The mineral extraction tax in the Russian Federation (mineral extraction tax) must be paid by all enterprises that have the right to use subsoil.
It is regulated by the Tax Code, Chapter 26. All natural resources located on the territory of the country are state property. Therefore, it is impossible to mine them without the knowledge of the government. First, a permit is obtained, after which the entrepreneur is registered as a taxpayer.
mineral extraction tax must be paid by all enterprises involved in this industry. Thanks to him, funds for the use of natural resources are used for the benefit of the population of Russia and the state. They plan to increase the tax, but this may negatively affect the rate of mineral extraction. Failure to pay the appropriate amounts on time will result in a fine. If an organization cannot pay on time, then it is possible to extend the tax payment period, but this requires compelling reasons.
What is mineral extraction tax
What is mineral extraction tax in simple words - this is the main expense item of the oil and gas business. For each ton of extracted products, a certain amount must be paid to the state. All money is sent to the federal budget.
Answering the question, mineral extraction tax - which tax is federal or regional, we can say that the mineral extraction tax is a direct federal tax that is levied on subsoil users. It is the main instrument for taxation of extractive industries.
The general characteristics of the tax on mineral resources show that with its help, funds for the use of natural resources are redistributed and directed to the benefit of citizens and the entire country.
Who is the payer
Which organizations are required to make contributions? Mineral extraction tax (MET for short) must be paid by enterprises that:
- work on sites located on the territory of the country and provided for use by the taxpayer;
- use products obtained from mining waste, if there is a license for extraction;
- extract minerals outside the country in areas leased from other states or under the jurisdiction of Russia.
Taxpayers of mineral extraction tax are all organizations that have received a license and carry out their activities on its basis.
Mineral extraction tax: general information
Mined minerals can be divided into the following groups:
- flammable substances (coal, peat, shale);
- hydrocarbon products, which include oil and produced gas with methane;
- ore;
- various types of non-metallic raw materials extracted by mining and mining chemical enterprises;
- Mineral extraction tax is also charged on rare metals;
- colored stones;
- quartz raw materials;
- precious and semi-precious metals, stones;
- salt;
- water for medicinal purposes and industrial, extracted from underground or natural, thermal springs.
The full list is specified in Art. 337 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The object of taxation of mineral extraction tax is the volume of mineral resources extracted on the territory of the Russian Federation and abroad (Article 336 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Raw materials obtained from sources that are not registered with the state and are not on balance sheet for government agencies are not subject to taxation. Raw materials from this category of subsoil can be extracted by an entrepreneur to meet his own needs.
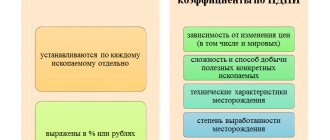
Tax rates for calculating the indicator
All rates are expressed in percentages and rubles. Coefficients are applied to some of them. The rate depends on:
- price fluctuations;
- method and level of difficulty of extraction;
- characteristics of the territory in which the deposit is located;
- price fluctuations on the world market;
- degree of depletion of the deposit.
All coefficients apply to certain types of natural resources. They have a specific meaning or are calculated differentially. The first ones change throughout the year.
The mineral extraction tax rate may be reduced:
- if an entrepreneur is looking for deposits at his own expense (conducting geological exploration of minerals). In this case, the indicator is 30% lower;
- when mining in the Magadan region, the tax is 40% lower. But this does not apply to carbon and common fossils.
Rates expressed as a percentage or ad valorem determine the cost of products obtained from the bowels of the earth. Mineral extraction tax rate and in rubles are specific rates for the amount extracted.
Reference: Ad valorem rates are determined as a percentage of the customs value of goods.
MET rate = R x Kc – Dm
- where R is the base rate of the mineral extraction tax (919 rubles in 2021);
- Kc is a coefficient characterizing the dynamics of world oil prices,
- Dm is an indicator characterizing the characteristics of oil production and determined in the manner established by Art. 342.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (see cost of oil production).
