If the amounts of VAT on goods (work, services), as well as fixed assets (FPE), intangible assets (IMA) and property rights were accepted for deduction, but then the objects began to be used in VAT-free transactions, then the tax must be restored. The rules for determining VAT in relation to fixed assets and intangible assets, which are involved in both non-taxable and taxable activities, have not been established by law. In the article, 1C experts talk about the procedure for tax restoration and the reflection of transactions in “1C: Accounting 8” edition 3.0, starting from the receipt of the operating system to the restored VAT in the sales book.
When does it become necessary to restore VAT?
If a taxpayer carries out transactions on which VAT is not paid for one reason or another, the input tax on the values (or works, services) used in them, previously accepted for deduction, should be paid to the budget (that is, restored). This is indicated by clause 3 of Art. 170 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
There are several reasons for carrying out such an operation, in particular:
- transfer of assets as contributions, including to a management company (or transfer to increase the target capital of non-profit structures);
- further sale of goods outside the Russian Federation;
- acquisition of goods and materials for the purpose of carrying out activities exempt from taxation;
- changing the taxation system to one that does not involve the accrual of VAT after the purchase of goods and their further sale without the accrual of tax.
More detailed information about possible options for VAT recovery can be found in the article “Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (2017): questions and answers.”
Another case when the obligation to restore VAT arises is export. More precisely, situations when unplanned export operations are carried out during the sale of goods. That is, when initially assets (works, services) were purchased exclusively for domestic sales, and were used for export operations. What to do with input tax in such cases? Restore. But you need to keep in mind that from July 1, 2016, the restoration of VAT, previously accepted for deduction, is made only in relation to goods, works, services, property rights that are used for export operations of raw materials. The explanation of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation on this issue is given in the material “VAT on goods that are used for the export of raw materials is restored.”
Find out the procedure for recovering VAT on fixed assets when exporting here.
If the sale of fixed assets took place on the territory of the Russian Federation, the obligation to restore VAT previously accepted for deduction does not arise. You can learn about this from the article “Sale of OS does not require VAT recovery.”
If fixed asset, previously used in activities subject to VAT, begins to be used in transactions not subject to VAT, then the VAT previously accepted for deduction must be restored in proportion to its residual value. Details in the material “Part of the OS was scrapped - the VAT deduction needs to be restored.”
The position of the Ministry of Finance on the issue of restoring VAT on goods, works, services for periods when the taxpayer had the right not to keep separate records of input VAT, and later these goods, works, services began to be used in transactions not subject to taxation or exempt from VAT, see in the material “Recovery of VAT amounts for periods without separate accounting.”
If there are receivables, the repayment of which is not possible, a controversial situation arises. If the seller, who cannot recover payment from the buyer for the goods shipped to him, has no reason to restore the VAT accepted for deduction at the time of purchase of the materials, then the situation may be different for the buyer.
Provided that the organization has decided to write off receivables recognized as bad, which were formed in the case of prepayment in the absence of further deliveries, the tax on advances should be restored when writing off this debt. Otherwise, disagreements may arise with the inspection authorities. The controllers’ position on this issue is reflected in the article “How to take into account VAT amounts when writing off accounts receivable?”
For information on how buyers should act in the event of the formation of receivables from advance payments paid and when to restore VAT , read the article “When and how can a buyer restore VAT from a transferred advance payment?”
After shipment of the goods, the seller must recover VAT from the advance previously received from the buyer. The article “How can a seller get a VAT deduction from an advance payment from a buyer” will help you do this correctly.
As for actions to write off your own debt, there are also controversial issues for both the seller and the buyer. Under what circumstances will it be necessary to restore the tax in full, and when is it not necessary? What consequences are possible in this or that case? Read our article “VAT when writing off accounts payable: problematic situations.” There are often situations when property belonging to an economic entity (fixed assets, materials, goods) becomes unusable. In this regard, the question often arises: is it necessary to restore the VAT that was previously paid? Read more about the actions of taxpayers in such circumstances in the following materials:
- “Procedure for VAT recovery when writing off goods”;
- “Should VAT be restored upon disposal of fixed assets and inventory as a result of their write-off, theft, damage, shortage, loss, wear and tear, etc.?”;
- Is it necessary to restore VAT on burnt property?
- “An accident is not a reason to restore VAT.”
The resulting discount to the price of the goods from the buyer leads to the need to restore VAT. Read more in the material “Volume discount may require VAT recovery.”
