Based on the legislative provisions of the Russian Federation (Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ), any operation relating to the repair of fixed assets requires registration using primary documents.
And here it is worth considering such an important point: both the movement of property and its acceptance after restoration work are subject to mandatory documentation.
The amounts that will be spent on current repairs can be written off in tax accounting as other expenses (clause 1 of article 260, clause 1 of article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
And it does not matter at all who will perform these works - the company independently or a third-party contractor.
To take into account the costs of repair work for tax purposes, you must provide documentary justification for the need for repairs.
In other words, it will be necessary to provide evidence that without repair work it is not possible to continue to use this property for work.
Previously, it was necessary to collect a huge amount of paperwork, but now this is far from the most difficult procedure.
What kind of documentation for the repair of fixed assets is provided for today?
What documents need to be completed so that the accountant can correctly take into account the costs of work in accounting and reduce the taxable base in tax accounting by their amount.
Read about accounting and tax accounting for repairs of fixed assets here.
Repair of fixed assets - what is it?
Repair of fixed assets (Fixed Assets) is a process that relates to both own and leased property. It is carried out in order to support or restore the functionality of the OS. The repair procedure consists of eliminating faults that have arisen, replacing worn parts or individual components of the object. Depending on the frequency and volume of work performed, repairs can be:
- current,
- average,
- capital.
However, in no case should the repair process lead to a change in the basic technical characteristics or purpose of the object being repaired, since such a change will already be regarded as modernization (reconstruction), which must be taken into account according to completely different rules (clause 2 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Carrying out repairs, unlike modernization (reconstruction), does not in any way affect either the initial or residual value of the object. All repair costs, whatever their value, are taken into account during the period of its completion. However, such expenses require economic justification and documentary evidence (letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 24, 2010 No. 03-03-06/4/29, dated February 25, 2009 No. 03-03-06/1/87).
Repairs can be carried out:
- attracted counterparty,
- on our own,
- in a mixed way.
Since 2022, to replace PBU 6/01, officials have approved 2 new FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed assets” and 26/2020 “Capital investments”. According to the new standards, OS accounting must be maintained according to new rules. You can begin to apply the standards earlier by establishing new accounting provisions in your accounting policies.
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to correctly take into account the costs of major, current and unscheduled repairs of OS when applying FSB 6/2020 and FSB 26/2020. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Procedure for compilation
This document refers to the primary one, so there is a procedure for its preparation:
- A number is assigned in order to the form.
- The details of both parties involved in the preparation of the act are written down.
- The details of the contract are indicated.
- All work that was performed under the concluded agreements is listed. In this paragraph, it is recommended to indicate all the services provided that are used for signing, in detail and preferably in detail.
- Information about what the result of the labor was during the transfer.
- Where the work was actually carried out, that is, indicate the location and date.
- If there are any shortcomings, then this phrase must be written down.
- Indicate the cost of obligations under the contract.
- Positions of representatives of both parties with seals.
Reference! The final form that the work completion certificate will have for self-employed citizens must be agreed upon and approved in the manner established by the enterprise.
Documentation of repairs
Repairs are preceded by drawing up:
- a defective statement reflecting the condition of the object, which can be made in 1 copy if the repairs are carried out on their own or in a mixed way, and drawn up in 2 copies if the repairs are carried out by a third-party contractor;
Read about what form a defective statement can take in the material “Drawing up a correctly defective report - sample.”
- estimates for repair work drawn up either by a third-party contractor or by its own department carrying out repairs;
- an order from the manager to carry out repairs, which reflects the timing of the repair work, the forces carrying it out, and, if necessary, decisions to replace temporarily absent OS;
- agreement for repairs, if it will be done by a third party;
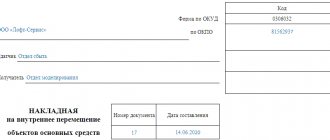
- invoice for the internal movement of fixed assets, if the object is being repaired in its own department.
Read about the rules for issuing such an invoice in the article “Unified form No. OS-2 - form and sample.”