Dm = Kndpi x Kc x (1 – Kv x Kz x Kd x Kdv x Kkan) – Kk,
- Kndpi is equal to 530 - from January 1 to December 31, 2015 inclusive, 559 - for the period from January 1, 2021;
- Kc – coefficient characterizing the dynamics of world oil prices (clause 3 of Article 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- CV is a coefficient characterizing the degree of depletion of a specific subsoil area,
- KZ is a coefficient characterizing the amount of reserves of a particular subsoil area,
- KKAN is a coefficient characterizing the production region and the properties of oil,
- CD – coefficient characterizing the degree of complexity of oil production,
- KDV – coefficient characterizing the degree of depletion of a specific hydrocarbon deposit,
- Kk - set equal to 306 for the period from January 1 to December 31, 2021 inclusive, 357 - for the period from January 1 to December 31, 2021 inclusive, 428 - for the period from January 1 to December 31, 2021 inclusive, 0 - from January 1 2021 (source: pravobez.ru).
Mineral extraction tax calculation with examples
At the moment, it is impossible to calculate the mineral extraction tax and fill out a mineral extraction tax declaration in the 1C program for all types of natural resources. But with the release of a new version, the program will support the corresponding codes. The direct amount of subsoil use tax is calculated using an accounting calculator using the formula:
The above formula applies to all natural resources that taxpayers extract, but some minerals have a number of features when calculated.
Oil
The Federal Tax Service has established that the tax on mineral resources for March 2021 must be calculated taking into account the following information:
- the average monthly price of Urals oil on the oil market, which is $63.58 per barrel;
- The average exchange rate of the dollar currency against the ruble equivalent, which was established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, is 57.0344 rubles / 1 dollar. CC = 10.6158. The formula used here is:
- CC is an element that shows price jumps in the world for a product, determined by the formula: Average oil prices are published every 15th of the month in Rossiyskaya Gazeta.
- DM is a standard that reflects the characteristics of product extraction, defined as follows:
- EF is a component that reflects the level of production of subsoil used in production;
- KZ - an element showing reserves in this area;
- CD - the indicator reflects the complexity of resource extraction in this well;
- KDV - indicates the level of oil product production in this well;
- KKAN - indicates the immediate area of oil product production.
The mineral extraction tax coefficient is currently 559, while in 2015 it was 530.
An example of calculating the tax on black gold with real data for February 2021:
- the tax base is calculated in tons;
- tax tariff - 919 rubles/1 ton;
- CC = 8.5698;
- KNDPI = 559;
- CV = 0.3;
- KZ = 1;
- CCAN = 1;
- CD = 1;
- KDV = 1;
- CC = 306.
Conventionally, the organization received 10,000 tons of oil in February 2021. Using the formulas, we get:
10,000 * (919 * 8.5698 - 559 * 8.5698 * (1 - 0.3 * 1 * 1 * 1 * 1) - 306) = 42,162,835 rubles.
This amount is the mineral extraction tax on oil production in a conditional example.
Coal
When calculating the mineral extraction tax, the organization takes into account the use of tax deductions, that is, whether the enterprise spends funds on employee safety and labor protection. The company makes these contributions in two ways: including it in the amount of other expenses or deducting it from the mineral extraction tax. When choosing one option or another, the organization consolidates it in the accounting policy of the enterprise and regularly uses the chosen method.
Without a tax deduction, the organization calculates the mineral extraction tax on coal according to the general rules:
- Determine the total amount of waste on safety and labor protection.
- The tax is calculated using the formula:
- Calculate the maximum amount of tax withheld:
- Compare the amount of actual costs for occupational safety and health. Sometimes expenses exceed the tax limit. In this case, it is included in the total amount of monthly deductions (up to 36 months).
Gas
Calculation formula:
When multiplying EUT, KS and TG, the result is a figure less than zero, then the rate will be zero. When calculating the EUT indicator, the monthly price tag and the coefficient reflecting the share of the extracted resource are taken into account.
Gas condensate
The mineral extraction tax for this condensate is calculated in the following way:
EUT and other data are calculated in the same way as gas indicators. The correction factor is calculated:
where KGP is an indicator that reflects income from gas exports.
Period, procedure and conditions for collecting payments
Taxpayers must pay a certain amount per calendar month (month – in this case, the tax period). At the end of the month, calculations are made for each type and money is paid to the budget depending on the location of the site.
