Bulatova Evgenia “THORY OF LAW”
The director of the company is responsible for everything that happens in it, including the state of settlements with creditors. What about the former director? Read about this in this article.
According to the legal position set forth in the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated June 2, 2015. No. 21 “On some issues that arose with the courts when applying the legislation regulating the work of the head of the organization and members of the collegial executive body of the organization,” as well as in the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013. No. 62 “On some issues of compensation for losses by persons included in the bodies of a legal entity”, the head of the organization (including the former) on the basis of Part 2 of Art. 277 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation compensates the organization for losses caused by its guilty actions only in cases provided for by federal laws (for example, Article 53.1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Article 44 of the Federal Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies " and etc.).
The liability of a former director, founder, or member of a company is possible on various grounds. The most typical options for civil liability are recovery of damages and bringing to vicarious liability. Read more about the subsidiary liability of a director in our article: “Subsidiary liability of the director and founder in bankruptcy. Why is it dangerous to “leave” a company?”
The responsibilities of a company director are divided into types:
- material or property (liability of a participant (founder) of the Company within the authorized capital. In other words, if the Company’s debts to creditors and counterparties significantly exceed the actual value of the authorized capital and property owned by the Company, then the owner (founder) of such a Company has the right not to cover the difference in debt with personal money funds or personal property.
- administrative (responsibility of the founders for committing administrative offenses committed by them in the performance of duties related to the registration of the Company (violation of the law on advertising, intellectual property, carrying out activities without a license, etc.);
- subsidiary (liability in the form of additional punishment of persons who may be subject to penalties on a par with a debtor who is unable to repay his debts on his own);
- criminal (liability of the founder (participants) of the Company for deliberately conducting unfair business activities, the losses of which amount to more than 250,000 rubles).
Read more about the liability of a director in our article: “Criminal and property liability of the general director and founder for the debts of the Company.”
How long is the CEO responsible after dismissal?
For administrative offenses and crimes and violations of varying degrees of severity, the law provides for different statutes of limitations:
- One year for an administrative offense and for causing material damage.
- Two years for minor crimes.
- Six and ten for medium and especially grave criminal offenses, respectively
- one year after the commission of administrative offenses;
- 1 year for claims for compensation for material damage;
- 2 years for minor violations of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
- 6 years for crimes of medium gravity;
- up to 10 years for serious crimes.
Methods for submitting claims
According to the Bankruptcy Law, creditors can choose one of three ways to present claims against the controlling person as part of a subsidiary obligation:
- Debt collection within the framework of bankruptcy proceedings.
- The sale of such claims by the insolvency representative to third parties as part of bankruptcy proceedings.
- Transfer of part of the claims to the creditor (with direct payments by the controlling person to such creditor and a proportional reduction in the creditor's claim against the company/debtor upon receipt of such payments).
Any funds received from controlling shareholders as a result of the above enforcement methods must be included in the debtor's assets, which are distributed to creditors.
The law gives priority to the second method of presenting claims, in which the claims are subject to sale, and the amount is included in the debtor’s property estate.
If the bankruptcy authority of a company is successful in retaining the directors and controlling persons of that company liable under the subsidiary liability and satisfying the claims of creditors, he or she can claim an award of 30% of the amount included in the estate. The Supreme Court makes it clear that this 30% constitutes a surcharge for persons bearing subsidiary liability.
Administrative responsibility
Occurs in the event of serious violations of official duties and powers and allows for exclusion from the possibility of working in the senior management of medium-sized and large enterprises and organizations.
The maximum period during which a negligent director can be subject to administrative punishment is one year from the moment the fact of abuse of power is established.
This punishment provides:
- inability to engage in business activities as a legal entity;
- serve on the board of directors (including executive directors);
- participation in foreign projects and foreign investments as a manager of any rank;
- prohibition on carrying out labor activities in executive bodies of state power.
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Vladislav Ivanovich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in family law. Knows everything about the law.
According to Article 3.11, before noting the termination of the employment contract with him, a corresponding entry about the imposition of an administrative penalty is made in the general director’s work book .