Upon completion of the repair work, the following is drawn up:
- certificate of acceptance of the object from repair;
For information on how to fill out such an act, read the material “Unified Form No. OS-3 - Form and Sample.”
- invoice for internal movement of fixed assets, if the object was repaired in its own department;
- a record of the repair performed in the OS inventory card.
For an example of making such a record, see the sample to the article “Unified Form No. OS-6 - Form and Sample”.
Find out how to write off materials for OS repairs in ConsultantPlus. See the authoritative opinion of K+ experts in the Ready-made solution by getting free trial access.
List
REFERENCE! Current repairs are possible according to the plan of the management company or at the initiative of the homeowners. The documentation is different in the two cases.
During scheduled repairs, the following documentation is maintained:
- contract;
- estimate;
- defective statement;
- materials write-off act;
- plan;
- project;
- technical task.
For property owners, a different list of documents is required:
- estimate;
- contract;
- plan;
- project;
- production log;
- technical task.
Reflection of repairs in accounting
Accounting for the cost of repairing fixed assets in accounting varies depending on how the repair work is carried out.
When carried out on their own (i.e., by one of the auxiliary departments), an order is opened for such work in the relevant department, for which direct costs associated with it are collected during the entire time the repair is in progress:
Dt 23 Kt 10, 69, 70.
If third-party contractors are involved for part of the work (i.e., a mixed method of repair), then account 60 will be added to the list of accounts reflected in this loan entry. In this case, a VAT entry may also arise if the services of a third-party contractor are subject to this tax:
Dt 19 Kt 60.
The overhead costs of the auxiliary department performing the repairs, distributed at the end of each month, will also be added to the total cost of the repair order:
Dt 23 Kt 25.
Upon completion of the repair, which will be recorded in the acceptance certificate of the object, the costs collected in account 23 for the corresponding order will be written off as overhead costs for the maintenance of the department in which the repaired OS is used:
Dt 25 (26, 44) Kt 23.
When repairs are carried out only by a third-party contractor, the costs for it will appear in accounting only on the date of signing the act of acceptance of the object from repair and will immediately be charged to overhead costs for the maintenance of the department in which the OS that has been repaired is used, with the allocation of VAT indicated in the documents :
Dt 25 (26, 44) Kt 60;
Dt 19 Kt 60.
In the posting for accounting for completed repair costs for both options (in-house or third-party), the list of accounts indicated by debit may also include accounts 23 and 29, if the accounting of overhead costs for them is organized using the boiler method or in separate subaccounts of these accounts. OS repair costs cannot be included in direct costs, since the objects are not involved in production during repairs.
According to the current accounting rules, a reserve for OS repairs is not created in the accounting department. Previously, this could be done, but since 2011, this possibility has been excluded from the Guidelines for fixed assets accounting, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2010 No. 186n).
Is it necessary to sign a certificate of completion of work with self-employed people?
Federal legislation does not regulate civil transactions and the sequence of their execution. Therefore, when collaborating with self-employed people, it is recommended to use the standards of the civil code. According to them, the fact of provision of services, their name, reflects the check generated by them through the “My Tax” program. In this case, a certificate of work performed with a self-employed person can also be drawn up, although it is not a mandatory document. It will be an addition that reflects:
- Number or period of service provision.
- Subject of cooperation.
- Algorithm for providing services.
- Sequence of fulfillment of obligations.
- Consequences if obligations are not fulfilled properly.
- Price.
- Payment procedure.
- Responsibility of both parties.
- The procedure for resolving disputes that arise.
- Requisites.
The legislative framework does not have regulations for filling out a work completion certificate for the self-employed, but the document must reflect the following information:
- A number assigned in order for registration in the accounting department.
- Document creation date.
- The number of contractual obligations on the basis of which the document is drawn up.
- Timeframes planned for the provision of services.
- The volume actually done is indicated.
- The price of the offer must include VAT.
- Account number to which funds must be transferred (bank account, recipient's card, or other).