Payment must be made no later than the 25th day of the month following the expired tax period. The procedure and conditions for payments for the use of subsoil are regulated by the Government of the Russian Federation.
The mineral extraction tax declaration is submitted to the relevant authorities at the location of the enterprise or residence of the individual entrepreneur. The document must be provided in paper or electronic form.
The deadline for paying the mineral extraction tax is determined by Article 344 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but the taxpayer can adjust them legally. It is important not only to make payments on time, but also to report this using a declaration.
According to the mineral extraction tax, the deadline for filing a declaration and payment can be postponed for 3 years in the event that an entrepreneur has serious financial difficulties. But there must be guarantees that he will still pay off the budget.
The KBK MET 2021 for legal entities was approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. The budget classification codes (BCC) also indicate interest, fines and penalties for the mineral extraction tax of the BCC.
Instructions: fill out the mineral extraction tax declaration
Mineral miners and subsoil users are required to report on their mining activities. The category of accountable persons includes all payers of this tax: both organizations and individual entrepreneurs. Such taxpayers must have a license permitting the use of subsoil.
From the moment of registration as a mineral miner and after receiving a license, a tax return on mineral extraction tax must be generated. Until registration as a MET taxpayer, a report is not submitted. If the use of subsoil is temporarily suspended, you will still have to report production taxes.
Due dates
All subsoil users have a single deadline for filing a mineral extraction tax declaration - monthly, on the last day of the month following the reporting period. That is, submit the declaration for August 2019 by September 30, the report for September by October 31, and so on until the end of the year. If the last day of the month falls on a non-working day, the deadline is transferred to the first working day.
Reporting period Deadlines for submitting the mineral extraction tax declaration in 2021
| For December 2018 | January 31 |
| For January | 28th of February |
| For February | April 01 |
| For March | April 30 |
| For April | May 31 |
| For May | 01 July |
| For June | 31 July |
| For July | 02 September |
| For August | September 30th |
| For September | October 31 |
| For October | December 02 |
| For November | 31th of December |
| For December 2019 | January 31 |
Where to take it
Taxpayers submit a declaration on the use of subsoil to the territorial offices of the tax inspectorate. Here's where to submit your mineral extraction tax declaration in 2021:
- for institutions that are large taxpayers (code 213 on the title page) - to the interdistrict tax office;
- for other taxpayers (code 214 on the title page) - to the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration;
- for foreign enterprises operating through Russian representative offices - at the place of operation.
A number of organizations enter into production sharing agreements. Participants in such an agreement are not provided with the opportunity to submit a mineral extraction tax declaration.
How to take it
As with any other report to the Federal Tax Service, the declaration on mining has two options for submission: on paper or electronically. The method of provision depends on the number of employees. If the institution employs up to 100 people, the report is submitted at the request of the taxpayer. This is a personal application to the Federal Tax Service or transfer of the register via telecommunication channels.
If a mining organization employs more than 100 people, it has no choice. The only available form of delivery is electronic.
Which form to use
From March 2021, a new declaration form will be submitted. Along with the form, the procedure for filling out the mineral extraction tax declaration has also changed. In 2019, to fill out reports on mineral resources, follow Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. ММВ-7-3/827. KND MET code - 1151054.
Instructions for filling
Mining reports include a title page and eight sections. Each paragraph corresponds to a separate type of extracted resource, therefore, the filling rules for each mineral are different. When entering information into report sections, follow a number of uniform rules. Here are general instructions for filling out the mineral extraction tax declaration in 2021:
- The report is completed for each period (month) separately. Factual information is provided for each month, rather than cumulative information.
- The declaration must only fill out sections with those minerals to which the enterprise is directly related to the extraction. If the taxpayer produces oil, then he generates information under section 2, if oil and gas, then the information is submitted under sections 2 and 3 of the mineral extraction tax. The remaining chapters are not completed.
- The report is provided only for minerals for which the production cycle has been completed. If a resource is under development, it is not reflected in the report.
- In each declaration, the title page and section 1, which accumulates data on mineral extraction tax, must be completed.
- Fill out all digital values and cost indicators according to the rules of the Federal Tax Service. Each cell contains separate information.
- All pages used are numbered in order. Leaving the field is unacceptable.
- Do not use correction fluid or correct errors manually.