In some situations, this punishment threatens a general director dismissed with a similar wording with a complete ban on ever holding a position at this level (Article 392, part one, Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
What to do if a criminal tax case has already been initiated against the director?
If a criminal case has already been initiated, then it is necessary to involve experienced lawyers specializing in taxes to protect your interests. They are the ones who must analyze the situation, assess the risks and work out further tactics and line of defense.
To do this, witnesses may be questioned, documents may be presented, including those confirming the reality of the transaction, due diligence and commercial diligence may be exercised, a financial analysis of the results of controversial transactions may be carried out, and procedural grounds may be used to deem a number of evidence inadmissible. As practice shows, these actions can only be carried out by a lawyer practicing in this area.
Criminal penalty
In addition, if the guilt of the general director is documented, criminal liability may arise for the harm and illegal actions caused by him (Article 165 of the Criminal Code of Russia).
The terms of criminal liability depend on a number of circumstances and the severity of the official crime committed and are determined within the framework of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. The minimum term of imprisonment is one year . Once the statute of limitations has passed, release from criminal punishment occurs.
If at least two years have passed since the dismissal of the general director from his position , and the crime is classified as a minor offense, according to Russian laws (Article 78 of the Criminal Code), criminal liability is not provided.
For moderate violations , six years must pass before the statute of limitations expires.
In situations where the former general director deliberately evades the judicial authorities and interferes with their work , the statute of limitations is temporarily suspended, and when it becomes clear that the investigation is being delayed, the criminal penalty is increased.
It should also be noted that the dismissal of the general director from the post of manager does not relieve him of financial responsibility and retains the state judicial authorities the right to materially recover from the former director the damage caused by him in full.
Author: Svetlana Valyunina chief accountant-consultant 1C-WiseAdvice
The head of a legal entity is responsible for everything that happens in the organization. Owners are usually not punished for current shortcomings in the work of the company, but in case of serious violations, claims may be brought against them.
What if the founder sold his business and the director quit? Let's consider under what conditions it is possible to hold former directors and owners of a company liable.
What guarantees can a director count on upon dismissal?
First of all, compensation is provided in the form of three times the average monthly earnings (Article 279 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, as noted above, there are cases when this compensation is not paid - upon dismissal as a result of bankruptcy of a legal entity, upon expiration of the contract and at the request of the employee.
Compensation must be paid if the owner of the organization’s property changes (Article 181 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, simply a change of company participants does not constitute a change of property owners.
The role of the general director in managing a business entity
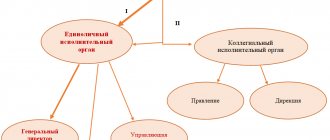
The General Director is the sole executive body (clause 1 of Article 40 of the Federal Law No. 14 of 02/08/1998), acting in the interests of the headed business entity.
He is hired and fired by the founders (or the founder, if he is one) and is responsible for almost everything that happens in the LLC.
The entire working team is subordinate to the general director, and he himself is accountable to the founders who hired him.
Taking into account the provisions of paragraph 3 of Art. 40 Federal Law No. 14, the functions of the general director include:
- representing the interests of the LLC before other persons and government agencies without a power of attorney (but with the right to issue it to any other representative);
- transactions;
- resolving personnel issues and approving relevant documentation;
- exercise of other powers not related to other management bodies of the LLC.
If the general director is absent from the workplace, his functions are performed by a deputy (often this is a staff member of an LLC holding a leadership position).
In the process of fulfilling his duties, the manager must be guided by the provisions of the LLC Charter, his employment contract, as well as regulations at various levels.
Violations in the field of finance and legal law
Classification of violations
Often, managers of existing organizations underestimate the role of accounting workers and even their financial directors. The importance of such employees is not at all in increasing KPIs, but in ensuring the conduct of business activities within the framework of current legislation, reducing tax and investment risks (failure to fulfill obligations to investors or financial organizations).
