To create safe working conditions for workers at the enterprise, everything is based on plans, be it repeated instructions, training and knowledge testing, medical examinations, and so on.
But there are situations when it is necessary to move away from planning and conduct unscheduled training on labor protection for employees of the organization.
Moreover, if you do not fulfill this obligation in a timely manner, then a protocol on an administrative offense may “arrive”, so read the article to the end and if you have questions, write comments.
- Order to conduct unscheduled briefing
Why was instruction needed outside of the plan?
Should training in certain basics of labor protection be carried out outside the approved plan and program? This requires a certain reason provided for by labor legislation.
GOST 12.0.003-90 regulates the rules for conducting all elements of training in the basics of labor protection. Unscheduled briefing is considered one of the most important procedures for special training of employees to prevent injuries and other accidents, along with initial briefing.
Reasons for unscheduled briefing:
- reaction to a sudden emergency situation;
- the need for training in response to changes in working conditions, technology or equipment.
Reasons for scheduling an unscheduled briefing
They fit into the two reasons listed above. Specific reasons requiring new training, noted in regulations, may be:
- introduction of new or revised standards, instructions, rules related to labor protection at a given enterprise;
- introducing any changes to existing labor safety regulations;
- introduction of new factors into the production process: change or renewal of equipment, tools, raw materials, replacement of technologies, etc.;
- requirement set by supervisory authorities;
- identified violation of labor safety requirements committed by employees or students, which led or could lead to damage to health or equipment;
- information received about accidents or accidents at similar enterprises;
- an interval of more than 2 months between permits to work, and for work in conditions of increased danger - more than 1 month.
Is it necessary to provide labor safety training for remote workers ?
More danger means more training requirements
If production is characterized by a greater degree of danger, in order to prevent injuries and emergency situations, unscheduled briefings must be carried out for additional reasons. These may include:
- getting injured at work;
- a month's break in the employee's work activity;
- the occurrence of an occupational disease in one or more employees due to working conditions;
- forced change of schedule or stop of the work process due to gross violation of labor safety rules;
- the employee is transferred to a new workplace;
- the employer or control body has issued a corresponding order.
IMPORTANT! If the reason was an accident or injury at this or another workplace. Then the briefing must be carried out “hot on the heels” - no later than three days after the incident.
Dates
The duration of training is directly dependent on the reason that caused its need. An exhaustive list of reasons is given earlier. For example, if an organization has established a violation of current work safety requirements, or information has been received about such a violation in a production facility of a similar profile, training is carried out within 3 calendar days from the moment the violation was discovered or information was received. But if new technologies are introduced in an institution, new equipment is installed, training should be carried out before starting work in the changed conditions.
Instructor - who is he?
Unscheduled briefing is usually carried out directly at the workplace itself. Remote conducting is not prohibited either - modern technologies allow the use of all kinds of technical means for this, primarily a computer.
The instructor is usually the immediate supervisor of the work being performed. Its functions can be performed by:
- executive;
- director of operations;
- representative of the management of the workshop or work site;
- master;
- foreman;
- occupational safety specialist, etc.
NOTE! There may be one person being instructed, or a group of employees undergo unscheduled training at once.
Order of conduct
The volumes, topics, and timing of the training are established by the employer. The program is adjusted for each specific instruction.
However, the general requirements for any program are:
- availability of information about existing risk factors;
- study of labor protection requirements in the institution;
- studying technical and operational documentation for the equipment used;
- safe methods and ways of working.
Each institution has its own specifics; accordingly, the conditions for conducting instruction are regulated by regulations of a specific industry. However, there are a number of provisions that apply when conducting training in any organization:
- identification of risk factors that may be hazardous to the health of the employee and familiarization of the latter with them;
- study of occupational safety instructions developed for a specific type of activity;
- studying safe working methods at a specific site;
- conducting a survey at the end of the briefing;
- recording the results in a journal of the established form;
- admission to work only of those employees who have successfully passed the occupational safety knowledge test.
Contents of unscheduled briefing
IMPORTANT! Recommendations for conducting unscheduled briefings from ConsultantPlus are available here
A program for instruction that needs to be given for a specific reason. It is determined precisely by this very reason. Depending on what became the reason for the need to undergo training in the basics of labor protection, the unscheduled briefing program may include certain information materials and practical skills training.
- Updating or refreshing knowledge about equipment and technological processes that make up the daily work functions of employees.
- Discussion of the reasons that led to dangerous situations and/or undesirable consequences. Establishing incorrect actions and affirming correct ones instead.
- Organization of workplace safety.
- How to properly prepare for the start of production activities.