When filling out the content of the mineral extraction tax, you must use the rules set out in Appendix No. 2 to Order No. ММВ-7-3/827 and Letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. SD-4-3/ [ email protected] , SD-4-3/ [email protected] from 04/18/2019.
Step 1. Fill out the title page
The title is a reflection of the registration information about the organization. The rules for filling out the title page in the mineral extraction tax are no different from the rules used to generate other reports. Be sure to fill out:
- INN and KPP of the taxpayer;
- page number (hereinafter all completed pages are numbered in order);
- adjustment number - if it is a primary declaration, then zeros are filled in; if the information is corrected, then 001, 002, etc.;
- tax period is the serial number of the reporting month;
- year of delivery;
- tax office code;
- code at the place of registration - 213 or 214;
- full or short name of the taxpayer (we write how the organization is registered with the Federal Tax Service);
- information about the taxpayer being liquidated (if available);
- telephone number for contacting the performer;
- the total number of completed pages of the declaration and the number of accompanying documents;
- information about the head or representative of the mining organization.
The title page data is certified by the signature of the manager, after which the date of submission of the mineral extraction tax declaration is filled in. To correctly fill in the period code, check the table:
Period Code
| For January | 01 |
| For February | 02 |
| For March | 03 |
| For April | 05 |
| For May | 05 |
| For June | 06 |
| For July | 07 |
| For August | 08 |
| For September | 09 |
| For October | 10 |
| For November | 11 |
| For December | 12 |
When reorganizing or liquidating an organization, please indicate the code:
Period Code
| For January | 71 |
| For February | 72 |
| For March | 72 |
| For April | 74 |
| For May | 75 |
| For June | 76 |
| For July | 77 |
| For August | 78 |
| For September | 79 |
| For October | 80 |
| For November | 81 |
| For December | 82 |
Step 2. Fill out section 1
The first paragraph is a summary. It is formed based on the cumulative result of filling out the entire mineral extraction tax declaration. Here the amount of tax is indicated, the KBK code by which it must be paid, and the OKTMO code - to allocate the budget of the region to which this tax is transferred.
If an institution extracts several minerals, then in section 1 several groups “KBK - OKTMO - amount of tax payable” are filled in for each type of production.
Step 3. Fill out section 2
This paragraph of the mineral extraction tax declaration is only for those enterprises that produce oil. Data is entered for each subsoil plot.
The organization fills out all codes and coefficients in accordance with Procedure No. ММВ-7-3/827. After filling out all the cells, the amount of tax (130), tax deduction (140) and final payment to the budget (150) is calculated. The result is the difference between the calculated tax and the mineral extraction tax deduction. If there is no deduction, then a zero value is entered in cell 140.
Subsections should include information about the name of the deposit and the amount of oil produced during the reporting period. The characteristics of oil are also described: its depth, density, reservoir permeability and saturated thickness of the formation.
Step 4. Fill out section 3
Gas producers are filling up. Information is generated both by BCP and by type of production - gas and gas condensate by subsoil areas.
By analogy with oil production, all codes are filled in: the code of the type of mineral and its unit of measurement, BCC. Then the amount of tax (040), tax deduction (045) and the amount of tax payable (050) are calculated. The deduction is made for gas condensate. After this, quantitative and qualitative production indicators are entered.
The subsections describe the indicators that were used to calculate the mineral extraction tax for gas and characterize hydrocarbon deposits.
Step 5. Fill out section 4
The fourth paragraph is reserved for information about offshore hydrocarbon deposits. This part of the mineral extraction tax declaration requires filling in codes, the name of the new offshore field, the month and year of the start of production.
The series and number of the license for mining activities must be indicated. Quantitative indicators for the reporting month, revenue from production sales (110), tax base (130) and calculated tax amount (140) are determined.
Step 6. Fill out section 5
This part of the mineral extraction tax declaration is completed for all other types of resources, except coal. According to the rules set forth in Order No. ММВ-7-3/827 (Part 7 of Appendix No. 2) for the formation of the fifth section, a declaration on the mineral extraction tax is completed when extracting sand.
Here the mineral code, BCC, unit of measurement coding and tax rate applicable to the extracted resource are determined.
