Dismissal by agreement of the parties presupposes the existence of an agreement between the parties to the employment relationship. Despite the similarity with voluntary dismissal, when terminating employment for this reason, there may be differences in monetary settlements with the employee.
Sometimes termination of a contract by agreement of the parties precedes mass layoffs or liquidation of the enterprise. Therefore, in some cases, dismissal may be accompanied by the payment of severance pay.
Features of providing severance pay
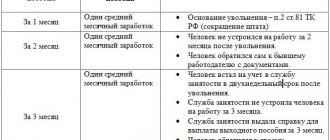
178 art. The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes that a laid-off employee can count on the provision of certain guarantees in the form of severance pay:
- For the first month from the date of termination of relations with the employer due to layoffs (entitled to each laid-off person, payable on the last working day);
- For the second month, if employment does not occur at the time of its end (the absence of a new job should be documented by providing a work book (you need to make a photocopy of the document) in which there are no new employment records, the benefit is paid at the request of the employee provided after the end of the 2nd month month, the application is drawn up in free form, addressed to the head of the company);
- For the third month, if a new job is not found even with the help of the employment service (you must have a written decision made by this service, compliance with the conditions for registering the employee with this service within 2 weeks from the date of termination of relations with the employer is required).
The deadlines for paying amounts for the second and third months have not been established, and therefore the former employee and the company management should independently agree on when this obligation will be fulfilled - this may be the nearest payday or another date.
The above type of payment is due to a laid-off person for the period of new employment due to his lack of work due to forced dismissal.
If a part-time worker with a main job is to be laid off, then he is not entitled to severance pay, since he has a job, and the laid-off person does not need employment.
If the part-time worker does not have a main place of work, then in case of layoffs at the part-time job, it is necessary to issue severance pay in the standard manner (up to 3 months from the date of termination of work).
When is the payment made?
Payment to the employee occurs on the basis of a dismissal order . If it is drawn up in free form, then it is necessary to include in it an additional order on the payment of severance pay. The amount and timing of the payment of funds to the employee are indicated.
The payment is carried out in accordance with the calculation note in form T-61, approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1. Information from:
- employee personal card;
- report card;
- pay slips;
- management orders regarding dismissal.
If an employee does not agree with the accrued amount, he can contact the organization’s management with a request for recalculation. Upon receipt of a refusal, if there is substantiated evidence, he can file a claim with the judicial authorities.
If the payment of severance pay is stipulated in local regulations, an employment contract or an additional agreement, then these documents specify the terms and methods for issuing funds to the employee. Typically, employees are paid off on their last working day. However, by agreement of the parties, it is possible to pay severance pay after dismissal within a specified time frame in a specified amount.
Payment of severance pay upon dismissal by agreement of the parties is made only if there is such an agreement with the organization. The amount can be fixed or calculated based on average monthly earnings. Cash is issued to the employee within the terms established by the agreements or on the last day of work.
Amount of severance pay
This payment is assigned in the amount of average monthly earnings , the amount of which is influenced by the time that the employee actually worked and the payments that he actually received. Moreover, for all three months the procedure for determining monthly earnings is the same.
To calculate these values, 12 calendar months preceding the month in which the reduction was documented are taken.
To calculate this value, you need to calculate the average earnings per day, and then multiply by the number of working days for the employee in the month for which the payment is made. That is, the amount of severance pay is affected by the specific month of calculations and the number of working days in it.
Common calculation errors
Error 1: To calculate average earnings, calendar days worked are taken, not working days.
It is important to take exactly the actual time worked in accordance with the employee’s schedule. It excludes weekends, holidays, vacations, sick leave, and maternity leave.
Error 2: The number of working days subject to payment does not include holidays.
It is important to include non-working holidays in the period for paying severance pay, if they fall within it. For example, if the layoff date is October 20, 2020, then you need to pay for the period from October 21, 2020 to November 20, 2020, which includes 22 working days and 1 non-working holiday. Thus, severance pay will be calculated as the product of average earnings by 23 days.
Calculation procedure
Calculation formulas
Severance pay = average daily earnings * number of working days in the month for which the payment is made.
Average daily earnings = salary for the billing period / number of days worked in this period.
Thus, to calculate severance pay, it is necessary to determine the following values:
- Billing period;
- The number of days that the employee actually worked;
- Total salary;
- The number of days recognized as working days in the month for which benefits are paid.
Calculated period of severance pay
The 12 calendar months preceding the month in which the employee is laid off are taken. For example, if an employee was laid off in May 2016. The estimated time period will be taken from 05/01/15 to 04/30/16.