- Familiarity with personal protective equipment and the rules for using them.
- Features of safe movement in production conditions.
- Specifics of transportation, loading and unloading.
- Possibilities for emergency stopping of mechanisms or blocking of certain components.
- Methods of informing about the danger that has arisen, including in the presence of background noise.
- Algorithm for behavior in emergency situations.
- Emergency measures.
What types of occupational safety training are there and how are they carried out?
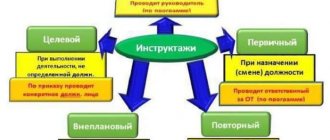
Based on the nature and timing of the briefings, they are divided into:
1. Introductory
Who receives induction training?
Introductory training on labor protection is carried out with all persons hired, as well as employees seconded to the organization and employees of third-party organizations performing work in a designated area, students of educational institutions at the appropriate levels, undergoing practical training in the organization, and other persons participating in production activities organizations.
How and when to conduct induction training?
Introductory briefing is carried out before starting work in a labor safety room or a specially equipped room using modern technical training tools and visual aids (posters, layouts, models, videos, etc.).
Introductory training in labor safety is carried out according to a program developed on the basis of legislative and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, taking into account the specifics of the organization’s activities and approved in the prescribed manner by the employer (or his authorized person).
Who conducts the induction training?
- introductory briefing is carried out by a labor protection specialist or an employee who has been assigned these responsibilities by order of the employer (or a person authorized by him), who has undergone training and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements in the prescribed manner
What documents confirm the conduct of introductory training on labor protection?
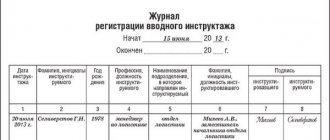
The conduct of induction training is confirmed by an entry in the introductory training log with the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing,
2. Primary at the workplace;
Who receives initial training at the workplace?
Initial briefing at the workplace before the start of production activities is carried out by:
- with all newly hired employees of the organization, including employees performing work under the terms of an employment contract concluded for a period of up to two months or for the period of seasonal work, in their free time from their main job (part-time workers), as well as at home (homeworkers) using materials of tools and mechanisms allocated by the employer or purchased by them at their own expense;
- with employees of the organization transferred from another structural unit, or employees who are entrusted with performing work that is new to them;
- with seconded employees of third-party organizations, students of educational institutions, undergoing practical training (practical classes), and other persons participating in the production activities of the organization.
- with builders performing construction and installation work on the territory of an existing enterprise;
(Note: Workers not involved in the operation, maintenance, testing, adjustment and repair of equipment, the use of electrified or other tools, the storage and use of raw materials and materials may be exempt from undergoing initial training at the workplace. List of professions and positions of workers exempt from undergoing initial training at the workplace, approved by the employer).
How and when to do it?
Initial training is carried out at the workplace.
Initial briefing in the workplace is carried out by the heads of the organization's structural divisions according to programs developed and approved in accordance with the established procedure in accordance with the requirements of legislative and other regulatory legal acts on labor protection, local regulations of the organization, instructions on labor protection, technical and operational documentation.
Conducting initial training at the workplace includes familiarizing workers with existing dangerous or harmful production factors, studying labor protection requirements contained in the organization’s local regulations, labor safety instructions, technical and operational documentation, as well as the use of safe methods and techniques for performing work. .
Initial instruction at the workplace is carried out with each employee or student individually with a practical demonstration of safe techniques and work methods. Initial instruction is possible with a group of people servicing the same type of equipment, and within a common workplace.
Initial briefing at the workplace ends with an oral assessment of the employee’s acquired knowledge and skills of safe work practices by the person conducting the briefing.
Who conducts initial training at the workplace?
Initial briefing at the workplace is carried out by the immediate supervisor of the work or the head of a structural unit (foreman, foreman, department head, warehouse manager, mechanic, director, etc.), who has undergone training and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements in the prescribed manner
What documents confirm the conduct of initial training at the workplace?
Carrying out the initial training at the workplace is confirmed by an entry in the registration log of the briefing at the workplace with the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing,
3. Internship
Who benefits from on-the-job training?
On-the-job training is carried out after completing initial on-the-job training:
- with all newly hired employees of the organization, including employees performing work under the terms of an employment contract concluded for a period of up to two months or for the period of seasonal work, in their free time from their main job (part-time workers), as well as at home (homeworkers) using materials of tools and mechanisms allocated by the employer or purchased by them at their own expense;
- with employees of the organization transferred in accordance with the established procedure from another structural unit, or employees who are entrusted with performing work that is new to them;
(Note: The management of a workshop, site, department, etc., in agreement with the labor protection service (specialist) and the authorized representative body of workers (if there is one), may exempt from internship an employee who has worked in his specialty for at least 3 years, transferring from one workshop to another, if the nature of his work and the type of equipment on which he worked previously does not change.)