- The name of the customer and the contractor in full, in accordance with the constituent papers.
- Stamps from both organizations.
- Signatures of both parties: the contractor and those who performed the actions specified in the contract.
Here is an example of a certificate of completion of work with a self-employed person:
Accounting for repairs in tax accounting
In NU, accounting for the costs of repairing fixed assets is possible in 2 ways (Article 260 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- The same as in accounting, i.e. by including costs in expenses during the period of completion of repairs (clause 1).
- Through the creation of a reserve (clause 3). The amount of contributions to it is determined in a special manner established by clause 2 of Art. 324 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The total amount of the reserve is subject to limits, but can accumulate over several tax periods. If a reserve is created, then all repair costs are taken into account and attributed to the reduction of this reserve. And only if its amount is exceeded, repair costs can be taken into account directly in the costs.
For more information on creating and using a reserve for repairs of operating systems at NU, read the material “Creating a reserve for repairs of fixed assets (nuances).”
The decision to create or not create a reserve in NU must be fixed in the accounting policy. If you decide to create it, the algorithm for calculating the amount of the reserve and the period for which it is formed are also written down.
Since the current accounting rules do not provide for the possibility of creating a reserve for repairs of fixed assets, differences will arise between the accounting and accounting data in terms of the reserve formed for the purposes of the accounting system.
Possible costs
The documents described above seem to reflect all aspects of the repair and take into account all the nuances. But you should understand that in general, in addition to the purchase of materials and payment for contract services, additional costs are possible, such as:
- ordering a project and plan;
- payment for accountant services (when preparing estimates);
- additional costs in case of unforeseen circumstances.
You can learn about what is covered by current repairs by law, how it differs from major repairs, what are the deadlines for scheduled maintenance in an apartment building, as well as the specifics of current repairs at the entrance on our website.
As it turned out, it is not so difficult to understand the documentation during routine repairs. But if you are doing repairs yourself, relying only on your own is not always the right and profitable solution - feel free to seek help from specialists who know their business.
Results
OS repair consists of implementing measures aimed at maintaining the operability of fixed assets, but it should not lead to a change in the technical characteristics or purpose of the OS.
Repair costs are taken into account in expenses in the amount of actual amounts upon completion of repair work, regardless of whose forces the repair is carried out: in-house or outsourced. Documented justification for the need for repairs is required. In the NU it is permissible to create a reserve for repairs, but this leads to differences between the BU and the NU. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
conclusions
Based on the above, if your organization has carried out work aimed at eliminating malfunctions and maintaining the premises, then they will be considered repairs and do not increase its cost. According to clarifications from regulatory agencies, such work does not fall under construction and installation work.
If you independently carried out construction work, during which the initial cost of the premises changed, they are recognized as construction and installation works. Don’t forget to add VAT on the cost of such construction and installation work, which can be immediately deducted.
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
How is it different from upgrading the OS?
Modernization of fixed assets and repair work are associated in many ways, so accountants often make many mistakes when preparing reports on work performed.
In order to correctly fill out the statements and make the appropriate entries, you must clearly understand the definition of each concept.
Repair is comprehensive work to troubleshoot and restore the functionality of objects in order to restore operational operations.
In addition, these measures are aimed at prevention in order to replace worn parts and structures.
Important: at the same time, repair work, even when replacing old parts of fixed assets with elements of the latest developments, should not lead to changes in the technical and economic indicators of the equipment as a whole.
The use of routine repairs can be carried out several times a year in order to eliminate minor problems, replace worn parts; the operation of the OS object does not stop during this event.
In general, the entire process is aimed at extending the operational life of the fixed asset.
Overhaul of the OS is carried out once a year with a complete temporary shutdown of the equipment; it involves disassembling the facility to replace components.
Important: for an accountant there is no distinction as to what type of repair was made.
OS modernization is a series of activities aimed at replacing parts and assemblies with more advanced options in order to increase equipment performance, its technological qualities and economic characteristics.
Important: the main feature of modernization is the replacement of existing components, and not failed ones, since in this case it will be a repair.
