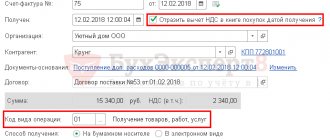
VAT deductibility must be restored in the following cases
- When transferring assets - fixed assets, intangible assets, inventories (MPI), property rights as contributions to the authorized capital.
This could be contributions to the authorized capital of business companies, partnerships, or the transfer of real estate to replenish the target capital of a non-profit organization. These can also be investment contributions to investment partnerships and mutual contributions to cooperative mutual funds.
VAT on inventories and property rights should be restored in the amount in which they were taken for deduction, and VAT on fixed assets and intangible assets - in proportion to the residual value of the asset without taking into account revaluation.
It will be useful to read: ⇒ “How to extract VAT from the amount (formula, examples)”
At the receiving party, amounts of recovered VAT are accepted for deduction.
- VAT must be restored in the case where the property, property rights on which VAT was accepted for deduction:
- begin to be used in activities that are not subject to VAT or exempt from VAT;
- begin to be used in activities that are not recognized as sales within the framework of Chapter 21 “Value Added Tax” of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- begin to be used by banks to carry out banking operations;
- when a VAT payer ceases to be a VAT payer or receives an exemption from VAT;
- when the place of their implementation ceases to be the Russian Federation.
In this case, as in the first case, VAT on inventories and property rights must be restored in full, and VAT on fixed assets and intangible assets - in proportion to the residual value of the asset without taking into account revaluation.
Amounts of restored VAT are not accepted for deduction, but are taken into account as part of other expenses under Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
VAT is restored in the tax period when one of the events listed above occurred, except for the transition to special taxation systems.
When switching to special taxation regimes (except for the Unified Agricultural Tax), the restoration of VAT amounts is carried out in the tax period preceding the date of transition to the special tax regime.
- VAT is restored in case of transfer of an advance (prepayment) for goods, work, services, property rights.
VAT restoration is carried out when goods, works, services, property rights for which an advance payment was previously made are received. This must also be done if there has been a change in the terms of the contract or its termination, resulting in the return of the advance payment.
- VAT is also restored in the event of a decrease in the value of goods, works, services, property rights.
Regardless of the reasons for the decrease in value - both with a decrease in price and with a decrease in the quantity (volume) of transferred goods, property rights, work performed, services rendered.
VAT subject to restoration is calculated on the amount of the difference between the original cost and the cost after reducing the price or quantity of goods, works, services, and property rights sold.
VAT restoration occurs in the tax period to which the earliest date applies:
- The date of the document that formalized the reduction in the cost of goods, works, services, and property rights sold.
- The date the adjustment invoice was received reflecting the change.
- VAT is restored in the event of receiving subsidies from the budget of the Russian Federation to reimburse the costs of paying for goods, work, services, and property rights. A similar procedure applies to reimbursement of tax costs when importing goods into Russia.
Reinstatement is made in the amount previously accepted for deduction.
Recovery occurs during the period in which the subsidy is received.
Amounts of restored VAT are not accepted for deduction or accounting as part of property, but are taken into account as part of other expenses under Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When the buyer made an advance payment
An LLC or individual entrepreneur using a prepayment scheme is required to issue an invoice to the counterparty for the entire amount of the advance received. There are two scenarios in which the buyer who received the deduction will be required to restore the tax on the payment received:
- by agreement between the parties, the advance payment is returned to the buyer;
- The ordered products are sent against the amount of money transferred in advance.
Important: If the cost of goods in the shipping documents corresponds to the amount of the advance payment, then VAT is refunded in full. If there is a discrepancy in the amounts, VAT is recalculated from the total amount specified in the invoice for the shipment of goods.
Features of restoring VAT amounts for some fixed assets
VAT amounts accepted for deduction on acquired or constructed fixed assets are subject to recovery not for all specified fixed assets, but for those that were used in the following operations:
- when carrying out capital construction by a contractor;
- when purchasing real estate (with the exception of space objects);
- when purchasing on the territory of Russia or importing into the territory of Russia sea, river and aircraft vessels and engines for them;
- when purchasing goods, works, services used in construction and installation work;
- when performing construction and installation work for one’s own needs.
Restoration of such objects occurs in all 5 cases discussed in the previous paragraph, taking into account some features.
Calculation
The amount of tax paid to the budget upon restoration will be equal to the amount of deductions on assets (with the exception of fixed assets).
The need for additional tax assessment appears on the date of the event. To do this, VAT is calculated on all valuables remaining in the warehouse.
Tax amounts will be calculated based on incoming invoices. This is due to the fact that in the warehouse the products may be recorded at a different price.
The price of fixed assets is calculated using analytical accounting cards, from which the price of the revaluation is subtracted. The basis for calculating the tax payable is the residual price.
VAT restoration: features for fixed assets under Article 171.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
VAT restoration is not carried out on fixed assets that are fully depreciated, or more than 15 years have passed since their commissioning.
The amounts of restored VAT are reflected in the VAT Declaration for the 4th quarter of each of the 10 years that have passed after the year in which depreciation on the fixed asset began to be calculated.
Each code, the amount of VAT subject to recovery, is determined as 1/10 of the amount of VAT accepted for deduction, in the corresponding share.