Actual days worked
The calculation takes into account the working days when employees actually performed their work functions.
Time spent is not taken into account: (click to expand)
- On annual leave;
- On a sick leave.
Total salary
You should sum up the employee’s salary accrued to him in each month of the billing period in accordance with the remuneration system established for him.
Not taken into account:
- Vacation pay accrued for annual main leave;
- Payment based on certificates of disability.
If the month is not fully worked, the salary should be determined corresponding to those days when the employee actually performs his work functions. To do this, the salary is multiplied by the number of days of the month that the employee actually worked and divided by the total number of days in this month recognized as working.
How to determine the duration of the billing period and the accrual amounts to be taken into account
The methodology for calculating the worked period is regulated by clauses 4 and 5 of Resolution No. 922. For these purposes, under any circumstances, a time period of 12 months before the month of termination of the employment relationship is applied. Moreover, if an employee leaves on the last day of the month, then he is also included in this period. The resolution clearly defines what time and what accruals are not included, and what is included in the calculation of the average employee’s salary.
It is possible that an employee had no earnings in the 12 months preceding the month of payment of benefits. In this case, it is necessary to use for calculations a similar period preceding the calculation period.
Example of calculating severance pay
An order to lay off storekeeper A.A. Bulkin has been prepared. The date of his dismissal is 05/25/2016. 05/27/2016 Bulkin registered at the employment center as an unemployed person. As of August 24, 2016, Bulkin was not employed due to the lack of a suitable workplace, despite the assistance of the employment service in finding employment.
The remuneration system prescribed for the position of storekeeper includes only the payment of a salary of 40,000 rubles. From November 2, 2015 to November 29, 2015, he was on basic leave, for which he was accrued vacation pay. From December 15, 2015 to December 22, 2015, he was on sick leave, for which he provided the corresponding certificate from the medical institution.
Bulkin worked a 5-day work week.
The employer’s task is to calculate severance pay for 3 months after dismissal (Bulkin provided all the necessary documentation).
Calculation: (click to expand)
- Billing period – from May 1, 2015. until April 30, 2016;
- The number of days actually worked during this time = 247 – 20 – 6 = 221 days (since Bulkin has a 5-day working week, in the indicated period 247 working days are provided for him, among which Bulkin rested 20 working days in November and 6 working days I was sick for days in December).
- Total salary = salary * 9 months. + salary in November 2015 + salary in December 2015 + salary in May 2021 = 40000*9 + 40000*(1/21) + 40000*(17/23) + 40000*(18/22) = RUR 424,197.25
- Average daily earnings = 424,197.25 / 221 = 1,919.44 rubles.
- Severance pay for the period from 05/26/2016 to 06/25/2016 = 1919.44 * 20 = 38388.80 rubles.
- Severance pay for the period from June 26 to July 25 = 1919.44 * 21 = 40308.24 rubles.
- Severance pay for the period from July 26 to August 25 = 1919.44 * 23 = 44147.12 rubles.
The total benefit to be issued to Bulkin based on the results of 3 months = 38388.80 + 40308.24 + 44147.12 = 122844.16 rubles.
The amount of the payment made can be increased at the request of the employer, as well as when the increased benefit amounts are stipulated in the employment agreement, collective agreement or other internal documentation of the company.
Payments to union members
Employees who were elected to the trade union and released from their main job are paid the average salary not by the organization, but by the all-Russian (interregional) trade union in the following order.
Their average earnings for the period of employment, but not more than six months, are retained upon dismissal due to:
- the inability to provide the previous or other equivalent job (position) at the end of the employee’s term of office in the trade union;
- liquidation of the organization.
If an employee undergoes retraining or training, then his average salary can be retained for up to a year after dismissal.
Such rules are established by Article 375 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Severance pay and personal income tax
The amount of the benefit paid is subject to taxation if it is more than 3 times the average monthly earnings. This event is possible if the company’s internal documentation (for example, a collective agreement) establishes an increased amount of payment for laid-off employees.
If the employer is guided only by the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and calculates severance pay in an amount equal to 3 times the monthly salary, then personal income tax does not need to be withheld from this payment.
There is also no requirement to charge compulsory insurance contributions on the benefit amount within three monthly earnings. From the amount accrued above the specified amount, contributions must be calculated and transferred to the fund accounts.
Payments in the Far North
Average earnings for a period of employment of up to three months (including severance pay) are retained for employees who work in the Far North and equivalent areas upon dismissal due to:
- liquidation of the organization;
- staff reduction.
