Every company, when starting its activities, asks itself which taxation system to choose. To do this, you need to either study the issue yourself or seek help from specialists who will help and suggest what is best to choose. For accounting, of course, the simplified system is much simpler. However, in order to use the simplified tax system, a number of conditions must be met. To do this, it is necessary to conduct certain types of activities, not have more than a hundred employees, and some other nuances.
Cases of returning goods
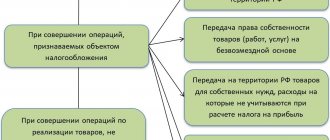
In accordance with the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), the return of goods can be carried out:
- according to the law: if the goods were delivered of inadequate quality or not at all what was specified in the contract (i.e., there is a failure to fulfill the contract);
- an agreement (such a clause on the return of goods of proper quality may be specified in the contract, or may exist in the form of implementing the rules on the buyer’s responsibility if he does not pay the full amount for it on time).
Based on Art. 454 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the seller transfers the goods to the buyer, who pays for it and takes ownership of it. At the same time, in accordance with Art. 223 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the moment of transfer of goods is at the same time the moment of transfer of ownership of it from the seller to the buyer. In addition, the contract may establish another moment for the transfer of ownership.
The grounds for returning goods are given in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. So, a refund can be made:
- in case of short delivery of goods (Articles 465 and 466 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- deliveries with a violation of the assortment (Articles 467 and 468 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- deliveries without proper packaging or in violation of the integrity of the packaging (Articles 481 and 482 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- the presence of a marriage (Article 475 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- detection of shortages (Articles 479 and 480 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the seller did not transfer accessories or documents related to the goods within the prescribed period (Article 464 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The contract may also provide for other grounds for returning goods.
In these cases, the buyer has the right to refuse to accept the goods and is not obliged to pay its cost, while the received advance payment must be returned by the seller upon the buyer’s first request.
The position of the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service regarding the return of goods with VAT simplified
In all situations when it comes to returning goods, the Federal Tax Service and the Ministry of Finance of Russia use two concepts: return of goods and reverse sales. At the same time, according to both the financial and fiscal departments, the return of goods takes place if the goods and materials were not capitalized by the buyer. But if the goods were accepted for registration by the buyer and then returned to the seller, then reverse sales take place. And an agreement with the seller to return the goods if for some reason it was not sold is nothing more than a sale.
But such differences (return of goods or their resale) are important if the buyer is subject to the general taxation system.
For more information, see the material “What is the procedure for accounting for VAT when returning goods to a supplier?” .
However, the financial department has already explained more than once what to do if the goods are returned by a simplifier who does not apply the deduction because he is not a VAT payer.
The Ministry of Finance of Russia, in its letter No. 03-07-15/8473 dated March 19, 2013, clearly indicated that it does not matter what kind of goods the simplifier returns (posted or not), the procedure for issuing invoices for the seller will be the same.
The Federal Tax Service of Russia, in its letter dated May 14, 2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected], confirmed compliance with the standards specified by the Ministry of Finance. At the same time, the fiscal department reminded that the seller can apply a deduction for returned goods only for a year from the date of formalized refusal of the goods or its return by the buyer (clause 4 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Simplified taxation system, general concept
The simplified tax system is one of the taxation systems that can be used by both organizations and individual entrepreneurs, usually running small and medium-sized businesses, and also subject to certain conditions:
- The limited liability company should not contain other organizations that own more than 25% of the authorized capital
- An LLC does not have the right to open branches, but if it does, it is necessary to switch to another tax system
- The number of employees should not exceed one hundred people
- Income from activities per year no more than 150 million rubles
- You can also switch to this system if your income for nine months after submitting the application is no more than 112.5 million.
Important! This system may imply “income” or “income-expenses”. The difference is that if you use the simplified tax system for income, you pay 4% of all income to your current account (the rate depends on the region), and if you have income minus expenses, you have the right to deduct them from income.
The declaration under the simplified system is submitted to the tax office at the end of the year. Advance payments must be made quarterly, which are calculated using the formula .
Returning goods from a simplifier
In Chapter 21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation there are no exceptions for the procedure for sellers to apply deductions when returning goods from a buyer who is on a simplified taxation system and therefore is not a VAT payer. To explain to taxpayers how to proceed in this situation, the Ministry of Finance has provided two options for the development of events, regardless of whether the goods accepted or not accepted for accounting by the buyer are returned (letter No. 03-07-15/8473):
- when the buyer returns the entire product;
- when the buyer returns the goods partially.
The seller has the right to a deduction in accordance with clause 5 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In the purchase book, he makes an entry either on the basis of a previously issued invoice or on the basis of an adjustment invoice. This will be discussed in more detail below.
Find out how to keep VAT records in a simplified manner here.
Full refund
In this case, the financial department (and after it the Federal Tax Service of Russia) recommends that the seller be guided by the standards specified in clause 5 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the invoice registered by the seller in the sales book when shipping goods is registered by him in the purchase book as the right to tax deductions arises, taking into account the provisions of clause 4 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
We will tell you more about the sales book and the purchase book here.
Return in parts
If the delivered goods are not returned in their entirety, but only in some part (and the reason for the return is unimportant), then there is a decrease in the quantity, and therefore in the cost, of previously shipped goods. This means, in accordance with paragraph 13 of Art. 171 and paragraph 10 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the seller must issue an adjustment invoice when returning goods from a buyer who is not a VAT payer.