Often in practice there are cases of formation of financial groups. As a rule, these are 3 or more organizations. One can act as a holder of fixed assets, the second can produce, the third can sell, and the fourth can reduce the burden of output VAT. Almost all holdings or financial groups sooner or later risk falling under Article 173.1 of the Criminal Code. It is quite simple to identify such companies by the composition of the founders and senior officials. In this case, affiliated persons may also fall under Article 174, which provides a detailed description of actions to legalize income received from business activities. Well, this article is steadily followed by Articles 197 and 199, which can bring officials to the dock for organizing fictitious liquidation of legal entities or direct tax evasion.
Situations of recognition of dishonesty and unreasonable actions of a manager
In practice, there are often cases when a manager does not act for the benefit of the LLC. When assessing the integrity and reasonableness of the decisions they make, senior management should determine the necessity and completeness of the tools used to achieve the goals of the LLC.
Thus, the following actions are considered unfair:
- ignoring responsibilities regarding settlements with the budget, which led to the imposition of penalties on the LLC;
- unjustified termination of employment contracts with subordinates, which entailed the payment of due funds to those dismissed and, if they filed a lawsuit in court, payment of legal costs, as well as compensation for damage caused;
- illegal receipt of excess benefits through an unauthorized increase in salary, resulting in the LLC causing losses or bankruptcy;
- others (for example, these include insufficient control over the actions of subordinates, which led to the unprofitability of the LLC).
How does the tax office detect tax evasion?
During desk and field tax audits. We will not go into these details now. Let's pay attention to the timing. If arrears are identified, inspectors make demands for payment of taxes:
- two months are given to the business to pay upon request from the inspectorate;
- 10 days to transfer information to the investigative committee if the company has not paid the arrears;
- a month to conduct a pre-investigation check and decide whether to initiate a criminal case;
- two months to investigate the criminal case. However, in practice, these deadlines are not observed and the investigation of the case can take six months or a year.
In practice, approximately 2.5–3 years pass from the start of an on-site tax audit to the verdict.
Responsibility of the General Director for non-payment of taxes
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Vladislav Ivanovich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in family law. Knows everything about the law.
The Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, in particular, Ch. 22 provides for all possible types of economic crimes for which a manager may be responsible. Among them, the most frequently committed is evasion:
- transfers of taxes (Article 199 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);
- fulfillment of obligations assumed as a tax agent (Article 199.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation);
- coverage of all available sources of funds subject to taxation (Article 199.2 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, paying taxes later than the deadline specified by tax legislation may also result in criminal liability.
The limitation period for prosecution is calculated from the moment of actual non-payment of tax.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 78 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the limitation periods for all the above offenses are:
- 2 years – for a crime under paragraph 1 of Art. 199 and 199.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation;
- 6 years – for the crime mentioned in Art. 199.2 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation,
- 10 years – for a crime recorded in paragraph 2 of Art. 199 and 199.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Liability provided for by the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation
The most serious violations of the law entail the imposition of punishment provided for by the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Offenses, the commission of which is fraught with criminal punishment, must have all the elements of a crime. Moreover, to attract this type of legal liability, all components of the crime must be present. During the investigation, special attention is paid to the subjective side of the crime, namely the presence of guilt.
As judicial practice shows, most often enterprise managers are punished for committing economic crimes, namely:
- obtaining a loan through illegal means. This refers to the use of false documents, misuse of credit funds, providing false information in order to obtain a loan;
- promoting deliberate bankruptcy;
- violations of tax legislation, in particular tax evasion. It does not matter whether the manager performed these actions independently or whether another person did it under his pressure. In the second case, punishment threatens both the general director and the direct executor;
- evasion of duties of a tax agent.
If the general director of an LLC evades taxes in several organizations of which he is the head, the punishment is imposed taking into account the rules of the totality of crimes.
Responsibility of the General Director for LLC debts from 2021
A feature of the management of the LLC is that neither the manager nor the founders are liable for the debts of the Company (clause 1 of Article 87 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The only thing they risk is the assets they contributed as a share in the management company.
However, it is worth distinguishing between debts resulting from the influence of the business environment and debts to creditors that arose due to the intentional introduction of the LLC manager into a state of bankruptcy, for the repayment of which the legal entity does not have enough assets (and, according to Article of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, it is liable for all debts your property).