How and when to do it?
All workers, after initial instruction at the workplace, must, during the first 2 to 14 shifts (depending on the nature of the work, the qualifications of the employee), undergo an internship under the supervision of persons appointed by order (instruction) of the head of the organization.
It is recommended to conduct on-the-job training according to programs for each profession or type of work,
An employee undergoes an internship at the workplace once after initial instruction under the guidance of persons appointed by order of the organization.
When an employee is transferred to another job (position, profession, etc.), he is required to complete the internship again in full.
Workers are allowed to work independently after an internship, testing of theoretical knowledge and acquired skills in safe working methods.
Who conducts on-the-job internships?
The internship at the workplace is carried out by a person appointed by order of the organization. As a rule, the most experienced employee or the immediate supervisor of the work is appointed,
What documents confirm the completion of an internship at the workplace?
The completion of an on-the-job internship is confirmed by an entry in the on-the-job training logbook with the obligatory signature of the person conducting the internship and the person undergoing the on-the-job internship, the number of internship shifts, the start and end dates of the internship, as well as the date of admission to independent work.
4. Repeated;
Who receives repeated training on labor protection?
Repeated instruction is carried out:
- with employees of the organization who received initial training at the workplace, incl. performing work under the terms of an employment contract concluded for a period of up to two months or for the period of seasonal work, in their free time from their main job (part-time workers), as well as at home (homeworkers) using materials, tools and mechanisms allocated by the employer or purchased by them for your account;
- with seconded employees of third-party organizations, students of educational institutions of relevant levels, undergoing practical training (practical classes), and other persons participating in the production activities of the organization.
- with builders performing construction and installation work on the territory of an existing enterprise.
How and when to conduct repeated occupational safety training?
Re-instruction is carried out at least once every six months (the frequency of re-instruction for some professions and positions may be reduced) according to programs developed for conducting initial instruction in the workplace.
Conducting repeated training on labor protection includes familiarizing workers with existing dangerous or harmful production factors, studying the labor protection requirements contained in the local regulations of the organization, labor protection instructions, technical and operational documentation, as well as the use of safe methods and techniques for performing work .
Repeated briefing is carried out individually or with a group of workers servicing the same type of equipment and within a common workplace according to the initial training program at the workplace in full.
Repeated instruction ends with an oral examination of the knowledge and skills acquired by the employee in safe work practices by the person conducting the instruction.
Who conducts repeated training on labor protection?
Repeated instruction on labor protection is carried out by the immediate supervisor of the work or the head of a structural unit (foreman, foreman, department head, warehouse manager, mechanic, director, etc.), who has been trained and tested for knowledge of labor protection requirements in the prescribed manner.
What documents confirm the repeated briefing on labor protection?
The repeated briefing on labor protection is confirmed by an entry in the logbook for registering the briefing at the workplace with the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing,
5. Unscheduled;
Who receives unscheduled occupational safety training?
Unscheduled briefing is carried out:
- with employees of the organization who received initial training at the workplace, incl. performing work under the terms of an employment contract concluded for a period of up to two months or for the period of seasonal work, in their free time from their main job (part-time workers), as well as at home (homeworkers) using materials, tools and mechanisms allocated by the employer or purchased by them for your account;
- with seconded employees of third-party organizations, students of educational institutions of relevant levels, undergoing practical training (practical classes), and other persons participating in the production activities of the organization.
- with builders performing construction and installation work on the territory of an existing enterprise.
How and when to conduct unscheduled safety training?
Unscheduled occupational safety training is carried out for certain reasons.
Reasons for conducting unscheduled briefing:
- upon the introduction of new or amended legislative and other regulatory legal acts containing labor protection requirements, as well as labor protection instructions;
- when changing technological processes, replacing or upgrading equipment, devices, tools and other factors affecting labor safety;
- when employees violate labor safety requirements, if these violations create a real threat of serious consequences (industrial accident, accident, etc.);
- at the request of officials of state supervision and control bodies;
- during breaks in work (for work with harmful and (or) dangerous conditions - more than 30 calendar days, and for other work - more than two months);
- by decision of the employer (or his authorized person).
Unscheduled briefing is carried out individually or with a group of workers of the same profession. The scope and content of the briefing is determined in each specific case, depending on the reasons and circumstances that necessitated its implementation. It is recommended to conduct unscheduled training according to the initial training program at the workplace in full.