From 07/01/2017, recipients of subsidies for reimbursement of expenses related to the purchase of goods, works, services or the payment of import VAT will have to restore VAT regardless of the level of the budget from which they were received. You can read about this change in legislation in the material “From July 1, 2017, the procedure for restoring VAT when receiving budget subsidies has been adjusted.”
Restoring VAT in 1C:Accounting 8 when using the OS in non-taxable transactions
We will consider the procedure for restoring VAT in the 1C: Accounting 8 version 3.0 program if a previously acquired fixed asset begins to be used simultaneously in taxable and non-taxable (tax-exempt) activities using the following example.
Example
| The organization LLC "Style", which applies the general tax system, in the third quarter of 2021 acquired and put into operation a fixed asset (multifunctional device - MFP) worth RUB 200,600.00. (including VAT 18% - RUB 30,600.00). Since the organization planned to use the MFP only for transactions subject to VAT, the amount of VAT presented by the seller in the third quarter of 2021 was declared as a tax deduction. In the fourth quarter of 2021, the organization began to use MFPs, along with transactions subject to VAT, also for tax-exempt transactions, which led to the need to restore the amount of input VAT on the purchased fixed asset (MFP). The sequence of operations is given in the table. |
Arrival of OS
Registration of the transaction of receipt of a fixed asset (operations: 1.1 “Accounting for received MFP”; 1.2 “Acceptance of MFP for accounting as a fixed asset”; 1.3 “Accounting for input VAT”) in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0, is carried out using the Receipt document ( act, invoice) with the type of operation Fixed assets (section Purchases - subsection Purchases or section Fixed assets and intangible assets - subsection Receipt of fixed assets).
After posting the document, the following accounting entries are entered into the accounting register:
Debit 08.04.2 Credit 60.01 - for the cost of the purchased MFP; Debit 01.01 Credit 08.04.2 - for the cost of the fixed asset accepted for accounting; Debit 19.01 Credit 60.01 - for the amount of input VAT.
An entry with the type of movement Receipt and the event Submitted by VAT by the supplier is made in the VAT presented register. Income is a potential entry in the purchase book, Expense is the presentation of VAT for deduction or write-off of tax on other grounds (for example, the amount of tax can be included in the price, written off from the net profit of the organization, etc.).
To register a received invoice (operation 1.4 “Registration of a received invoice”), you must enter the number and date of the incoming invoice in the fields Invoice No. and from the document Receipt (act, invoice), respectively, and click the Register button. In this case, the document Invoice received will be automatically created, and a hyperlink to the created invoice will appear in the form of the basis document.
The fields of the Invoice document received will be filled in automatically based on information from the Receipt document (act, invoice).
Besides:
- in the Received field the date of registration of the Receipt document (act, invoice) will be entered, which, if necessary, should be replaced with the date of actual receipt of the invoice. If an agreement has been concluded with the seller on the exchange of invoices in electronic form, then the date of sending the electronic invoice file by the EDF operator, indicated in its confirmation, will be entered in the field;
- in the line Base documents there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding receipt document;
- in the Transaction Type Code field the value 01 will be reflected, which corresponds to the acquisition of goods (work, services), property rights in accordance with the appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ;
- The Receipt Method switch will be set to Hard copy if there is no valid agreement with the seller to exchange invoices electronically. If there is an agreement, the switch will be in the Electronic position.
As a result of posting the document Invoice received, a registration entry is made in the Register of Invoices.
From 01/01/2015, taxpayers who are not intermediaries (forwarders, developers) do not keep a log of received and issued invoices. In the Invoice document received in the Amount line, it is indicated that the amounts to be recorded in the accounting journal are equal to zero. In this case, the Invoice Journal register entries are used to store the necessary information about the received invoice.
According to paragraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when purchasing fixed assets, the deduction of the amount of VAT presented by the seller is made in full after the registration of these fixed assets.
To reflect transaction 1.5 “Presentation for deduction of input VAT”, you need to create a document Formation of purchase ledger entries (section Operations - subsection Closing the period - hyperlink Regular VAT operations).
Filling in the information on the Purchased Assets tab is done automatically using the Fill command.
As a result of posting the document Formation of purchase ledger entries, the following entry will be entered into the accounting register:
Debit 68.02 Credit 19.01 - for the amount of VAT accepted for tax deduction.
Data on the amount of VAT is entered into the Purchase VAT register to generate purchase ledger entries.
Also, after posting the document Formation of purchase ledger entries, an expense entry is made in the VAT register presented.
