General concepts
Successful business conduct is impossible without a detailed analysis of the financial and economic indicators of the economic activity of an economic entity.
In order to assess the property and financial position of an organization and make the right management decisions in a timely manner, it is necessary to determine important solvency and profitability ratios. One of the key calculation indicators is the calculation of the value of net assets on the balance sheet. The organization's net assets (NA) are the amount of funds of an economic entity, determined by calculation, which will remain at the disposal of the company after full repayment of debt obligations. In other words, the value of net assets is calculated as the arithmetic difference between the total indicators of the company’s property, material and financial assets and assumed liabilities.
Note that calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is mandatory for organizations. The indicator is calculated once a year based on accounting data. Indicators are reflected in the third section of the report on changes (movements) of capital; net assets are (in the balance sheet) line 360 of this reporting form.
How to Determine Fair Value
IFRS 13 identifies three approaches to determining the fair value of an asset. An organization may use one or more of these approaches (clause 62 of IFRS 13).
Market approach
This is the simplest and most popular approach. Most often, if fair value can be determined using the market approach, other methods are not used or considered.
An asset is worth as much as the same or comparable assets, taking into account adjustments, are worth on the market.
Valuations use prices and other information based on the results of market transactions for the same or similar assets, liabilities, or a group of assets and liabilities, such as a business.
Income approach
The most difficult and labor-intensive approach in practice. It involves complex financial models using many input parameters and cumbersome calculations.
The asset is worth as much as the money it is capable of bringing in in the future during its entire operation is worth now.
The approach uses valuation techniques that convert future amounts, such as cash flows or income and expenses, into a single current (discounted) value. Fair value is measured based on the value indicated by the market's current expectations of specified future amounts.
Cost-effective approach
This approach is easier than the income approach, but it can be very difficult or even impossible to obtain high-quality input data. Therefore, it is also used less often than the market one.
The asset is worth as much as it would take to buy or build another one of the same kind.
The cost approach uses a valuation method that reflects the amount that would be required now to replace the operating capacity of the asset (often called current replacement cost).
Formula for calculating net assets
The key procedure for calculating the value of net assets on the balance sheet is determined by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and is presented in a separate order No. 84n dated August 28, 2014. Please note that previously a different procedure was in effect, but it is not currently used.
This formula for net assets on the balance sheet is applicable to the following range of economic entities:
- public or non-public joint stock companies;
- state or municipal unitary enterprises;
- limited liability companies;
- production cooperatives or housing cooperatives;
- business partnerships.
Net assets formula:
NA = (AO - DU - ZA) - (OB - DBP),
Where
- JSC - the amount of non-current and current assets of an economic entity as of the reporting date;
- DE - debt of the founder incurred to the enterprise for the formation of the authorized capital;
- FOR - debt on own shares generated upon issue;
- OB - the sum of the company's short-term and long-term liabilities;
- DBP - future income in the form of state financial support or gratuitous transfer of property assets.
How to calculate net assets according to balance sheet lines?
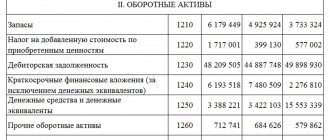
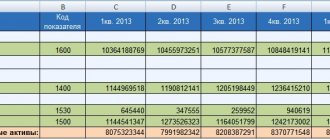
To calculate the net asset value on the balance sheet, the calculation lines use the following:
NA = (line 1600 – DU) – (line 1400 + line 1500 – DBP).
Calculating the amount of net assets in the balance sheet (the lines indicated above) using a pencil calculator is not enough. This calculation must be documented. However, a unified form for reflecting calculated data is not provided for in Order No. 84n. Organizations are required to independently develop a form and regulate it in their accounting policies.
Note that before the approval of Order No. 84n, the old form was in force (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 10 and the Federal Commission for the Securities Market of Russia dated January 29, 2003 No. 03-6/pz). In the new instructions, the Russian Ministry of Finance has not prohibited the use of this form, therefore, firms can use it to prepare calculations of net assets in the balance sheet (the document lines contain all the necessary information).
When is fair value determined?
The fair value of assets must be used from the beginning of 2021; this requirement is enshrined in FAS 5/2019 “Reserves”, approved.