In the second case, from 2021, the general director of the LLC is held vicariously liable as part of a bankruptcy case of a legal entity and repays debts to counterparties from his own funds (but only if the court decides that their amount should be collected from him into the total bankruptcy estate).
However, for the following property defined in Art. 79 Federal Law No. 229 dated October 2, 2007, the penalty is not applied.
the only dwelling and the land below it;
- personal items not related to luxury items;
- means of carrying out professional activities;
- other property specified in Art. 446 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
- the execution or approval by the manager of transactions that infringe on the property rights of creditors of the bankrupt LLC;
- damage to financial and reporting documentation, making it impossible to carry out procedures provided for by bankruptcy legislation
The direct involvement and interest of the LLC director in bankruptcy will be proven if at least one of the conditions listed in paragraph 4 of Art. 10 Federal Law No. 127 of October 26, 2002, in particular:
Also, the basis for bringing the general director to such liability will be his ignoring the procedure and deadlines for filing an application for financial insolvency (clause 2 of article 10 of Federal Law No. 127).
If the submitted application is unfounded, then the manager is also responsible for the damage caused to creditors by the initiation of bankruptcy proceedings (Clause 3 of Article 10 of Federal Law No. 127).
Thus, the general director is responsible for causing damage not only to the LLC, but also to third parties.
Responsibility of the manager established by labor legislation
The financial liability of the general director of an LLC is established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. According to the norms of this regulatory legal act, the manager is obliged to compensate for losses incurred by the enterprise as a result of his unlawful or unreasonable actions. The possibility of collecting funds from the general director is provided for in paragraphs 277 of Article of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Note! The financial liability of the general director arises by force of law, that is, its application is not affected by the presence or absence of such a clause in the employment contract, nor by the fact of concluding an additional agreement on financial liability.
Consequences of appointing a nominee general director by the founders
Some founders believe that hiring a “nominee” general director who has nothing to do with the management of the business entity and exercising independent management through him will help avoid liability. Such a measure is not only ineffective, but also implies certain risks borne by the owner.
Firstly, he can be held accountable if the fact of shadow leadership is revealed (this point is mentioned in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated July 25, 2013 No. AS-4-2/13622, regarding on-site inspections).
Secondly, he may be denied registration of an LLC whose general director is appointed nominally (1.4 letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 8, 2015 No. GD-4-14 / [email protected] )
In addition, the nominee director also faces liability under the law for dishonest actions.
Intent for non-payment is the most important condition for initiating a criminal case against the director
All tax crimes are committed with direct intent. This is when the company's top managers:
- realized that they were not paying taxes, although they were required by law to do so;
- understood that they were breaking the law;
- carried out actions aimed at non-payment of taxes.
What are actions aimed at non-payment of taxes? Creation of one-day companies and subsequent work with them, artificial fragmentation of a business without a business purpose, failure to register some employees as employees so as not to pay insurance premiums for them, and so on.
The Investigative Committee and the Tax Service are faced with the task of proving that taxes were not paid intentionally. In this case, the tax office will be able to impose a fine of 40%, and the Investigative Committee will have the opportunity to initiate a criminal case. How is intent proven in practice? Using the procedures described in the Code of Criminal Procedure and the Tax Code, such as:
- taking testimony;
- search of the office;
- notch;
- requesting documents from the company itself and its counterparties;
- requests to the bank;
- conducting financial and accounting examinations.
A classic example: the tax office or investigators seized the company’s computer and found documentation there on behalf of a disputed counterparty. The properties of the file indicate that it was compiled by employees of the company being audited, which means that the counterparty is fictitious and taxes were not paid intentionally. After all, fictitious document flow is created only intentionally.
Back in 2021, the Tax Service and the Investigative Committee issued a joint letter dedicated to proving intent to commit a tax crime.
Is it possible for the CEO to avoid liability?
When taking office, the CEO must make sure that there was nothing criminal in the work of his predecessor. In this way he can protect himself from liability. To do this, you should follow this procedure:
Create a commission for delegation of powers, indicating responsible persons and deadlines.