Subsection 5.1 provides quantitative characteristics for the reporting month of production and the license number for the mineral extraction tax. Subsection 5.2 is reserved for calculating the amount of tax. If an organization extracts several types of resources using one BCC, then a detailed calculation is given for each asset, and in section 1 the amount of calculated tax is summed up under a single BCC.
Step 7. Fill out section 6
In this part of the example of filling out a mineral extraction tax declaration, the cost of a unit of production is determined. All direct and indirect expenses that relate to production for the reporting month are filled in. Then the total amount of all expenses is determined.
Subsection 6.2 details costs for individual resources. There is an important nuance here: no matter how many resources the organization extracts, part 6 of the mineral extraction tax declaration is filled out in a single copy - according to the total indicators for all extracted minerals.
Step 8. Fill out section 7
The seventh part of the mineral extraction tax declaration includes all the same information on production, but only for coal. It is necessary to fill in the BCC, details of the coal mining license, unit of measurement, OKTMO and coefficient of the mining territory - KTD.
Subsection 7.1 details the actual production for the reporting month by subsoil area and by type of coal resource. In subsection 7.2, provide the tax calculation taking into account all amounts of expenses. Subsection 7.3 calculates tax deductions.
Step 9. Fill out section 8
The final section of the declaration is for filling out information on production and calculation of the mineral extraction tax on oil, on which the tax on additional income from the production of hydrocarbons is calculated.
This is a new part of the report, but the procedure for filling it out is similar to the previous parts. In the first subsection (8.1) all codes are entered, and in the second (8.2) the tax on the subsoil plot is calculated. This takes into account oil export indicators, which affect the final amount of the mineral extraction tax.
How to punish for violations
For late submission or failure to submit mandatory reporting, mineral extraction tax taxpayers bear both administrative (Article 2.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation) and tax liability (Article 106 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The violator faces a fine of 5% of the amount of unpaid mineral extraction tax.
Source: https://gosuchetnik.ru/shablony-i-formy/instruktsiya-zapolnyaem-deklaratsiyu-po-ndpi
Tax base for mineral extraction tax
The tax base is:
- The amount of minerals (hereinafter referred to as PI) that were mined. This applies to enterprises engaged in natural gas, oil, gas condensate, except for those extracted from new offshore fields, coal, and multicomponent ores, which are obtained at sites in the Krasnoyarsk Territory.
- Cost of mined PI. If they deal with oil, natural gas, gas condensate in new offshore fields and other useful substances. The cost depends on sales prices, prices excluding subsidies, and the estimated price of products.
Calculation formulas
The calculation is carried out as follows:
- To find out the cost, you need to multiply the total number of PIs by the unit cost.
- To determine the price per unit of PI, sales revenue is divided by the amount of minerals sold.
- Proceeds from the sale of minerals = price excluding VAT and excise tax - the amount of taxpayer expenses for the delivery of the mineral.
The entrepreneur himself must calculate the tax base. Data is required for each element.
Example for calculating the mineral extraction tax for oil production in 2019
The mineral extraction tax is calculated and paid by taxpayers on a monthly basis. To do this, the Federal Tax Service publishes once a month the data necessary to calculate the mineral extraction tax for oil production. In a message from the Federal Tax Service dated June 18, 2019, the agency notes that the calculation of tax deductions for the period June 2021 should be performed based on the following indicators:
- the average price level for Urals oil on the crude oil markets in June 2021 was $62.37 per barrel;
- The average value of the dollar to ruble exchange rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for all days of the tax period is 64.2314 rubles. for a dollar.
- the value of the Kc coefficient is 11.6576.
Determining the base for tax calculation
In order to correctly calculate the amount that needs to be paid to the budget, you must first understand what the taxable base is:
- The amount of natural resources (tons, cubic meters, etc.) that was developed at a deposit registered with the authorized government agency. This applies to oil, gas, coal, etc.
- The cost of natural resources that are not included in the list of mineral resources approved by tax legislation.