By Order of the Ministry of Finance dated November 15, 2019 No. 180n. From 2022 there will be even more such situations. Here's when this type of assessment comes into play:
| When to Determine Fair Value | Which assessment to use | Base |
| Mandatory from January 1, 2021, but can be applied earlier | ||
| Acquisition of inventories under contracts providing for the fulfillment of obligations (payment) in whole or in part in non-cash | Fair value of transferred property, property rights, works, services or Fair value of the inventory acquired if the first option is not possible | clause 14 FSBU 5/2019 |
| Free receipt of supplies | Fair value of inventories received | clause 15 FSBU 5/2019 |
Initial and subsequent assessment:
| Fair value of such inventories | clause 19 FSBU 5/2019 |
| Mandatory from January 1, 2022, but can be applied earlier | ||
| Valuation of fixed assets at revalued values | Fair value of such fixed assets | clause 15 FSBU 6/2020 |
| Capital investments under contracts providing for the fulfillment of obligations (payment) in whole or in part in non-cash | Fair value of transferred property, property rights, works, services or Fair value of acquired property, property rights, works, services included in capital investments, if the first option is not possible | clause 13 FSBU 26/2020 |
| Property included in capital investments that the organization receives free of charge | Fair value of this property | clause 14 FSBU 26/2020 |
| Products, secondary raw materials, and other material assets that are received during capital investments and that the organization intends to sell or otherwise use And Material assets remaining unused when making capital investments | The fair value of such assets (or their net realizable value, the cost of similar assets), but not higher than the amount of costs from which this value is deducted | para. 2, 3 clause 15 FSBU 26/2020 |
| Other (non-monetary) consideration provided by the tenant under the lease agreement | Fair value of consideration determined at the date of provision of the leased asset | pp. “c” clause 7 FSBU 25/2018 |
Cost of the rental item:
| Fair value of the leased item | clauses 12, 15, 25, 26, 33-35, 50 FSBU 25/2018 |
In these cases, determine fair value according to the rules established by IFRS. The main standard is IFRS 13 “Fair Value Measurement”, put into effect in the Russian Federation by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated December 28, 2015 No. 217n.
How to calculate net assets on a balance sheet, example
Let's look at a specific example of how to calculate net assets on a balance sheet.
Vesna LLC prepared annual financial statements, including a balance sheet in the OKUD form 0710001.
Based on the balance sheet data, the following calculations were made:
NA = (13,800 +19,283 – 0) – (12,930 – 0) = 20,153 rubles.
Calculation of fixed assets
Fixed assets of a company are defined as part of the company's property that is used to meet production needs for more than one year. They are not goods and are used for commercial purposes. Their acquisition occurs in large transactions. For an objective assessment, three types of cost are used:
- balance sheet;
- residual;
- restorative.
The total book value is determined by the purchase price plus expenses. Residual value is calculated as the difference between the original price and depreciation. Replacement cost is determined based on the current market price. In the balance sheet, the cost of fixed assets is reflected in line 1130.
Analysis of indicators
Having completed the arithmetic calculations, we move on to analyzing the result obtained. With a positive amount of net assets in the balance sheet, we can conclude that the company is profitable and has high solvency. And, accordingly, the higher the indicator, the more profitable the enterprise.
Negative net assets are an indicator of the low solvency of an enterprise. In other words, a company with a negative NAV will most likely go bankrupt soon; the company will simply have nothing to pay off its debts. However, in such a situation, exceptional circumstances must be taken into account. For example, the company has just been formed and has not yet covered its costs, or the company received a large loan for expansion.
An increase in net assets can be achieved by increasing the authorized, reserve or additional capital or by reducing the founder’s debts to the enterprise.
What is the book value of assets used for?
The resulting calculation is used to solve a large number of issues, but first it is a financial analysis of the profitability of the enterprise. By studying it, you can find out how much each ruble spent will bring.
Also, the book value is the basis for calculating the asset turnover ratio, an indicator of their effective use by the enterprise.
In addition, you can calculate the significance of a transaction by determining the amount of property that the company risks losing during its implementation. According to the norms, a transaction as a result of which a company may lose 25% of its property is considered large and a meeting of shareholders is required to confirm participation in it.
Important: if the calculation of the balance sheet indicator was carried out incorrectly, then a transaction that has already taken place may be considered invalid.
A correctly calculated BSA makes it possible to join companies that are subject to tax monitoring, applied since 2016 in the Russian Federation. Such companies are not subject to tax and desk audits. Federal Tax Service specialists monitor the company’s reporting through remote access, paying special attention to transactions with risks.
To be included in the number of such enterprises, the conditions established by clause 3, art. 105.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Important: the correct calculation of BSA is an assessment of the enterprise’s property, the efficiency of its use and confirmation of the legitimacy of transactions.