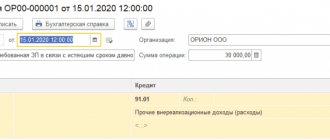
The invoice issued by the MFP seller will be registered in the purchase book for the third quarter of 2021 (section Reports - VAT subsection) (Fig. 1) with transaction type code 01 (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] ).
Rice. 1. Purchase book for the third quarter of 2021
Restoration of VAT upon transition to the simplified tax system
If in the course of work the subject decides to switch from the general system to a different taxation regime that eliminates the need to charge VAT, then the tax previously accepted for deduction will have to be restored. This applies to goods purchased but not yet sold to customers, as well as fixed assets and intangible assets.
The main stages of the transition procedure are listed in our article “Procedure for VAT recovery when switching to the simplified tax system (nuances)”
The transition of an organization from the general system to other (preferential) tax regimes implies the restoration of VAT on purchased goods (services and property rights) in full. If we consider fixed assets and intangible assets, then a tax is subject to restoration in an amount proportional to their residual value. You can read more in the article “VAT during the transition to the simplified tax system with OSNO: accounting and restoration of tax.”
If the transition to the simplified tax system is carried out from the general taxation system, which was combined with imputation, then VAT restoration must be made only for those goods that were not taken into account in activities subject to imputation tax and are intended for use in “simplified” activities. Read more in our material “When the transition to the simplified tax system does not require VAT restoration .
Fixed assets on balance sheet
Fixed assets are those elements of a company's property that have served it, that is, are listed on the balance sheet for at least a year at a cost exceeding 40,000 rubles. Accounting clearly defines the procedure for their reflection on the balance sheet in the corresponding paragraph of PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”:
- On the balance sheet, fixed assets are listed at their original cost, which is the amount spent on their acquisition or creation.
- During the useful life period assigned by the company, the initial cost of the asset is regularly reduced by the amount of depreciation.
NOTE! If a fixed asset was acquired before January 1, 2002, its useful life cannot be changed, with the exception of an increase in the cases provided for by letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 16-00-14/80.
Postings when restoring tax
Actions with tax previously used as a deduction when paying to the budget are reflected in accounting on accounts 19, 68, 91, etc. For more information about transactions for VAT restoration , read our article “The nuances of VAT restoration and what transactions are used in this?” .
Reflection of operations to recover VAT from advance payments is also accompanied by recording of accounting entries. You will find complete information about them in the article “Procedure for recovering VAT from advances (postings).”
Documentation of the sale
The operation to sell a fixed asset at its residual value, as well as at its original value, should be properly formalized.
For registration, you can use standardized forms or develop and approve forms yourself. When using unified forms, be guided by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia No. 7 of January 21, 2003:
- when selling a unit of fixed assets, use the OS-1 form, with the exception of buildings and structures;
- when selling homogeneous groups of objects, except for real estate and structures, - form OS-1b;
- reflect the sale of real estate and other structures in the OS-1a form.
Acceptance and transfer certificates (form OS-1) must be drawn up on the date of transfer of ownership of the property to the purchasing organization. Typically, the transfer date is the day on which the shipment was made, unless otherwise provided in the purchase and sale agreement. For real estate and structures, the act is drawn up solely on the date of transfer of ownership of the object.
Transfer acts are drawn up in two copies - one each for the seller and the buyer. When compiling OS-1 you should use:
- technical documentation;
- inventory card;
- statement of accrued depreciation;
- accounting statements and other accompanying documentation, for example, information on modernization and (or) revaluation of the object.
Accounting for profit or loss from the sale of fixed assets
For a long time, the profit from the sale of fixed assets was considered to be the difference between the NSR and the residual book value, to which was added the inflation index (IRI), published by the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation. However, since this index is not applied to profits from the sale of assets, Goskomstat no longer publishes it.
For tax purposes, profit from the sale of fixed assets represents capital expenditure, from which the following are sequentially subtracted: the residual book value of the fixed asset and sales costs.
Sometimes it happens that the implementation of an OS is carried out to the detriment of the company.
A loss from the sale of fixed assets is recognized if the residual value, together with sales costs, exceeds the NSR, that is, the revenue received.
Such a loss cannot be taken into account on the balance sheet immediately after sale, so that its amount reduces the income tax base. The lost funds will have to be distributed in equal parts over the months that remain from the moment of the transaction until the end of the useful life of the sold OS. This is reflected in the tax register “Accounting for deferred expenses”.