Thus, the general director is responsible for virtually all processes occurring both within the business entity and outside it (in terms of settlements with counterparties). For ignoring or negligent performance of his duties, he may be subject to financial, administrative or criminal liability.
A limited liability company is a company that can be owned by several founders. The organization is managed solely by an elected general director.
The CEO, as an official, is responsible for all aspects of business activities. Dismissal from a position does not relieve the manager of responsibility for the decisions he makes.
- Responsibility of the CEO after dismissal
- Administrative
- Criminal penalty
- Material liability
- For debts
- How long does liability last after dismissal?
- “Safety rules” for the general director of an LLC
- Infographics: administrative or criminal?
- The legislative framework
“Safety rules” for the general director of an LLC
- The directors of the organization are considered to be the director of the company, his deputies, the chief accountant and the chief engineer. All of them are responsible for their decisions within the scope of their competence.
- The general director must monitor the legality of not only his actions, but also the decisions of his subordinates.
- The list of violations in this article includes only the main violations, although liability may also arise for other violations of environmental, technical and labor legislation in the activities of the company.
The specificity of the responsibility of top management is that it is responsible for the activities of the entire organization. Therefore, it is necessary for a new CEO to check the legality of his predecessor's activities before taking office. Otherwise, he will become an accomplice to ongoing offenses and will be jointly responsible for them.
Sources
- https://kopomko.ru/trudovoe-pravo/vidyi-otvetstvennosti-generalnogo-direktora-posle-uvolneniya-za-chto-i-kak-dolgo-dlyatsya
- https://delatdelo.com/organizaciya-biznesa/otvetstvennost-generalnogo-direktora.html
- https://otrude.com/uvolnenie/direktora/otvetstvennost-i-obyazannosti-pered-ooo-posle-uhoda/
- https://www.Yurist-online.net/article/778/otvetstvennost-generalnogo-direktora-posle-uvolneniya
- https://truddogovor.ru/vidy-otvetstvennosti-gendirektora-posle-uvolneniya/
- https://www.buhgalteria.ru/article/srok-iskovoy-davnosti-dlya-direktora-i-bukhgaltera
Responsibility of the CEO after dismissal
As the sole head of the organization, the CEO has extensive job responsibilities in accordance with his area of competence. When a director is dismissed and replaced by a new one, the responsibility of the displaced manager does not disappear.
The general director bears responsibility for all offenses during his reign until the statute of limitations expires in proven cases. The director bears the consequences of decisions made regardless of the reason and circumstances of leaving office.
The director is also punished in cases where, when examining accounting documents and reporting, their incompleteness or unreliability is revealed. According to Article 227 of the Labor Code, liability for the general director is provided for in case of neglect of duties or violation of the company's charter.
Also, the director bears personal and joint liability for any criminal acts committed by him, his deputies, the chief engineer or accountant.
Administrative
The administrative responsibility of the organization and its leader are separate sanctions imposed independently of each other. The director responds with fines under certain articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses prescribed for officials. Administrative penalties are divided into the following categories of penalties:
- penalties;
- disciplinary;
- administrative.
The widest list of violations involves the introduction of penalties. Collection of up to 5,000 rubles is provided for under the following articles of the Administrative Code:
- for violation of consumer rights and sanitary standards (Articles 6.3, 14.7 and 14.15);
- for illegal lending (Article 14.11);
- for minor violations of tax legislation (Articles 14.1, 14.5,15.1, 15.3-6, 15.11, 15.25).
Fines from 5 to 30 thousand rubles are provided for violations of articles of the Code of Administrative Offenses:
- regarding antimonopoly norms (Articles 14.10 and 14.33);
- for conducting a fictitious bankruptcy procedure (Article 14.12);
- sale by an organization of low-quality services and goods (Article 14.4);
- refusal to cooperate with authorities (Articles 15.25, 19.7.3 and 19.8);
- failure to comply with the procedure for holding general meetings (Article 15.23.1);
- violations of state registration of LLC (Article 14.25);
- violation of customs clearance rules (Article 16);
- violation of the rules for advertising placement (Article 14.3).