The organization's accountant needs to calculate the tax base. As with other taxes, deliberate understatement can lead to problems during a tax audit and subsequent additional assessment of unpaid tax and penalties. The cost of natural resources developed during the reporting period is determined in the following ways:
- From the average level of sales prices for mineral resources as of the reporting date;
- From the average level of sales prices of mineral resources as of the reporting date, not including budget subsidies;
- Cost calculation taking into account all costs of production, processing, etc. applied in a situation where during the reporting period the organization did not sell the extracted raw materials. The calculation is carried out on the basis of accounting and tax accounting, as when calculating income tax.
Direct and indirect costs
The estimated cost is determined taking into account:
- Direct expenses. They refer to all expenses for wages, the use of funds for production, and the amount of insurance premiums.
- Indirect costs. These are funds spent on repairing equipment, developing natural resources, eliminating fixed assets that are being taken out of service, mothballing and re-mothballing production facilities, and others.
To obtain data on the indicator, it is necessary to select from the total amount of expenses the part that corresponds to the extraction of a certain substance.
Amount of tax deductions
Tax Code of the Russian Federation, mineral extraction tax is calculated in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 343.
The mineral extraction tax formula is as follows:
tax = tax base * tax rate
The calculation must be carried out in compliance with the following rules:
- Each deposit and all types of extracted mineral deposits must be taken into account separately.
- Calculation methods must be enshrined in the payer's accounting policies for the year. You can only change the method at the end of the year.
- Calculation of the mineral extraction tax is carried out taking into account raw materials that have gone through the full technological cycle.
- For some elements, increasing and decreasing coefficients are used.
How to calculate the mineral extraction tax so as not to make a mistake when paying taxes? All changes in calculation rules are displayed on the official tax website.
Example:
Calculation of the mineral extraction tax for sand should be carried out taking into account:
- Relevance rates for sand. It is positioned as a non-metallic raw material.
- The criteria for calculating the base defined in Article 340 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
To obtain the required amount, the first indicator is multiplied by the second.
Also, key indicators in calculating the mineral extraction tax of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are the quantity of goods extracted and sold, delivery costs and VAT amounts. It is also important whether the organization developing and implementing these resources participates in a regional investment project and receives subsidies from the state.
Tax deduction for oil production
From January 1, 2021, a tax deduction is also provided for oil production in subsoil areas located entirely within the boundaries of the Nizhnevartovsk region of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug - Ugra, the license for the use of subsoil resources of which was issued before January 1, 2016 and the initial recoverable oil reserves of each of which are 450 million tons or more as of January 1, 2016.
The amount of tax deduction for the tax period is determined in the amount for the named subsoil areas and amounts to 2,917 million rubles. The right to provide this tax deduction is fixed until December 31, 2027.
From January 1 last year, 2 more types of tax deductions were introduced:
- deduction established by Art. 343.3 Tax Code, Russian Federation for the production of natural gas from all types of hydrocarbon deposits produced in a subsoil area located wholly or partially in the Black Sea. This deduction can be used from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2020;
- deduction legalized by Art. 343.4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when extracting gas condensate from all types of hydrocarbon deposits. This deduction is applied when three points are simultaneously fulfilled:
- the gas condensate produced by the taxpayer organization is sent by it and (or) another organization registered in the Russian Federation, which has the right of ownership and (or) use and (or) disposal in relation to the specified gas condensate, for processing on technological equipment owned by the Russian organization;
- from the gas condensate produced by the taxpayer using technological equipment belonging to a Russian organization, a wide fraction of light hydrocarbons was obtained during its processing;
- the fact of obtaining a wide fraction of light hydrocarbons from gas condensate produced by the taxpayer is documented. Source: hpravobez.ru.
How are natural gas and gas condensate producers taxed?
The tax rate is multiplied by the base value of a unit of standard fuel and by a coefficient that characterizes the degree of complexity of extracting combustible natural gas and gas condensate from carbon deposits.
Calculation of the mineral extraction tax on gas condensate is carried out taking into account the established correction factor.
When calculating the tax rate for natural gas, the product of the base rate, the base value of a unit of standard fuel and the production complexity coefficient are summed up with the value of the cost of transporting the fossil fuel.
The estimated price for gas sales outside the territories of the member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States or the Mineral Extraction Tax CDZ for July 2021 is RUB 15,552. per 1000 cubic meters of gas excluding value added tax.