If the work is done poorly
If deficiencies are discovered in the services provided, the following steps must be taken:
- If any shortcomings or deviations from contractual obligations are noticed, you must inform the self-employed person about this.
- If the document does not indicate any defects, then the customer has no right to refer to it.
- When defects are discovered after the self-employed and the customer have signed the work completion certificate, the latter is deprived of the right to make claims or can try to resolve this issue in court.
Attention! If a dispute arises about the quality of services provided, an examination can be performed at the legislative level. Payment of the latter is made by decision of the parties or the court.
Major and current repairs of the OS, unlike other recovery methods
In the production activities of organizations during the operation of the operating system, wear and tear of the operated objects naturally occurs, and breakdowns occur. Their timely restoration allows you to increase their service life and avoid the cost of purchasing new equipment. Recovery is possible through modernization, reconstruction and repair. Modernization and reconstruction are recognized as work that improves or creates new technical and economic characteristics of an object. Whereas repair includes a set of measures aimed at replacing individual structures, parts, and maintaining its working condition.
Repairs are divided into current and major. Current repairs are aimed at prevention, maintaining the facility in working order and eliminating minor faults. Capital - guarantees the restoration of the technical parameters of the object and its working condition.
Overhaul can be comprehensive, covering the entire facility, or selective, including the repair of individual parts of the facility.
The validity of OS repairs is established by the technical services of organizations by determining the order of scheduled preventive maintenance, while assigning the type of repair.
A feature of accounting for major repairs compared to other types of restoration is that repair costs are included in current costs, while costs for modernization and reconstruction are included in capital costs.
For key differences between repair and OS modernization for tax purposes, see ConsultantPlus. Trial access to the legal system is free.
Conceptual apparatus
Before proceeding directly to carrying out repair work, the institution should determine what type of work being performed will be: major (current) repairs or reconstruction. Indeed, in case of incorrect qualification of work and payment for the wrong type of expenses, the institution may be held liable for misuse of funds.
To do this, it is necessary to refer to the regulations governing activities in the field of construction, since the current accounting and tax legislation does not contain definitions of these concepts.
In accordance with clause 3.8 of MDS 81-35.2004, major repairs of buildings and structures include work on the restoration or replacement of individual parts of buildings (structures) or entire structures, parts and engineering equipment due to their physical wear and destruction with more durable and economical, improving their performance.
For reference: preventive (current) repairs consist of systematically and timely work to prevent wear and tear on structures, finishes, and engineering equipment, as well as work to eliminate minor damage and malfunctions.
In the course of analyzing the above definitions, we can conclude that during routine repairs only minor work can be carried out, therefore, all major work must be performed during major repairs. For example, partial repair of the roof, taking into account the insignificance of material and labor costs, will be considered a current repair, and a complete change or replacement of all types of roofing will be a major one.
According to clause 3.4 of MDS 81-35.2004, during the reconstruction (reconstruction) of existing workshops of the enterprise and facilities of the main, auxiliary and service purposes, as a rule, without expanding the existing buildings and structures of the main purpose associated with improving production and increasing its technical and economic level and carried out Under a comprehensive project to modernize an enterprise in order to increase production capacity, improve quality and change the range of products, mainly without increasing the number of employees while simultaneously improving their working conditions and environmental protection, the following activities can be carried out:
- expansion of individual buildings and structures for main, auxiliary and service purposes in cases where new high-performance and more technically advanced equipment cannot be placed in existing buildings;
- construction of new and expansion of existing workshops and auxiliary and service facilities;
- construction on the territory of an existing enterprise of new buildings and structures of the same purpose to replace those being liquidated, the further operation of which, due to technical and economic conditions, is considered inappropriate.
Thus, if an institution plans to replace the roof covering, this will be recognized as a repair (current or major), and if it wants to equip offices in the attic or build an attic on the roof, then this work will already be a reconstruction.
Note that similar norms are in the Town Planning Code.
