/P-22 “On approval of the List of industries, workshops, professions and positions with hazardous working conditions, work in which gives the right to additional leave and a shortened working day” ( hereinafter referred to as the List), which establishes the duration of additional leave for harmful working conditions in working days.
The minimum duration of annual additional paid leave for work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions is now seven calendar days (Part 2 of Article 117 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). If the profession or position of an employee who is entitled to compensation is included in the List and the duration of vacation indicated in it is more than seven calendar days, when determining the amount of compensation, it is necessary to be guided by the List (Decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated January 14, 2013 No. AKPI12-1570). The same should be done if the duration of additional leave according to the List exceeds that established in the collective agreement or local act. This conclusion follows from the analysis of Part 4 of Art. 8, part 3 art. 50, part 3 art. 219, part 1 art. 423 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Please note that the employee retains the right to additional leave established based on the results of workplace certification carried out before 01/01/2014, that is, before the date of entry into force of Federal Law No. 426-FZ, which introduced a special assessment of working conditions instead of certification. According to Part 4 of Art. 27 of Federal Law No. 426-FZ, the employer may not conduct a special assessment of working conditions in workplaces for which certification was carried out before 01/01/2014, if five years have not passed from the date of its completion. Exceptions are the cases specified in Part 1 of Art. 17 of Federal Law No. 426-FZ.
From all of the above it follows that:
- if the employer has not yet conducted a special assessment of working conditions at the workplace, it is necessary to apply the duration of additional leave established by the List;
- if the employer has conducted a special assessment of working conditions, the number of additional days of leave for harmful working conditions is determined by the local regulations of the organization, but cannot be less than seven calendar days.
Vacation pay calculation
The principle of financing vacation under a fixed-term contract is directly related to the amount of his average salary. The latter is calculated in accordance with Art. 139 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The average salary must be multiplied by the number of vacation days. The resulting value will be the amount of funds that the employer must allocate.
Average earnings per working day × number of vacation days = amount of vacation pay for a fixed-term employment contract.
Example
A fixed-term contract was concluded with employee Shelyagina I.S. to perform seasonal work. Starting in April 2021, Shelyagina worked for 6 months in a row. The monthly salary was 50,000 rubles.
In September of the same year, the contract came to an end. It's time to calculate vacation pay. How much does the employer ultimately have to pay?
First you need to calculate the average salary. To do this, you need to know Shelyagina’s total income that she received for the entire period of seasonal work: 50,000 rubles. × 6 months = 300,000 rubles. Now you can calculate the average income per day. Employee Shelyagina worked honestly for 154 working days.
| April | 26 days |
| May | 24 days |
| June | 25 days |
| July | 27 days |
| August | 26 days |
| September | 26 days |
In total, she received 300,000 rubles: 154 days. = 1948.05 rubles for one working day. When Shelyagina worked for 6 months, she was entitled to a vacation of 6 months. × 2 days/month = 12 days. Vacation pay will be: 12 days. × 1948.05 rubles/day = 23,376.6 rubles.
The same principle of calculation is also valid for those “conscripts” whose employment agreements are concluded on standard terms. In other words, they do not fall under the previously mentioned exceptions to Art. 115 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For example, Shelyagina worked for the same 6 months, but no longer in seasonal work. Let's say she replaced another employee in an organization. In this case, vacation pay would be calculated differently. Instead of 12 days, the employee was entitled to at least 28. And then the employer’s costs would be 28 days. × 1948.05 rubles/day = 54,545.4 rubles.