Fixed Asset Accounting
An asset can be recognized as a company's fixed asset only if it meets the following criteria:
- purpose – production activity of the company
- The intended use period is 12 months or more.
- the owner does not plan to put this asset up for sale
- property is a resource and can bring benefits
Such verification of an asset for compliance is prescribed by the PBU accounting for fixed assets and is mandatory for all companies.
It turns out that only buildings, equipment, transport, as well as breeding livestock and plantings can be recognized as OS, taking into account the criteria.
IMPORTANT: when creating a list of fixed assets, always take into account the cost criterion for assigning assets, set out in your accounting policy.
Which operating systems are taken into account when calculating the limit?
If you exceed the 150 million mark, keep the following in mind. Only depreciable fixed assets are taken into account in the calculation of this indicator (clause 16, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Since land plots are not depreciable property, their value is not taken into account when determining the limit.
In a letter dated July 31, 2013 No. 03-11-06/2/30602, the Russian Ministry of Finance considered a situation where a company bought transport vessels at a cost that exceeded the permissible OS limit and registered them in the Russian International Register of Ships (RMRS). Since ships registered with the RMRS are excluded from the list of depreciable property (clause 3 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), their value does not need to be taken into account when determining the limit on fixed assets.
Accounting for receipt of fixed assets
Accounting accounts are designed to carry information about all movements of objects, including the receipt of fixed assets. All procedures are clearly regulated. In fact, all accountants in the country use the same operations when a company acquires fixed assets: guidelines for accounting for fixed assets dictate uniform rules. You can choose the option of calculating depreciation amounts and the cost limit for assignment to fixed assets.
IMPORTANT: materials, finished products, and objects for resale are not considered fixed assets, even if all other recognition criteria are met.
Who is subject to the property value limit?
The Tax Code contains a direct indication that the mentioned limitation on the value of fixed assets applies only to organizations (clause 16, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There is no such restriction for individual entrepreneurs.
However, financiers only agree that entrepreneurs can switch to the simplified tax system without taking into account the limit on the residual value of property (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 21, 2010 No. 03-11-11/147). But they will be able to retain the right to use the simplified tax system if they meet the requirements of paragraph 3 of Article 346.12 of the Tax Code, including the cost of fixed assets, which is determined according to accounting data (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 13, 2015 No. 03-11-12 /6555, dated January 18, 2013 No. 03-11-11/9, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated January 15, 2013 No. ED-3-3/69).
One can argue with this position. After all, the provisions of subparagraph 16 of paragraph 3 of Article 346.12 of the Tax Code apply only to organizations. In addition, individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are not required to keep accounting records at all, and therefore to determine the residual value of fixed assets (clause 1, clause 2, article 6 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
But, taking into account the opinions of officials on this issue, entrepreneurs will have to defend this point of view in court.
Read also “Value of property for applying the simplified tax system”
Inventory accounting of fixed assets and intangible assets
The unit of accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets is an inventory object. It can be a cabinet, a computer, or an entire production complex. The main thing is that all parts of the asset have the same useful life. Otherwise, they must be taken into account in parts.
Account 01 “Fixed assets”
Analytical accounting of fixed assets is carried out at their original cost, which consists of the actual costs of bringing a particular asset to working condition. Since 2021, there is a different limit for accounting for fixed assets, and in tax and accounting it may be different.
Fixed assets in accounting 2017 cost
40,000 and above - this is the limit for fixed assets in accounting now. Perhaps, starting from 2021, the legislator will raise the bar to 100,000 and the limit will be equal to the tax limit. This will avoid unwanted timing differences. But for now, fixed assets are accepted for accounting according to the old rules, while in tax accounting there is already a limit of 100 thousand rubles. and above, starting from 01/01/16. But what if the object lasts more than 12 months, but costs less than the established limit? According to current rules, it can be immediately written off as an expense.
IMPORTANT: you need to carefully calculate the initial cost of the object, since the final amount directly affects the decision - to write off or depreciate the asset.
Actual expenses that form the initial price of the OS:
- payment to the seller and contractor under the contract
- costs for delivery and final installation of the asset
- customs payments and import fees
- state duties on the object
Fixed assets in the accounting of a budgetary institution or commercial enterprise calculate the initial price of the object according to uniform rules. No indirect costs can increase the cost of a company's inventory resource, regardless of the company's legal form. The accounting unit of fixed assets is a capital object or non-current asset, all parts of which transfer their value to costs according to the same rules.