The unscheduled briefing ends with an oral assessment of the employee’s acquired knowledge and skills of safe work practices by the person conducting the briefing.
Who conducts unscheduled safety training?
Unscheduled briefing on labor protection is carried out by the immediate supervisor of work or the head of a structural unit (foreman, foreman, department head, warehouse manager, mechanic, director, etc.), who has been trained and tested for knowledge of labor protection requirements in the prescribed manner
What documents confirm the conduct of unscheduled training on labor protection?
Conducting an unscheduled briefing on labor protection is confirmed by an entry in the logbook for registering the briefing at the workplace with the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing. When registering an unscheduled briefing, the reason for it is indicated.
6. Target
Who receives unscheduled occupational safety training?
Targeted briefing is carried out with all persons who are to perform: one-time work:
- not related to direct responsibilities in the specialty (loading, unloading, cleaning the territory, one-time work outside the enterprise, department, site, etc.);
- liquidation of consequences of accidents, natural disasters and catastrophes;
- production of work for which a permit, permit and other documents are issued;
- conducting a tour of the enterprise;
- organizing mass events.
How and when to conduct unscheduled safety training?
Targeted briefing is carried out before the start of work.
Targeted training is carried out individually or with a group of workers who are to perform work. The scope and content of the briefing is determined in each specific case, depending on the reasons and circumstances that necessitated its implementation.
Targeted instruction ends with an oral examination of the employee’s acquired knowledge and skills of safe work practices by the person conducting the instruction.
Who conducts unscheduled safety training?
Targeted instruction on labor protection is carried out by the immediate supervisor of the work or the head of a structural unit (foreman, foreman, department head, warehouse manager, mechanic, director, etc.), who has undergone training and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements in the prescribed manner
What documents confirm the conduct of unscheduled training on labor protection?
Conducting an unscheduled briefing on labor protection is confirmed by an entry in the Target briefing with employees carrying out work under a work permit, permit, etc., recorded in a work permit or other documentation authorizing the work, with the obligatory signature of the person being instructed and the person instructing,
Control of absorption
Instruction involves mandatory monitoring of the acquired knowledge and skills of trained employees. The form of control is set individually:
- it could be a survey
- written report,
- practical test of skills,
- The use of computer training programs and other technical training aids is not excluded.
If the mastery of the material is considered unsatisfactory, such an employee is not allowed to continue the work process. He will need repeated instruction after a certain time.
How exactly to remove an employee who has not undergone training and testing of knowledge and skills in the field of labor protection?
What will happen if you don’t
Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation in Art. 5.27.1 defines the penalties applied for violation of occupational safety requirements. The employer must provide not only for the provision of labor safety training, which is mandatory, but also for the organization to have documents confirming the training (magazine).
Otherwise, the following penalties will apply:
- for a legal entity - in the amount of 100,000 rubles to 130,000 rubles;
- for an official - in the amount of 15,000 rubles to 25,000 rubles.
Such significant numbers are a convincing argument in favor of both training and its correct recording.
However, violation of established occupational safety requirements may result in criminal liability. In accordance with Art. 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, if a violation of occupational safety caused serious harm to health or the death of a person, not only fines, but also disqualification, forced labor, and, in the most serious cases, imprisonment are provided as penalties.
Documentation and registration
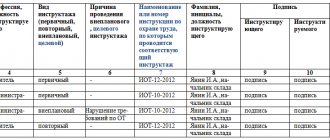
Records of unscheduled briefings, as well as other forms of reporting on training in the basics of labor protection, fall under administrative responsibility. The logbook for such briefings is approved by GOST 12.0.004-90.
The following information is entered into this log:
- about the reason for conducting the briefing outside the plan;
- its date;
- personal information and position of the instructor;
- about persons who have undergone instruction;
- about its volume and content.
This information is sealed with the signatures of the instructor and each person instructed.
If an employee's personal card , information about unscheduled briefings is also entered into it, and the number or name of the corresponding program is indicated.
How is the briefing completed?
A signature is placed in the journal.
The preparation of briefings should not be left to chance, much less neglected at all. Perhaps nothing will happen at first, but one day “thunder will strike” and signatures will have to be collected retroactively.
At enterprises, all managers must have training logs in the established form. They should reflect the numbers of instructions or regulatory documents according to which the instruction is carried out.
The same line must contain the signatures of the person who carried out and received the instructions, with the obligatory date.
If you do not put the date and year, then it will hardly be possible to prove that the conversation was held on that very day.