Find out about the adjustment invoice from the article “What is an adjustment invoice and when is it needed”.
The value indicated on the adjustment invoices must correspond to the amount for which the goods were returned from the buyer.
It is important that the buyer registers the returned goods and prepares the necessary supporting documents.
Free legal consultation: ON PROTECTION OF CONSUMER RIGHTS
Example: I took out loans from a microfinance organization to renovate an apartment and treat an illness.
I realized late that these were unaffordable loans for me. They call and threaten with various methods of influence.
What should I do? Moscow St. Petersburg By clicking the SEND button, you accept the terms and conditions Send Send
Moscow Government
Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation
Rospotrebnadzor Latest questions Full comprehensive service From the moment you contact us until the issue is completely resolved, we are ready to accompany our clients, providing them with the necessary services and advice. Free detailed analysis of the situation Our specialists will study your situation in detail, review all available documents, and draw up a clear picture of the problem.
We recommend reading: Relocating a doorway in a residential apartment documentation
Working for results We are interested in the success of your business!
Your victories are our victories. We are exclusively results-oriented. Drawing up documents If necessary, the lawyers of our company will take upon themselves the preparation of all the necessary documents for a positive resolution of the case. Free study of options Only after a detailed analysis of the available documents and immersion in the current situation will we be able to work out solutions and the feasibility of their use.
Submitting documents We take care of everything.
Compilation. Collection of the necessary package of documents.
Reflection in accounting
In the event of returning goods that have not been received by the buyer, the seller makes adjustments in accounting:
Dt 62 Kt 90 (reversal) - revenue from the sale of low-quality goods has been reduced;
Dt 90 Kt 41 (reversal) - the cost of low-quality goods has been reduced;
Dt 90 Kt 68.2 (reversal) - reduced VAT on shipped low-quality goods;
Dt 62 Kt 51(50) - the buyer’s money was returned.
If a quality product that has been accepted by the buyer for registration is returned, the following entries are used:
Dt 41 Kt 60 - the seller accepted the goods returned by the buyer for registration;
Dt 19 Kt 60 - VAT included;
Dt 62 Kt 51 - the seller returned the money to the buyer for the returned goods;
Dt 60 Kt 62 - debt adjustment.
The following materials will tell you about the nuances of using the simplified tax system:
- “Is a cash register needed under the simplified tax system in 2019?”;
- “The Ministry of Finance denies individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system the right to accept business travel expenses”;
- “They want to allow simplifiers not to submit reports.”
What documents are used to document the return of goods?
If a low-quality product is detected, a report on the identified defects is drawn up. This act is drawn up by the buyer, and it can also be signed by a representative of the seller. The form of the act can be presented in the supply agreement or developed by the buyer in accordance with its accounting policies. Based on this act, a claim is made to the seller, and the buyer will be able to recover from him losses associated with the supply of low-quality products (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus District dated January 31, 2014 No. A53-27651/2012).
When returning a defective product that was previously accepted by the buyer for accounting, in addition to the acceptance certificate for the defective product, the TORG-12 form is also filled out, on which the note: “Return of goods” is made. This procedure is provided for in clause 2.1.9 of the Methodological Recommendations for accounting and registration of operations for the receipt, storage and release of goods in trade organizations, approved by Roskomtorg letter No. 1-794/32-5 dated July 10, 1996.
This set of documents was also approved by existing judicial practice (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated 08.08.2013 No. A45-22984/2012, which was confirmed by the ruling of the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia dated 21.10.2013 No. VAS-14900/13).
Find out how to fill out a return shipping slip in this publication.
The invoice should indicate that a report on the identified deficiencies has been drawn up and a claim has been filed with the supplier. In this case, the act itself must be drawn up immediately after the discovery of deficiencies. If you have correctly executed documents, the buyer has a chance to confirm in court the fact and shelf life of the defective goods, and therefore compensate for their expenses for storing the defective goods until they are exported by the seller (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District dated November 20, 2013 No. A55-34907/2012 ).
When returning a quality product by mutual agreement, the parties must sign a return agreement. The transfer of goods itself is formalized by drawing up a consignment note (the TORG-12 form is most often used, on which the note: “Return” is made).
Find out about the updated formats of TORG-12 by following the link.
Results
When returning goods from a buyer who is on the simplified tax system, the seller has the right to deduct VAT in any case. That is, for tax accounting it is completely unimportant for what reason the goods are returned.
In this case, the seller makes an entry in the purchase book when preparing documents for the return of goods by the buyer on the basis of:
- previously issued invoice (if the product is returned in its entirety),
- or an adjustment invoice (if part of the previously shipped goods is returned).
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
VAT under simplified tax system
- transfer this VAT to the budget in full at the end of the quarter, namely no later than the 25th day of the month following the quarter in which the invoice was issued (Article 163, paragraph 1, paragraph 5, Article 173, paragraph 4, Art. 174 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- submit your VAT declaration in electronic form to your Federal Tax Service Inspectorate also no later than the 25th day of the month following the quarter (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are not VAT payers (clauses 2, 3 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), they should not issue invoices with the allocated tax amount when selling their goods, works, services (hereinafter referred to as goods). But sometimes buyers force simplifiers to issue such invoices, because... They will be able to deduct the VAT indicated in them, which is of course beneficial for them.