Features of taxation of individual minerals
Let us give some nuances of tax calculation that explain the application of the articles of Chapter. 26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Oil
The tax is applied to oil purified from water, salts, and stabilized (crude oil that does not boil at normal pressure and temperature). A specific rate per ton applies. It is refined by multiplying by the price coefficient - Kc, which describes the change in world oil prices. Kts is published in information letters of the Federal Tax Service. For example, in May of this year, a coefficient of 13.9764 was applied (Doc. SD-4-3/11375 dated 06/13/19), and the oil tax rate was 919 rubles. for t. was adjusted based on it. The adjusted rate was 12844.3116 rubles/t.
You can calculate the value of the coefficient yourself using the formula Kc = (C - 15) x P / 261, where C is the average price of Urals oil in dollars per barrel, P is the average dollar exchange rate.
The calculation also includes a complex indicator that takes into account the peculiarities of oil production - Dm. A separate article of Tax Code - 342.5 is devoted to its calculation. Dm reduces the value obtained by multiplying the bet and Kts.
Gas and condensate
A fixed rate is taken into account. It is multiplied by the Eut indicator - the value of a unit of standard fuel and Kc - a coefficient showing the degree of difficulty of extracting the specified PIs.
If we talk about gas condensate, then the Kkm indicator is also used - of a corrective nature - the rate for condensate must be multiplied by it. Calculations for natural gas assume that the product of the base rate, Eut and Ks is increased (by summing) by the transport cost indicator Tg.
Calculation methods and explanations for them can be found in Art. 342.4 NK. As already noted, 0% rates may be applied for gas, condensate and oil in accordance with Art. 342-1 NK.
Coal
The rate for it is in rubles per ton; deflators are also taken into account - coefficients established by orders of the Ministry of Economic Development on a quarterly basis, by type of coal.
The mineral extraction tax can be reduced by costs related to labor protection (Article 343.1 of the Tax Code). They are taken as a tax deduction for the mineral extraction tax or included in the income tax base (Chapter 25 of the Tax Code). This article assumes the use of the Kt coefficient when calculating the maximum tax deduction. It takes into account the saturation of the formation with methane and the degree of danger of spontaneous combustion of coal. The calculation of the indicator is done according to the rules approved by the Government (No. 462 of 10/06/11). The tax amount is multiplied by this coefficient, depending on the location of PI production. The limit value of Kt is 0.3.
Precious metals
They are taken into account according to:
- Federal Law-41 dated 03/26/98 “On Precious Metals”;
- Government Decree No. 731 dated 28/09/2000
These documents contain the rules for accounting, storing this type of PI, and preparing reports on them. Extracted precious metals are valued based on sales prices for chemically pure metal (excluding VAT), reduced by the costs of purification from impurities and delivery to the consumer.
If there is no information on prices in the current period, calculations for previous months are taken. The cost of a unit of mined PI is determined taking into account the share of chemically pure precious metal in a unit of mined PI and the cost of a unit of purified metal.
In other words, the cost of a unit of mined PI = the share of pure metal in the mined PI (in natural meters) * the cost of pure metal sold (excluding VAT) – purification costs (refining) – transport costs / quantity of metal sold.
The tax base is the cost of the mined precious metal, calculated by multiplying the cost of a unit of mined PI by the volume of its production. The calculation features are reflected in Art. 339 (clause 4, 5), 340 (clause 5) of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When making calculations, the production area coefficient (CTD) can be used. Its dimensions are determined by art. 342.3, 342.3-1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. KTD is associated with the status of a territory of rapid economic development and resident producers in these territories (FZ-473 dated 12/29/14) or with the status of a participant in an investment project in the region (Article 25.8 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How are precious metals taxed?
The mineral extraction tax for the extraction of alluvial gold and other precious metals from ore, technogenic and alluvial deposits is determined in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on precious metals.
The assessment of the value of extracted precious minerals is carried out depending on the taxpayer’s prices for the sale of chemically pure metal in the corresponding period, excluding VAT, costs of extraction and delivery to the recipient. The mineral extraction tax rate on silver, gold and other metals depends on this.
If prices for the sale of pure precious metal have not been compiled in the tax period, regardless of whether there is a semi-concentrate containing precious metals, calculations are carried out taking into account the prices that were added up in the previous or preceding tax period.