The list of main works carried out during current and major repairs in relation to social and cultural facilities is given in VSN 58-88(r), and in relation to production facilities - in MDS 13-14.2000.
In accordance with clause 1.1 of VSN 58-88(r), this provision applies to municipal and socio-cultural facilities, regardless of the form of ownership. According to Appendix B to SP 118.13330.2012 “Public buildings and structures. Updated version of SNiP 06/31/2009”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated December 29, 2011 No. 635/10, public buildings and premises include:
- buildings and structures for facilities serving the population;
- buildings of facilities serving society and the state (in particular, court buildings and prosecutor's offices, as well as law enforcement organizations (police, customs)).
Please note: the list of additional work carried out during major repairs is given in Appendix 9 to VSN 58-88(r).
According to clause 5.1 of VSN 58-88(r), major repairs must include troubleshooting of all worn-out elements, restoration or replacement (except for the complete replacement of stone and concrete foundations, load-bearing walls and frames) with more durable and economical ones that improve the performance of the buildings being repaired . At the same time, economically feasible modernization of a building or facility can be carried out: improving the layout, increasing the quantity and quality of services, equipping with missing types of engineering equipment, and improving the surrounding area.
When reconstructing buildings (facilities), based on the existing urban planning conditions and current design standards, in addition to the work performed during major repairs, the following can be carried out:
- changing the layout of premises, erecting superstructures, extensions, and, if necessary justification is available, their partial dismantling;
- increasing the level of engineering equipment, including the reconstruction of external networks (except the main ones);
- improving the architectural expressiveness of buildings (objects), as well as landscaping the surrounding areas.
When reconstructing municipal and socio-cultural facilities, it may be possible to envisage the expansion of existing and construction of new buildings and structures for auxiliary and service purposes, as well as the construction of buildings and structures for the main purpose included in the complex of the facility, to replace those being liquidated.
The list of main works performed during routine repairs is presented in Appendix 4 to VSN 58-88(r).
Acceptance of services under the act
The customer must accept the services provided by the contractor. An algorithm has been established for this:
- The administrative document appoints an acceptance commission.
- A check is being carried out.
- An acceptance document is prepared in the absence of any comments; if the latter are found, then the deadline for their elimination can be indicated in the act.
- The certificate of completed work from the self-employed is signed by the members of the commission and approved by the chairman, after which payment is made. This condition should be discussed with the contractor.
Acceptance and write-off of materials: we prepare documents
The article from the magazine “MAIN BOOK” is current as of June 7, 2013. L.A. Elina, economist-accountant
We thank Elena Sergeevna Shatalova, chief accountant of Technolux Metal LLC, for the proposed topic.
Moscow. Now it is not necessary to use unified primary forms, including those provided for accounting for materials and their movement.
Therefore, organizations are slowly beginning to reshape Goskomstat forms to suit themselves. And on this wave, accountants are once again asking the question: what document will be the basis for accepting materials for accounting and writing them off as expenses? Speaking about materials, we will consider production materials and raw materials, and office materials, for example, stationery.
The posting of materials implies not only their physical receipt by the financially responsible employee of the organization (for example, a storekeeper), but also their reflection on the accounting accounts (as a rule, this is a debit posting to account 10 “Materials”).
There are several options for documentation, and they often depend on the situation that arises when receiving materials, as well as on the structure of the organization and the internal document flow system adopted in it. Receipt order according to form No. M-4. It is used if there are no comments on the quality and range of materials.
Only the form No. M-4 is quite large.
Therefore, you can easily remove from it some details that are not related to the mandatory details of the primary document (hereinafter referred to as the Accounting Law):
- passport number (it makes sense to leave it only if you are bringing materials containing precious stones and metals);
- information about the insurance company;
- column with the unit of measurement code.
- numbers of forms according to OKUD and OKPO;
The stamp on the invoice replaces the receipt order and is placed in similar situations - when materials are received without any discrepancies in quantity, quality and assortment. Such a stamp should contain the main details of the receipt order: who received it, how much, when (hereinafter referred to as the Methodological Instructions); ; .