Unlike the general rule, such employees do not need a decision from the employment service to maintain their average earnings for the third month of employment. This is stated in Part 1 of Article 318 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, the average earnings in these cases can be retained for such employees for a period of up to six months based on the decision of the employment service. This is possible if, within a month after dismissal, the employee contacted this service, but was not employed by it. These are the rules of Part 2 of Article 318 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
A similar procedure for dismissal due to liquidation of an organization or reduction of staff applies to employees working:
- in areas not classified as regions of the Far North and equivalent areas, but included in the list of territories where regional coefficients and percentage increases in wages are paid (determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of November 11, 2005 No. 53-B05-9). For example, in the southern regions of the Irkutsk region and Krasnoyarsk Territory;
- on the territory of closed administrative-territorial entities (clause 4 of article 7 of the Law of July 14, 1992 No. 3297–1).
Penalties for late payments
On October 3, 2021, amendments to Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, which tighten liability for late payment of wages, vacation pay and other amounts due to the employee. Therefore, if within a year from the date of the violation the company is visited by the State Tax Inspectorate, it may be brought to administrative liability (Article 4.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses establishes the statute of limitations for violations).
Delays in the payment of wages, compensation for unused vacation, and bonuses upon dismissal entail financial liability for employers under Art. 236 TK. From October 3, 2021, this amount of compensation is one hundred and fiftieth of the current refinancing rate for each day of delay in amounts not paid on time. Moreover, the employer’s liability for delays in amounts due to the employee occurs automatically.
Moreover, if the employer still does not pay the money, then during the inspection it will be revealed that he has a continuing offense, for which the State Tax Inspectorate has the right to bring administrative liability within a year from the date of discovery of this violation.
What is an abbreviation
There are two types of layoffs in which employees are laid off. This is downsizing and downsizing. When downsizing, the number of employees in a particular department is reduced. For example, out of three legal advisers they decide to retain only one. This means two will be laid off. But when staffing is reduced, a specific unit or all identical staff units must be eliminated. For example, reduction of the logistics department or reduction of all secretaries.
In any case, redundancy is a rather lengthy procedure that requires documentation and payment of benefits when staffing or numbers are reduced. And to do this, you need to know how severance pay is calculated when staffing is reduced.
Rules for paying compensation for unused vacation
Upon dismissal, the employee is paid compensation for all unused vacations (Article 127 of the Labor Code). In matters of calculation, counting vacation days that an employee has earned, determining the period for which compensation must be paid for unused vacation, and applying the rules for determining this period, one must be guided by the Rules on regular and additional vacations (approved by the People's Commissariat of Labor of the USSR on April 30, 1930 No. 169).
If an employee quits during the first working year, the rules of clause 28 apply: “When dismissing an employee who has not used his right to vacation, he is paid compensation for unused vacation. At the same time, employees dismissed for any reason who have worked for this employer for at least 11 months, subject to credit towards the period of work giving the right to leave, receive full compensation.”
Thus, if in the first working year a person worked for 11 months and decided to quit, then he is entitled to compensation for vacation as for 28 calendar days.
If an employee leaves during the first year of work due to a reduction in staff or numbers, the employer must also focus on the Rules on regular and additional leaves. They, in particular, state the following: full compensation is received by employees who have worked from 5 1/2 to 11 months if they are dismissed due to the liquidation of the enterprise, reduction of staff or work.
Cases of staff reduction occur quite often. And usually employees who have been recently hired are usually laid off. That is why questions often arise about determining the days for which compensation for unused vacation is due. According to the Rules on regular and additional leaves, in this case full compensation must be paid. The Letter of Rostrud dated 08/09/2011 No. 2368-6-1 also reminds us of this.
Clause 35 of the Rules states that “when calculating the terms of work that give the right to proportional additional leave or compensation for leave upon dismissal, surpluses amounting to less than half a month are excluded from the calculation, and surpluses amounting to at least half a month are rounded up to full month." At the same time, when applying clause 35, it is important to remember that since an employee earns the right to vacation during the working year, vacation begins to be calculated from the date of conclusion of the employment contract.
So, if an employee was hired on June 17, 2021 and quits on August 30, 2021, then when calculating the length of service giving the right to leave, the following calculation is obtained: first month - from 06/17/19 to 07/16/19; second month - from 07/17/19 to 08/16/19; third month - from 08/17/19 to 08/30/19. Since the third month has not been fully worked, compensation for unused vacation is paid only for two months.