Postings for accounting for the receipt of fixed assets at the enterprise:
| Dt | CT | Content |
| 01 | 08 | Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting |
| 68.2 | 19 | VAT refund |
| 26 | 02 | Depreciation on computers |
| 20 | 02 | Depreciation of production machines |
| 01 | 10,60,70,69 | Modernization of fixed assets accounting and tax accounting |
| 08 | 60 | Buying a new machine |
| 19 | 60 | Tax on capitalized assets |
| 60 | 51 | Settlements with the supplier |
Using specific examples
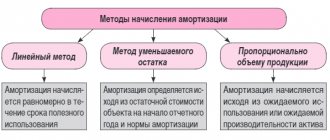
Since the accounting procedure and calculation of deferred tax liability in practice often causes difficulties, we will analyze this situation using an example. Let's say that in March 2021, the company bought production equipment for 48,000 rubles. In the same month, the property was put into operation in accounting as an asset. Its useful life is 4 years (48 months). Depreciation is carried out using the straight-line method.
In tax accounting, property is not classified as depreciable. Since its cost is less than the established limit, it is fully included in expenses at the time the asset is accepted for accounting, that is, in March 2016. What kind of transactions during this period will need to reflect the property in accounting, see the table.
Depreciation on fixed assets in accounting is accrued from April. In our case, depreciation per month is equal to 1,000 rubles: (48,000 rubles / 48 months) × 1 month. The amount of depreciation is not taken into account in tax expenses; it reduces the taxable temporary difference by 1,000 rubles and partially extinguishes the deferred tax liability by 200 rubles: 1,000 rubles × 20%, where 20% is the income tax rate. And so on throughout the entire depreciation period of the equipment.
In the balance sheet, the credit balance of account 77 is reflected in line 1420 “Deferred tax liabilities.” In the income statement, changes in deferred tax liabilities are reflected on line 2430.
Accounting for disposal of fixed assets
The reasons for the disposal of assets from accounting in an organization may be the following actions and events:
- the company sold the property
- the company wrote off an obsolete or dilapidated asset
- The legal entity transferred the object as a treasure to the capital of another company
- re-registration of property by exchange
- transfer of property as a gift
This is just a short list of reasons for recording the receipt and disposal of fixed assets simultaneously for several companies. One of the basis for new accounting entries is the lease agreement.
Accounting for lease of fixed assets
The contract is based on the rules of law set out in Chapter. 34 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The object can be any property. For organizations, this is most often OS; the main thing is that the asset meets the criteria of thematic PBU 6 01.
Accounting for leased fixed assets is carried out depending on the selected balance holder. This may be a tenant or a landlord-owner. When it comes to operating leases, the owner always keeps records.
To account for leased property, the following subaccounts are provided in account 03 Income investments in MC:
03.1 MC in the organization
03.2 MC in possession and use
03.3 MC for temporary use
Most often they are used by leasing companies when recording property leased to their counterparties. Next, these objects are depreciated according to general rules using subaccount 02.2 Depreciation of objects account. 03.
If renting is the main activity, the postings will be as follows:
| Dt | CT | Content |
| 08 | 60 | Purchase of a non-current asset |
| 19 | 60 | VAT on asset for leasing |
| 60 | 51 | Payment to supplier/contractor |
| 68.2 | 19 | VAT refund |
| 03 | 08 | Transfer of an object for financial lease |
| 62 | 90 | Accrual of rental revenue |
| 90 | 68.2 | VAT on leasing payment |
| 51 | 62 | Receiving rent money from a client |
| 20 | 02.2 | Depreciation is calculated every month |
If the lease is long-term with subsequent purchase, the object will be transferred to the balance sheet of the tenant, and in the owner’s accounting it will be reflected in the off-balance sheet account 011 fixed assets leased.
In connection with the practice of convergence of RAS and IFRS, there is a tendency to reflect leases according to the rules of international standards:
- operating lease – always on the owner’s balance sheet
- finance lease – only on the balance sheet of the lessee
Features of fixed assets accounting for financial leases
The organization of accounting for fixed assets under financial lease according to IFRS has its own nuances. But first you need to determine whether the agreement meets the recognition criteria for a finance lease:
- The term of the contract is equal to the useful life of the property
For example, the SPI of a machine is 6 years, the term of the lease agreement is 5.5 or 6 years - financial lease according to IFRS criteria
- At the end of the lease period, the property can be purchased at a reduced price
If the contract is established for a number of years approximately equal to the SPI, and the redemption payment at the end of the term is conditional, say, 1,000 rubles. is a finance lease
- When one lease term ends, the tenant can extend it
For example, renting a car is 50,000 rubles/month, the tenant leased the car for 3 years, but can extend the contract on preferential terms - this is FA
Once the FA criteria are met, the accountant must make the following conclusions:
- synthetic accounting of fixed assets is carried out by the tenant on his balance sheet
- for the tenant this is income from the placement of working capital
- the owner does not charge depreciation, but reflects the remuneration
For example, the following accounting entries are possible:
Accounting for fixed assets in finance leases
| Dt | CT | the name of the operation |
| 08 | 60 | Purchase of the leased asset by the lessor company under a financial lease (leasing) agreement from a supplier agreed upon by the parties |
| 19 | 60 | VAT is reflected on the principal amount of payment for fixed assets under leasing |
| 03.1 | 08 | The posting is generated when the asset is ready to be leased |
| 76 | 98 | For the entire amount of the contract when transferring property to the lessee’s balance sheet (lessor’s cost) - will be reduced monthly according to the rental service/revenue accrual schedule |
| 03.9 | 03.1 | Disposal of an object based on the contractual contract (supplier cost) |
| 97 | 03.9 | The cost of the leased item under the agreement with the supplier will be written off as current expenses of the period on a monthly basis (analogous to depreciation) |
| 011 | Off-balance sheet accounting of the leased asset - the financial lease object in the accounting of the owner-lessor |
Tax accounting of fixed assets in 2021
Starting from 2021, in accordance with tax law, there is a new value limit in accounting - 100 thousand rubles. This means that all objects whose value is below the limit are subject to a one-time write-off without depreciation.