The mineral extraction tax in the diamond mining industry allows you to fully replenish the budget of the regions in which these minerals are mined.
Rate
Mineral extraction tax rates are set differentially depending on the type of resource, that is, each element has its own percentage. The mineral extraction tax rate for 2021 is divided into two types: percentage expression and in rubles.
Every year the tax rate undergoes changes, and each year the rate increases rather than decreases. But the reduced tariff, benefits and 0% rate make it easier to get busy.
- If the mineral extraction tax tariff on oil in 2021 was 857 rubles per ton, then in 2021 it increased to 919 rubles. At this time, the tariff has not increased further.
- The mineral extraction tax on gold in 2021 is 6%, and the tariff on other precious metals is 6.5%. According to Federal Law No. 41, the amount of tax on precious metals is calculated on the territory of the deposit.
- Gas and natural condensate is measured not only as a percentage, but also in rubles, which makes it more expensive: condensate - 42 rubles. for 1 thousand m3, 35 rubles. - natural fuel.
- The coal coefficient varies greatly between types of resource: the tariff for the extraction of brown coal is 11 rubles. per ton and 47 rubles. costs 1 ton of anthracite. The latter rate has been maintained since 2021.
Privileges
For some organizations, a reduction factor of 0.7 is provided. An enterprise uses it if it meets the requirements:
- before 07/01/2001, a company or individual entrepreneur paid OVMSB, but did not pay this duty for work on developed fields;
- the enterprise searched for and developed new deposits at its own expense, and government subsidies were compensated.
Zero rate
The 0% tariff rate is regulated by Art. 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which contains information about natural resources that are not subject to duty. Mineral extraction tax is not paid in the following cases:
- in case of standard losses of obtained fossil raw materials during the work process;
- during the production of sand, associated, natural gas, its condensate, very thick oil;
- during the production of qualified associated tin ores;
- when receiving groundwater that contains minerals;
- when processing residues after the extraction of a natural resource;
- during the extraction of medicinal waters;
- when extracting water for agriculture. needs.
Also in paragraph 21 of Art. 342 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation indicates specific geographical zones where extraction of natural resources is carried out free of mineral extraction tax.
How coal taxation works
A specific rate applies to it. This means that you need to pay for coal in rubles per ton. Rates are set for each type of coal every three months. At the same time, they take into account how coal prices have changed in the territory of the Russian Federation during this period.
Deflator coefficients used earlier are also used. They are identified and published publicly.
The legislation in Article 343.1 of the Tax Code provides for the possibility of reducing the tax if there are expenses that will provide safe conditions for all workers.
The business owner can take this into account when calculating the tax amount or indicate the amount as a tax deduction. He must also independently calculate the amount of the deduction.
Typical errors in applying mineral extraction tax
Coefficients that change the tax rate. Each organization must very carefully and correctly calculate and apply the coefficients provided for by law for different types of resources. Otherwise, in the event of a violation, the tax inspectorate has the right to add the unpaid tax to the budget, as well as charge penalties and fines.
Determination of standard losses. Each organization has the right to establish a certain level of standard losses within the framework of its production, which also affects the calculation of the mineral extraction tax. Moreover, if such standards are not established for the reporting period, the organization has the right to use the value established in previous periods.
What changes are expected
The mineral extraction tax in 2021 is included in the program of the new tax regime. The government plans to introduce a profit tax (added income tax) for oil companies, which will come into force on January 1, 2019. Currently, the objects of taxation include oil and gas, for which oil companies pay mineral extraction tax.
Before calculating oil royalties, they take into account how much oil prices have changed in the world, whether reserves and production volumes have been depleted.
The approval of the new tax regime has already been carried out by the Government, but the size of the new tax rate has not yet been provided.
Changes in the mineral extraction tax on oil will apply to fields located in Eastern and Western Siberia, some fields in western Siberia that have already been depleted, as well as those fields that benefit from a reduction in export duties.
The Energy Minister claims that this tax will only affect new projects that are being developed by Russian oil companies.
The Ministry of Finance is convinced that if the tax burden on the oil industry is increased, this could negatively affect the rate of mineral extraction in traditional areas.