Is it possible for early departure at the request of the employee?
As is known, by law the manager must notify employees who are subject to staff reduction 2 months before the upcoming termination of contracts.
That is, the person is warned, then he works for another 2 months as usual, and only after this period he is fired and the required amounts are paid, including severance pay.
It is possible that the employee subject to layoff does not want to wait for the notice period to expire.
If a citizen does not need severance pay, then you can simply write a letter of resignation of your own free will (clause 3 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and, after working for 2 weeks, resign with payment of salary and vacation pay compensation. Of course, on this basis, the dismissed person will not receive severance pay.
If a person still wants to receive an additional payment, then you can try to negotiate with management about early dismissal, but with the issuance of severance pay. In this case, you need to write an application for early dismissal due to staff reduction.
If the director is ready to accommodate and fire ahead of schedule, then he has the right to do so. If the manager does not want to do this, then he has every right to do this, then he will either have to leave of his own free will without severance pay, or continue to work until the expiration of the two-month period before the day of reduction.
Thus, severance pay can be paid in case of early dismissal, but only if an appropriate agreement is reached with management.
Payments to consider
Payments due to employees who have been laid off include:
- Severance pay, which is paid one-time during dismissal, should be at the level of the average official salary. If the employment contract states that redundancy benefits must be paid in an increased amount, then the employer must make such a payment.
- Social assistance based on the average salary, which is retained by the citizen for the period of searching for a new job.
Social assistance in some cases can be extended for another month, but such a decision is made by the employment authorities. A citizen must contact the employment authorities within two weeks, which includes both working days and weekends, starting from the date following the date of dismissal.
The payments include the amounts of remuneration stipulated in the second paragraph of the Regulations on the specifics of the procedure for calculating the average salary.
At the same time, when calculating the reduction benefits and average earnings, compensation is not accepted.
They take into account those payments characteristic of remuneration (salary), and which are recognized as such by Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Salary includes payment for work depending on the employee’s qualifications, quality, complexity, quantity and working conditions. This also includes compensation and incentive payments (bonuses, additional payments and allowances and other incentives).
Compensation is considered to be monetary payments established for the purpose of reimbursing employees for costs associated with the performance of labor or other duties determined by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other regulations (Article 164 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, monetary compensation for vacation is classified as compensation payments, and therefore it is not taken into account when calculating average earnings. In addition, you need to know that compensation is accrued on the day the employee is dismissed, which means it is not included in the payments taken into account for the calculation period.
You should pay attention to the following point.
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, if an employee falls ill within thirty days from the date of dismissal due to reduction, then he can turn to his former manager for additional payment due to “temporary incapacity for work.”
The employee must be notified of layoffs due to the closure of the enterprise two calendar months before the date of liquidation of the company. In this case, the employee has the right to resign earlier, but financial assistance is not provided, or wait until the enterprise is liquidated and receive payment.
If the boss dismisses an employee before the liquidation of the company, then he is entitled to a larger compensation (this also includes a one-time payment equal to the average salary for the period from the date of dismissal until the termination of the organization’s activities).
The redundancy payment and all compensation due to it are paid on the day the citizen is dismissed.
Answers to questions from our readers
¿ Question 1 from Nikolay: an employee pays alimony for his child, if his staff is reduced, he is assigned severance pay, is it necessary to withhold alimony from him >>> answer.
¿ Question 2 from Anna Vitalievna: an employee is drafted into the army for military service, does he need to be paid severance pay and in what amount >>> answer.
¿ Question 3 from accountant Olga: please explain when it is necessary to pay an employee wages for three months, and when for two weeks >>> answer.
How to formalize the dismissal of an employee during staff reduction in 2019
When dismissing personnel due to a reduction in numbers or staff, the requirements established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation must not be violated. They are spelled out in Articles 179 and 180. Even a minor violation of the procedure may result in the employee being reinstated in his position with payment for forced absence in accordance with Article 394 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
The employer must follow the following algorithm:
- issue an order to reduce numbers or staff;
- find out whether any employee has a priority right to keep his job;
- draw up a list of positions (employees) that need to be reduced;
- write a notice of dismissal;
- offer the laid-off employee an alternative in the form of a transfer to another place;
- approve the transfer of employees who have agreed to another position;
- notify the labor exchange and trade union organization of the upcoming layoff;
- coordinate with the trade union a resolution on the dismissal of its members;
- make payment of compensation and severance pay;
- dismiss employees who refuse to be transferred to another location.
Sample order for reduction: