What is land tax for individuals?
Land tax is a tax levied on individuals who own land plots on the right of ownership, the right of permanent (perpetual) use or the right of lifelong inheritable possession.
The tax is not levied on individuals in relation to land plots held by them under the right of free use or transferred to them under a lease agreement.
Land plots of the following categories are not subject to taxation:
- included in the common property of an apartment building
- limited in circulation in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, which are occupied by especially valuable objects of cultural heritage of the peoples of the Russian Federation, objects included in the World Heritage List, historical and cultural reserves, objects of archaeological heritage, museum-reserves
Land tax belongs to the category of local taxes and, as a consequence, rates are established by regulatory legal acts of representative bodies of municipalities.
What to do if the tax notice has not arrived
Articles 6.1 and 52 of the Tax Code establish that the notice must be properly served on the taxpayer. Methods of delivery include:
- personal delivery (against receipt);
- via registered mail with return receipt requested;
- through the taxpayer’s personal account.
That is, the tax authorities must be sure that the notice has been delivered to the addressee, it will not fall into the hands of anyone else, and the executive body will be able to prove delivery if a controversial situation arises. If the payer has a personal account, the letter will be sent electronically. Almost all entrepreneurs have a personal account, therefore, if the paper version is the most convenient way to receive a letter, you need to write about it to the tax office through the same personal account. But in order to use this option, you need to get a strengthened signature. To do this, you can personally contact the tax office. In the future, the signature may be useful several more times, and the service is free. The procedure for regulating tax correspondence of this kind is regulated in detail by the Letter of the Tax Service of the Russian Federation (N BS-4–11/15377) dated August 22, 2016.
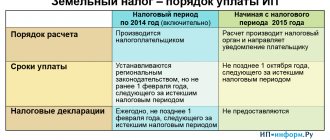
The notice is sent to the payer one month before the tax payment date. Article 409 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides that the payment deadline cannot occur earlier than the notification is served. Therefore, if you received a notice on May 1, and the payment deadline is May 2, then the late payment will be on the conscience of the tax office.
If the tax amount does not exceed 100 rubles, then no notification is sent. And also, in accordance with Article 52 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the payer will not receive a letter if the land plot is exempt from taxation due to the application of the benefit.
The notification is a letter indicating the details of the payer, the amount of calculated tax, etc.
Sometimes it happens that the tax office sent a notification on time, but the payer still did not receive the letter. This may be due, for example, to a temporary lack of access to the taxpayer’s personal account. In such cases, responsibility falls on the payer (Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, if you know approximately the time frame for receiving a letter, but it has not been delivered, you need to adhere to the following plan:
- Contact the tax service for notification.
- Notification of the tax service about the presence of taxable objects.
To receive the notification yourself, you can contact the tax office that is most convenient geographically for the payer. For example, at the place of residence or at the location of the site. You can also send a request through your personal account. Article 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that if the notification has not been received, then the payer is obliged to notify the Federal Tax Service about this before the end of the year following the reporting year. The payer is also obliged to provide information about the availability of a land plot, and information about this object must be supported by certifying certificates:
- registration certificate;
- contracts (including purchase and sale);
- inquiries, extracts, etc.
Until 2021, when a taxpayer sent information about the land he owned to the tax office, the tax office could not order payment of the fee for the previous year if the tax had not been paid before. And now Federal Law 52-FZ establishes that the tax office can claim tax for the previous 3 years. Of course, this rule applies to those lands, the right to which arose earlier than 3 years before the tax was paid. For example, in January 2021 a plot was purchased. In 2021, the tax authority will send a notification with tax calculations only for 2 years (previously this was not possible).
Information about the occurrence of a taxable object must be sent in the form of a message by registered mail or delivered in person. When delivering in person, you need to ask the inspector to issue a receipt for the document. A receipt will guarantee that your message will not be “lost.”
Since January 2021, another rule has been in effect: if you have never received a notice of tax on land that you own and have not sent messages about it to the tax authority, then a fine of 20% of the unpaid tax may be imposed (Article .129.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation). As a rule, there are no exceptions in such cases; the tax office is happy to fine non-payers.
Calculation and rates of land tax
The land tax can be calculated using the formula: Land tax = KST * D * ST * KV KST - cadastral value of the land plot; D – size of the share in the right to the land plot; ST – tax rate; KV – land ownership coefficient (applies only in case of ownership of a land plot for less than a full year).
The cadastral value of a land plot is calculated by Rosreestr (Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography). The tax rate is established by regulations of the representative bodies of municipalities (laws of the federal cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol). Thus, the tax rate differs in different localities (municipalities). For example, the land tax rate in Moscow is 0.025% for the so-called “dacha land”, while in the Moscow region the prevailing rate is 0.3%. In addition to the differences in the rate depending on the municipality of the site, the rate varies depending on the category of land. There is an upper limit on the tax rate fixed at the federal level. 0.3% for land plots:
- classified as agricultural lands or lands within agricultural use zones in populated areas and used for agricultural production;
- occupied by the housing stock and objects of engineering infrastructure of the housing and communal complex (except for the share in the right to a land plot attributable to an object not related to the housing stock and objects of engineering infrastructure of the housing and communal complex) or acquired (provided) for housing construction;
- purchased (provided) for personal subsidiary plots, gardening, market gardening or livestock farming, as well as summer cottage farming;
- limited in circulation in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, provided to ensure defense, security and customs needs (Article 27 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation);
1,5%
in relation to other land plots. Detailed information about established tax rates and benefits can be found at any tax office or by using the following link.
Calculation of land tax when selling/purchasing a plot
In a situation where ownership of a land plot was for less than a full year, for example, when selling or buying a plot, the ownership coefficient is used to calculate the tax. The land plot ownership coefficient is the ratio of the number of full months during which this land plot was owned (permanent (perpetual) use, lifelong inheritable ownership) by the taxpayer to the number of calendar months in the tax (reporting) period - 12 months. When purchasing a plot of land
, the month is considered complete if ownership arose before the 15th (inclusive) of the month of purchase.
In the case of a sale
, a month is considered complete if ownership is terminated after the 15th of the relevant month. In other cases, the month is considered incomplete and is not taken into account when determining the ownership ratio.
Simultaneous application of ownership and change factors
According to the Federal Tax Service (letter dated May 23, 2018 No. BS-4-21/9823), supported by the Ministry of Finance (letter dated June 6, 2018 No. 03-05-04-02/38570), a tax with the simultaneous application of ownership and change coefficients other than 1, calculated by the formula:
Ni = KS1 × Sn × Kv × Ki1 + KS2 × Sn × Kv × Ki2,
Where:
Neither is the tax on the site, the value of which has changed;
KS1 - initial cadastral value;
Сн - tax rate;
Kv - ownership coefficient;
Ki1 - change coefficient equal to the ratio of the number of months of ownership before the change in value to the total number of months of ownership;
KS2 - new cadastral value;
Ki2 is the change coefficient equal to the ratio of the number of months of ownership after the change in value to the total number of months of ownership.
How to find out the cadastral value of a land plot?
You can find out the cadastral value of a land plot using the online service of Rosreestr called “Public Cadastral Map”. This site contains an interactive map of all subjects of the Russian Federation. After selecting the plot of land you are interested in, detailed information on it will be shown: type, cadastral number, status, address, category of land, form of ownership, cadastral value, area, etc. Searching for a site is possible using GPS coordinates, but this functionality does not always work correctly. All information about the land plot is available free of charge and without registration.
Payment order
Payment orders for payment of land tax are drawn up by legal entities and entrepreneurs. Based on this payment document, the bank transfers money from the payer’s account using the details of the tax authority. The procedure and rules for issuing orders are regulated by the following documents:
- Bank of Russia Regulation No. 383-P dated June 19, 2012;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 107n dated November 12, 2013.
An order is a document in the form of a table with fields and columns. Each column has a number:
- Payer status (field 101) - here you need to enter 01, which corresponds to the “Taxpayer” status.
- Priority of payment (field 21) - enter the number 5, since taxes are paid in fifth place.
- KBK (field 104) - indicate the budget classification code.
- OKTMO (field 105) - enter the code of the municipality in whose territory the site is located.
- Basis of payment (field 106) - here you should put “TP” (current payment) or “ZD” (if there is a debt).
- Tax period (field 107) - here we indicate the payment frequency code separated by a dot, for example “QV” if the payment is quarterly, then 2 digits - the quarter number and 4 digits - the year.
- Document number (field 108) - for current payments and when repaying debt without a request from the Federal Tax Service, set it to 0, and if the payment is at the request of the inspection, set the request number.
- Document date (field 109) - here for current payments of land tax or in the case of voluntary repayment of debt in the absence of a demand, set 0, for tax for the year we indicate the date of signing the tax return, for payments on claims - the date of the demand.
By order of the Ministry of Finance dated December 16, 2014, the KBK related to land tax changed. For those who use the Sberbank business online system, filling out a payment will not be a problem, since the system offers a choice of the necessary codes and details. You only need to enter the date and name of the recipient yourself. If the order is filled out manually, for example, using Office-Word, then the necessary codes, including KBK penalties, can be found on the tax website (Codes).
The payment order can be downloaded on the Internet and filled out using computer programs
Land tax benefits for pensioners
In 2021, the President of the Russian Federation signed Federal Law No. 436-FZ “On Amendments to Parts One and Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation.” In accordance with this law, a tax deduction is introduced that reduces land tax by the cadastral value of 600 square meters of land area. In fact, we are talking about the so-called 6 acres. All pensioners are eligible for this benefit.
, as well as the following categories of citizens: Heroes of the Soviet Union, the Russian Federation, disabled people of groups I and II, disabled people since childhood, veterans of the Great Patriotic War and military operations, etc. The tax for 2021, which will need to be paid in 2021, will be calculated based on this benefit.
Tax deduction is provided only for the cadastral value of 6 acres. If the area of the land plot is larger, then the tax will be calculated for the remaining area. For example, if the area of a land plot owned by a pensioner is 20 acres, then the tax will be charged only for 14 acres. Another feature of this law is that the deduction will be applied only to one plot of land
at the choice of the “beneficiary”, regardless of the category of land, type of permitted use and location of the land plot. In order to independently select a land plot to which the benefit will be applied, you must contact any Federal Tax Service Inspectorate with a Notification of the selected plot. If the notification is not received from the taxpayer, the deduction will be automatically applied to one plot of land with the maximum calculated tax amount.
Results
Organizations calculate the tax amount independently. They pay the tax quarterly (if local authorities have introduced advances) and at the end of the year. Payment deadlines have been changed from 2021.
Individuals and individual entrepreneurs receive a tax notice from the Federal Tax Service and pay tax at the end of the year no later than December 1 of the year following the reporting year.
Sources:
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Law of Moscow “On Land Tax” dated November 24, 2004 No. 74
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Accounting entries
Taxes in accounting are reflected in account 68 “Taxes”; a subaccount must be opened for each tax. In the case of land tax, the subaccount is called “Land Tax”. This occurs through the approval of the working chart of accounts for the organization, which is an integral annex to such an important and necessary document in accounting as the “Accounting Policy”.
Antonina Subbotina, economist
Payment of land tax must be reflected in accounting documents. The method of reflection in accounting depends on the type of activity in which the use of the site is involved:
- account 20, if expenses relate to the main production;
- account 23, if expenses relate to auxiliary production;
- account 25, if general production costs;
- account 26, if general expenses;
- account 29, if costs relate to service farms and production;
- score 44 if these are sales costs.
Postings for land tax when calculating the balance are as follows:
| Debit | Credit |
| 20, 23, 25, 26, 29, 44 | 68 (land tax subaccount) |
If the land is leased, then paying the tax for this plot is considered other costs. But other costs are recognized as such only if this is not the main activity, but only a way to use unused property. When classifying tax as other expenses, it must be reflected in account 91.2. In this case, the wiring looks like this:
| Debit | Credit |
| 91.2 | 68 (land tax subaccount) |
When paying land tax, the posting is expressed a little differently:
| Debit | Credit |
| 68 (land tax subaccount) | 51 |
To prepare financial statements, you can contact independent auditing firms
Possible fines
Fines for violating the procedure for paying this tax are a consequence of liability. Liability for such a violation may be tax and criminal.
Tax liability may be imposed on the violator for incomplete payment or failure to pay the calculated tax. And criminal liability arises when the taxpayer hides part of the income or property, if land tax can be paid at the expense of this property.
Article 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides comprehensive information on fines for tax violations related to land tax. So, if the landowner unintentionally delayed payment of the tax, did not pay or paid only part of it, then the fine will be 20% of the unpaid amount. If the payer knew about the need to pay, had the opportunity to do so, but did not pay, then such non-payment is called intentional, and the fine increases to 40%. The amount of the penalty for payment violation does not exceed 8% of the unpaid amount.