IMPORTANT: The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not offer taxpayers the right to choose: the cost limit of 100,000 for NU is the same for everyone, regardless of the accounting policy of the enterprise.
It turns out that you can write off relatively cheap items according to the rules of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation faster than in accounting, where there is a limit of up to 40,000 rubles. This means that temporary tax differences will arise that must be reflected in accounting in accordance with PBU 18/02.
Tax accounting of fixed assets in simplified format
As for the cost limit, it is accepted for everyone: both simplifiers and companies using OSNO take into account fixed assets in the same way. Although there are some nuances for the simplified tax system:
- the ability to write off the cost of fixed assets as period expenses in parts (its own specifics of value transfer)
- the right to attribute investments in material assets to expenses immediately at the time of payment (analogy with the cash method of accounting)
However, accountants using the simplified tax system must proceed from the same limit of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for depreciable property as specialists in companies operating under the general regime.
We spoke in detail about the features of accounting for non-current assets of enterprises to help avoid errors and inaccuracies associated with changes in current legislation.
The facility was received under a concession agreement
According to the Ministry of Finance, when determining the limit on the value of fixed assets, simplified companies should take into account real estate acquired under a concession agreement (letter dated August 26, 2015 No. 03-11-09/49191).
Since the letter deals with the transfer of property under a concession agreement, financiers turn to the provisions of Federal Law No. 115-FZ of July 21, 2005 “On Concession Agreements” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 115-FZ).
According to Part 1 of Article 3 of this law, under a concession agreement, one party (the concessionaire) undertakes to create or reconstruct real estate, the ownership of which belongs or will belong to the other party (the grantor). In addition, the concessionaire undertakes to carry out activities using this property. In turn, the grantor undertakes to provide the concessionaire with the right to use and own this property.
At the same time, Law No. 115-FZ also establishes that property transferred under a concession agreement is reflected on the balance sheet of the concessionaire (and not the grantor), and separately from the rest of its property. The concessionaire maintains independent accounting for this object and also charges depreciation on it.
Based on this, the Ministry of Finance draws the following conclusion. The residual value of the property received under the concession agreement must be taken into account by the “simplified” person to calculate the limit on the value of fixed assets for the purpose of applying the simplified tax system (clause 16, clause 3, article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And if the residual value of fixed assets received under the concession agreement exceeds the permissible limit, the “simplified” concessionaire loses the right to apply this special regime.
Read also “Concession agreement under the simplified tax system: we charge VAT”
New procedure for depreciation of fixed assets in 2021
When compiling accounting entries, experts are wondering what the new depreciation regulations for fixed assets look like in the coming 2017?
From the beginning of next year, in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the state dated July 7 of this year No. 640, a new version of the Classification and an amended edition of the OKOF will come into force.
OS classified according to the 2021 scheme are based on OKOF OK 013-94.
To replace it, in 2021, the new Classifier 013-2014 (SNA 2008) will begin to be used.
Important: starting from 2021, the structure of the OKOF code is changing dramatically.
As in the current one, the new OKOF OK 013-2014 specifies ten depreciation groups, some of which have changed fixed assets.
It follows from this that in 2021 it will be necessary to set a different period of use for these groups.
For example, metal fences with the old OKOF code 12 3697050, which is simultaneously included in two groups in 2021. fences made of metal and brick (combined) belong to the sixth group, and exclusively metal ones - to the eighth.
The new Systematizer of OS classes defines all metal fences without exception in group No. 6, according to OKOF code - 220.25.11.23.133.
Consequently, the service life of metal fences is reduced by ten years.
Important: Due to the redistribution of depreciation groups, the service life of some assets may change significantly.
The transition to the new systematization should be carried out for those assets whose operation will begin after the beginning of 2021.
Regarding old objects, a revision of depreciation and a change in service life is not necessary.
Therefore, inventory cards in form No. OS-6 also do not need to be adjusted.
Rosstandart has approved special transition keys (reverse and direct) between both versions of OK OKOF.
To avoid confusion, the department plans to launch a hotline consultation line by the end of the year to explain the features of the transition to the new system.
back to menu ↑