But the corresponding share is determined as the ratio of the amount of goods sold, works, services, property rights not subject to VAT to the total amount of sales for the corresponding year.
The amount of VAT recovery determined in this way for a specific year is taken into account as part of other expenses under Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Export operations
Since 2015, tax legislation has changed the requirements for the restoration of VAT in relation to export transactions. Direct requirement to restore the tax after shipment of goods to foreign partners, Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain.
However, VAT can be deducted on goods intended for export only after the taxpayer presents to the tax inspectorate a package of documents justifying the application of a zero tax rate.
If a deduction for an exported product was declared earlier, at the time of its acquisition by the exporter, then the VAT restoration date should be the day when the cargo crossed the Russian border.
Other cases of VAT recovery
Despite the fact that all cases of VAT restoration are directly named in Articles 170 and 171.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, regulatory authorities in their explanations constantly find new reasons for VAT restoration. Each taxpayer has to decide for himself whether to follow such clarifications or not.
After all, if you do not follow, there may be claims on their part, and you will probably have to defend your position in court.
Some cases are shown in Table 1.
Table 1
| No. | An operation for which it is necessary to restore VAT, according to the regulatory authorities | Explanatory document |
| 1 | There was a write-off of illiquid or obsolete goods | Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2016 No. 03-03-06/1/1997 |
| 2 | The property was disposed of due to damage | Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 19, 2015 No. 03-07-11/15015 |
| 3 | Not fully depreciated property was liquidated (except for liquidation as a result of an accident) | Letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 04/14/2016 No. 03-07-11/21297, dated 02/17/2016 No. 03-07-11/8736 |
| 4 | Theft of property was recorded | Letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation from 04.07.2011 3 03-03-06/1/387, dated 05/19/2010 No. 03-07-11/186 |
| 5 | During the inventory, a shortage of property was recorded | Letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation from 04.07.2011 3 03-03-06/1/387, dated 05/19/2010 No. 03-07-11/186 |
At the same time, we must not forget that if there is arbitration practice in which the opposite point of view is expressed, supervisory authorities should be guided in their work by arbitration practice.
An example of arbitration decisions containing conclusions that there is no need to restore VAT in cases of loss of property as a result of theft, damage, etc. or impossibility of further use due to moral or physical wear and tear, the following solutions may serve:
- Decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2011 N 3943/11
- Decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of October 23, 2006 N 10652/06.
Accounting entries when restoring VAT
table 2
| Operation | Posting by debit | Loan posting |
| When transferring property as a contribution to the management company | ||
| VAT on property transferred to the authorized capital has been restored | D 19 | K 68.02 |
| The amount of restored VAT is included in the initial cost of the share in the authorized capital (posting is possible - the amount of restored VAT is included in the calculations for payment of the share in the authorized capital) | D 58.01 (D 76) | To 19 (to 10) |
| When switching to simplified tax system | ||
| Recovered VAT on materials in stock | D 19 | K 68.02 |
| The amount of recovered VAT is included in other expenses | D 20 (26) | K 19 |
When writing off goods (in case of shortage)
When inventorying property in a warehouse, a shortage of inventory items may be identified. The products were intended for activities that are subject to VAT. The shortage identified during the property inventory did not change the purpose of the previously purchased products.
In the Tax Code you can see a list of situations in which VAT is subject to restoration. The list is closed, meaning no new situations can be added to it. The identified shortage is not indicated in this list. In this regard, the situation is not clear and does not have an accurate interpretation.
In 2006, the Supreme Arbitration Court issued a decision according to which it is strictly prohibited to increase the list of situations for VAT recovery. On this basis, we can draw the following conclusion: it is not necessary to restore VAT when writing off inventory items based on identified shortages.
When can you ignore a tax inspector's request?
The ambiguity of interpretation of the provisions of Article 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by fiscal authorities leads to the fact that tax inspectors make claims to LLCs or individual entrepreneurs regarding the need to restore VAT in controversial situations:
- theft or identified shortage of material assets;
- liquidation of assets due to natural disaster or fire;
- write-off of a fixed asset due to the impossibility of using it due to breakdown, wear and tear or accident before the end of depreciation;
- write-off of damaged, expired goods or lost stock;
- claimed deduction for unfinished construction;
- write-off of materials spent on the production of defective products.
The demands of tax officials regarding the mandatory upward adjustment of VAT in the listed situations are illegal, since the list of grounds for carrying out the procedure for revising the amount of tax in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is closed and exhaustive.
Any new argument in favor of restoring VAT must be enshrined in law.
Please keep in mind: Failure to comply with the tax inspectorate's request to restore the tax on controversial grounds may lead to additional VAT charges and the collection of fines and penalties. You can appeal the decision of the Federal Tax Service in the Arbitration Court, which in such cases clearly takes the side of the taxpayer.
When carrying out reorganization measures and forming a new legal entity, LLC has the right to choose any taxation system. If a company switches from the general regime to a preferential scheme (UTII, simplified tax system, unified agricultural tax), and as a legal successor receives the right to use the assets of the “old” LLC, then tax inspectors demand that the “input” VAT be restored on the entire value of the transferred property.
Such an interpretation of tax legislation is not legal, and the reorganized legal entity is not obliged to adjust the tax amount.
The same opinion is shared by the judicial authorities who are challenging the requirements of the Federal Tax Service.