In parallel with a fine of 5-30 thousand rubles. The manager may be disqualified for 3 years.
Large fines from 30 thousand rubles to the amount of the illegal transaction are provided for violations of the Code of Administrative Offenses:
- violation of fire safety rules (Article 20.4);
- violation of migration legislation by hiring unofficial labor (Articles 18.9 and 18.15);
- carrying out illegal currency transactions (Article 15.25).
Sanctions for such violations additionally require other types of penalties.
Expert opinion
Mikhailov Vladislav Ivanovich
Lawyer with 6 years of experience. Specializes in family law. Knows everything about the law.
In addition to financial punishment, there is a separate category of administrative punishment for the manager - disqualification. This measure involves entering a note in the work book about the ban on holding any leadership positions.
Disciplinary action is not regulated by law - the decision to apply it is made at the general meeting of founders for any misconduct and promises the dismissal of the director at the initiative of the employer.
Criminal penalty
Criminal liability arises for the director if he commits offenses that entail a violation of the rights of citizens or serious economic consequences for the organization. Such acts are punishable by prison terms and particularly large fines.
The list of acts of the general director for which criminal punishment is imposed is specified in the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Many articles of criminal punishment are reflected in administrative legislation.
For example, for violation of the rules for registering a legal entity and fictitious bankruptcy, both administrative (up to 1.5 million rubles) and criminal liability are provided.
The general director bears personal criminal liability in cases of violation of the following legislative norms:
- refusal to hire or dismissal of a woman with a baby in accordance with Art. 145;
- delay of salary for more than 2 months for mercenary purposes under Art. 145.1;
- copyright infringement under Art. 146, 147;
- abuse of official powers under Art. 201;
- commercial bribery under Art. 204 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Economic crimes for which the director of an organization is criminally liable are listed in Chapter 22 of the Criminal Code. The general director may also be personally liable for the organization’s violation of tax laws, but only if the debt is more than 2 million rubles. over a period of 3 years.
Sanctions of the criminal code for the director of an organization are imposed depending on the nature and severity of the crime and are divided into minor and serious, implying the following punishments:
- fine up to 300 thousand or up to 1 million rubles;
- arrest up to 6 months;
- community service up to 480 hours or up to 5 years;
- imprisonment for up to 7 years or up to 12 years.
Depending on the severity of the crime, the statute of limitations for an offense is 2 years for a minor crime, 6 years for a serious crime and more than 6 years if intentional acts caused particularly large damage.
Material liability
The head of the organization bears joint responsibility for the activities of the chief accountant of the enterprise on the basis of the signature under the reporting documents. To avoid abuse, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for financial liability for the director for erroneous decisions.
If direct losses are caused, the general director must compensate losses and expenses to the affected persons. Income not received due to proven erroneous actions or inaction of the director shall be compensated at the expense of the responsible official.
Negligent actions of the director, followed by financial liability, and its amounts for them are prescribed in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
For debts
The director can also be held financially liable by creditors who have suffered losses and proven the extent and degree of guilt of the general director through the court. In the legal form of a limited liability company, the debts of the legal organization are transferred to the director only within the limits of the authorized capital and his share in the company.
Creditors can collect debt in excess of this amount only by proving intent to bring the organization to insolvency, using Law No. 127 Federal Law.
conclusions
Almost any on-site tax audit leads to the initiation of a criminal case against the director of the company.
The Criminal Code contains several elements of tax crimes. In case of VAT refund from the budget, the case may be initiated under Art. 159 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation - “Fraud”.
Tax crimes fall under the jurisdiction of the Investigative Committee. This authority may receive information about a tax crime from various sources, but usually from the tax office, which conducted a tax audit and identified violations. Information may also come from the police or citizens who have filed a statement about tax violations by the company.
If a criminal case has already been initiated or a pre-investigation investigation is underway, then it is better to hire an experienced lawyer who will help you choose defense tactics and knows the nuances of procedural law.